Deep vein thrombosis is an acute pathological condition in which a blood clot (thrombus) forms in the lumen of a vessel, leading to impaired blood circulation and trophism in this area. Most often the disease affects the lower extremities. The clinical picture of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities may include symptoms such as pain, swelling, discoloration and local increase in temperature of the affected limb.
The incidence of deep vein thrombosis of the thigh and leg is approximately 1 in 1,000 adults. The healthcare system of the Russian Federation spends 1.8 million rubles every year on the treatment of this pathology.
In half of the cases the disease is asymptomatic, which can result in fatal complications that end in death. The most significant are the following two complications: pulmonary embolism and postthrombotic syndrome. As a rule, deep vein thrombosis of the leg is less likely to cause the formation of a massive embolus.
At the Yusupov Hospital, each patient can undergo a full phlebological check-up and receive advice from competent specialists regarding further treatment tactics for deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) - what is it?
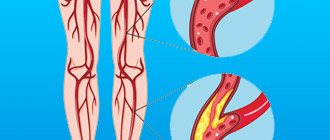
Deep vein thrombosis is a disease in which blood clots (thrombi) form in the lumen of the deep veins. The lower extremities are most often affected.
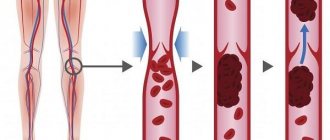
The mechanism of development of deep vein thrombosis
As the disease progresses, the health of the deep vessels is at risk. If treatment is not prescribed in time, there can be serious consequences.
What is thrombophelitis and thrombosis
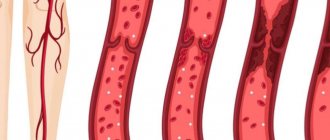
I am often asked about such a problem as vein blockage, what is meant by this concept. The fact is that such a simple, everyday word most often means such a dangerous complication as thrombosis. So, the vein in our leg has several membranes. The inner lining of the veins is represented by a thin layer of thin vessels. This layer of thin vessels is called the endothelium and this layer is nourished by oxygen from moving blood. Only moving blood, giving and taking oxygen, nourishes this membrane. If the movement of blood through the vein ends and the blood does not move or moves chaotically up and down, in this case phenomena arise that can lead to hypoxia of the inner lining of the vein wall, that is, the normal exchange of oxygen is disrupted. And this leads to the development of inflammatory phenomena. Inflammation in the wall of the vein, which occurs due to the adhesion of various formed elements to it, poor nutrition of the vein wall itself, and oxygen starvation causes and triggers a thrombus formation reaction. Formal elements begin to form in the area of the vein wall, sticking like a snowball to its wall. First of all, platelets. Platelets release active substances that form fibrin strands. And these fibrin threads, like a mesh, blocking the lumen of the vessel, cause the formation of a dense clot, which is called a thrombus or, in common parlance, a blockage of the veins. This thrombus itself can cause inflammation of the adjacent section of the vein and again everything will happen again, the formed elements will become inflamed again and the next section of thrombosis will become inflamed again.
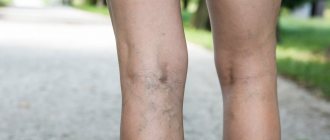
Deep vein thrombosis with varicose veins
Very often, deep vein thrombosis becomes a complication of varicose veins.
Deep vein thrombosis is often a complication of varicose veins
The severity of the disease will depend on the location of the blood clot and its size. If there is no complete blockage of the vessel, there may be no symptoms of the disease.
What is the danger of blockage (thrombosis) of the veins in the legs if it is not treated?
Diagnosis of leg vein thrombosis and timely initiation of treatment are extremely important not only for maintaining health, but also for the life of the patient. After all, if a blood clot formed in a vein completely blocks its lumen, this can lead to an embolism. In turn, this condition can cause insufficient blood flow to the organs. For example, a blood clot that breaks off and blocks a pulmonary artery can lead to the development of a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition that is often fatal.
What other complications should you be aware of in order to start treatment of thrombosis on time?
blockage of blood vessels
- If left untreated, chronic venous insufficiency may develop.
- The situation may be aggravated by the addition of inflammation to thrombosis - in this case, the patient develops thrombophlebitis.
- We should not exclude the possibility of developing decompensation of varicose veins - a condition that occurs when the deep veins in the legs are completely blocked. As a result, a person develops trophic ulcers - long-healing wounds that cause pain and serious discomfort.
blood vessels, disease
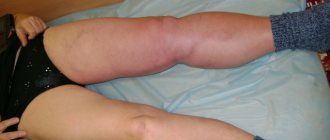
- The presence of blood clots negatively affects the appearance of the lower extremities, causing psychological discomfort to patients (especially women). Swelling and bluish tint of the legs can interfere with your personal life and negatively affect social adaptation. This creates a vicious circle: a person begins to feel embarrassed about his condition, tries to limit his social circle and go out as little as possible - as a result, this leads to a decrease in physical activity, which further aggravates the symptoms of thrombosis.
Correlation between diseases of the circulatory system and mortality from them
Deep vein thrombosis - causes of DVT development
Deep vein thrombosis most often occurs when several factors combine:
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- when blood flow slows;
- in case of damage to the vascular walls.
There are risk factors that provoke the occurrence of thrombosis, these are:
- elderly age;
- smoking;
- overweight;
- the use of certain medications, including oral contraceptives;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- some operations;
- injuries that damage blood vessels.
What symptoms develop with deep vein thrombosis?
As a rule, symptoms do not appear immediately, only if the blood clot enlarges. If a clot ruptures, shortness of breath, chest pain, and hemoptysis may occur.
The development of the disease can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the legs;
- bluish skin tone;
- pain when moving.
The main symptom of deep vein thrombosis is leg pain!
If you have these signs, you most likely have deep vein thrombosis. Stages or variants of the course determine the method of treatment.
Thrombosis of the lower extremities - symptoms
An additional danger of thrombosis is that the disease may not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms appear when the blood clot reaches a large size and spreads up the vessel. Then the patient begins to complain of pain, which decreases at rest and increases with physical activity. Then, due to the deterioration of blood outflow, swelling is added to the pain. The skin on the leg turns pale (to the point of cyanosis) and “tightens”, acquiring a glossy shine.
To diagnose the localization of a blood clot, an ultrasound of the veins is performed, and in particularly difficult cases, angiography, an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels.
Deep vein thrombosis - diagnosis
The main method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis today is ultrasound duplex scanning. With ultrasound scanning, you can determine the location of the thrombus, its size, and condition (is it attached to the walls of the vein or dangling in the lumen - floating).
Doctor Malakhov A.M. performs ultrasound diagnostics of deep veins of the lower extremities
Phlebography and radionuclide scanning are also prescribed to assess venous blood flow. The state of microcirculation is assessed based on rheovasography data.
Prevention
Prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities should be carried out in patients at risk for developing pulmonary embolism. The greatest attention is paid to thromboprophylaxis in surgery, but gradually its need arises in therapeutic practice.
Mechanical prevention
For patients at risk, the simplest and most effective prevention of thrombosis is to elevate the lower extremities. It contributes to a significant increase in blood flow and a decrease in the diameter of the deep veins. The next stage of thromboprophylaxis is wearing compression hosiery - a fairly simple and safe method of mechanical prevention. Stockings create pressure on the ankle, shin and knee, improving venous outflow. They are contraindicated in people with severe peripheral vascular disease. Excessive compression can lead to tissue necrosis. In addition to stockings, there is a special single-chamber system. It provides temporary compression of the entire lower leg. Typically, a pressure of 40-60 mm is used to compress the tibia. Hg This increases the rate of venous return and improves fibrinolytic activity. The effect of tissue factor inhibition of the blood coagulation system cannot be excluded. Other methods of mechanical prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities include daily walking and leg extension exercises.
Drug prevention
Along with mechanical prevention, drug therapy using various drugs is widely used. To date, the following drugs have proven their effectiveness:
- Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). With its use, there is a lower likelihood of bleeding and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia than with unfractionated heparin;
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH) inhibits the main enzyme of the blood coagulation system, thrombin. Its use is fraught with the development of spontaneous bleeding and heparin-induced osteoporosis and thrombocytopenia;
The main contraindication for the use of LMWH and UFH is persistent, uncontrolled bleeding.
- Vitamin K antagonists (warfarin) - its administration for the purpose of thromboprophylaxis can be started before surgery and in the postoperative period. Contraindicated for use in prenatal prevention of thrombosis, as it can penetrate the placenta and have a teratogenic effect on the fetus;
- Monotherapy with acetylsalicylic acid, according to studies, has shown less effectiveness than other means of prevention;
- Dabigatran is a new generation drug, an oral thrombin inhibitor. The drug is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, has good bioavailability and does not require monitoring of the blood coagulation system;
- Fondaparincus is an indirect selective factor Xa inhibitor. It also does not require constant laboratory monitoring of coagulogram parameters.
How long thromboprophylaxis will last depends on the level of risk of developing deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities.
Surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis
If a patient has a severe form of thrombosis of the lower extremities, the most effective treatment method is surgery - thrombolysis. A timely operation makes it possible to restore full blood flow if the diagnosis is deep vein thrombosis. Only timely intervention can completely cure the patient from this serious condition. Thrombolysis is performed only in hospital settings and by very experienced endovascular surgeons. Treatment after surgery is also aimed at the same goal - resorption of blood clots.
In addition to thrombolysis, there are two more surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis - thrombectomy with angioplasty and installation of a blood clot trap - a vena cava filter.
Surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis
Blockage (thrombosis) of veins in the legs: treatment
blockage of blood vessels
Therapy should begin with a consultation with a phlebologist and an examination. Diagnosis usually requires a visual examination, checking for pulsation, assessing the color, temperature of the limbs and their diameter. To detect the number of blood clots and assess their size, it is necessary to perform duplex ultrasound of blood vessels or, in some cases, perform MSCT with the introduction of a contrast agent.
!
To assess blood composition and the tendency to thrombus formation, a general blood test and coagulogram are prescribed.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor decides how to treat venous thrombosis in this particular case.
Treatment is designed to solve the following problems:
- Reduce blood viscosity.
- A safe way to eliminate a blood clot.
- If there is an inflammatory process, relieve inflammation.
For these purposes, medical and surgical methods are used:
- Anticoagulants. These drugs thin the blood and prevent the formation of new blood clots. They must be taken according to an individually developed regimen under the constant supervision of a physician, since an incorrectly selected dosage can lead to the development of bleeding. Some anticoagulants (such as warfarin) require regular INR blood tests.
- Thrombolytics. The action of drugs in this group is aimed at lysis (dissolution) of the blood clot and restoration of normal blood flow. It should be taken into account that treatment with thrombolytics has contraindications. They should not be taken after recent operations on internal organs, with severe arterial hypertension, the risk of internal bleeding, or in the presence of vascular diseases of the brain.
Blocked veins in the legs, treatment
- Venotonics. Drugs in this group are aimed at increasing vascular tone, eliminating congestion, and relieving swelling. They can be prescribed both for oral administration (in the form of tablets) and for external use (in the form of creams, gels and ointments). Particularly popular are products based on rutin and plant extracts (for example, horse chestnut).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs are prescribed if thrombosis is accompanied by an inflammatory process and the patient develops thrombophlebitis.
- Surgical intervention.
Expert opinion
In modern medical practice, surgical treatment of thrombosis (thrombectomy) is resorted to if vein thrombosis cannot be eliminated by other methods. The operation should be performed under the guidance of experienced vascular surgeons. It is also possible to install a vena cava filter into the vein - a mesh trap that blocks the penetration of blood clots into the lungs.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
vein blockage
Deep vein thrombosis - treatment in Moscow
Modern Moscow medicine offers several methods of treating deep vein thrombosis, the use of which depends on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, you can get by with thrombolytic drugs if you have deep vein thrombosis. Treatment (Moscow is a city where there are world luminaries in phlebology) must be very qualified. In the later stages, such therapy is dangerous due to the possible separation of the blood clot and the occurrence of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery. If severe circulatory disorders and deep vein thrombosis are observed, treatment is surgery (thrombectomy).
Deep vein thrombosis - conservative treatment
Conservative treatment can only stop or slow down the progression of the disease. Such therapy can also be prescribed as part of complex treatment.
Principles of conservative therapy:
- compression therapy (elastic compression) – the result of such an effect is the elimination of the mechanisms of progression of varicose veins; without such therapy, conservative treatment is impossible;
- the required level of compression is achieved through the use of special knitwear (special medical product), in this case it is important to choose the correct size of the compression knitwear;
- compression hosiery can relieve swelling, pain and increased fatigue of the lower extremities;
- the desired result is achieved with constant use of elastic compression.
Deep vein thrombosis treatment with medication
This involves a course of treatment with anticoagulants (drugs that prevent blood from clotting). The average duration of such a course is at least 3 months, and sometimes longer. A combination of drugs differing in their mechanism of action is provided. An important stage in the drug treatment of DVT is the selection of blood thinning drugs. To prevent gastrointestinal complications, some medications are administered parenterally.
Pharmacotherapy is often carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe forms of the disease, patients who have suffered thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery or thrombosis of the vena cava are annually hospitalized in the therapeutic or cardiology department for 2-3 weeks, where infusion hemorheological and cardiotonic therapy is carried out.
Deep vein thrombosis - treatment at home
Today, along with traditional methods of treating the disease, traditional medicine is practiced if deep vein thrombosis is determined. Treatment with folk remedies is used as a complement to the main treatment.
The first thing to do is thin the blood. If you have deep vein thrombosis, treatment with traditional methods includes consuming the following products:
- onion and garlic;
- sunflower seeds;
- cocoa;
- beets;
- Apple vinegar;
- tomatoes or tomato juice;
- Hercules;
- oatmeal;
- cranberries;
- oatmeal;
- lemon;
- cherries;
- viburnum.
Blood thinning should be approached with caution so as not to provoke bleeding. It is not recommended to consume fatty and meat products if you have deep vein thrombosis. Photos and results of improper treatment are available on the Internet.
Every day you can eat one spoon of a mixture made from crushed garlic, two tablespoons of unrefined vegetable oil and one tablespoon of honey.
Blockage (thrombosis) of a vein in the leg: what to do for prevention?
Rationalization of work and rest schedules, wearing special compression garments and correcting nutrition - all this has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels and helps reduce the risk of thrombosis of the leg veins.
Preventative exercise
When the first symptoms of thrombosis appear, the patient is advised to reconsider his attitude towards physical activity. It is advisable to avoid staying in any static position for a long time - either sitting or standing, or lying down. During the day, you need to perform not very difficult physical exercises, and if this is not possible, then at least change your body position as often as possible.
Massage
As a preventive measure, you can practice self-massage, as it relieves the feeling of tightness and improves blood flow. However, remember that if you have thrombophlebitis with dilated and painful veins, you cannot do a massage.
foot massage
Compression underwear
Since one of the reasons for the development of blockage (thrombosis) of the veins of the lower extremities is varicose veins, wearing special compression products - stockings, tights, knee socks, elastic bandages - gives good results in the fight against this problem. Their use has a beneficial effect on the speed of venous blood movement. Each patient can choose the type of compression garment that suits them, depending on the level of pressure exerted by the product on the lower extremities.
compression underwear
Hirudotherapy
Installing medical leeches is an effective means of preventing varicose veins on the legs. The saliva of leeches contains a special component - hirudin, which is a natural anticoagulant. This substance reduces blood viscosity, improves blood flow in the lower extremities, and increases local and general immunity.
!
It is worth considering that hirudotherapy has contraindications (oncology, purulent processes, etc.)
In addition, the placement of leeches cannot be combined with the use of medicinal anticoagulants, as this can lead to complications, such as the development of bleeding.
Nutritional Features
A properly formulated diet allows you to lose excess weight, which puts additional pressure on the lower limbs, and also reduce blood viscosity. To achieve these goals, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Drink enough clean drinking water daily (up to 2 liters per day). Reduce coffee consumption, give up alcohol, limit, or better yet completely eliminate, milk and dairy products.
- Eat foods rich in heavy animal fats: fatty meats, butter, lard. Healthy sources of fat and protein are sea fish, seafood, vegetable oils (olive, flaxseed, MCT oil), replace milk with soy, almond, coconut.
- Completely exclude from the diet trans fats, margarine, smoked and salty foods, fatty sauces, chips and snacks, sweet carbonated drinks, milk chocolate, baked goods, bread, fast food.
- The daily menu should include vegetables, herbs, and fruits, which contain fiber.
- It is recommended to further enrich the diet with foods that include vitamins C, E and Beta-carotene. They are natural antioxidants that help reduce blood hypercoagulability. Such products include citrus fruits, kiwi, cranberries, raspberries, blueberries, apples, spinach, sea buckthorn, green tea, carrots, bell peppers, red beans, nuts, sunflower seeds. It is also worth eating foods that contain vitamin P (rutin). It maintains vascular tone at a high level, ensures their strength and elasticity. Contained in cherries, tomatoes, garlic, chokeberries, sorrel, buckwheat.
- Don’t forget about foods that increase the production of elastin, a protein that ensures the elasticity and strength of blood vessels. These include seafood, red grapes, and beef liver.
PLEASE NOTE: The recommendations described above are general guidelines. Therefore, it is advisable that the daily diet be compiled by a doctor taking into account an assessment of the patient’s general health.
Deep vein thrombosis - reviews from our patients.
Feedback from our patient about the treatment of deep vein thrombosis in
Anita, 38 years old, Moscow.
I would like to thank the clinic staff for their professionalism. With their help, I began to trust traditional medicine again. Before I went to the clinic, I was repeatedly subjected to various medical procedures for deep vein thrombosis in my legs. At first I had varicose veins with a complication, for which I had an operation to “stitch the veins.” As a result of this, I practically became disabled. On the advice of my friends, I turned to the doctors of the MIFC clinic, who returned me to a full life. It’s good that everything worked out without surgical intervention. Anita, 38 years old, Moscow.
Patient's review of the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in our center
Andrey, 40 years old, Krasnogorsk.
Due to frequent stressful situations and bad habits, I developed problems with my legs, or rather, poor circulation. My legs often swelled, turned blue, and sometimes hurt when walking. I accidentally saw an article on the Internet about vein thrombosis, and the symptoms described coincided with my feelings. I was just recently recommended to a phlebology clinic, and I decided to go for a consultation. Doctor Malakhov A.M. diagnosed: acute deep vein thrombosis. At first they calmed me down and told me that in this case it would be impossible to do without surgical intervention. Since there was no other choice, I agreed and did not regret it. The operation in the vascular department of the city hospital, where I was urgently hospitalized, to remove the blood clot was successful and without complications. Now my life is not in danger, thanks to the doctors of the MIFC clinic for their professionalism and “humane” attitude towards patients! Andrey, 40 years old, Moscow.
Causes of leg vein thrombosis
Thrombosis (vein blockage) is the process of blood clots forming inside the veins, which attach to their walls and interfere with normal blood flow. Depending on the location, thrombosis of superficial and deep veins is distinguished. Interestingly, the process of blood clot formation is not initially pathological: a blood clot should form in response to vessel injury, preventing the development of bleeding. In such a situation, the body intensively synthesizes platelets and fibrin, “sealing” the damage. However, in some cases, this mechanism is triggered even if the vein wall has not been injured. What situations are we talking about?
- Hypercoagulation.
Expert opinionViolation of the drinking regime, poor nutrition, metabolic failures, elevated body temperature, the presence of cancer and chronic inflammatory processes in a person, taking oral contraceptives and some other medications - all this leads to the blood coagulation system over the anticoagulation system, increased blood viscosity and the possible formation of blood clots.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
- Narrowing of the lumen of the arteries. The development of this problem can be caused by the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in a person.
- Heart diseases. Atrial fibrillation, heart failure and other cardiac pathologies can negatively affect the condition of blood vessels and the composition of the blood.
- Inflammatory processes and injuries to the walls of blood vessels. The walls of the veins can become inflamed as a result of a violation of their integrity due to frequent injections, catheter installation, bone fractures, bruises and burns, and surgical interventions.
- Hypercoagulation. If a person remains in a sitting/lying position for a long time, there is a risk of developing blood clots in the veins of the legs.
- Overweight. Excessive body weight increases the load on the lower extremities, leading to poor circulation and creating preconditions for the development of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities.
why are blood vessels blocked?
Frequently asked questions from our patients on the Internet about deep vein thrombosis
How to understand that there are blood clots in the veins?
Only a specialist, phlebologist or vascular surgeon can reliably understand that there are blood clots in the veins. And even a specialized specialist will need instrumental support and ultrasound examination of blood vessels. You can assume that you have blood clots in your veins based on the following signs:
- Edema.
- Blueness of the skin.
- Soreness, swelling of tissues, redness of the skin along the veins.
If there are blood clots in the veins, how to recognize them, symptoms and treatment?
Blood clots in veins can be recognized using duplex ultrasound scanning. The presence of blood clots in the veins is indicated by the following symptoms: swelling, pain, discoloration of the limb. The best option for diagnosis, as well as subsequent treatment, is to contact a good phlebological center.
How to recognize a blood clot on the leg?
In order to recognize a blood clot on the leg, you must seek professional medical help. As an option, do an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower limb. The best solution would be to consult a specialist, a phlebologist.
How to identify blood clots in the legs?
From the point of view of modern diagnostics, the best way to determine blood clots in the legs is ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower extremities.
A blood clot in a vein, how does it form?
A blood clot in a vein is formed as a result of a complex chain of biochemical reactions, during which a network of insoluble fibrin molecules is formed from fibrinogen molecules. Blood cells are fixed in the latter, creating a dense intravascular structure, which is a thrombus.
How to identify a blood clot?
A thrombus can be detected using various methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and good ultrasound. The latter method has the best price-quality ratio and is the gold standard for diagnosing thrombosis.
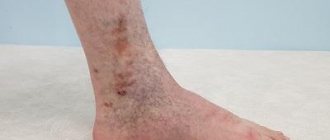
Blockage (thrombosis) of veins in the legs: symptoms
The initial stage of the pathological process is usually asymptomatic, so many patients seek medical help when the disease reaches a late stage. The intensity of symptoms depends on a number of factors: the size of the blood clot, the number of thrombosed veins, lifestyle and the general health of the person.
Blocked veins in the legs: symptoms
The presence of thrombosis can be suspected by the following signs:
- Swelling and swelling of the lower extremities.
- Swelling of veins.
- The appearance of a pronounced vascular network and “stars”.
- The appearance of small pinpoint hemorrhages on the affected leg - petechial rash.
- A feeling of fullness and heaviness in the legs, increasing in the evening or after a long stay in an upright position. Unpleasant sensations are reduced if a person lies on his back and raises his legs above the level of his heart.
- The lower extremities acquire a bluish tint, and sometimes there is a feeling of numbness and tingling. The affected leg may also appear pale and cold to the touch.
- If thrombosis is accompanied by an inflammatory process and a person develops thrombophlebitis, an increase in local and general body temperature is possible.