If the brain dies, this means the onset of biological death. The death of the tissues that make it up is irreversible. Without neuron signals, the body will not be able to maintain heartbeat and breathing.
In the world, it is customary to distinguish several types of death - biological, clinical, brain death.
Clinical death is considered reversible. Degenerative processes begin to occur, from which a person can die, but there is still a chance to restore the vital functions of the body. If the outcome is favorable, you can fully regain your health and continue to live a full life. In this case, necrosis of tissues and organs does not occur.
Biological death is associated with the death of all organs and systems. This process is already irreversible, as neuronal damage and necrosis are observed. Vital functions are completely lost, death occurs.
What are the criteria for brain death? It is associated with the death of neurons. If the brain dies, this process is also irreversible. The body is no longer able to maintain vital functions; the respiratory and cardiovascular systems do not work. This is analogous to biological death. When brain death occurs, necrosis of its tissues is necessarily observed.
Sometimes brain decortication is performed - partial surgical removal of the cortex. Such a serious operation is performed only for special indications.
Causes
Brain death can be caused by different reasons, but they trigger the development of the same pathological processes. Blood circulation is impaired, and this dysfunction is persistent. This provokes acute oxygen starvation, which causes metabolic products to stagnate in the tissues. Irreversible brain damage develops.
The main reasons are as follows:
- diseases, including inflammatory processes in brain tissue;
- injuries;
- circulatory disorders (hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke);
- multiple organ failure;
- poisoning (alcohol, lithium, drugs);
- tumor (cancer causes numerous tissue destructions);
- heart diseases, etc.
The phenomenon of vascular occlusion is extremely dangerous. At the same time, their patency is impaired, and oxygen starvation of the tissues occurs. Occlusion of arteries and veins that lead to the brain is especially dangerous. Often, pathological anatomy of the deceased reveals complete blockage of blood vessels. This can be a consequence of injury, disease and causes damage to neurons.
The brain stem may be damaged primarily or secondary. With a primary lesion, direct damage occurs (if there is a fracture of the base of the skull, the functions of the trunk itself are impaired). In case of secondary damage, the trunk suffers due to the resulting edema and dislocation syndrome. With swelling, the tissue begins to protrude strongly through the opening of the back of the head, due to which the trunk is excessively compressed, blood circulation stops and necrosis begins. This is why protecting the brain from swelling is so important.
All of the above reasons are considered extreme; they have an extremely negative effect on neurons. The brain stem and its cortex are primarily affected. The task of the trunk area is to maintain cardiac activity, breathing, control blood pressure, and the cortex is responsible for thought processes, consciousness, etc.
Cardiac arrest does not immediately lead to brain death, but everything happens very quickly. A person without blood circulation can live only a few minutes. 3 minutes without blood supply can lead to irreversible death of neurons, resulting in coma. If the cerebral cortex has died, vital functions will be lost and death can occur almost immediately.
The time that the body can survive without cardiac activity is influenced by a whole range of factors:
- age;
- general condition of the body;
- presence of diseases;
- the reason that caused this condition;
- ambient temperature, etc.
After just three minutes of oxygen starvation, neurons begin to die. This is an irreversible process, since dead tissue is not restored. In a healthy young person, brain death may slow down slightly. If the ambient temperature is low, the brain will die more slowly. If resuscitation is performed correctly at this time, the person can be brought back to life.
The consequences of circulatory arrest can be unpredictable. Sometimes a person wakes up from a coma, blood supply to the brain is restored, but it turns out that a significant part of the neurons have already died. If the brain dies, but the heart works, it will no longer be possible to return the victim to normal life. He can only exist, and is not even able to breathe on his own.
Symptoms
The following symptoms indicate brain death:
- there is no consciousness, and this process is persistent;
- there are no reactions to tingling, stroking, handling, no tactile sensitivity;
- no movement of the eyeballs;
- the heart has stopped, as evidenced by a straight line on the ECG;
- there is urinary and fecal incontinence;
- breathing is impaired, the chest does not rise.
Determining whether a patient has died is an extremely important task. Doctors do not immediately diagnose death. Even if all of the listed signs are detected, the person is monitored in the hospital for up to 12 hours. Sometimes, although rarely, signs of brain activity may appear. If during this time the patient does not react in any way, there are no trunk reflexes, then biological death can be stated.
It is important how the brain dies, what triggered the death of neurons. If poisoning has led to such serious consequences, the patient should be monitored for at least a day. If the cause is TBI, the observation time is reduced to 6 hours. The specific decision must be made by the neurosurgeon. It is important that the doctor monitors the patient from the onset of this condition, then he will have a complete picture of events that will allow him to make the right decision.
The onset of biological death is determined exclusively by a neurologist. It is based on subjective and objective criteria. If signs of brain death are clearly identified, the person must be disconnected from life support. This difficult decision is especially difficult to make if the disaster happened suddenly. Often relatives are literally horrified by such a message. If a person is sick for a long time, his loved ones eventually become at least a little accustomed to the idea that their loved one will be gone. In any case, this decision is very difficult.
How does a doctor feel when he disconnects a person from the machines and takes away his organs?
Photo from vitals.nbcnews.com
- And another question, maybe not for you. If a person dies on the table, and you understand that he is a potential donor. That is, he died, but his organs can be removed and transplanted into someone else.
— I went to heart sampling several times.
I remember two months ago I went to a Moscow hospital. The guy is twenty-three years old, he was simply beaten near the metro, but they hit him with something so hard that his head was broken into two parts. They found his relatives, they signed permission to harvest his organs. A child needed a kidney, a woman and a man needed a liver - they divided it into two parts, a thirty-year-old man needed a heart. And now all the documents are signed, the patient is connected to the machines, and you stand on the fence, see this open skull and begin to put yourself in this guy’s place.
If you just came, the device turned off - that’s all. After all, brain death has already been declared, and you know that in 2-3 days irreversible changes will occur throughout the body. People with their heads cut into two parts cannot live. But I have to check all the documents again and again and sign that I agree to the fence. And then very carefully conduct the dynamics - so that God forbid the heart does not suffer from hypoxia, asystole. After all, the heart must be taken “alive”, warm.
I sometimes have dreams: the patient wakes up and says: “Why are you taking my heart?”
In general, this organ harvesting can be more difficult than even unsuccessful resuscitation. Because there you were doing something, fighting death, and here you have a living corpse lying. Nothing can be done, absolutely. Yesterday he lived, and then he was hit, or there was an accident, or a KAMAZ ran over him - there were many cases.
Screenshot from youtube.com
And when you turn off the devices, you shake all over, because you understand: “The person was just there, and now he’s gone.” And they begin to take away his organs.
And then you drive around the city with this heart with flashing lights. Then they went to save a thirty-year-old man. He served in the army, fell ill with a sore throat, and developed severe cardiomyopathy: his heart collapsed, only a transplant could save him. I also made a call from the clinic where the organs were taken away that I was bringing a heart, and the doctors made a skin incision in the patient and began to isolate the old heart. Not a minute is wasted here.
And then you see the same heart in another person, it works like your own, and the patient with a mask on his face after surgery shows you with a gesture: “I’m fine!” And here you switch things up a little, because, yes, one died, but thanks to him the life of the other was saved.
That time five people were saved, they will continue to live, continue their family line. And you understand that this is humane towards them - we did not let them die. And about the donor - again you think about fate: well, who really knew that he would go to the metro...
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, the doctor must collect anamnesis. He must find out how long ago the patient fell into such a dangerous state, under what conditions he lost consciousness, and whether he had speech or motor activity. It is important to know what event preceded the loss of consciousness. An examination is carried out by a neurologist, he necessarily assesses the patient’s level of consciousness and checks his reflexes.
It is extremely important that the doctor excludes all those factors that can cause simulated brain death. It is sometimes caused by severe poisoning, including drugs. For this reason, a toxicological analysis is prescribed. It will help detect toxins or drugs that mimic the appearance of death.
Body temperature must be measured. If the temperature is below 32.2°C, it may distort the picture and show a false death. In this case, the person may be alive, but tests will show the opposite, since physiological processes literally freeze from the cold.
A blood test is prescribed that will help determine whether the metabolism is disturbed, whether there is hormonal dysfunction, and at what level the glucose levels are.
To correctly diagnose brain death, inpatients resort to instrumental research:
- encephalogram (EEG);
- contrast study of cerebral vessels;
- test with irritation of the eardrums (ice water is dripped onto them through the ear canal);
- apneic oxygenation test.
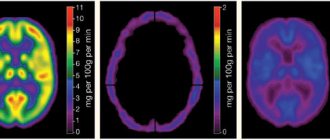
Oxygen starvation is extremely destructive for neurons, even if it is not long-term. Literally after a few minutes of complete lack of oxygen supply, tissues begin to die. The electroencephalogram in this case will show a zero line. This means that there is no brain activity at all.
Encephalography examines brain activity. In this case, the device registers biocurrents, their work is reproduced on paper in the form of curves.
The diagnostic protocol also includes the study of cerebral vessels using a contrast agent. It cannot always be accomplished, as there may be financial restrictions, and sometimes there is simply no equipment. The essence of the test is that a contrast agent is injected, which enters the brain vessels through the bloodstream and identifies possible areas of necrosis. If the brain is dead, the substance does not enter its vessels. This is one hundred percent confirmation of death.
Apneic oxygenation involves temporarily removing the patient from a ventilator. The goal is to observe whether spontaneous respiratory movements have appeared. The monitor monitors the level of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is carbon dioxide that stimulates the body to produce breathing movements. If after 8-10 minutes breathing does not appear, and the level of CO2 in the blood jumps by 20 mm Hg. Art. higher than the original, we can definitely talk about death.
Application of the electroencephalographic study method to establish the diagnosis of brain death
An EEG study is used to make a diagnosis of brain death:
- in children, if it is possible to determine all clinical criteria for brain death;
- in adult patients and in children in the absence of the ability to determine one or more clinical criteria for human brain death.
At the same time, establishing the absence of bioelectrical activity of the brain based on the results of an EEG study is not in itself an independent criterion for establishing a diagnosis of brain death and is used in conjunction with the main methods - observation and panangiography of the vessels of the head.
To perform EEG studies, encephalographs with at least 8 recording channels are used. An electroencephalogram (hereinafter referred to as EEG) is recorded and analyzed in bipolar and monopolar leads.
The absence of bioelectrical activity of the brain is evidenced by an EEG recording in which the amplitude of activity from peak to peak does not exceed 2 μV, subject to the following conditions:
- recording is carried out from scalp electrodes with a distance between them of at least 10 cm in adult patients and at least 8 cm in children;
- at least 8 electrodes are used, located according to the “10-20%” system, and 2 ear electrodes;
- the interelectrode resistance must be at least 100 Ohms and no more than 10 kOhms;
- the safety of switching and the absence of unintentional or intentional creation of electrode artifacts is determined;
- recording is carried out on encephalograph channels with a time constant of at least 0.3 seconds. with a sensitivity of no more than 2 µV/mm (the upper limit of the frequency bandwidth is not lower than 30 Hz).
The electrical silence of the cerebral cortex under these conditions should remain for at least 30 minutes of continuous recording. If there is doubt about the electrical silence of the brain, repeated EEG registration is necessary.
Assessing EEG reactivity to light, loud sound and pain:
- the total stimulation time with light flashes, sound stimuli and painful stimuli should be at least 10 minutes;
- the source of flashes fired at a frequency of 1 to 30 Hz should be located at a distance of 20 cm from the eyes;
- the intensity of sound stimuli (clicks) is 100 dB, the speaker is located near the patient’s ear;
- stimuli of maximum intensity are generated by standard photo- and phonostimulators;
- For painful stimulation, strong injections with a sterile needle are used on the patient’s skin.
To establish the absence of bioelectrical silence of the brain, EEG recording by telephone or methods of automatic, mathematical (spectral, coherent) EEG analysis should not be used.
If the results of an EEG study do not establish the absence of bioelectrical activity of the brain, the procedure for diagnosing human brain death is terminated.
The results of the EEG study are attached to the protocol for establishing the diagnosis of brain death.
If the body is accidentally discovered
If an ambulance team finds a victim without signs of life, doctors have no information how long he remains in this condition. In the absence of cadaveric spots, doctors cannot confirm in the field that biological death has occurred. In this case, resuscitation is mandatory.
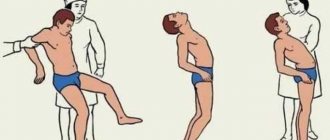
Resuscitation measures include artificial ventilation of the lungs and closed heart massage. If there is bleeding, it is important to stop it so the victim does not bleed out. Damage to a large artery or head is extremely dangerous. If resuscitation measures are carried out correctly, a person can be brought back to life.
“What if he wakes up as a vegetable?”
Photo from health.usnews.com
— As far as I know, the same quantitative standards exist for resuscitation - according to the instructions of patients, it is necessary to resuscitate a certain number of minutes. What in practice?
- Six months ago there was a case when we resuscitated 245 minutes - and in general, according to the standards - half an hour.
Such a long resuscitation is a unique case, it is generally unrealistic. A young guy with a very severe heart defect. He was being prepared for surgery, and suddenly he began to die. We first gave him a closed cardiac massage, then an open one - the surgeons opened the chest. As a result, he came to life. Yes, then I was sick - there was cerebral edema, decompensation, multiple organ failure, respiratory failure. But he still had heart surgery, he was transferred to the ward and discharged, everything is stable there.
- So, according to your words, I understand that it is necessary to resuscitate until the last minute?
— We say, “until the victory.”
— Did you understand in your mind at that time that a guy could wake up like a vegetable, for example?
— Somewhere they understood, of course. But the guy, firstly, is young - he is nineteen years old. And we just felt that we had to go to the end - we administered special drugs in liters. But we saw from the monitors that there is hope. We see sinus rhythm - with disturbances, but we understand that we can fight it later, there are such drugs. They understood that all the regulations had already been exceeded, but they went on until the victory. And the boy was eventually saved.
It’s just that each specialist does his own thing. For example, a journalist is at war, and bullets fly past him. And he writes. You save. After all, nothing is known in advance exactly: what will happen to this person. What if everything will be fine?
- Go on the attack.
- Yes. You see, medicine is not mathematics.
It happens, for example: a patient is brought in and the operation of coronary artery bypass surgery went perfectly - literally from the incision to the skin suture. Male, safe, fifty years old, three shunts. After the operation, we are transported to the intensive care unit - suddenly there is asystole. Death.
Or vice versa - patients with severe cerebral edema, who were turned on, were pummeled with shocks, burned through the skin right to the bone and pumped to the point of broken ribs - they simply broke the sternum, but pumped the heart so that “the head would not fly off.” And in the end they had operations, post-resuscitation plastic surgery - and they came back, and everything was fine.
“There is an opinion that the doctors themselves, who imagine the resuscitation process and the possible consequences of severe diagnoses, ask: “Don’t pump me out.”
- I haven’t encountered anything like this. I saw something else. For example, an operation begins, and you put the patient under anesthesia, explain to him what will happen now - he will be tied to the table, he will fall asleep, and you explain what will happen when he wakes up. And several times patients, especially older ones, asked: “If I die, don’t open me up.”
I remember there was an incident - it was just some kind of mysticism, now I remember it, I still can’t wrap my head around it. The patient was engaged in making monuments.
And so he lies down on the table and says: “If I die, don’t open it. But in general, I’ve already knocked out a monument for myself, with a photograph, the full date of birth, but I didn’t sign the date of death.”
And I stand there, I have goosebumps: “What is he saying?” I thought I would cancel the operation altogether now. But then he calmed down and decided: “Okay, the person is just worried.”
This patient underwent surgery. Everything went perfectly, although it was hard - she walked for twelve hours. They bring him to the intensive care unit, he wakes up, everything is normal. And suddenly - once - cardiac arrest. We resuscitate him for an hour and a half, but he dies. The monument came in handy.
— How do doctors cope with the fact that they have done everything, and the person died? It turns out that what depends on the doctor?
- When this happens, then you think about it all the time, you replay the situation. Moreover, there can be several operations a day: you can leave with one and immediately go to pump a child who is dying in front of you.
Here it is important to repeat to yourself: you are not omnipotent, probably this is the fate of a person. And you shouldn’t give yourself any slack as a specialist – a surgeon, resuscitator or anesthesiologist. But sometimes I cry. You start thinking about life: “Why did he die so young?” You were with him, you went through some kind of hell, you tried to snatch him from death, but you couldn’t. These thoughts are in my head all the time. I don't know the answers.
How to tell your family
Recently, it has become common to resort to the help of a psychologist in such cases. It will help family members come to terms with their loss.
Making a decision to disconnect a patient from life support is extremely difficult even for experienced doctors. Relatives are always unprepared for such a tragic development of events, so they literally lose their minds. Relatives tend to believe that they can still try to do something. They are often asked to wait at least a few days. If there is accurate evidence of brain death, the doctor must find the right words to explain the current situation to the relatives.
According to the rules of bioethics, if brain death is definitely established, the patient should be disconnected from devices that support life processes. There is no point in expecting him to come back to life if all tests have confirmed the absence of neuronal activity. This will be a humane decision.
Relatives should definitely ask what diagnostic research methods were used. The doctor must show a document confirming the established brain death. Only relatives have the right to decide to disconnect the victim from life-sustaining devices. The doctor’s task is not to succumb to emotions, but to make the right decision based on the specific results of the patient’s examination.
It is important to exclude the human factor and rely only on test results.
How long to keep the victim on life support is decided individually in each case. After a person is disconnected from the devices, Lazarus syndrome may occur. It consists in the fact that the deceased experiences individual muscle twitches. The head may turn involuntarily, the person may bend an arm or leg. It even happens that an already dead person arches. This is the result of contraction of the back muscles. It is important that the doctor warns the patient’s relatives in advance that such manifestations are possible. This does not mean that the victim comes to life.
Additional examinations
Of the additional examinations that may affect the diagnosis, electroencephalography (EEG) and angiography are permitted. EEG is indicated for those patients for whom it is difficult to determine reflexes - in case of injuries or suspected injuries of the cervical spinal column, ruptured eardrums. An EEG is performed after all tests, including apnea. In brain death, it shows the absence of any electrical activity in the nerve tissue. If the indicators are questionable, the study can be repeated or using stimuli (light, pain).
non-collapsed cerebral vessels are normal on angiography
If EEG is indicated in clinically complex cases and does not affect the duration of general observation, then panangiography of the carotid and vertebral arteries is designed to shorten this time as much as possible. It is carried out at the final diagnostic stage and confirms the irreversibility of the cessation of brain activity.
For example, in case of possible intoxication, the patient should be observed for at least three days, but brain death can be determined early if, immediately after the appearance of signs of loss of its functions, the main arteries of the brain are examined twice with an interval of at least half an hour. In the absence of contrasting of the arteries, we can talk about a total and irreversible stop of cerebral blood flow, and further observation becomes impractical.
Video: example of an EEG to confirm brain death
Clinical diagnosis of biological brain death is labor-intensive, requires constant monitoring and maintenance of vital functions, so for many years the search has been underway for another method that would allow us to establish a reliable diagnosis with no less accuracy than the clinic. However, no matter how hard the experts try, none of the proposed methods is comparable in accuracy and reliability to a clinical assessment of the state of the brain. Moreover, other techniques are more complex, less accessible, invasive or not specific enough, and the result is greatly influenced by the experience and knowledge of the doctor.
The desire to speed up the process of ascertaining brain death is largely due to the rapid development of a new branch of medicine - transplantology. Considering the diagnosis of brain death from this position, we can say that the price of a conclusion about brain death may be not one, but several lives - both of the potential donor and of other people in need of organ transplants, therefore haste or non-compliance with the observation algorithm is unacceptable.
When deciding to declare brain death, the doctor must remember the ethical side of the issue and the fact that the life of any person is priceless, therefore strict compliance of his actions with the established rules and instructions is mandatory. A possible mistake increases the already high degree of responsibility, forcing you to repeatedly play it safe and doubt, double-check and weigh every step.
The diagnosis of brain death is established jointly by a resuscitation specialist and a neurologist, and each of them must have at least five years of work experience. If additional examination is necessary, specialists of other profiles are involved. Transplantologists and other persons involved in the collection and transplantation of organs cannot and should not participate in or influence the process of diagnosing brain death.
Consequences
Brain death does not always lead to biological death. Sometimes medical intervention can save a life, if such a condition can be called that. In fact, after brain death, only certain vital functions can be maintained. The consequences of total neuronal death are terrible, this is complete dementia. Any vital indicator is so low that the body cannot cope without the support of devices. Such people are no longer able to continue living a full life. They live like plants and can die at any moment.
Even in order to maintain basic vital functions, continuous administration of medications will be required. Without medical equipment, the patient will not be able to breathe, and his heart will not be able to beat.
In the medical literature there are several descriptions of a case of a person returning to life after death. There is some confusion here. Most likely, such patients “resurrected” after clinical death, rather than biological death. This happens quite often. Clinical death can occur with serious damage, and with proper care, body functions are restored.
Even clinical death is not identical to brain death. It is the death of neurons that leads to the most tragic consequences.
In theory and in life
Photo from bigthink.com
— If, let’s say, we know miracles in the history of medicine, although their percentage is insignificant, what guides the doctor when deciding to turn off the equipment?
— This decision is made not by one doctor, but by a council. Many factors are taken into account. Duration of management of this patient, duration of mechanical ventilation, associated complications: bedsores, secondary infection. It happens that antibiotics do not help, because the bacterial microflora is already tolerant to them, and the immune system is zero. The patient then dies from a secondary infection.
Having compared all these factors and data from all instrumental methods and blood tests, the council makes a decision to turn off mechanical ventilation. There is a special scale with a set of criteria.
It also takes into account whether the patient is in a separate sterile box or in a general intensive care unit. In general intensive care there is a high risk of contracting nosocomial infections to other patients. Sometimes in the periphery, where the management of such patients is poor, they simply compare several factors, understand that they cannot cope with the management of such a patient, and make a decision to disconnect. In Moscow, where there are the necessary drugs and better equipment, they fight longer, although if a hospital-acquired infection occurs, it is still bad.
— That is, at some point, death becomes just a set of quantitative indicators, you can literally feel it with your hands?
- Yes, we practically probe like this - we shine a light, prick during reflexology, we see whether the patient is hopeless or not hopeless.
Reanimation
The consequences of brain death are irreversible. Just because a person is unconscious does not mean that he needs to perform resuscitation measures (ventilation, cardiac massage).
Cardiac massage is strictly contraindicated if the victim’s heart is beating, even abnormally. In this case, massage can, on the contrary, interfere with the correct contraction of the heart muscles.
Mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose breathing, as well as chest compressions, are performed only if there is no heartbeat. Such events can save a person's life. If you ensure the supply of oxygen to the body and improve blood circulation, irreversible necrotic changes will not occur. Body functions can be completely restored.
If a pregnant woman is injured, it is important to monitor not only her vital signs, but also the condition of the fetus. The patient must be taken to the hospital as quickly as possible, since the child may die due to injury and stress.
It is extremely important to thoroughly master resuscitation techniques. Any of us can master them and, if necessary, save a person’s life.
Forecasts
Clinical death does not always mean that the patient will definitely die. Sometimes doctors manage to bring a person out of a state of clinical death. The prognosis will be influenced by what circumstance led to such a condition and what resuscitation measures were taken. The main condition is to restore blood circulation in the first 3-5 minutes. Sometimes resuscitation is carried out for up to 20-40 minutes.
Even if partial extinction and death of neurons has occurred, the functions of the medulla can be restored. If biological death or brain death is established, it is impossible to bring the patient back to life, you need to come to terms with this.
The peculiarity of the human brain is that it strives to preserve its functions by any means. If some neurons die, their tasks can be redistributed to other zones. Patients who have suffered a stroke, ischemia, and even serious TBI often return to a full life.
Features and criteria for declaring brain death
In medicine, the concepts of clinical and biological death refer to the entire body, implying the reversibility or irreversibility of changes occurring. Applying this parameter to nervous tissue, we can speak of clinical brain death in the first 5 minutes after breathing stops, although the death of cortical neurons begins already in the third minute. Biological death characterizes a total disorder of brain activity that cannot be reversed by any resuscitation or treatment.
The need to assess the state of the brain usually arises in comatose and similar conditions, when the patient is unconscious, contact with him is impossible, hemodynamics and heart function may be unstable, breathing is usually supported by a device, the pelvic organs are not controlled, there is no movement and sensitivity, reflexes and muscle tone fades away.