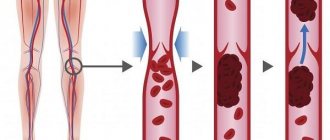
Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities (clinical and anatomical forms)
- Deep vein thrombosis of the leg
Complaints of swelling of the foot, pain and tension in the calves, pain when pressing on the calf muscles. If thrombosis does not spread, it is almost asymptomatic. Sometimes there is thromboembolism of small branches of the pulmonary artery with cough and the development of pneumonia (pneumonia). Treatment of thrombosis of the veins of the leg can be carried out on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a phlebologist with control ultrasound examinations.
- Thrombosis of the popliteal vein
Has a clear clinical picture. Severe swelling and tension of the lower leg, swollen saphenous veins, severe pain when walking. Thrombosis of the popliteal vein is very dangerous due to frequent pulmonary embolism, so treatment is best carried out in a vascular hospital. Most often, conservative therapy is carried out with antithrombotic drugs (heparin). If the patient had a thromboembolism, then urgent surgical treatment is necessary - ligation of the femoral vein above the thrombus.
- Clinic for deep vein thrombosis of the thigh and iliofemoral segment (ileofemoral phlebothrombosis)
It is characterized by a severe general condition, pronounced swelling of the entire lower limb, and severe pain. The saphenous veins are sharply dilated, the leg takes on a bluish color. With ascending deep venous thrombosis, thrombosis of the entire venous bed is possible with a block of venous outflow and the development of venous gangrene (blue phlegmasia), which is accompanied by high mortality. Pulmonary embolism often occurs with a fatal outcome. Treatment of ileofemoral phlebothrombosis is only in a hospital. For occlusive thrombosis, conservative treatment is possible, but it is better to remove the thrombus so that post-thrombotic disease does not develop. In case of floating thrombosis, urgent removal of the thrombus (thrombectomy) using innovative methods is necessary. A vena cava filter can be installed in cancer patients.
- Thrombosis of the inferior vena cava
The most dangerous disease. Clinically, it is manifested by a severe general condition, swelling of both legs. Kidney failure and blood in the urine often develop. With thrombosis of the liver segment, liver failure develops resulting in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Treatment of acute thrombosis of the inferior vena cava should be active. It is necessary to remove thrombotic masses, as surviving patients may develop severe inferior vena cava syndrome. For this, it is good to use our innovative methods and systemic thrombolysis. The effectiveness of this treatment
- Asymptomatic thrombosis
It should be said right away that there are silent thromboses, that is, completely asymptomatic. Therein lies a great danger. This problem is becoming more and more acute, because with the expansion of ultrasound examination of veins, signs of previous thrombosis are being found more and more often. According to some phlebologists, by old age, most people experience such asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis. In quantity they even exceed those that can be diagnosed without the use of ultrasound methods. The patient does not even feel any health problems, and serious complications occur in the midst of complete well-being, in the event of an increase in blood clot and closure of the main veins. It is not uncommon for the disease to be discovered only after the patient dies from these complications. From this position, if there are no signs of the disease and you are at risk, there is only one way out - you need to direct all your efforts to prevention.
Diagnosis of acute deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is very difficult. Signs of deep vein thrombosis appear only in certain localizations of the process. This is primarily due to the absence of clinical symptoms. According to some data, out of 1000 venous thromboses, only 100 have any clinical manifestations. Of these, 60 patients will develop PE, but only 10 will have clinical signs.
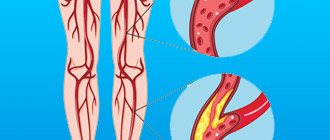
It should be recognized that today there is not a single clinical symptom, laboratory or instrumental sign that would indicate with absolute certainty the presence of PE and DVT. Clinical manifestations of thrombosis and ultrasound results can be the basis for the correct diagnosis of venous thrombosis. The clinical picture of deep vein thrombosis consists of a complex of symptoms that characterize a sudden disturbance of venous outflow with preserved arterial blood flow to the limb. Swelling, cyanosis of the limb, bursting pain, local increase in skin temperature, overflow of the saphenous veins, pain along the vascular bundle are characteristic to one degree or another for thrombosis of any localization. Movements in the joints of the limb and sensitivity remain virtually unchanged. General signs such as low-grade fever, weakness, adynamia, and slight leukocytosis occur in most patients. The diagnosis of thrombosis largely depends on the location of the lesion and the level of distribution of thrombotic masses.
Thrombophlebitis: symptoms and signs
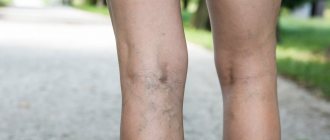
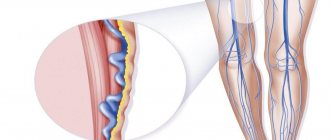
External signs of thrombophlebitis depend on the form of the disease. In addition, it is often associated with other pathologies. It is often preceded by varicose veins, so patients with this pathology need to consult a qualified doctor as soon as possible, who will develop an effective program to prevent the formation of blood clots.
In any case, the appearance of thrombophlebitis does not go unnoticed, since the walls of the vein undergo significant changes, blood pressure increases due to impaired blood flow, and the inflammatory process causes an increase in body temperature. Pain occurs in the area of the affected vessel (especially sharp in the acute form). Regional lymph nodes may enlarge.
A blood clot that breaks away under the pressure of the bloodstream clogs smaller vessels. This can also happen in the brain, lungs, and heart. The patient has symptoms of myocardial infarction, stroke, mesenteric thrombosis of intestinal vessels, and pulmonary embolism. The most common signs of a broken blood clot are:
- sharp pain;
- cold extremities;
- blue skin;
- lack of air.
It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, as a blocked vessel can cause death .
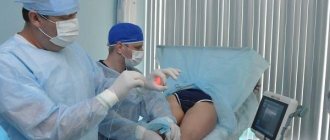
Contrast venography
A method of direct staining of deep veins using the injection of a contrast agent under x-ray control. Phlebography is performed immediately before endovascular intervention for venous thrombosis. In our clinic, the study is carried out with a safe contrast agent - carbon dioxide, which does not have a harmful effect on the kidneys. Phlebography allows you to answer questions about the localization of blood clots, the mechanical reasons for their formation, and the condition of bypass tracts. During phlebography, the surgeon can perform interventions such as installing a vena cava filter to prevent pulmonary embolism, dissolving blood clots, or installing a stent in the area of narrowing of the deep vein.
How to treat thrombophlebitis?
Depending on the form and severity, thrombophlebitis is treated at home or on an outpatient basis. Treatment can be carried out at home for damage to the superficial vessels of the hand, forearm, foot, and leg. In this case, the patient’s physical activity is limited, special ointments are applied locally to improve blood circulation, cold, and elastic bandages. Inside – anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - magnetic therapy, pulsed currents, etc. Particular attention is paid to prevention.
Treatment for symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities, characterized by damage to the deep veins , is carried out exclusively in a hospital, as there is a threat of embolism. Surgery may be necessary to remove a large blood clot, suppuration, gangrene, etc.
Why is it important to undergo treatment in a modern clinic?
Thrombophlebitis can be easily cured without surgery if the patient does not delay going to the doctor and does not self-medicate at home. This is why it is important to see a doctor at the first symptoms. The causes of the disease - inflammation of the vessel wall and blood clotting disorders - can only be eliminated through professional medical care provided by experienced doctors in a modern clinic. Not to mention acute forms of the disease, treatment of which is carried out only on an outpatient basis, since there is a risk of a threat to life.
Prevention
Prevention of DVT involves several measures that eliminate the cause of the pathology. First of all you need:
- eliminate such a bad habit as smoking;
- stop consuming foods high in cholesterol;
- treat diabetes mellitus;
- do not wear high-heeled shoes;
- eliminate intense loads on the lower limbs;
- Healthy food;
- do leg exercises regularly.
If there is a suspicion of blood clots, the patient should stop wearing tight trousers, pressure belts and corsets, avoid visiting baths and saunas, and do not take hot baths.
Our doctors
Drozdov Sergey Alexandrovich
Cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
47 years of experience
Make an appointment
Malakhov Yuri Stanislavovich
Doctor - cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Reasons for education
Blood clots stick together much faster in the area where the pathological lesion occurred. This provokes a more rapid narrowing of the lumen and disruption of tissue nutrition. Key factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
- excess weight;
- lower limb injuries;
- varicose veins;
- incorrectly administered injection;
- the presence of tumors in the digestive system;
- low level of physical activity;
- previous operations;
- pregnancy;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- hormonal treatment and contraception;
- autoimmune processes.
Women are at higher risk of developing the disease due to high estrogen levels. It has also been proven that COVID-19 in 70% of cases causes an overreaction of the immune system, which causes a large number of blood clots to form.
Literature
1. Side-effects and complications of foam sclerotherapy of the great and small saphenous veins: a controlled multicentre prospective study including 1025 patients / JL Gillet // Phlebology. – 2009. – Vol. 24, N4. – P. 131–138.
2. Russian clinical recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic venous diseases // Phlebology. – 2013. – T. 7, No. 2. – P. 1–47
3. Kirienko, A.I. Compression sclerotherapy (a practical guide for doctors) / A.I. Kirienko, V.Yu. Bogachev, I.A. Zolotukhin. Ed. Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Russian Academy of Medical Sciences V.S. Savelyeva. – M.: Publishing house NTsSSKh im. A.N. Bakuleva RAMS, 2004. – 40 p.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is effective for the chronic form of superficial thrombophlebitis and includes a number of measures:
- infrared rays;
- Sollux;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- pulse currents.
These methods are not used in the presence of trophic formations and during periods of exacerbation. A trip to a balneonological resort is possible only after consultation with a doctor and requires a special appointment.
Separately, it is worth noting hirudinotherapia - treatment with leeches. This method is applicable in the acute form and if the patient experiences intolerance to anticoagulant drugs (reducing blood viscosity). In this case, the role of these drugs is played by hirudin, contained in the glands of leeches and entering the patient’s blood. However, their use is strictly individual, has serious contraindications and requires mandatory consultation with the attending physician.
Images
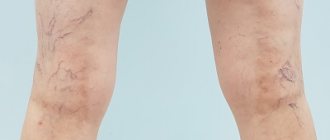
Dilated occlusive-thrombosed medial sural vein
The saphenous vein, sclerosed as a result of foam scleroobliteration, is located suprafascially at the level of the upper third of the leg.
Scleroobliterated saphenous veins and sural vein thrombosis
- Views: 3763
- Comments:
Did you like the post? Do you find it useful or interesting? Support the author!
Drug treatment
Prescription of medications for thrombophlebitis should be comprehensive:
- anticoagulants reduce blood clotting;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics act on the very cause of blood clots – infection;
- for severe pain, painkillers are used;
- special external ointments help dissolve blood clots; anti-inflammatory gels are also applicable;
- Enzyme therapy is carried out to dissolve the blood clot and eliminate swelling;
- the action of venotonics is aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels and increasing their elasticity;
- Angioprotectors may also be additionally prescribed.
For the treatment of thrombophlebitis, the use of rutin is important. It increases the tone of large vessels, strengthens their walls, reduces swelling and inflammation. Heparin contained in ointments is no less important. Their use allows you to avoid taking medications internally.
In the absence of severe complications, the effect of drug therapy is felt within a few days.