Immature granulocytes are reduced
As already mentioned, the norm is when there are no immature granulocytes in the human blood (with the exception of newborns and pregnant women).
How can we talk about their reduced levels in the blood in this case? In this case, we are talking about a decrease in the production of neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils by the bone marrow. When foreign agents (toxins, pathogenic agents) enter the body, mature leukocytes begin to destroy them, dying themselves. However, the bone marrow cannot supply the required number of new cells, including immature ones, to replace the failed white blood cells.
The low content of granular leukocytes, both mature and immature, is caused by many reasons. Moreover, neutrophils have their own reasons, and eosinophils and basophils have their own.
- Neutrophil deficiency is most often observed with:
- neoplasms in the bone marrow (myelofibrosis, leukemia),
- radiation sickness,
- congenital Kostman syndrome,
- autoimmune pathologies (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and others),
- hypersplenism,
- various types of anemia,
- biological depletion of the body due to chronic alcoholism, cachexia,
- taking a number of medications.
- A deficiency of eosinophils is caused by:
- some acute bacterial infections,
- burns,
- taking a number of hormonal drugs,
- anemia,
- numerous injuries,
- physical overload.
- A lack of basophils leads to:
- adrenal dysfunction,
- hyperthyroidism,
- chemotherapy,
- some hormonal medications.
Granulocytes in blood test results
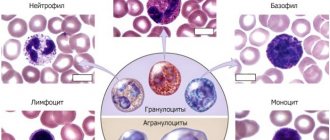
Granulocytes are represented by the following elements:
- From 1 to 5% are eosinophils.
- From 0 to 1% are basophils.
- From 40 to 70% are neutrophils.
Granulocytes make up about 50-70% of the total number of leukocytes in the blood. That is, there can be from 2500 to 7000 cells in 1 ml of blood. To calculate the number of granulocytes, you need to subtract the number of lymphocytes and monocytes from the total number of leukocytes.
If the level of these blood cells is elevated, this is a sign of inflammation that develops against the background of infection. The level of basophils increases during allergic reactions in the body, the number of eosinophils increases against the background of parasitic invasion and allergies.
Table: norms of granulocytes (eosinophils, neutrophils) and other leukocytes:
Normally, the physiological level of granulocytes can be increased under the following conditions:
- Second half of pregnancy.
- Childbirth.
- Beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Active physical activity.
- Heavy meals.
If the level of granulocytes is below normal, then a viral infection, collagenosis or liver disease can be suspected.
Bone marrow diseases and medications (sulfonamides, anticancer drugs, antibiotics, etc.) can also lead to a drop in granulocyte levels. Their deficiency may also be due to hereditary pathologies. The lower the level of mature granulocytes in the blood, the more often a person suffers from skin and respiratory infections.
The leukocyte level in older children is equal to the leukocyte level in an adult. In addition, in the leukocyte form, individual cells are counted, not all leukocytes as a whole. Moreover, in children, the level of neutrophils increases after 6 years, in accordance with the decrease in lymphocytes.
Some leukocytes move freely in the blood, while others are attached to the endothelial cells of blood vessels and “wait” for the time when they are needed. Therefore, granulocytes counted in the leukocyte formula represent only a part of these cells. These will be the granulocytes that move freely in the bloodstream. Normally, in an adult, the number of leukocytes is 5.0 * 1011, that is, about 2000-9000 cells in one cubic millimeter of blood. In children, the number of granulocytes is slightly lower (at the age of 3-6 years), since there are more lymphocytes in their blood. This is a physiological norm.
Norm
In a healthy person, with the exception of pregnant women and newborns, granulocytes are not detected in the blood, since they are located in the bone marrow.
The presence of immature neutrophils in the circulatory system in significant quantities indicates the development of a serious pathology. To estimate the blood cell content, both absolute and relative values are considered .
For adults
In an adult, the normal concentration of neutrophils ranges from 1.2 to 6.8 * 109/l, or no more than 70% of the total number of leukocytes. The norm does not depend on gender, it is the same for men and women.
For a child
In children, the norm of granulocytes in the total volume of leukocytes varies depending on age:
- up to 12 months – from 15 to 30%;
- up to 6 years - from 25 to 60%;
- up to 12 years - from 35 to 65%;
- from 16 years and older – 40–70%.
The percentage of immature neutrophils should be at the level of 4% before reaching one year, 5% in subsequent periods.
The highest concentration is observed in newborns, since passing through the birth canal and entering a new environment is a kind of stress for the baby. The reaction of the child’s body to such a situation is the increased production of young neutrophils.
During pregnancy
The norm for women carrying a child is the same as for other adults. But in some cases, pregnant women may exceed it slightly, which is not considered a deviation. A large number of granulocytes appear under the influence of the hormone progesterone.
- If immature granulocytes are elevated, what does this mean?
At this time, the content of segmented cells can increase up to 75%, or 10 * 109/l, including immature ones - up to 6% . This indicator is considered normal, and if the concentration is 20*109 or more, then this indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
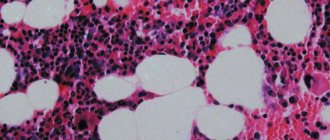
Granulocytes - what are they?
Granulocytes contain nuclei that have an irregular shape. These nuclei are divided into 2-5 particles, so the second name for granulocytes is polymorphonuclear cells.
Granulocytes make up about 75% of all leukocytes. They are represented by eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils. These cells are present not only in the blood, but also in human tissues. Depending on the cause of inflammation that occurs in the body, various granulocytes come into play. This does not mean that they function in isolation from each other; they always interact with each other and with other substances. Thus, neutrophils act in tight association with macrophages, eosinophils with basophils.
Granulocytes are born in myeloblasts. After myeloblasts mature, they transform into promyelocytes and then into myelocytes. Large myelocytes are immature maternal forms, and small myelocytes are classified as mature daughter cells. In the form of myelocytes, granulocytes can no longer divide; they possessed this ability only during the period when they were represented by promyelocytes. Myelocytes cannot be detected in the blood. Normally, they do not leave the bone marrow. If emergency situations occur when all neutrophils are involved in other reactions in the body, then immature granulocytes come to their aid. Only in this case can they be detected in the blood.
For anaerobic glycolysis, granulocytes take energy even from swollen and inflamed tissues that are not supplied with sufficient oxygen. The lifespan of granulocytes is 2-10 days, which depends on the type of cell. Having fulfilled their function, they die, and new granulocytes take their place.
Granulocyte test
Read the article: Increased number of white blood cells in the blood
A blood test for granulocytes is carried out in many diseases and when various pathologies are suspected. The presence of immature forms most often indicates a disease. Typically, a test for neutrophils occurs during a general blood test marked “detailed analysis,” which is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. Blood is taken from a finger. The day before, it is recommended to avoid alcoholic beverages, fatty and fried foods. At least eight hours must have passed since your last meal. It is not recommended to engage in sports or heavy physical work the day before. It is necessary to stop taking medications that may distort the results. If this is not possible, you should inform your doctor. In emergency cases, blood can be taken from a vein at any time of the day.
Modern analyzers allow you to count the number of immature granulocytes with a high degree of accuracy. Automatic calculation significantly reduces the time of analysis and delivery of the finished result.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
An increase in the level of immature granulocytes clearly indicates the onset of inflammation in the body. The immune system turns on and begins to actively form neutrophils to remove pathogens. There are reasons for the different origins of immature granulocytes that characterize deviations from the norm.
An increase in indicators is observed when:
- poisoning, intoxication;
- severe bleeding;
- thermal, chemical and other types of burns;
- pulmonary, myocardial infarction;
- malignant formations;
- abscesses, peritonitis;
- blood diseases;
- An increase is also possible after taking certain medications and as a reaction to a given vaccination.
Intoxication of the body
However, neutrophils can also increase in cases of ordinary physical processes:
- second trimester of pregnancy, childbirth;
- increased physical activity;
- period;
- stress;
- after a heavy meal.
Immature neutrophils are elevated in newborns, this is due to the fact that, being in a favorable intrauterine environment, the child experiences unprecedented stress after birth.
The small organism is just beginning its work in new conditions, therefore it responds to the shock situation by increasing the production of granulocytes.
In all other episodes, an increase in indicators should be a guide for medical workers and parents to action, namely a comprehensive examination.
- Granulocytes - what are they? Granulocytes in the blood: increased, decreased, normal
The number of young neutrophils in a general blood test in children tends to increase when:
- acute otitis media;
- pneumonia;
- appendicitis;
- burns;
- purulent inflammations and the like.
A slight increase in granulocytes indicates the initial stage of the disease. But a rapid, sharp increase indicates blood poisoning.
A decrease in the level of granulocytes can be observed with the following ailments:
- hepatitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- infectious diseases - sore throats, meningitis, acute respiratory infections, influenza;
- tuberculosis;
- skin diseases;
- blood leukemia in the acute stage;
- low hemoglobin indicates anemia of various origins, etc.
A low number of immature granulocytes signals lead poisoning, radiation sickness, and other autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.).
Experts do not recommend vaccinating children if cases of decreased granulocytes are detected during a blood test.
A suspicious change in the number of immature granulocytes towards an increase or decrease indicates the presence of serious diseases, so you must definitely visit a hematologist, undergo a comprehensive examination and begin adequate treatment. You should not self-medicate.
Mandatory consultation with a doctor