Why do they take a creatinine test before a CT scan?
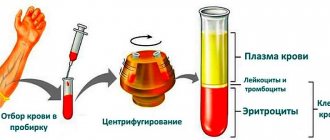
Examination is recommended for patients before CT with contrast. Contrast involves that before scanning, a special iodine-containing drug is injected into the patient's brachial vein using an injector. It is distributed throughout the circulatory system, “staining” soft tissues and vessel walls on scans (CT angiography), thus increasing the information content of the study.
Contrast is not always performed, but only in cases where it is necessary to examine blood vessels or check organs and soft tissues for damage and tumors, especially oncological ones. The effectiveness of CT with contrast in this case is based on the fact that in places where malignant tumors are localized, the blood supply differs from normal: it is more or, conversely, less intense. Malignant neoplasms appear to be the site of abnormal (pathological) accumulation of the contrast agent, and are more clearly visualized on CT scans.
After the examination, the iodine-containing drug is excreted from the body through urine naturally. Our center uses Omnipaque contrast from the group of the safest non-ionic drugs.
The contrast is excreted from the body by the kidneys within 1-2 days. A laboratory biochemical blood test for creatinine (“Rehberg test” or “serum creatinine”) is necessary in order to exclude kidney pathologies, or more precisely, impaired excretory function.
3.How to measure creatinine clearance?
Glomerular filtration rate reflects the functioning of the kidneys. If the kidneys begin to function poorly, then creatinine clearance also decreases.
There are two main ways that doctors use creatinine to measure kidney function:
- Daily urine analysis, in which all the urine in one day is collected in a special container;
- Glomerular filtration rate can be measured using a one-time blood test, the results of which are inserted into a special formula for calculation.
Blood tests are used much more often because... it is more convenient.
What does creatinine show in the blood?
Creatinine is the end product of metabolism (chemical waste). Creatinine molecules are formed at the end of a rather complex creatine-phosphate reaction induced by muscles, liver, and pancreas. The function of the creatine phosphate reaction is to supply the body with energy and saturate cells with water molecules.
Creatine is formed from creatine, a nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid, which is independently synthesized by muscles and organs; sometimes it is additionally taken by athletes as an auxiliary nutritional supplement. Ultimately, creatinine is released into the blood and excreted from the body through the kidneys and urine.
A high amount of metabolite in the blood indicates that the kidneys or urinary system cannot filter creatinine, that is, they cannot cope with the excretory function, most often due to renal failure. On the other hand, high creatinine/creatine may not be associated with urinary dysfunction.
For example, high creatinine in the blood is observed due to:
- Taking certain sports supplements (creatine);
- Excess animal protein in the diet;
- Taking certain medications (sulfamethoxazole);
- Liver pathologies;
- Intoxication;
- Muscle damage;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, in particular thyrotoxicosis;
- Some autoimmune diseases;
- Excessive blood loss.
If, according to the results of a biochemical blood test, the creatinine level is too high, then a computed tomography scan with contrast is not performed. The patient can have a CT scan without contrast, or another diagnostic method is preferred.
If the creatinine level is very low, contrast examination is also contraindicated. However, the causes of this condition are not related to pathology of the kidneys and urinary system. Creatinine can also be reduced in a healthy person if his diet is low in animal protein, during fasting and strict diets.
Creatinine may also be reduced due to:
- Exhaustion of the body;
- Decreased muscle mass or wasting due to illness;
- Dehydration;
- Liver cirrhosis;
- Pregnancy (in the first trimester);
- Extensive inflammatory process.
To exclude false results from a blood test for creatinine, the examination is performed on an empty stomach. The day before, it is necessary to reduce the amount of meat in the diet, eliminate alcohol and intense exercise the day before.
Contraindications and restrictions
Factors influencing research results
1. Hemolysis of a blood sample. 2. Pregnancy (especially the first and second trimesters). 3. Factors that increase performance 4. Excess muscle mass, such as in some athletes (possibly increased creatinine levels despite normal kidney function). 5. Increased concentration in the blood of some endogenous metabolites: glucose, fructose, ketone bodies, urea. 6. Use of medications: ascorbic acid, levodopa, cefazolin, cefaclor, reserpine, nitrofurazone, ibuprofen, barbiturates, clonidine, kanamycin. 7. Extensive muscle injury.
When is it necessary to take a creatinine test before a CT scan with contrast?
Analysis is not required if:
- The patient's age is less than 70 years;
- There is no history of kidney disease or organ surgery;
- There is no history of diabetes mellitus;
- There is no history of gout;
- There is no history of arterial hypertension.
In other cases, there is a high risk of contrast intolerance, up to anaphylactic shock.
You can clarify the advisability of a blood test for creatinine before a CT scan with contrast during a consultation with your doctor or by calling our center’s helpline.
Patient preparation rules
The morning portion of urine is placed in the toilet. Collect urine for a day in a clean container, including the morning portion of the next day. After the last urine collection, mix all collected urine, determine its volume and record it. Pour 35-40 ml and deliver to the nearest branch of ML “DILA” within 2 hours. Keep the container with biomaterial in a cool place, protected from light, during collection. Maybe:
To collect daily urine, the patient is asked to purchase a container with a volume of 2.0 liters at the price price (the cost of the container is not included in the cost of the study).
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Taking care of loved ones: check-up for adult men
It has long been noticed: most men really do not like going to doctors and undergoing many examinations. There is an exit! Invite your husband, brother, father, or loved one to take a set of tests designed specifically for men. All it takes is one trip to the laboratory.
The main argument in a conversation with a representative of the stronger sex is this: many chronic diseases begin gradually. But if you monitor some indicators, you can replace incipient diseases in time, begin treatment and prevent them from becoming chronic, and therefore maintain youth, energy and taste for life.
You only need to donate blood once on an empty stomach (usually this is done in the morning before breakfast). Within a day, in his personal account on the website, a man will receive results for more than two dozen parameters. The form indicates the normal values, and he will immediately see where everything is not in order. Often, from this data it is even clear which specialty doctor it is time to make an appointment with.
Age of Courage
The HERE AND NOW complex is intended for men 41-49 years old. This is the period when most representatives of the stronger sex first feel that they are not as young and strong as before. A timely check-up of the body will help support problem areas of health in a timely manner. In this complex, 21 blood parameters are checked. Among them, for example:
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) will show whether there is any hidden inflammatory process in the body.
- A clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula will help assess the general condition of the body: whether there is anemia and blood diseases, whether there are hidden viral infections, possible allergies, or decreased immunity. Often, it is from this analysis that it becomes clear why a person constantly experiences fatigue, drowsiness and weakness.
- Bilirubin will clarify whether there are liver diseases.
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) will assess whether there is damage to the liver and heart.
- Total protein indicates whether the liver is normal or whether there is chronic kidney disease.
- Creatinine, urea and uric acid are the main markers of kidney condition and are needed to assess the risk of urolithiasis and gout.
- Glucose will show whether there is a risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Lipoprotein(a) and lipid profile will tell you whether a person is developing atherosclerosis. The first “bells” of this disease appear around the age of 40, and a man can feel great. A laboratory test will allow you to identify dangerous changes in advance and avoid future coronary heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
- Homocysteine, among other things, will show how high a person’s risk of thrombosis or some other vascular catastrophe is.
- Total testosterone is an analysis for the most important male hormone. Its decrease manifests itself in decreased libido and sexual dysfunction, loss of muscle volume, brittle bones, weight gain, deterioration in memory and thinking, and reaction speed.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a marker of diseases of the prostate gland, which is called the “second heart of a man.” This is how prostate diseases are diagnosed.
Serious approach
At the age of 50-65 years, early diagnosis becomes especially important. Not all serious diseases in men manifest themselves at an early stage with some clinical symptoms. We can all remember sad stories when a mature man never had any pain, and then suddenly it turned out that extensive surgery and chemotherapy were required.
A complex of laboratory tests WITHOUT EXTRA PROBLEMS will help men over 50 years old to avoid unpleasant discoveries. The test set includes as many as 26 health parameters. These are partially the same indicators that we described above. Some are excluded as uninformative for this age period, so that you do not pay for unnecessary research. Plus, several more tests have been added that become important after 50 years. Among them:
- Ultrasensitive C-reactive protein is an important marker of ongoing processes in the walls of blood vessels. Heart disease risk indicator...
- Glycated hemoglobin is one of the most accurate ways to diagnose diabetes; the same indicator is important when assessing the effectiveness of diabetes treatment
- Parathyroid hormone is a hormone of the parathyroid glands that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. Together with an analysis of total calcium, it helps to understand whether the functioning of your thyroid and parathyroid glands has gone wrong, whether your bones are becoming brittle; an increase can signal a lack of vitamin D in the body.
Treatment
Low creatinine levels can indicate a variety of medical conditions, so your doctor will use the test results to determine underlying problems. If low creatinine levels, along with other symptoms, indicate liver disease, treatment most likely begins with medications and lifestyle changes. These changes may include eating healthier and avoiding alcohol.
If a person has a muscle disorder, treatment may include exercise therapy, medications, or surgery.