Some numbers
There are more than 95 thousand kilometers of blood vessels in the body of a healthy adult. More than seven thousand liters of blood are pumped through them every day. The size of the blood vessels varies from 25 mm
(aortic diameter)
to eight microns
(capillary diameter).
Down with atherosclerosis!
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common vascular diseases. It is characterized by the formation of fatty plaques on the walls of the arteries. Find out how to prevent atherosclerosis.
Where is the largest artery in the body located?
The largest vessel in the human body, which plays an important role in the blood supply system, has a complex arrangement. Its ascending part begins from the left ventricle, then the trunk goes in an arc, going down. It is at the bottom that there is the descending part, which is divided into abdominal and thoracic. A feature of the ascending line is the supply of arteries that carry blood to the heart. Such arteries are called coronary.
The aortic arch carries blood to the subclavian artery, as well as to the common carotid (left and brachiocephalic trunks). These vessels carry oxygenated nutrient fluid to the brain, cervical spine and arms.
What types of vessels are there?
All vessels in the human body can be divided into arteries, veins and capillaries
.
Despite the difference in size, all vessels are constructed approximately the same. The inside of their walls are lined with flat cells - endothelium. With the exception of capillaries, all vessels contain tough and elastic collagen fibers and smooth muscle fibers that can contract and dilate in response to chemical or nerve stimuli. Arteries
carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to tissues and organs.
This blood is bright red
, which is why all the arteries appear red.
Blood moves through the arteries with great force, which is why their walls are thick and elastic. They are composed of a large amount of collagen, which allows them to withstand blood pressure. The presence of muscle fibers helps turn the intermittent blood supply from the heart into a continuous flow to the tissues. As they move away from the heart, the arteries begin to branch, and their lumen becomes thinner and thinner. The thinnest vessels that deliver blood to every corner of the body are capillaries
.
Unlike arteries, their walls are very thin, so oxygen and nutrients can pass through them into the cells of the body. This same mechanism allows waste products and carbon dioxide to move from cells into the bloodstream. The capillaries through which oxygen-poor blood flows are collected into thicker vessels - veins
.
Due to the lack of oxygen, venous blood is darker
than arterial blood, and the veins themselves appear bluish.
Through them, blood flows to the heart and from there to the lungs to be enriched with oxygen. Vein walls are thinner than arterial walls because venous blood does not create as much pressure as arterial blood.
Human circulatory system: briefly and clearly about blood circulation
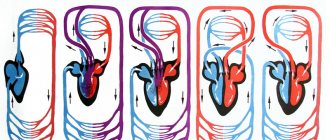
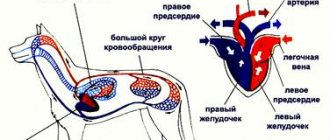
Closed circulatory cycles form circles in which blood moves from the heart to the internal organs and back. The human cardiovascular system includes 2 circles of blood circulation - large and small.
Blood circulating in a large circle begins its journey in the left ventricle, then passes into the aorta and through adjacent arteries enters the capillary network, spreading throughout the body. After this, a molecular exchange occurs, and then the blood, deprived of oxygen and filled with carbon dioxide (the end product of cellular respiration), enters the venous network, from there into the large vena cava and, finally, into the right atrium. This entire cycle takes an average of 20–24 seconds for a healthy adult.
The pulmonary circulation begins in the right ventricle. From there, blood containing large amounts of carbon dioxide and other breakdown products enters the pulmonary trunk and then into the lungs. There the blood is oxygenated and sent back to the left atrium and ventricle. This process takes about 4 seconds.
In addition to the two main circulation circles, in some physiological conditions a person may have other pathways for blood circulation:
- The coronoid circle is an anatomical part of the large and is solely responsible for feeding the heart muscle. It begins at the exit of the coronary arteries from the aorta and ends with the venous cardiac bed, which forms the coronary sinus and flows into the right atrium.
- The circle of Willis is designed to compensate for insufficiency of cerebral circulation. It is located at the base of the brain where the vertebral and internal carotid arteries converge.
- The placental circle appears in a woman exclusively during pregnancy. Thanks to it, the fetus and placenta receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother's body.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force with which blood presses against the walls of the arteries. It increases when the heart contracts and pumps out blood, and decreases when the heart muscle relaxes. Blood pressure is stronger in the arteries and weaker in the veins. Blood pressure is measured with a special device - tonometer
.
Pressure readings are usually recorded in two numbers. Thus, normal blood pressure for an adult is considered to be 120/80
.
The first number, systolic pressure
, is a measure of the pressure during a heartbeat.
The second is diastolic pressure
- the pressure during relaxation of the heart.
Such dangerous excess weight
Professor Sergei Boytsov, chief specialist in preventive medicine at the Russian Ministry of Health and Social Development, talks about how extra pounds affect the heart and blood vessels.
Pressure is measured in the arteries and expressed in millimeters of mercury. In the capillaries, the pulsation of the heart becomes invisible and the pressure in them drops to approximately 30 mm Hg. Art. A blood pressure reading can tell your doctor how your heart is working. If one or both numbers are higher than normal, this indicates high blood pressure. If it’s lower, it means it’s reduced. High blood pressure indicates that the heart is working too hard: it requires more effort to push blood through the vessels. It also indicates that a person has an increased risk of heart disease.
Heart
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that performs the function of a pump. The heart rhythmically pumps blood through the vessels through contractions and relaxations.
The heart cavity is divided by partitions into 4 chambers: 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Contraction of the chambers of the heart is called systole, and relaxation is called diastole.
The heart of an adult is comparable in size to the size of his fist. Weight is approximately 260–330 grams. The heart works around the clock, without stopping. So, over 70 years, 2.6 billion heartbeats occur.
Rice. 1. Human heart.
Three types of tissue form the heart:
- The endocardium is the inner layer that lines the inside of the chambers of the heart.
- The myocardium is the middle layer that makes up the bulk of the heart wall. Represented by cardiac muscle tissue.
- The epicardium is the outer layer covering the surface of the heart.
The heart is located in the center of the chest and is shifted to the left side. The organ is reliably protected by the skeleton (ribs) from possible external damage.
The work of the heart is regulated by the nervous system. In short, it gives the heart impulses that signal the needs of certain organs. In response, the heart strengthens or weakens its activity.
How to keep blood vessels and heart healthy?
The narrowing of the lumen of the arteries leads over time to atherosclerosis, a disease in which the vessels become denser and less elastic.
Atherosclerosis can cause even more serious diseases - such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, and so on. These diseases are practically untreatable, so prevention is extremely important for every person. It is advisable to start improving the circulatory system by changing your lifestyle. This is especially true for overweight people. They should make every effort to normalize it. Moderate and regular physical activity and a proper diet will help you quickly cope with extra pounds, normalize your metabolism and make your circulatory system an effective mechanism for actively supplying the body with all the necessary substances. As for eating habits, a person striving for healthy heart function should exclude animal fats from the diet, which saturate the body with cholesterol and triglycerides. It is also important to limit the consumption of products such as margarine and palm oil (as a result, most confectionery products). Preference should be given to olive oil and fatty sea fish - products rich in polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids. A healthy circulatory system is a guarantee of your excellent health, vigor and full functioning of all internal organs. Do you want to be healthy? So, take care of the circulatory system! Photo: flickr.com Tags:
- Heart and blood vessels
- Circulation
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
Features of the structure of arteries
We indicated that arteries are much stronger vessels than veins. The structure of any artery is three-layered. The first layer is endothelial cells. It is called internal. The middle layer consists of smooth muscle fibers and elastic tissue. This is the most important difference between arteries and each other. Depending on the predominance of specific fibers, the arteries themselves differ. Large ones have a large amount of collagen and elastin. Small ones (arterioles) are almost 90% composed of muscle elements. The outer layer is connective tissue.
Features of the arterial system in men
The most important difference between the male arterial system and the female one is the presence of testicular vessels. It is noted that cardiovascular diseases are more common among the male half of the world's population. Moreover, the greatest damage is caused to the circulatory system by cholesterol, which contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. This phenomenon also causes the development of myocardial infarction.
Features of the arterial system in women
Thanks to the presence of special hormones, women's blood circulation is protected from the effects of cholesterol. But at some point, estrogen stops being produced, which creates a risk of developing hypertension. A difficult situation arises during pregnancy, as this leads to an increase in the volume of circulating blood.
Structure of vascular walls
Arteries have outer, middle and inner layers. The outer layer is connective tissue. In the middle layer there are elastic fibers that maintain the shape of the vessel, and muscle fibers. Muscle fibers can contract and change the lumen of the artery. The inside of the arteries is lined with endothelium, which ensures a calm flow of blood without obstacles.
The walls of veins are much thinner than arteries. They have very little elasticity, so they stretch and fall easily. The inner wall of the veins forms folds: venous valves. They prevent the downward movement of venous blood. The outflow of blood through the veins is also ensured by the movement of skeletal muscles, which “squeeze” blood when walking or running.
Types of Veins
Arteries and veins are designed roughly the same, but veins are thinner and have less muscle, which allows them to hold more blood. Veins typically contain about 70% of the body's blood at one time.
Venules are the smallest type of vein. They have very thin walls in order to hold a lot of blood. They pump low-oxygen blood through capillaries from the arteries directly into the veins. The blood then returns to the heart through a series of veins of increasing size and muscle.
There are two main types of veins: pulmonary and systemic.
Systemic veins are further classified into:
- Deep veins : These veins usually have a corresponding artery nearby and are found in muscle tissue. These veins may have a one-way valve to prevent blood from flowing backwards.
- Superficial veins : These veins do not have an artery of the same name nearby and are found close to the surface of the skin. They may also have a one-way valve.
- Connecting veins : These small veins allow blood to flow from the superficial veins to the deep veins.
Why does hypotension occur?
Low blood pressure (hypotension) is not dangerous for humans. However, people experiencing hypotension feel weak in the body. Dizziness often occurs, concentration decreases and fatigue increases. Therefore, hypotension can cause great discomfort. The most unpleasant consequences of this phenomenon are considered to be a decrease in intellectual activity. Girls face hypotension, and the World Health Organization states that a low blood pressure level is 100/60 mmHg. Art. for women and 110/70 mmHg. for men. It is worth noting that some feel quite comfortable even with constant hypotension.
Circulation circles
Circulation circles were described back in the 17th century by William Harvey. The aorta emerges from the left ventricle, beginning the systemic circulation. Arteries that carry blood to all organs are separated from it. Arteries are divided into smaller and smaller branches, covering all tissues of the body. Thousands of tiny arteries (arterioles) break up into a huge number of the smallest vessels - capillaries. Their walls are characterized by high permeability, so gas exchange occurs in the capillaries. Here arterial blood is transformed into venous blood. Venous blood enters the veins, which gradually unite and eventually form the superior and inferior vena cava. The mouths of the latter open into the cavity of the right atrium. In the pulmonary circulation, blood passes through the lungs. It gets there through the pulmonary artery and its branches. Gas exchange with air occurs in the capillaries that weave around the alveoli. Oxygen-enriched blood travels through the pulmonary veins to the left side of the heart. Some important organs (brain, liver, intestines) have peculiarities of blood supply - regional circulation.
Foundation of life
The circulatory system consists of more than just the heart, blood, and blood vessels. This is only one of two complementary systems - cardiovascular and lymphatic. The latter serves to transport lymph - a colorless liquid with many lymphocytes. The lymphatic system is also extremely important, because human immunity largely depends on it. It is these two systems - cardiovascular and lymphatic - that make up the largest human circulatory system with a total length of more than 100,000 km. This complex mechanism is driven by the heart. This living motor, consisting of muscles, works with amazing performance, pumping more than 9,500 liters of blood per day. In this way, blood is supplied to every cell.
Structure of the vascular system
The aorta, emerging from the left ventricle, forms the ascending part, from which the coronary arteries are separated. Then it bends, and vessels extend from its arc, directing blood to the arms, head, and chest. The aorta then goes down along the spine, where it divides into vessels that carry blood to the organs of the abdominal cavity, pelvis, and legs.
Veins accompany arteries of the same name. Separately, mention should be made of the portal vein. It drains blood away from the digestive organs. In addition to nutrients, it may contain toxins and other harmful agents. The portal vein delivers blood to the liver, where toxic substances are removed.
Arteries and veins: conclusions
Arteries are a type of blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood back to the heart. Along with capillaries, these blood vessels are responsible for moving blood to the tissues around the body.
The heart pumps blood through a complex system of blood vessels. There are several types of arteries and veins with different functions. For example, some contain more muscle to change the amount of blood they carry.
The cardiovascular system is essential to life. Changes in the heart or blood vessels can be serious and sometimes fatal.