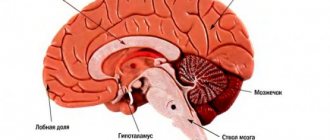
Types of stroke
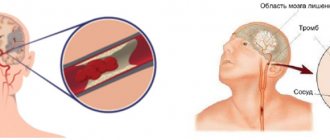
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Assistance in transporting a patient in an ambulance during a stroke
First of all, no attempt should be made to transport the patient to the hospital by private or public transport. In case of a stroke, a specially equipped ambulance is required, with qualified personnel, medications and a siren. Transportation is carried out to a specialized neurological hospital or to the intensive care unit of the nearest general hospital, where doctors have already been warned in advance.
As a rule, doctors have, at best, an hour and a half to provide care to a patient. Those who were close to the patient during the attack should accompany him to the hospital in order to tell the doctors in detail and constructively about the details of what happened and the first aid provided.
The following measures can be taken in the ambulance:
- Prevention of breathing disorders (if necessary - tracheal intubation, artificial ventilation).
- Smooth decrease in blood pressure.
- Maintaining water and electrolyte metabolism using saline droppers.
- Administration of anticonvulsants.
- When transporting a stroke patient, they are guided by the principle of “transporting with the least loss to the body.”
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Patterns of development of the pre-stroke state
Primary signs of a pre-stroke condition in elderly women may be nonspecific. May appear:
- frequent headaches;
- nausea;
- malfunction of the sense organs.
Similar symptoms can appear with the progression of many diseases, including hypertensive crisis, a drop in sugar levels, and others.
However, despite the nonspecificity of the symptoms, it is still possible to recognize a pre-stroke condition. There are several factors that allow you to determine pathology at an early stage:
- The pre-stroke state was preceded by a long period. It is clear that transient ischemia cannot develop suddenly over a few days or hours. There is always an initial stage from which signs are taken into account. This stage usually takes 14-21 days, but in some patients it can last longer.
- The general condition worsens. In women, pre-stroke is much more severe than in men and often ends in necrosis.
- The manifestations are more pronounced. This factor is directly related to the previous one.
- The likelihood of an emergency occurring is much higher. Most often it is characterized by tissue death.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Ischemic stroke: symptoms, consequences, treatment - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Forms of ischemic stroke
- Causes of ischemic stroke
- Main symptoms
- Diagnosis of stroke
- Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
- Nutrition after stroke
- Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
- Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Ischemic stroke
is a condition that occurs against the background of damage to brain tissue due to impaired blood circulation in its vessels and is accompanied by various neurological signs. As a result of its appearance, the functioning of parts of the brain is disrupted (depending on the focus of the disease).
Of the three existing types of strokes, ischemic stroke is the most common, occurring in 80% of cases. The other 20% are subarachnoid hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke.
Stroke has especially dangerous consequences: impaired cognitive and neurological functions, paralysis, problems with oral and written speech, etc.
Forms of ischemic stroke
There are several classifications of stroke: by reason of occurrence, by the degree of damage to brain tissue and by severity.
- Reasons for appearance:
- Lacunar – the syndrome affects a tissue area up to 15 mm in size and is accompanied by a small number of neurological symptoms
- Thromboembolic - occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus
- Hemodynamic - in this case, vascular spasm is prolonged, and brain cells stop receiving the necessary nutrients
- Transient attack - the lesion is small, and neurological signs quickly disappear
- Small – brain functions are restored within 21 days
- Progressive - its neurological signs do not appear immediately and accumulate over time; after treatment, some of these symptoms may persist
- Extensive - signs of its appearance are recorded for a long time, including after treatment
- Mild – symptoms are mild and disappear within a few days
- Medium – signs appear, but are not accompanied by a disorder of consciousness
- Severe – in this case consciousness is depressed and brain tissue is severely damaged
Causes of ischemic stroke
The causes of stroke include diseases and dysfunctions of the body such as:
- Hypertension
- Cardiac ischemia
- Arrhythmia
- Bleeding disorder
- Various diseases of the vascular system
- Pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head
- Migraine
- Kidney diseases
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Obesity
- Thrombophlebitis
The following people are also at risk:
- Heavy and frequent smokers
- Experiencing constant psycho-emotional overload
- Those who have suffered blood loss
- Suffering from chronic headaches
- Excessive alcohol drinkers
- Regular overeaters
Given the above factors, men and women over 50 years of age are especially at risk of ischemic stroke.
Main symptoms
Signs of ischemic stroke consist of general signs characteristic of all types of stroke and symptoms that reflect the nature and location of damage to brain tissue.
- General symptoms:
- Fever
- Vomiting and nausea
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Problems with orientation in space
- Inability to move limbs or move incorrectly
- Dizziness
- Speech difficulties - problems with reading, speaking, understanding what is said, writing, counting
- Visual dysfunction – sudden deterioration, double vision
- Swallowing dysfunction
- Inability to perform simple everyday activities (comb your hair, etc.)
- The occurrence of amnesia and other serious memory impairments
- If the left hemisphere is affected, paralysis may also occur
- With damage to the temporal lobe - depression, impairment of cognitive and logical functions
Diagnosis of stroke
A qualified neurologist can determine the presence of a stroke quite quickly. But in order to prescribe the most effective treatment, he needs to identify both the localization of the lesion and the causes of its appearance, concomitant diseases. For this, the following diagnostic procedures and equipment are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Cerebral angiography using contrast agent
- Blood biochemistry for sugar and cholesterol
- ECHO-KG
- Electroencephalogram
- ECG
- Coagulogram (blood clotting test)
Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
Since this phenomenon disrupts brain function, ischemic stroke requires treatment that will be complex and long-term. Otherwise, swelling, thromboembolism and other negative consequences may occur.
- A patient in acute condition is sent to the ward or intensive care unit
- First of all, medical personnel restore the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory systems
- If necessary, surgery may be performed to remove the blood clot.
- Medicines can also be used to liquefy the clot.
- In general, in the process of treating a patient, the following types of drugs are used: anticoagulants, blood thinners, vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors, neurotrophics, antioxidants
Remember, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous!
Nutrition after stroke
If the patient is diagnosed with ischemic stroke, treatment should not be limited to hospital stay. An important part of the fight against the consequences of a stroke is proper nutrition and rehabilitation measures.
It is necessary to include in the diet such products as:
- Porridge
- Lean fish, meat and seafood (boiled)
- Vegetables (cabbage, spinach, beets, etc.)
- Berries (blueberries, cranberries, etc.)
- Fruits
- Dairy
- Vegetable oil
The following should be strictly avoided:
- Fried
- Smoked
- Fat
- Dishes with a lot of spices
- Flour products
It is also necessary to reduce the amount of salt in food.
It is important to remember that after a stroke you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
Since a stroke can lead to many negative consequences (impaired speech skills, memory, cognitive functions, paralysis), it is better to undergo rehabilitation procedures in a specialized institution (sanatorium). To restore a number of functions, you need to contact professionals:
- Speech therapist – for restoration of speech and graphic skills
- Physical therapy specialist – to improve coordination and motor function
- Specialist in physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation, reflexology, etc.) - to accelerate the regeneration of nerve tissue and improve blood supply
- Neurologists and psychologists – to eliminate cognitive and emotional disorders, restore memory
Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
If concomitant diseases or other risk factors persist, ischemic stroke may recur. Therefore it is necessary:
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations of the circulatory system and heart
- Treat hypertension and other concomitant diseases in a timely manner
- Contact a doctor immediately if you feel unwell
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition
According to statistics, the occurrence of a stroke ends in death in the first weeks in 25% of cases, in 50% of cases the patient lives after a stroke for about 5 years, the remaining 25% can live at least 10 years.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- A full range of services for the management of patients with stroke: from stabilizing the patient to prescribing rehabilitation procedures and therapy
- MEDSI specialists are candidates of medical sciences, have high qualification categories and have extensive experience working with stroke patients
- Experienced surgeons of a specialized department perform precise operations on blood vessels through mini-accesses using the latest expert-level equipment
- All studies and procedures are in one place
- MEDSI doctors provide follow-up care for patients who have suffered a stroke, including at home
- At the first signs of a stroke in you or your relatives, call 8 (495) 7-800-500
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Risk factors
- Severe arterial hypertension. This also includes persistently high blood pressure. Pathologies are observed in 70% of elderly people. Over the course of a year, 3–4 hypertensive crises occur, which after 80 years of age often provoke a stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation (another name is atrial fibrillation). It is a heart rhythm disorder that causes uneven blood flow and blood clots in the heart. When blood clots enter the brain, they cause a stroke.
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. In older people, lipid metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which excess cholesterol begins to settle on the walls of blood vessels. Over time, blood flow becomes more difficult and, in severe cases, stops completely.
- Obesity in combination with the metabolic syndrome characteristic of the elderly (metabolic disorders, production of vital hormones and other processes). Increases the load on the heart.
- Myocardial infarction. Heart failure in people over 85 years of age. They are signs of the development of atherosclerotic processes that affect all vessels, including cerebral ones.
- Floor. There is a predisposition in females up to 80 years of age, and in males after 82 years of age.
- Alcoholism and smoking. They worsen the condition of the cardiovascular system and provoke obesity.
- Uncontrolled use of medications that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the heart muscle. For example, taking estrogen-containing contraceptives by women who smoke and have hypertension increases the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity. Provokes slow blood circulation and obesity.
- Constant stress, increased mental stress, nervous exhaustion. Contraindicated for older people who have already had a stroke before.
Important! The presence of two or more factors in an elderly person increases the risk of a fatal stroke.
Also at risk are older people who have:
- congenital defects in the structure of the myocardium and valve apparatus;
- chronic diseases that provoke an increase in blood pressure, but are not pathologies;
- acquired defects of the cardiac folds, leading to disruption of blood flow;
- narrowing of the paired artery;
- damage to the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head;
- IHD;
- inflammatory process in the arterial vessels of the legs;
- holding your breath during sleep;
- inflammatory process of an autoimmune nature of the walls of blood vessels;
- muscle and joint diseases affecting the cardiovascular system.
The causes of a spinal stroke can be:
- injuries, surgeries and other physical impacts;
- atherosclerotic pathological processes;
- embolism.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.