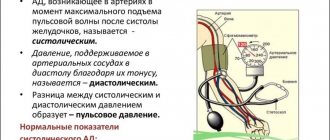
Blood pressure (BP) is an integral indicator of systemic blood flow. It includes two main values: experts call them systolic and diastolic pressure, and common people talk about upper and lower, respectively. The presence of a tonometer in almost every home allows you to monitor blood pressure levels at any time: morning and evening, at night, after meals, physical activity, etc.
Most patients roughly understand what numbers indicate increased or decreased indicators, especially if they change in direct proportion to each other. What to do if non-standard values appear on the tonometer and how to decipher them? This article will focus on just such a case – a pressure of 140 over 70. What this blood pressure level means, whether it is normal and whether correction of values is necessary is discussed below.
Blood pressure 140 over 70 - what does this mean?
When the pressure reading is 140 to 70, we are talking not so much about hypertension or hypotension, but more about pulse hypertension, a serious increase in blood pulse pressure (PBP), which is the main evidence of the elasticity of blood vessels, calculated as the difference between the upper and lower blood pressure readings. Based on it, the cardiologist draws conclusions about the condition:
- arterial walls;
- vascular patency;
- aortic valves;
- myocardium.
A normal reading is considered to be at least one-fourth of the systolic reading, about forty units on average. If the pressure is 140 over 70, it is almost twice as high, which indicates serious problems or malfunctions in the cardiovascular circulatory system. A reduced rate is less dangerous, often accompanies blood loss, and is the main symptom of heart failure.
What is pulse hypertension
Pulse hypertension is an excess of normal blood pressure levels. As a rule, it is formed due to loss of elasticity of the walls of blood vessels in elderly people. May be caused by high physical activity or nervous tension. Exceeding the indicator poses a great danger to human health, since the load on a number of vital organs, including the heart, increases - they wear out faster and work worse.
Possible complications
If pulse pressure rises frequently, this may be an indication of the presence of serious pathologies. They can provoke quite serious consequences over time. Here is a list of the most dangerous of them:
- stroke;
- brain abnormalities;
- wear and tear of the heart;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- kidney diseases;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- oxygen starvation;
- myocardial infarction;
- hypertonic disease.
To prevent their occurrence, do not delay diagnosis and treatment. And if episodes of pulse hypertension have already occurred, then you should regularly measure blood pressure for monitoring and prevention purposes.
Why is there a big difference between upper and lower pressure?
If a decrease in the PBP norm is often caused by stress, bad habits and nervous strain, then pulse hypertension is almost always a serious symptom of one of the following diseases:
- increased intracranial pressure;
- pre-stroke or pre-infarction condition;
- anemia;
- heart block;
- tuberculosis.
If the blood pressure level is regularly exceeded, it is necessary to undergo examination by a doctor to find out the reason for the difference between the upper and lower limits of blood pressure values. This condition, accompanied by dizziness, nosebleeds or fainting, is a serious risk factor for heart attack or stroke, cerebral hypoxia for both young and elderly people.
Causes of high upper pressure
Hypertension is a high systolic indicator; it can be caused by a number of reasons, from hereditary predisposition to changes in atmospheric pressure or other changes in weather conditions. Bad habits that negatively affect the condition of blood vessels - smoking, systematic drinking - play an important role. Poor nutrition—regular consumption of fatty and salty foods—has a negative effect on blood pressure. A sedentary lifestyle and nervous tension also lead to arterial hypertension.
Low lower pressure - causes
Reduced lower pressure is associated with a number of factors; it is a consequence of physical or nervous stress, violation of rest or nutritional regimen, chronic fatigue, and lack of sleep. At retirement age, hypotension - a condition when diastolic pressure is low - is caused by a number of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system, such as:
- cerebral stroke;
- chronic heart failure;
- cardiac ischemia;
- tachycardia or bradycardia.
Preventing high blood pressure
In order to maintain normal blood pressure, you must:
- Maintain a daily routine.
- Avoid unhealthy foods, the consumption of which can lead to obesity and increased cholesterol levels.
- Stop drinking alcohol and tobacco products.
- Avoid stressful situations.
A healthy lifestyle is a great way to normalize blood pressure over the long term. Elderly people are recommended to undergo systematic examination by a cardiologist, as well as regularly take medications, the main task of which is to control vascular tone.
Pressure 140 over 70 - what to do
There are drug and non-drug methods for reducing pulse pressure. You need to understand whether we are talking about a regular condition, rare attacks or frequent surges in pulse hypertension due to increased stress, for example. In any case, if the difference between the upper and lower pressure is 70, you need to consult a doctor to determine the cause of blood pressure fluctuations, receive recommendations for lifestyle correction, and prescribe a course of drug therapy, if necessary.
- How to get a tax deduction when buying an apartment
- Diet menu No. 5 for the week
- How to come up with a beautiful and original signature for your last name in your passport
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's heart, as well as other internal systems and organs, are subject to increased stress. Almost eighty percent of pregnant women experience hypertension, especially in the first and third trimester. It provokes increased pulse pressure. It is necessary to carefully monitor your condition and regularly consult with your specialist, since elevated blood pressure can affect the well-being and development of the fetus.
In older people
Due to the fact that in old age the body experiences natural wear and tear of all organs and systems, including the cardiovascular system, normal blood pressure indicators are different, they fluctuate within the range of 110/130 to 60/80. Pulse hypertension over the age of sixty can be dangerous and lead to hypertensive crisis. as well as a number of other serious conditions. That is why, as you age, it is recommended to regularly measure your blood pressure, periodically maintain your health with drug therapy, and undergo regular examinations by a doctor.
How can it manifest itself? Associated symptoms
The severity of symptoms directly depends on the individual characteristics of a particular organism. Some people practically do not feel pressure fluctuations and discomfort, while others develop characteristic signs. The more pronounced the symptoms, the worse the impact of the indicators on health. Here is their full list:
- apathy;
- fatigue and increased fatigue;
- poor concentration;
- dizziness;
- severe headaches (mainly in the temporal and occipital regions);
- nosebleeds;
- facial redness;
- excessive sweating;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- memory problems;
- nausea, vomiting (bringing minor relief);
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- weather sensitivity;
- knocking in the temples;
- drowsiness;
- increased heart rate;
- chills, cold sweat;
- disorientation in space;
- feeling of lack of air;
- fainting;
- numbness of the limbs.
The risk group includes athletes, expectant mothers (especially in the last trimester), and elderly people (over fifty years old). Also, all people whose professional activities involve heavy physical work.
It should be said that even if there are practically no symptoms, disorders can still have an extremely negative impact on the body. He will accumulate all his strength in order to adapt and normalize his condition, but over time he will get tired of fighting. The consequences in this case creep up unnoticed. For this reason, cases of heart attacks, strokes, and heart attacks among young people against the background of imaginary well-being have become more frequent.
How to normalize blood pressure at home
People suffering from hypotension and hypertension know very well how to quickly stabilize their condition when their blood pressure rises. Hypertensive patients always keep Corvalol on hand, use lemon balm decoctions, tincture of valerian or hawthorn. For hypotension, take tincture of ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, and other means that stimulate blood circulation and excite the nerve centers. Healthy, adult men and women, to prevent pressure surges, should lead an active lifestyle, follow a diet, diet, and worry less.
Diagnostics
In order to establish the cause of the pathology, the doctor prescribes daily blood pressure monitoring and other clarifying studies for such patients. The most common:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- lipid profile;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- coagulogram;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and renal vessels.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed to undergo consultation with other specialists:
- vascular surgeon;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist.
Folk remedies for lowering blood pressure
If you have hypertension, it is not necessary to regularly swallow pills or other medications. There are many traditional methods of treating this disease:
- Freshly squeezed juices from beets, cucumbers, carrots, celery with parsley and spinach help a lot.
- You can prepare a garlic tincture, grind lemon with cranberries and honey, and make lotions from natural apple cider vinegar.
- An effective herbal mixture of hawthorn, St. John's wort, oregano, rose hips, and motherwort.
What to do?
If the deviations are temporary, then medical intervention is not required. Of course, if such a problem appears on a regular basis, you need to go to a consultation with a therapist and get examined.
If surges in blood pressure are associated with any serious disease, then you need to undergo a course of therapy that is aimed at getting rid of the pathology. After the root cause is eliminated, pressure readings return to normal.
In case of rare manifestations under the influence of external factors, you can use improvised methods and means to reduce pulse pressure at home. Among them:
- drinking a few drops of valerian tincture diluted with water;
- taking nitroglycerin tablets;
- walk in the fresh air;
- rotational movements of the head from one side to the other;
- legs raised high;
- exercises for the shoulder girdle.
Usually these measures are enough to eliminate pulse hypertension.
Self-massage
Massage or self-massage of the collar area can normalize blood pressure. The procedure helps to effectively warm up the muscles and increase blood circulation in the cervical spine. As a result, blood flows well to the brain and headaches go away.
Technique:
- begins with light stroking and rubbing of the muscles on both sides of the spine;
- then the intensity is gradually increased and the muscles are kneaded;
- At the end, smoothing must be performed.
The optimal duration of each session is 15 minutes.
Medicines
Medications are selected only by a doctor after interviewing the patient and thoroughly examining him. Using them on your own is unacceptable, so as not to provoke complications. It can be:
- ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Methiopril, Enam, Enalapril, Benazepril). They block the enzymes that produce active angiotensin. Contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, renal failure.
- Calcium channel blockers (Verapamil, Diltiazem, Amlodipine, Nimodipine, Nifedipine). They help restore normal blood flow and stabilize pressure, preventing blood vessels from narrowing. Contraindications: arrhythmias, ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, narrowing of the aorta.
- Diuretics. Potassium-sparing, loop and thiazide diuretics (Furosemide, Diacarb, Spironolactone, Amiloride, Retapres, Indapamide). They remove excess fluid from the body and lower blood pressure. They are prescribed with caution, as they remove potassium from the body along with fluid. And it plays an important role for the heart.
- Angiotensin antagonists (Cozaar, Valsartan, Teveten, Losartan). They prevent angiotensin from affecting blood vessels.
- Adrenergic blockers (Atenolol, Propronolol, Timolol, Betaxolol). Prevents the effects of adrenaline on vascular walls. Reduce pulsation rate and reduce the biosynthesis of adrenaline and norepinephrine
If indicated, antispasmodics, sedatives, and antiemetics may be prescribed.
Nutrition
Also, to normalize blood pressure, it is very important to establish a proper diet and drinking regime. This will prevent the appearance of edema and will improve the functioning of the urinary system. A number of products should be excluded from the menu:
- caffeinated drinks, strong teas;
- sweet soda, packaged juices;
- fatty and fried foods;
- marinades, pickles;
- smoked meats, semi-finished products.
It is healthy to eat a variety of cereals, vegetables, fruits and herbs. It is especially worth noting foods rich in iron and folic acid:
- sauerkraut;
- potato;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- apples.
The average amount of clean water you drink per day should be two liters.