What is GGTP?
Gamma-GT (synonyms: gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase, GGTP, gamma-glutamyltransferase) refers to an enzyme that is produced during a number of biochemical processes. This substance takes part in the metabolism of amino acids and is regularly found in and inside cell membranes. It is most present in the following organs:
- liver;
- kidneys;
- prostate;
- pancreas.
If gamma-GT is elevated, the causes in women may lie in diseases of the listed organs. Since women do not have a prostate, the gamma-GT level will normally be lower than in men. Gamma-glutamyltransferase is present in small quantities in other organs, but its importance is not decisive.
An increase in the indicator never passes without leaving a trace; it always signals a problem in the body. GGTP is most abundant in the liver tissues, so damage to them should first be ruled out.
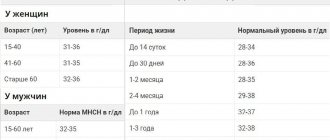
For women, the normal value is 6-32 IU/liter, or 10-66 units/liter (depending on the measurement in a specific laboratory).
For comparison, in men the figure is 18-100 units/liter, in children it varies by age. It is worth citing the most common reasons for the increase in indicators in women:
| Increased GGTP enzyme | Possible reason | What else could the problem mean? |
| More than 10 times | Liver tumors | Acute hepatitis |
| 5-10 times | Chronic hepatitis | Cirrhosis, gallbladder disease |
| Less than 5 times | Alcoholism | Taking hepatotoxic drugs |
The blood test is taken on an empty stomach and is prepared within 24 hours. Afterwards, the doctor draws conclusions about the possible preconditions for an increase in the enzyme.
Correctly selected compression stockings have a powerful therapeutic effect, they are comfortable to wear every day, and the products look aesthetically pleasing on the legs. Read more in the article: “how to choose compression stockings for surgery.”
The norm of GGT in human blood
Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, the norm of which depends on the sex and age of a person, differs in women and men, but not too much. The case is completely different in adolescents and newborns.
The GGT norm for people is as follows:
- Reactive arthritis in a child, have you ever encountered this?
- in men, indicators are up to 49 U/l;
- and in women up to 32 U/l;
- in newborns, GGT is increased 2-4 times.
Blood test for GGT
The norm for a biochemical blood test ggt in adults ranges from 6 to 70 units per liter of blood, do not forget that in girls the norm is lower than in men. If we talk about children, then their indicators can jump to 185/1 liter of blood, six-month-olds will show 200 U/l. For children, such results are acceptable, so there is no need to worry, all because their liver is not yet able to produce the enzyme.
Interesting fact: depending on race, the GGTP blood chemistry test may be higher or lower.
We have already understood that blood GGT depends on age; below we will provide a table with test results for both women (F) and men (M).
(AND)
| Age | Norm |
| 5 days after birth | Close to 185 units. per liter |
| From 5 days to 6 months | Not higher than 202 units. per liter |
| From 6 months up to 1 year | 34 units |
| 1-3 years | Close to 18 units. |
| 3-6 years | Not higher than 22 units. |
| 6-12 years | 16 units |
| 12-17 years old | Not higher than 33 units. |
| 18 and older | 6-42 units |
During pregnancy
| 1st trimester | 0-17 units |
| 2nd trimester | Up to 33 units |
| 3rd trimester | 32 units per liter |
Results may vary due to: analysis equipment, units. measurements and races of women.
Protein levels may rise sharply, but temporarily, which is not bad. Such a jump depends on the expectant mother’s consumption of many vitamins.
(M)
For representatives of the stronger sex, the numbers will be higher:
| Age | Norm |
| 5 days after birth | Not higher than 185 units. per liter |
| From 5 days to 6 months | Not higher than 202 units. per liter |
| From 6 months up to 1 year | Close to 34 units. |
| 1-3 years | Up to 18 units |
| 3-6 years | Not higher than 22 units. |
| 6-12 years | 16 units |
| 12-17 years old | Not higher than 45 units. |
| 18 and older | 10-71 units |
The prostate gland contains more enzyme for the male sex; a strong increase in GGT in the blood warns of a deviation in the functioning of the internal organs.
Preparing for analysis
To avoid false indicators in the final results table, it is recommended to follow preparation measures. By following the rules listed below, the results will be the most reliable, which will help to correctly diagnose or refute the disease.
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach. To avoid deviations in blood counts caused by activation of enzymes due to food intake.
- Refuse to eat fatty, highly salted, spicy, overcooked foods that are difficult for the body for at least twenty-four hours (preferably forty-eight hours).
- It is recommended to give up physical activity two days in advance, since physical effects on the body also affect the final results;
- A visit to a sauna, steam bath, or hot bath the day before can lead to fluctuations in normal values. You should avoid visiting places where the body is exposed to thermal effects;
- Limit alcohol intake and cigarette consumption at least 24 hours before the upcoming test;
- Stop using medications at least two days before the test. Drugs of certain groups can affect the parameters of a biochemical blood test.
Come to donate blood 10-15 minutes in advance. This is necessary so that the body calms down, shortness of breath goes away, and the body acclimatizes to the temperature conditions of the room (especially after a cold street). If you are very hungry, it is better to take food with you and satisfy your hunger immediately after blood collection.
Flu and colds take you by surprise, because you can get infected with them in any crowded place, at work or from a loved one. Treatment must be approached comprehensively, and then viral diseases will end without complications. Read more in the article: “an effective remedy for colds and flu.”
Normal indicator for adults and children
Advertising:
The normal range of gamma-glutamyltransferase levels differs between men and women. The norm for women is no more than 30 units per liter (U/l), and for males - no more than 50. The reference values are given for informational purposes only.
In each laboratory, standards may differ depending on which test systems are used to determine the activity of this enzyme in blood serum. Taking this into account, it is better to study GGT levels over time in the same clinical diagnostic laboratory.
You should not try to decipher the analysis results yourself. Let a specialist handle this.
Normal GGT levels are higher in children than in adults and vary depending on the age of the child. In the first week of a child's life, the GGTP level should not exceed 180 units per liter. Then the enzyme level can increase, but not more than 200 units during the first half of the year. By the first year of a child’s life, the level of gamma-glutamyl transferase decreases to a level of no more than 35 units per liter.
During the growth and life of a child, the level of glutamyl transferase does not change much. Around the age of twelve, normal levels of the enzyme become the same as for an adult. A change in the activity of the enzyme glutamyltransferase above the reference values indicates pathology. In addition to diseases, taking medications can lead to deviations from the norm.
Prices
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT) | 60 ₽ |
All prices
Name in English: Gamma-GT
Gamma-GT (gamma-glutamyl transferase, GGT, GGT, Gamma-glutamyl transferase) is an enzyme found primarily in the cells of the liver and pancreas. Changes in the activity of this enzyme in blood serum are of great importance for the diagnosis of diseases of the liver and biliary tract, since it is more sensitive to pathological processes in liver cells than ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase.
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is an enzyme (protein) of the liver and pancreas, the activity of which in the blood increases with liver disease and alcohol abuse. General information about the study
Bile is produced in liver cells and is secreted through a system of microtubules called bile canaliculi. They then unite to form the hepatic ducts, which extend beyond the liver to form the common bile duct, which drains into the small intestine. Bile is necessary for the absorption of fats from food. Some drugs are also released through bile. It is constantly formed, but enters the intestines only during and after meals. When it is not needed, it accumulates in the gallbladder. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is an enzyme that is found in the cells of the liver and biliary tract and is a catalyst for certain biochemical reactions. It is not contained in the bloodstream, only in cells, when destroyed, their contents enter the blood. Normally, some cells are renewed, so a certain GGT activity is detected in the blood. If many cells die, its activity can increase significantly.
The GGT test is the most sensitive test for bile stagnation - cholestasis. The activity of GGT when the outflow of bile is obstructed, for example due to stones in the bile ducts, increases earlier than the activity of alkaline phosphatase. However, this increase is nonspecific, since it occurs in most acute diseases of the liver and bile ducts, for example, in acute viral hepatitis or cancer, and usually this result is not very informative in identifying the specific disease or condition that caused liver damage. Unlike other liver enzymes, GGT production is triggered by alcohol, so its activity may be elevated in alcohol abusers even in the absence of liver disease. In addition, GGT production is stimulated by some medications, including phenobarbital and paracetamol, so you can expect an increase in GGT without liver damage while taking them. GGT is also found in the kidneys, spleen, pancreas, brain, prostate, and an increase in its activity is nonspecific only for liver disorders.
How to detect an increase in gamma GT?
With a number of symptoms, one can suspect that the gamma-GT level in women is increased. Only a slight increase in it may not give a clinical picture. Typically, with all pathologies of the hepatobiliary system that accompany the growth of gamma-HT, there is stagnation of bile. This condition can manifest itself:
- jaundice of the skin, yellowing of the sclera;
- heaviness, pain in the liver area;
- sharp pain after eating;
- weakness, decreased performance.
Advertising:
No less often, the patient develops dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Sometimes constipation occurs instead of diarrhea. Since even heart disease can be the cause of an increase in GGTP, they may be accompanied by chest pain, pallor, fainting, and shortness of breath.
Cholestasis is the main reason for the increase in the indicator
With pathologies of the hepatobiliary system, cholestasis occurs - this condition means that bile reduces the rate of excretion. The reason is both the cessation of its transport through the biliary tract and the slowdown in production in the liver.
Gamma-GT concentrations in women most often increase due to liver disease.
Blockage of bile outflow can occur in advanced stages of cirrhosis, with severe fatty hepatosis. If the levels of AST and ALT of the liver are simultaneously increased, one can suspect viral hepatitis A, B, and less often C. Outside of the inflammatory process, the level of gamma-glutamyltransferase increases with toxic liver damage, poisoning, and sclerosing cholangitis. All of these diseases cause intrahepatic cholestasis, which is also accompanied by an increase in bilirubin.
Extrahepatic cholestasis can have the same consequences, when the work of ducts located outside the liver is disrupted. This means that the gallbladder is affected in the following diseases:
- stones in the organ;
- slang syndrome (thickening of bile);
- neoplasms;
- acute and chronic inflammation of the organ - cholecystitis.
Advertising:
All these pathologies often cause a concomitant increase in alkaline phosphatase in the blood. Treatment will be aimed at improving the flow of bile and blocking inflammation.
Tumor processes
Cancer of the liver and other organs of the hepatobiliary system can be primary or metastatic. If cancer cells multiply in organs, liver function tests and gamma-GT begin to be released in increased volume. For large tumors, the analysis transcript shows a serious excess of the indicator - 10 times or more.
In the initial stages of oncology, the excess of the enzyme can be moderate.
Among other things, a pancreatic tumor can cause changes in tests. This organ is responsible for the production of a number of amino acids, which include gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Therefore, after treatment, the amount of enzyme in the blood stabilizes, and in case of relapse it usually increases. A moderate increase in the number can indicate the presence of cysts and other benign tumors.
Effects of alcohol
The release of GGT is directly related to the consumption of alcohol - even when determining the initial high levels of the enzyme in the blood, giving up alcohol reduces the GGT content by 2 times after 10 days. If after a month the GGT level returns to normal, this means there is no pathology. If the indicators are close to exceeding the norm, it is worth thinking about completely giving up alcohol, since it is this that causes alcoholism and such serious conditions as cirrhosis, injuries while intoxicated, and delirium tremens.
In the case of a single alcohol intoxication, a period of abstinence is sufficient for the indicators to return to normal.
A test for GGT, done in conjunction with other studies of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), can determine not only alcoholism, but also alcoholic steatohepatitis - an inflammatory process with the parallel formation of areas of necrosis under the influence of ethanol metabolic products.
In other words, a penchant for drinking alcohol that has not yet developed into alcoholism. Some companies have made such a test mandatory during a medical examination, and in case of a positive result, it becomes a reason for recognizing professional unsuitability. Treatment of the identified pathology depends on the stage of the disease and is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is an enzyme (protein) of the liver and pancreas, the activity of which in the blood increases with liver disease and alcohol abuse.
Research method
Kinetic colorimetric method.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is an enzyme that is found in the cells of the liver and biliary tract and is a catalyst for certain biochemical reactions. It is not contained in the bloodstream, only in cells, when destroyed, their contents enter the blood. Normally, some cells are renewed, so a certain GGT activity is detected in the blood. If many cells die, its activity can increase significantly.
What is the research used for?
To confirm liver and bile duct disease.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment for alcoholism or alcoholic hepatitis.
- For the diagnosis of diseases affecting the biliary tract.
- To determine whether the increase in alkaline phosphatase activity is due to liver disease or bone pathology.
What do the results mean?
| Age, gender | Reference values |
| 12 - 17 years old, male | |
| 12 – 17 years old, female | |
| > 17 years old, male | 10 – 71 U/l |
| > 17 years old, female | 6 – 42 U/l |
Most often, the following statement is true: the higher the GGT activity, the more severe the damage to the liver or bile ducts.
Reasons for increased GGT activity
Damage to the liver and biliary tract
- Mechanical jaundice associated with obstruction of the bile ducts. — Bile duct stones, bile duct scars after surgery. — Tumors of the bile ducts. — Cancer of the head of the pancreas, stomach cancer due to mechanical compression of the common bile duct.
- Alcoholism. After quitting alcohol, GGT activity returns to normal within a month.
- Liver cancer, metastases of tumors of other organs to the liver.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Acute and chronic hepatitis of any origin, especially alcoholic.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Other reasons
- Pancreatitis is acute inflammation of the pancreas.
- Prostate cancer.
- Breast and lung cancer with liver metastases.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Myocardial infarction. GGT may rise after 3 to 4 days, reflecting liver involvement secondary to heart failure.
- Heart failure.
- Hyperthyroidism – increased function of the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes.
Reasons for decreased GGT activity
- Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the function of the thyroid gland is reduced.
Other possible reasons
Advertising:
Regular examinations and blood tests are recommended for anyone undergoing long-term treatment. Many tablets cause cytolysis (cell death) of the liver. This provokes the release of large amounts of liver enzymes into the blood. In women, this often happens when taking a course of estrogens and corticosteroids. The following gives the same effect:
- drugs for tuberculosis;
- a number of antibiotics, especially tetracyclines;
- barbiturates;
- neuroleptics;
- chemotherapy;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
For treatment, you should take a course of hepatoprotectors - Essentiale, Heptral. All poisons, including alcohol, have a toxic effect on the liver. In chronic alcoholism, the amount of the enzyme can always be increased, and even after quitting alcohol it does not return to normal immediately. Among the rarer reasons for the increase in gamma HT in women are:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- kidney tumors;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart failure.
In some cases, the enzyme is elevated in thyrotoxicosis - hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. All of these pathologies do not occur without additional symptoms and are easily identified during examination.
Reasons for reducing GGT
Thyroid pathology can cause a decrease in GGT
There are not many reasons for a decrease in GGT; it is mainly due to endocrinological pathology of the thyroid gland:
- Congenital underdevelopment of the thyroid gland;
- Hereditary disorder of the synthesis of thyroid hormones;
- Autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland associated with a decrease in its function (hypothyroidism);
- Conditions after surgery on the thyroid gland;
- Lack of iodine in food.
How to treat pathology?
Advertising:
As for medications that can normalize gamma HT levels, they should be prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the reasons for the increase in the enzyme. In other words, in order to reduce the concentration of the enzyme, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, stop taking inducer medications or alcohol. Since an increase in gamma TG is most often associated with choletasis, Urdoxa, Ursosan, Urso, Ursofalk, as well as other drugs based on ursodeoxycholic acid are prescribed. In some cases, vitamin C can reduce gamma-GT levels.
Liver functions are improved by Essentiale, Livolin, Rezalut and other essential phospholipids. If the increase in gamma-GT is associated with stagnation of bile, Alahol, Hofitol and other choleretic drugs are recommended. Alkaline mineral waters can also be prescribed, which will help reduce the viscosity of bile and facilitate its removal.
For pain in the liver area, Besalol, Spasmolitin, No-shpa and other antispasmodics are prescribed.
Skin itching, which often accompanies bile stagnation, is well relieved by Rifampicin or Cholestriamine. The gamma GT test is a very sensitive test that gives the specialist more information than alkaline phosphatase, ALT and AST. Therefore, it is often used not only to assess a person’s health status, but also to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Why is a blood test for GTP so important?
A general blood test ranks first among the mandatory methods of testing our health, but biochemical serum indicators - protein, glucose, urea, bilirubin, liver transaminases (ALAT, AST) are no less valuable... There is another objective method of monitoring - a blood test for gammaglutamyl transpeptidase (GTP). Why is it so important?
GTP is a protein enzyme that is a specific catalyst for intracellular biochemical reactions and amino acid metabolism.
It is found mainly in the cells of the liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas and prostate glands. Accordingly, it enters the bloodstream mainly in case of: • acute or chronic liver damage (hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors),
• cholelithiasis,
• cholangitis,
• obstructive jaundice,
• pancreatitis,
• prostate and pancreatic cancer,
• alcohol abuse,
• taking certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal contraceptives, sedatives, antibiotics, etc.).
It should be understood that the desired enzyme is found in large quantities in the prostate, therefore, even normally, the concentration of GTP in men is higher than in women. And yet, in routine clinical practice, a blood test for GTP is primarily a biochemical liver function test or an indicator of the functioning of the biliary system. Therefore, doctors mainly associate high rates with a violation of the formation, secretion and outflow of bile - cholestasis, which is manifested by general weakness, insomnia, heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, itching, jaundice. Of course, cholestasis is not an independent disease, but a condition inherent in many diseases of the liver and biliary tract. Therefore, an increase in the level of GTP only suggests the possibility of a disease, but does not determine the diagnosis or the true cause of the pathology. Prescribing a blood test for GTP is also justified when diagnosing anicteric forms of hepatitis, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for alcoholism, liver tumors, pancreatic and prostate cancer, and assessing the hepatotoxic effect of drugs.
If there is any increase in GTP in the blood, you should consult a doctor (general practitioner or gastroenterologist) to find out the cause. Priority studies for high GTP should include a complete blood count, biochemical analysis for ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, total and direct bilirubin, total protein and albumin, as well as ultrasound of the abdominal organs. If an increase in GTP occurs due to the use of alcohol or medications, you should stop taking them and repeat the analysis after a few weeks.
Vladimir KHRYSCHANOVICH, Doctor of Medical Sciences.