Author
Pikulik Natalya Sergeevna
Leading doctor
Cardiologist
until October 31
We're giving away RUR 1,000 for all services per visit in October More details All promotions
Electrocardiography
(ECG) is a study of the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure carried out using sensors attached to the patient's chest, during which the bioelectric potentials arising during operation are recorded. The results are recorded on a special tape recorder or in digital form. The document with the results of the study is called a cardiogram (electrocardiogram). An ECG, that is, an electrocardiogram, is necessary for any suspicion of heart problems. An ECG is a diagnostic minimum that forms the foundation of cardiac examination and treatment.
Why does an ECG help us judge the condition of the heart?
ECG
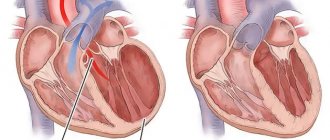
The human heart is essentially a pump that keeps blood moving. To do this, the heart muscle either contracts or relaxes. The rate of contraction of the heart forms the heart rhythm. A healthy heart contracts at regular intervals, and the duration of this interval should also fall within the norm, which depends on age. A normal resting heart rate usually ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. In children under 12 years of age, higher values will be normal (for example, under the age of 1 year, the average value is 130 beats per minute). With age, the heart rate slows down: in older people, the normal heart rate is 60-65 beats per minute.
The contraction of the heart muscle is regulated by electrical impulses generated in the heart itself. The main role belongs to a group of cells that form the so-called sinus node, located in the right atrium. It is he who generates impulses that normally set the contraction of the heart. In this case, the bioelectric mechanism of the heart is designed in such a way that the muscles of the atria contract almost simultaneously, pushing blood into the ventricles of the heart, and the muscles of the ventricles also contract simultaneously, but with a delay relative to the atria of about one tenth of a second. This time is necessary for the ventricles to fill with blood. Any violation of this complex and precise mechanism of generation and propagation of electrical impulses leads to disturbances in the functioning of the heart, manifested in the form of symptoms of heart disease. Conversely, heart pathology affects the accuracy of the bioelectric mechanism. Therefore, when symptoms of heart disease occur, first of all, an ECG is done.
Ultrasound of the heart
Ultrasound examination of the heart or echocardiography is a method of studying the anatomy of the heart muscle. During the procedure, the diagnostician directs a special device to the heart. The device passes ultrasonic waves through the body. Our organs reflect and partially absorb waves. The ability of different human tissues to reflect/absorb ultrasound differs. The ultrasound machine receives the reflected waves and converts them into an image on the monitor.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
- Valve condition.
- Pathologies, for example, a tumor or a previous microinfarction.
- The speed of blood flow in the heart.
- Vessel diameter.
- Changes in the thickness of the walls of the ventricles and atria.
- Changes in large vessels.
- Blood clots.
- Is there fluid in the pericardial sac?
A professional cardiologist uses ultrasound results to detect many heart diseases. The doctor makes a conclusion based on the results of the study, taking into account age, gender, lifestyle and many other factors. Therefore, during the examination, answer the doctor’s questions in detail and honestly.
Indications for cardiac ultrasound
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the heart according to the following indications:
- weakness and dizziness;
- fainting and recurring headaches;
- nausea due to high blood pressure;
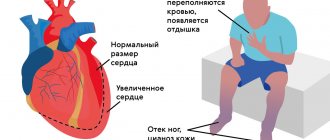
- dyspnea;
- swelling on the body in the late afternoon, especially on the legs;
- constant and recurrent pain in the chest or under the shoulder blade;
- rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations;
- pale or bluish skin;
- heart murmurs;
- suspicion of congenital or acquired heart disease;
- vascular pathology, for example, varicose veins or thrombophlebitis;
- suspicion of rheumatism, lupus erythematosus or scleroderma;
- upcoming surgery if there is a history of cardiac problems or if the patient is over 50 years of age.
If after a routine echocardiography the doctor still has doubts, he may prescribe an ultrasound of the heart through the esophagus. Such a study causes some discomfort to the patient, but gives a more accurate result.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination. It is safely prescribed to everyone, including children and pregnant women.
Information content and diagnostic capabilities of ECG
An ECG can reveal:
- heart rhythm disturbances (diagnosis of various types of tachycardia, as well as atrial fibrillation, parasystole and other types of heart rhythm disturbances);
- cardiac conduction disorders. This leads to a shift in the generation of impulses from the sinus node, as well as to its blockade in any part of the heart;
- decrease in coronary circulation in one or another part of the heart (coronary heart disease);
- focal changes in the heart (scar tissue formed after inflammatory diseases, myocardial infarction and other diseases);
- myocardial hypertrophy (thickening of the myocardial walls).
Rhythm disturbances and blockades on the ECG
Normally, impulses arise in the sinus node; on the ECG, the doctor sees sinus rhythm. Arrhythmias
(rhythm disturbances) are most often represented by extraordinary contractions of the atria (supraventricular, or supraventricular, extrasystole) and ventricles (ventricular extrasystole).
Arrhythmias can also occur as rhythms that occur outside the sinus node (supraventricular, AV nodal and ventricular tachycardias, atrial fibrillation and flutter, etc.). A disturbance in the conduction of an electrical impulse through the conduction system of the heart is called blockade
. Blockades are different, depending on the level - sinoatrial, atrioventricular, bundle branch blocks (complete and incomplete). Some blockades are constantly present, and some appear and disappear (transient, transient).
Indications for ECG
ECG is performed:
- for any diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- if you suspect such diseases, for example, chest pain, shortness of breath, swelling of the legs;
- people who are at risk of developing heart disease (those with a hereditary predisposition, those suffering from obesity, atherosclerosis, bad habits - smoking, alcoholism) to determine the condition of the heart;
- in case of risk of complications from the heart, in particular with hypertension, after infectious diseases (for example, tonsillitis), after a stroke;
- when planning and managing pregnancy;
- to assess the effect of medications on the body (in particular, to confirm the absence of side effects when taking them);
- to check the operation of pacemakers.
Diagnosis of heart disease using electrocardiography
When diagnosing various diseases and pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, several different methods are used, which are selected in direct dependence on how the initial examination and medical history went. The choice of technique lies entirely with the doctor. One of the safest, but at the same time extremely effective options is ECG - electrocardiography. Therefore, they resort to it very often when a wide range of diseases and pathologies are suspected.
1. What is it
An ECG is a very simple and extremely painless test that monitors the electrical impulses of the heart. Thanks to an ECG, a doctor can assess the condition of a special structure that causes heart contractions, analyze the frequency and rhythm of cardiac movements, examine the conduction pathways of the heart, and also obtain numerous other data that will allow a more accurate diagnosis. In general, an ECG can be done if almost any cardiac pathology is suspected, which is why an ECG is one of the most common types of procedures for examining the heart and blood vessels.
2. Indications
As mentioned above, an ECG can be prescribed for almost all potential abnormalities in the heart that are identified after an initial examination and medical history.
First of all, an ECG is prescribed if there is a suspicion of:
- insufficient blood circulation of the heart;
- rhythm disturbances;
- hypertrophy of the heart muscle;
- thinning of the heart muscle;
- post-infarction problems.
In these cases, the use of an ECG will not only be indicative, but also safe; it will not lead to any potential deviations or complications. The situation is similar with other problems and pathologies related to the heart.
Angina pectoris is a reason for diagnosis.
If we talk about specific symptoms that may be a reason for an ECG, then these are:
- dizziness;
- hypertonic disease;
- interruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- increased heart rate;
- chronic diseases of the respiratory system;
- pain in the chest area;
- fainting conditions;
- severe shortness of breath;
- angina pectoris;
- myocarditis;
- endocarditis;
- age: for women - from 45 years old or for men - from 40 years old.
Sometimes an ECG is performed without any specific reasons, simply for the purpose of performing a general examination and preventing heart disease. The high safety of this research method allows you to do ECGs in any quantity without any problems.
3. Contraindications
Although an ECG is quite harmless, it is still strongly not recommended to carry out this examination when a person has an exacerbation of infectious diseases. Sometimes an ECG may not be informative enough, for example, if testing for coronary artery disease is performed without stress tests. In general, ideally it is worth conducting an ECG as part of a comprehensive study, for example, supplementing it with echocardiography and so on. For some pathologies, it is not very reasonable to limit yourself to just an ECG.
4. Patient preparation
An ECG does not require any specialized training; it can be performed virtually at any time and in any condition of a person. Therefore, you can come to it without any preliminary preparations. The only thing that is very important to observe is stillness. The entire study lasts approximately three to five minutes, during which time the patient must not move, lie as relaxed as possible, so that the results are as detailed and reliable as possible, reflecting the correct picture of his condition at the current moment.
5. How is diagnosis carried out?
Diagnosis is carried out as follows: special electrodes, which look like small metal contacts, are placed on a person’s legs, arms and chest. They detect the strength as well as the direction of electrical currents that appear in the heart with each contraction. The electrodes are connected to a device that records the impulses, usually on a moving paper tape, in the form of a kind of graph depicting vibrations. When studying it, you can evaluate in detail various indicators related to the work of the heart.
Stress tests with ECG.
A common approach to performing an ECG is to conduct so-called stress tests.
They show whether a person has coronary heart disease, how damaged his coronary arteries are, and so on. All this is very problematic to identify if a person is at rest. Therefore, a person sits on a special bicycle and begins to pedal it, or moves on a treadmill at an ever-increasing pace. All this time, an ECG is recorded, and at certain intervals they also note what the person’s blood pressure is at the moment. Sometimes a functional test of the lungs occurs in parallel in order to weed out other symptoms that could theoretically lead to the development of exactly the same problems. If shortness of breath or pain in the chest occurs, the study is stopped without completing it. If a person does not have the opportunity to be exposed to any serious stress, then they resort to an alternative approach - the person does nothing, instead, a special substance is injected into his vein, which worsens blood flow in the coronary arteries. This is a true simulation of the impact of the load. After this, you can diagnose coronary heart disease or other similar problems that give changes in electrocardiogram readings precisely with a noticeable increase in load. An alternative method is continuous ambulatory ECG recording, because sometimes problems are not so easy to detect. In this case, the person is given a small device that runs on a battery. It continuously reads and records. A person records in a special diary any symptoms that appear to him, as well as the time of their specific manifestation. After this, the recording is analyzed on a computer, and the symptoms noted by the person are compared with the readings recorded by the device.
6. Decoding the results
You should not try to decipher the result yourself - this is the task of your doctor. When the research is completed, the most important part begins, deciphering the results in order to identify what exactly is happening to the human heart. The cardiogram displays every nuance of heart activity. Each heartbeat begins with an impulse that originates in the sinus node, the main center responsible for heart contractions. This impulse excites the atria, that is, the upper chambers of the heart, which are displayed on the cardiogram as a special tooth. Next, the impulse spreads to the ventricles, which are the lower chambers of the heart, here the excitation can be displayed with different polarities. Another tooth displays a wave of repolarization when the impulse moves through the ventricles in the opposite direction. The doctor studies all these details, as well as a number of others, after which he can draw certain conclusions regarding the patient’s condition. If the need arises, an ECG that requires urgent interpretation can be transmitted via computer to the necessary specialists, who sometimes may not be nearby. Sometimes, in parallel with the ECG, devices in the doctor's office also record an electroencephalogram, which records the electrical activity of the brain. Then the decoding of these readings can occur in parallel. The data is compared, this allows us to avoid many overlaps, for example, that heart rhythm disorders will be mistakenly confused with epileptic seizures and so on.
7. Possible complications
This diagnostic method is safe. Brief complications can only arise from various additional elements of testing, for example, from stressful physical activity and so on. In extremely rare cases, a mild allergy to the material from which the electrodes are made may occur, but it is not dangerous and occurs in isolated cases.
How is an ECG done?
The ECG procedure is simple and does not cause significant discomfort. To take an electrocardiogram you will need to lie down on a couch. Electrodes are attached to the chest, legs and arms and connected to an ECG machine.
Usually you need to lie still for 5-10 minutes, maintaining a natural breathing rhythm. In some cases, the doctor may ask you to hold your breath.
You can have an ECG done at any of the Family Doctor clinics.
Sometimes more data is needed to evaluate your heart condition. In this case, 24-hour (Holter) ECG monitoring may be suggested. The information will be collected by a portable device that will need to be worn throughout the day. This will allow you to obtain data on the work of the heart in everyday life.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Electrocardiogram
The heart is our “electric motor”. Electrical impulses are generated in a special group of cells in the atria. They cause parts of the heart to contract. An ECG is a recording of the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a waveform. Electrodes are placed on your body to take ECG readings. To increase the passage of electric current, the diagnostician lubricates the areas under the electrodes with a special gel. The procedure itself lasts several minutes. The study is usually carried out in a resting position, lying or sitting. There are types of ECG: stress testing, daily ECG monitoring according to Holper.
What does the ECG show?
- Heart rhythm disturbances: bradycardia and tachycardia, extrasystole, atrial fibrillation.
- Myocardial ischemia.
- Improper conduction of impulses or blockade.
The disadvantage of an ECG is that the study will show those disturbances in the functioning of the heart that affect its functioning at the time of recording. False-positive results are not uncommon for ECGs. If the doctor has doubts about the reliability of the ECG, he will additionally prescribe an ultrasound of the heart.
Indications for ECG
The cardiologist prescribes an electrocardiogram according to the following indications:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- hypertension;
- infection, inflammation or other heart pathologies;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- pregnancy;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- previous sore throat;
- increased health requirements by profession for pilots, drivers, military personnel, athletes, etc.
Doctors prescribe an ECG for 80% of patients admitted for hospital treatment. There are no contraindications to the study. Now you can take an electrocardiogram even outside the hospital. For example, at the pharmacy or at the gym.
Remember! If you feel the slightest discomfort or pain in the heart area, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Take care of your heart and be healthy!
ECG leads
During recording, 12 leads
, which help evaluate the electrical potentials of all parts of the heart. Currently, ECG recording can be carried out not only in medical institutions, where the manipulation is performed by a nurse. Using special devices the size of a cell phone, an ECG can be recorded by the patient himself (both at home and anywhere) and transmitted through the phone to special centers (tele-ECG), where this recording is received on a computer in the form of a regular 12-channel ECG . The interpretation and evaluation of the ECG is carried out by a doctor (cardiologist, functional diagnostics doctor, therapist).
In the Krasnoyarsk Territory, using modern tele-ECG technology, you can record an electrocardiogram in many pharmacies, and receive the result in your hands in a few minutes. In emergency situations, the doctor conveys recommendations and instructions for action.
ECG transmitted by telephone to the Center ( https://www.cardioagent.ru)
, helped diagnose a man’s heart attack.
The author of the article is cardiologist N.S. Veselkova.