Experts from the World Health Organization believe that a stroke is a rapidly developing total or focal impairment of brain function that lasts more than 24 hours or leads to death. Stroke in women occurs between the ages of 18 and 65. The disease affects the patient’s quality of life and can lead to disability or death. The main reason is that women present with strokes a few days after the onset of the disease, when doctors have to deal with the consequences of the disease, and not with the disease. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital quickly diagnose stroke using modern examination methods:
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- video electroecephalogram;
- electromyography.
Such methods allow you to quickly identify the signs of stroke in women and apply appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of stroke in women are most often atypical. The patient may accidentally confuse the first sign with a simple malaise or another disease. Signs of a stroke in a woman have the following characteristics:
- age. In women, stroke develops mainly between the ages of 18 and 65;
- type of disease. Most often, women develop a hemorrhagic stroke due to a rupture of a cerebral artery against the background of high blood pressure. This is facilitated by emotional shock, sudden changes in hormonal levels, increased sensitivity to stress;
- hormonal background. Pregnancy, childbirth, taking contraceptives leads to changes in blood clotting and increases the susceptibility to stroke by 20-22%;
- course of the disease. Women are more likely than men to develop stroke complications and have a higher mortality rate. The disease is characterized by a severe course; warning signs of a stroke in a woman occur suddenly;
- ignoring the disease. The first symptoms of a stroke in women do not cause alarm.
Often, the precursors of stroke in women are vegetative-vascular dysfunction and transient cerebrovascular accidents.
Precursors of stroke in women
Stroke occurs more often in women than in men.
Signs of an impending stroke in women:
- limbs move worse or do not move, weakness in the arm and leg on one side;
- weakness, drowsiness, increasing headache, which leads to nausea, lethargy;
- decreased sensation in a limb or one side of the body;
- impaired speech perception and ability to speak;
- loss of balance, ability to navigate in space.
Cause of development and risk groups
Stroke is one of the most serious diseases that occurs in the blood vessels of the brain. It leads to a serious disruption of blood circulation in any part of the circulatory network.
Since most of the functions of the human body are controlled by the nervous system, and it is, accordingly, controlled by the brain, any pathological processes and disturbances in its work will lead to failure of the motor processes of the limbs, paralysis or even death. Patients lose their speech, develop serious problems with memory and vision, and lose sensitivity and balance.
The risk group includes people suffering from the following disorders:
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- arrhythmia;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hemophilia.
Women most often experience stroke after 60 years of age. Patients with factors that can provoke a stroke need to be especially careful. These include:
- regular severe stress;
- physical exhaustion or fatigue;
- blood pressure surges;
- changes in atmospheric pressure (if the patient is weather dependent);
- heavy alcohol intoxication;
- overheat;
- hypothermia.
Signs of a stroke
A stroke is localized in the brain or spinal cord.
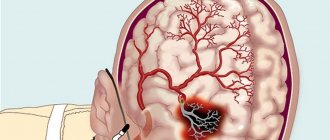
It is divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. In an ischemic stroke, part of the brain tissue dies due to circulatory failure. The hemorrhagic type occurs when the vessel wall is damaged and blood flows into the brain tissue. It occurs suddenly, more often during the day. It is preceded by a hypertensive crisis.
The first signs of a stroke in women:
- gradually increasing headache;
- weakness;
- speech disorder;
- vomit;
- loss of consciousness, coma;
- pupils of different sizes;
- frequent noisy breathing;
- weakness in the limbs on one side, paralysis in the arm or leg on one side (hemiparesis);
- speech disorder.
The stroke that occurs in older women (after 50-60 years) is in some way different from the one that develops in women 30-35 years old or 40-50 years old.
Difference between stroke in young and old age:
- The course of the stroke.
- Greater aggressiveness, pathology, and rate of damage to brain tissue in women over 70-80 years of age.
- In the consequences after a stroke in elderly women.
- How favorable the prognosis after a stroke can be for women over 60-80 years of age.
- Signs of stroke in young women.
Kinds
The main classification of strokes (according to ICD-10) takes into account the cause and mechanism of stroke.
- An ischemic stroke is characterized by a cessation of blood flow to the brain tissue. The reason is a violation of blood flow, blockage of an artery with a blood clot and/or narrowing by an atherosclerotic plaque (atherothrombotic), vasospasm, and a decrease in pressure. Most often develops at the age of 50-69 years. The incidence is 64-75% among all types of stroke.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a hemorrhage into the substance of the brain or under the arachnoid membrane due to rupture of a vessel as a result of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, vasculitis, aneurysms, coagulation disorders. Patients aged 50-69 years are at high risk. At 39-49 years old it is less common. The incidence is 15-20% among all types of stroke.
There are classifications that distinguish types of stroke taking into account other signs.
1. By severity:
- minor, including microstroke (transient ischemic attack) - a passing disturbance of cerebral circulation with complete disappearance of neurological symptoms within 1 day to 3 weeks;
- moderate severity;
- severe, extensive stroke of the brain - damage to a large area with pronounced neurological symptoms and severe condition, sometimes with falling into a deep coma.
2. By location
- left or right hemisphere. Each side is responsible for different functions, so the symptoms will be different. For example, if the left half is affected, the movements of the right side of the body suffer, speech and memory are impaired. The person loses the ability to read and write.
When the right hemisphere is damaged, the movement of the left side of the body, the perception of oneself, one’s body, and the surrounding space are impaired, and mental disorders develop.
3. By quantity
- primary stroke (first) and repeated strokes (second, third, fourth). Repeated strokes are more severe because the lesion area increases each time.
4. By age
- in children, starting from the prenatal period, young, elderly. The severity of clinical manifestations and prognosis depend on the patient’s age, the cause of concomitant pathology, and the timeliness of diagnosis. The most difficult prognosis is for delayed detection of a stroke, a large lesion, a weakened body due to concomitant diseases, bad habits, and vitamin deficiency.
5. By localization
:
- in the vertebrobasilar basin with damage to the occipital lobe of the brain, cerebellum and brainstem - visual disturbances develop, gait changes;
- frontal lobes - speech and swallowing suffer;
- temporal lobes - memory, writing, speech deteriorate;
- parietal lobe - speech and speech understanding suffer.
First aid for stroke
It is impossible to determine the nature of a stroke in the first hours, therefore it is necessary to normalize vital functions (breathing, blood circulation) and ensure the prevention of possible complications (pneumonia, thromboembolism, bedsores).
The first step is to call an ambulance. It is advisable to reassure the patient and measure blood pressure. If there is vomiting, place the patient on his side and place his hand under his head. Do not bend your neck, because blood flow cannot be impaired. The airways need to be clear. In case of severe respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation must be started.
If breathing is impaired, it is necessary to free the patient from tight clothing. Free the oral cavity from foreign objects, mucus, and vomit. If the patient is indoors, access to fresh air is necessary. If a person is conscious, it is advisable to cheer him up and calm him down.
If you lose consciousness, you need to make sure that the person is not injured or bruised.
There is no need to take medications so as not to worsen the patient’s condition.
If it is not possible to call an ambulance, then you must transport the victim to the hospital yourself.
How to avoid getting sick?
Neurologists admit that it is better to prevent a stroke than to treat it. Restoring lost functions of the human brain is extremely difficult. How to avoid a stroke?
- Monitor your blood pressure. Since the most common cause of apoplexy is high blood pressure, doctors urge to fight it. It is important to monitor him and take all necessary medications.
- Quit alcohol and smoking. By quitting smoking, even the most heavy smokers reduce the risk of cerebral hemorrhage by 4 times.
- Eat a balanced diet and avoid foods rich in cholesterol.
- Fight excess weight.
- Increase physical activity.
- Monitor your emotional health.
- Do not overdo it with the uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs, both contraceptives and during menopause.
If it was not possible to avoid a dangerous disease, then only intensive therapy in the next 2-3 hours can increase the chances of a favorable outcome.
The relationship between brain regions and the clinical picture of stroke
If the right lobe is affected, this is expressed by paralysis of the left limbs or loss of sensitivity in them.
The patient has a pronounced depressive state and a decrease in the desire for recovery. If the hippocampus area is affected, then the patient cannot grasp objects with his hand, loses the ability to navigate in space, cannot remember what happened yesterday, but memories of a longer period are preserved.
The hippocampus is responsible for emotions, short-term and long-term, spatial memory necessary for orientation in space.
If the left lobe is affected, then paralysis, decreased or loss of sensitivity in the right half of the body is characteristic, the patient does not perceive speech and speaks inarticulately.
If the cerebellum is affected, there is a lack of coordination, the patient feels nausea and dizziness. When the stem structures are damaged, the patient may experience double vision, the act of swallowing is disrupted, and involuntary movements occur.
Calling a doctor to your home
An experienced neurologist visits the patient’s home and provides first aid for signs of a stroke. What a doctor can do at home:
- Diagnostics . The neurologist examines the patient, measures pulse, blood pressure and temperature, and conducts motor and speech tests to assess the severity of the condition.
- Emergency hospitalization. When an acute pre-stroke condition or a stroke itself is recognized, the medical team quickly and safely transports the patient to the clinic.
- Eliminate symptoms. If the patient’s condition does not cause acute concern, the doctor conducts therapy at home. The complex of medications helps restore cerebral circulation, eliminates disturbances in heart rhythm and blood pressure.
Treatment methods
After a comprehensive diagnosis, an individual recovery program is formed for the patient based on methods of drug therapy and physiotherapy for pre-stroke conditions.
Drug therapy
- ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, ganglion blockers - for vasodilation and treatment of arterial hypertension, normalization of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Anticoagulants and antithrombic - to eliminate blood clots in blood vessels and prevent thrombosis, restore healthy blood flow.
- Statins - for removing cholesterol and already formed cholesterol plaques from blood vessels, normalizing lipid balance.
- Angioprotectors - to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and increase their elasticity, stimulate the regeneration processes of the cardiovascular system.
- Neuroprotectors - to restore connections between brain neurons and improve signal transmission, increasing the protection of brain cells from damage after circulatory disorders.
- Nootropics - to improve cellular metabolism and cerebral circulation, restore and stimulate the cognitive functions of the brain: thinking, speech, memory, concentration, coordination of movements.
- Sedatives, anxiolytics, antidepressants - for the treatment of increased anxiety, panic attacks, depressed mood - stress factors for the recurrence of the pre-stroke state.
- Analgesics, antispasmodics - for the treatment of headaches, muscle spasms and other painful symptoms of pre-stroke.
Physiotherapy
- Medicinal electrophoresis. Administration of drugs using direct electric current of low strength and voltage. Improves absorption and increases the concentration of drugs in a course of drug therapy, prolongs their effect. Stimulates the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers, improving brain function.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). The effect of magnetic impulses on the brain improves intercellular interaction and normalizes blood microcirculation, restores nerve connections, and is used in the rehabilitation of motor and speech skills.
- Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES). The effect of electrical impulses on brain structures has an analgesic effect, helps stimulate the regeneration of brain cells and normalize blood pressure, and increases the body's adaptive capabilities to protect against stress factors.
- Hydrotherapy. Radon and sodium chloride therapeutic baths help normalize blood circulation, dilate blood vessels, lower blood pressure and strengthen the heart muscle. And pine baths have a sedative effect, reduce emotional stress and increase stress resistance.
Hospitalization to the clinic
In case of acute cardiovascular, motor and speech disorders, we recommend hospitalization of the patient in the hospital of our clinic. Advantages of inpatient treatment:
- Full diagnostics. In a hospital setting, the patient undergoes comprehensive instrumental diagnostics: a biochemical blood test for glucose and cholesterol levels, electrocardiography and daily monitoring, ultrasound and Dopplerography of the carotid arteries of the neck, magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the soft tissues of the brain.
- Identifying the causes of the attack. A thorough hardware examination helps to detect the cause of the pre-stroke condition - atherosclerosis, hypertension, disorders of the pumping function of the heart and other pathologies. And making an accurate diagnosis allows you to begin the necessary treatment and prevent the risk of stroke in the future.
- 24/7 care. In the hospital, the patient is provided with 24-hour medical supervision. Experienced medical staff will be able to prevent a new attack in time, or provide emergency assistance if your health worsens, and minimize the consequences.
- Comprehensive restoration. The patient undergoes a program to restore healthy functioning of the cardiovascular system and cognitive functions of the brain. At the same time, he is in a safe, comfortable environment, maintains a healthy sleep schedule and proper diet, and is isolated from the stress factors of the home environment.