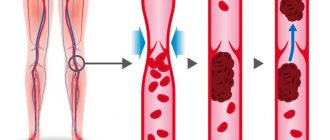
Causes of thrombosis and its signs
- If the integrity of the vascular wall is compromised, the development of thrombosis begins. This usually happens as a result of injuries, during pregnancy, when the vessels narrow and become deformed, or if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed after operations.
- When blood stagnation occurs - due to insufficient physical activity or prolonged bed rest. Venous congestion often leads to deep vein thrombosis and varicose veins. To reduce the risk of developing blood clots, it is recommended to use venotonic agents for varicose veins: for example, Normaven® Leg Cream. This product was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, has undergone clinical studies and has all the necessary documents and quality certificates confirming its effectiveness and safety. As a result of the testing, it was found that a three-month course of using Normaven® Leg Cream helps to improve the condition of the blood vessels of the lower extremities, due to which cramps disappear, the severity of the venous pattern decreases, swelling and a feeling of heaviness in the legs disappear.
- When the number of platelets and red blood cells in the blood increases, blood clotting parameters change. The cause may be hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders and oral contraceptives.
- Thrombosis can develop in patients with cancer, as well as with kidney dysfunction.
Factors that increase the risk of thrombosis:
- injuries;
- obesity and excess weight;
Obesity and excess weight are factors in the development of thrombosis
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- smoking;
- infections;
- long-term and frequent trips and air flights;
- age from 40 years;
- taking medications that increase blood clotting;
- surgical intervention on joints and abdominal operations under anesthesia;
- bone fracture;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Why are blood clots dangerous?
Thrombosis is so insidious that it can not make itself felt for a long time, and then lead to dire consequences. What is the nature of a blood clot, why are these formations so dangerous and how to identify them, said surgeon-phlebologist Andrei Maryasov.
— What is thrombosis? — Thrombosis is the formation of dense masses from the blood. They are capable of blocking blood vessels, moving along them with the blood flow (for example, from the vessels of the lower extremities to the pulmonary artery) and can be fatal.
— Why do blood clots form? — In order for the blood to coagulate and form a blood clot, 3 conditions must be met: a violation of the integrity of the inner wall of the vessel, a slowdown in blood flow and a change in blood viscosity. The prerequisites for this triad are different: taking hormonal drugs or hormonal imbalance, lack of mobility, some chronic diseases, injuries (for example, when wearing a cast for a long time), extensive surgical interventions, varicose veins and others. By the way, studies have shown that varicose veins increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities by 5 times. Statistics also show that the vast majority (more than 90%) of thrombosis is associated with the deep veins of the lower extremities. Blood clots formed in these vessels are able to migrate and move to the heart and pulmonary artery.
— How can you suspect thrombosis? — Some blood clots do not manifest themselves at all, but in most cases thrombosis is an acute condition. Swelling of the limb occurs (if we are talking about deep vein thrombosis of the legs) and bursting pain, the temperature of the limb decreases, and this condition requires an urgent call to the ambulance. Thrombosis of the superficial veins is less dangerous and has pronounced symptoms: swelling, redness, pain in the projection of the vein. In this case, it is easier to make a diagnosis and you can start treatment faster. With such symptoms, they turn to a surgeon, and urgently, otherwise the disease progresses and the blood clot can move into the deep veins.
— Are there degrees of complexity of the disease, when will prevention help, when will medications help, and when will only surgery help? - It depends on the blood clot itself. If it is floating, that is, there is an unattached element in the lumen of the vein, there is a high risk that it will come off, especially if it is more than 7 cm. In such cases, hospitalization and surgery are required. Small blood clots, securely attached to the walls of the vessel, are treated with medication. But in order to identify the type of blood clot, you must undergo an examination, do an ultrasound or MRI of the blood vessels and begin treatment.
— How long does it take for a blood clot to “mature” and why does it break off? “This happens very quickly, the blood clots in seconds. Blood clots tend to enlarge, so they can grow. And separation occurs because the part of the thrombus not attached to the wall becomes too long and heavy. A fresh blood clot is a soft, jelly-like structure, so in the first days blood clots are most dangerous. Gradually, the formation thickens, becomes stronger, and the risk of blood clot rupture decreases.
— Does the separation of a blood clot always lead to death? - Not always. Sudden death occurs if the blood clot is very large and, having come off, it closes the entire lumen of the vessel. But small blood clots are also dangerous: they can, for example, clog small pulmonary arteries and lead to partial death of some segment of the lung.
— There is a lot of advice on the Internet on how to thin the blood. Some people advise taking Aspirin. What blood thinning tips work and are universal? — You should not take any medications without a doctor’s prescription, and even more so, diagnose yourself with increased blood clotting. Only a doctor can come to this conclusion after studying the patient’s coagulogram, and if high blood viscosity is detected, medications are prescribed if necessary.
Prevention of thrombosis is an active lifestyle, proper drinking regimen and wearing compression stockings for people with chronic diseases (for example, varicose veins).
Still have questions? You can make an appointment with a phlebologist.
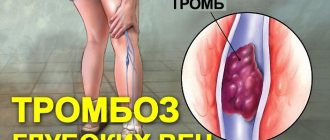
Signs of vein thrombosis in the legs: what precedes it
In healthy people, blood flows freely through arteries and veins.
Signs of thrombosis:
- The speed of blood flow in certain areas decreases. This may be due to heart failure, heart defects, varicose veins or atherosclerosis.
- Blood density increases
- The blood vessels narrow. The causes of this may be the following diseases: endocarditis, arteritis.
- Blood clotting factors are deficient, and blood clots worse.
The disease occurs in the veins; inflammation of the walls usually occurs, followed by venous thrombosis. Shock and severe bleeding provoke thrombus formation.
Thrombosis is a reaction to acute diseases. It is important that the nervous and endocrine systems have sufficient response to protect against the onset of any disease. Thrombosis poses a great threat to life in diseases of the brain and changes in hormonal levels.
Expert opinion
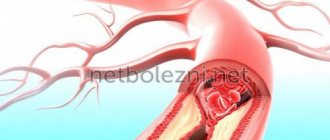
With arterial thrombosis, a fibrin film forms at the injured site, to which platelets with a negative electrical charge begin to flock. Blood clots become fixed to the walls. Then they begin to increase in size, collecting leukocytes, red blood cells and fibrin films.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
Blood clots can be:
- red (blood flows slowly, but clots well),
- white (blood flows quickly, clots slowly).
Layered blood clots that form over a long period of time are capable of splitting on their own. This phenomenon is referred to as revascularization (the throughput of the vessel is restored). It is possible to trace the signs and symptoms of thrombosis only if at least 10-50% of the vessel is affected.
First signs of thrombosis
The formation of blood clots is painful, with a feeling of heaviness and swelling.
If the blood clot is located in the femoral or iliac vein, the entire leg swells and the skin takes on a blue tint. Due to altered blood flow, clots are redistributed into the veins under the skin. A vascular network appears, which is noticeable on the abdomen along the protruding veins. The patient indicates weakness, chills, and body temperature above normal.
When blood clots form in small veins, signs of thrombosis for various reasons may not be expressed for a long time. And only unpleasant sensations when walking will signal a problem.
Signs and features of thrombosis
Signs of thrombosis depending on the location of the thrombus
- The portal vein facilitates the flow of blood from unpaired organs in the abdominal cavity (from the stomach, intestines, spleen, pancreas). From them the blood is sent to the liver (where it is cleansed). If thrombosis occurs in the portal vein, the risk of liver disease increases.
Symptoms of portal vein thrombosis include abdominal pain and bloating, intestinal distress, vomiting, rarely black stools, and an enlarged spleen.
- The pulmonary artery becomes blocked after blood flows from the veins of the legs and pelvis. The number of clots, the reaction of the lungs to them and the action of the homeostasis system are important. The smaller the clot, the less severe the symptoms. Large blood clots interfere with gas exchange in the lungs, and hypoxia develops.
Symptoms: chest pain; the skin turns pale and blue; veins swell in the neck; a cough with bloody discharge and wheezing appears; loss of consciousness.
- Thrombosis of the lower extremities accounts for up to 70% of the total number of thromboses. It is especially dangerous when the deep veins in the thighs and below the knees are thrombosed (it is necessary to monitor for signs of lower leg thrombosis). The first symptoms are invisible.
Swelling, pain when walking or bending the lower leg, pain in the inner thigh and foot, reddened skin and cramps are all signs of the development of the disease. If the acute form occurs, the person begins to suffer from shortness of breath, his temperature rises, he becomes dizzy and loses consciousness. You can compare the signs of thrombosis of the lower extremities from the photo, but the diagnosis must be made by the attending physician.
- In the upper extremities, thrombosis is less common (subclavian vein thrombosis), and it is difficult to distinguish its initial symptoms from arm injury. They manifest themselves in swelling, pain and blueness. The patient feels a burning sensation, his hands go numb, and his skin becomes insensitive.
- The vessels of the brain connect with veins and arteries, where blood clots can also appear, and this leads to a stroke. Symptoms of cerebral thrombosis are more pronounced than with thrombosis of other vessels. The disease is accompanied by headaches, dizziness, decreased hearing and visual acuity, loss of consciousness, and periodic convulsions. The person is feeling sick.
- Blood clots also settle in the veins of hemorrhoids, this is considered a complication of hemorrhoids. Signs of thrombosis of hemorrhoids (Haemorrhoids): pain, the affected area itches, fever, swelling.
- The central retinal vein is also affected by thrombosis. Signs of the disease may not be expressed, and the person loses vision as a result.
- Thrombosis of the mesenteric veins of the intestine is manifested by prolonged abdominal pain. Other signs: bloating, high fever, vomiting and nausea. In the early stages, it is difficult to determine the disease by symptoms. Usually they talk about a complication of the pathology.
- If the femoral and iliac veins are affected, then we are talking about ileofemoral thrombosis. It is accompanied by swelling of the legs (the skin changes color from reddish to blue), when pressure is applied, brown marks appear, the legs and groin hurt, and the body temperature rises.
Treatment and diagnosis of venous thrombosis
Stray thrombus: a health hazard
21.10.2019
If you believe the statistics, wandering blood clots cause the death of more than 9 million people every year. The reason for the appearance of these “killers” in the body is often people themselves. There are bad habits that accelerate their formation. It is necessary to get rid of them so as not to become a victim of a blood clot .
Fatty food
A diet high in fat increases the amount of cholesterol in the blood . It sticks to the walls of blood vessels in the form of cholesterol plaques and blood clots. At any moment they can break off and rush through the bloodstream. This is dangerous for human life. Therefore, it is useful to eat fresh vegetables along with fatty foods. They will reduce the harmful effects of fat.
Sedentary lifestyle
If a person moves little, gets to work by car, or takes an elevator to the floor, then cholesterol settles faster of blood vessels To prevent cholesterol plaques from settling, you will have to move for at least 40 minutes 3 times a week. Evening walks, swimming and skiing are useful.
Smoking
Smoking is dangerous to life, especially after a meal. When eating food, the blood , and nicotine activates the process of their deposition on the walls of blood vessels . If a person cannot help but smoke, then he must at least refrain from the bad habit in the first hour after eating.
High heels
Women love high-heeled shoes. However, they provoke varicose veins. This, in turn, activates the growth of blood clots. Heels higher than 4 cm should not be worn.
Danger of blood clots
When cholesterol plaques form in the vessels clot adheres to them . When it grows large, it breaks off and “travels” through the circulatory system. When a blood clot clogs a blood vessel in the brain , a stroke occurs. If heart vessel in a heart attack . If a blood clot blocks an artery in the lungs, the person dies. Doctors use an ultrasound to detect an enlarged blood clot , from which the blood clot . Then the person will be saved by surgery . The cardiovascular surgeon inserts a filter into the vessel , which intercepts the dangerous clot.
Useful products for blood vessels
To strengthen blood vessels, it is wise to include the following foods in your diet:
- you need food containing vitamin E. It increases the firmness and elasticity of the walls of blood vessels , preventing cholesterol plaques from settling on them. This vitamin is sufficient in eggs, green onions, liver , lettuce, peas and beans;
- You also need to eat more foods with vitamin C. It strengthens capillaries, thins the blood , and blood promotes thrombus formation. To enrich the body with this useful element, you will have to drink tea with rose hips and lemon, eat cabbage, sweet peppers, garlic, oranges and grapefruits;
- It is necessary to include products with bioflavonoids in the menu. These substances can dissolve intravenous blood clots. To replenish the supply of this unique substance, you need to eat berries and red fruits every day. These are apples, lingonberries, cranberries and cherries.
Many people love to enjoy fried potatoes. If you don’t have the strength to give it up, then you need to at least add less salt.
Who is at risk for a wandering blood clot?
- If a person consumes a lot of fried and smoked food, then the occurrence of a blood clot increases sharply.
- When a woman suffers from varicose veins and uses contraceptives for several years, her risk of developing a blood clot increases.
- Smoking more than 5 cigarettes a day and bone also provoke the formation of blood clots.
Daily walks, eating vegetables and fruits, the absence of varicose veins and smoking cigarettes will exclude a person from among the victims of a wandering blood clot .
Published in Cardiology Premium Clinic
Signs of thrombosis and treatment
The severity of the disease is indicated by signs of thrombosis; treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease.
What to do? First of all, an accurate diagnosis is necessary. The doctor must determine where the blood clot is located, clarify its size and mobility. It is necessary to understand how firmly the blood clot is fixed and what is the likelihood that it will come off.
!
There are several main methods of therapy: surgery, thrombolysis, medication and implantation of a vena cava filter.
Heparin injections and anticoagulant drugs are also prescribed. Additionally, they can also prescribe a complex of venotonic vitamins and plant extracts, as well as prescribe a therapeutic diet.
Thrombolysis involves surgically dissolving blood clots using a catheter through which a substance is injected to dissolve the blood clot.
Surgical treatment of thrombosis
Doctors resort to surgical intervention only in case of complications, and here the location of the blood clot is important. It is possible to eliminate the entire thrombotic mass.
A vena cava filter is a metal device similar to an umbrella. It is implanted into the lumen of the inferior vena cava endovascularly.
Recovery after thrombosis
Recanalization is the restoration of the capacity of an artery or vein after thrombosis. It can occur through medical intervention or naturally. Recanalization occurs no earlier than after 6 months with long-term treatment. It requires constant prevention.
After thrombosis, the clot in the vein goes away over time and normal blood flow is restored. Sometimes recanalization does not occur. Even after complete cleansing, the vein cannot function normally.
Thrombosis destroys its internal valves, and they are responsible for the outflow of blood in one direction. As a result, the outflow of blood from the limb is disrupted, the pressure in its venous system increases, and the disease develops again. Therefore, signs of recanalization of thrombosis may be short-lived.
Expert opinion
Unfortunately, thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities has a tendency to recur even after the clot has resolved. Therefore, it is extremely important to make lifestyle changes and follow the preventive measures recommended by your doctor to reduce the risk of recurrent blood clots.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
Thrombophlebitis or thrombosis?
If blood clots form in the deep veins of the lower extremities, then we are not talking about thrombophlebitis, but about thrombosis. What is the difference between these two diseases?
Thrombophlebitis is a disease that occurs mainly as a result of injury to the vein wall. It is accompanied by inflammation, which, together with a slowdown in blood flow, causes the formation of blood clots. Venous thrombosis of the lower extremities is a disease caused by a malfunction of the blood coagulation system. It is not associated with varicose veins, nor is it preceded by damage to the veins, although the presence of injuries increases the risk of thrombosis. And it poses no less danger to the body than thrombophlebitis, since there is a possibility of blocking blood flow or breaking off a blood clot.
Among the factors contributing to the development of thrombosis are:
- elderly age
- increased body weight, decreased physical activity
- taking oral contraceptives
- pregnancy (during this period, a woman’s blood clotting properties may change)
- smoking
- surgical operations
Suspicion of thrombosis
To properly treat thrombosis, you need to make an accurate diagnosis. Different methods are used for this:
- Duplex scanning. With its help, visualization of blood vessels is created and blood flow is examined.
- X-ray contrast venography. In this case, a contrast agent is injected into the vessel.
- In case of doubt, MR-CT angiography is performed when making a diagnosis.
- If there is a risk of pulmonary thromboembolism, the patient undergoes a chest x-ray and scintigraphy.
- Impedance plethysmography is performed if there are signs of leg thrombosis. This method uses a cuff that compresses the lower leg for subsequent short-term occlusion of the veins. The new vessel volume after blood flow is then measured. This analysis provides an accurate diagnosis (up to 90%) and allows one to recognize the presence of deep venous thrombosis in the area above the knee.
At the first suspicion of thrombosis, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication at home is very dangerous.
Video: how to recognize thrombosis?
is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented in this video clip. Source - Phlebologist Ignatov V.N.
Sources:
- NEW APPROACHES TO ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OF THE LOWER LIMB. Sukovatykh B.S., Belikov L.N., Savchuk O.F., Chernyatina M.A. // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. – 2008. – No. 3. – pp. 74-78.
- STRUCTURE OF RISK FACTORS FOR ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OF THE LOWER LIMB. Usov S.A., Rovenskikh D.N., Sartakov G.G. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2012. – No. 4 (86). – pp. 106-107.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261258086_Scientific_Publications_on_Portal_Vein_Thrombosis…
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7711586_Ultrasound_criteria_for_embologenicity_of_venous_th…
- https://thrombosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/
- https://www.isth.org/page/JTH
Thrombophlebitis is a dangerous complication of varicose veins
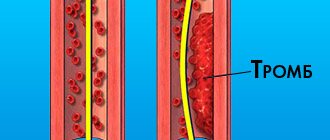
Slow movement of blood through the superficial veins, as well as damage to the vascular walls (and sprains often lead to them) are two factors that play a big role in the formation of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities. Symptoms of this disease are pain in the leg, redness, and thickening along the vein. All this is a consequence of the formation of a thrombus, a blood clot in the lumen of the vessel. Often, a blood clot can completely close a vein. The detachment of a blood clot is also dangerous, since in this case it can block another vessel, for example, the pulmonary artery.
Thrombophlebitis is a disease of the superficial veins, which is most often a complication of varicose veins. If the disease occurs on its own, without previous varicose veins, the cause is usually disturbances in the functioning of the blood coagulation system. Symptoms of thrombophlebitis without varicose veins always attract the attention of doctors, and this situation requires additional examinations.
Let us emphasize once again that everything described applies to superficial veins. If we are talking about thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower extremities, symptoms and treatment... Can we talk about this disease?