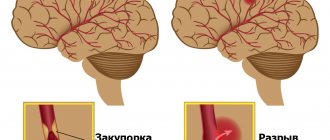
Hemorrhagic stroke is a condition of acute circulatory disturbance in the brain, accompanied by hemorrhage into the cranial cavity and leading to the formation of hematomas.
Today, hemorrhagic stroke is a serious condition leading to disability. The disease mainly affects men, but most often it is women who die. Mortality is very high, with hemorrhage leading to the death of almost 50% of patients. This occurs within 30 days after the attack occurred.
But even after the crisis is over, the struggle must continue, because problems with blood circulation that began in the brain have many consequences. But in this case, rehabilitation after a hemorrhagic stroke, along with the patient’s gradual return to normal life, is possible.
How does a hemorrhagic stroke occur?
Cerebral hemorrhage during a stroke is a spontaneous phenomenon. The functioning of the brain requires large amounts of oxygen from the blood. Nutrition is produced thanks to two carotid and two vertebral arteries, which form a circle between themselves passing through the base of the brain.
When a vessel is damaged, acute blood failure occurs, which is necessarily compensated by healthy vessels. However, over time, the effectiveness of such a mutual assistance system decreases. The appearance of cerebral hemorrhage during a hemorrhagic stroke is caused by sudden ruptures of the vascular walls or their increased permeability due to other chronic diseases.
During a cerebral hemorrhage, the death of brain cells that are damaged by blood contact occurs. In nearby areas of the brain, oxygen deficiency begins, since blood does not reach them and cannot move further through the vascular system.
Rehabilitation
A stroke is an acute circulatory disorder in the brain. This condition is accompanied by loss of consciousness, as well as paralysis.
After a hemorrhagic stroke, a long recovery period is required for a person to live a normal life or close to it.
In medical practice, recovery methods are used:
- speeches;
- vision;
- memory;
- motor skills;
- motor function.
With an integrated approach, techniques individually selected by a doctor will be incredibly effective.
The more difficult question is timing.
The amount of time it takes to recover depends on several factors:
- The type of stroke suffered. Thus, with a hemorrhagic stroke, the recovery period is shorter than with an ischemic stroke.
- Number of lesions and extent of damage.
- When did rehabilitation begin? One rule applies here: the sooner measures were taken, the better.
- Correctly selected treatment and quality of therapy.
- Psychological state of the patient.
- Other diseases and individual characteristics.
If rehabilitation is successful, improvements will be noticeable within the first 20 days. As a rule, people have the opportunity to communicate within a period of 10 days to 3 calendar months.
It will take 1 to 5 months to restore limb function.
But the timing is individual and depends on each individual person.
- Recovery after a stroke: how to restore speech, vision, memory and motor skills?
Medications
Immediately after a diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke has been made, hemostatic drugs must be taken. Among them:
- Ditsian (800 rub.).
- Cyclomed (845 RUR).
- Etamzilat (180 RUR).
Angioprotectors are used simultaneously with them. Among them:
- Pentoxifylline (250 RUR).
- Troxevasin (280 RUR).
- Trental (450 rub.).
Since a stroke is characterized by an increase in blood pressure, its reduction is required. For normalization, Clonidine (68 rubles) and Droperidol (72 rubles) are used.
If the above drugs do not help, then ganglion blockers are used. The most common of them are Benzohexonium and Pentamin.
Patients are required to be prescribed neuroprotectors. These drugs promote accelerated rehabilitation. Among them are Cerakson and Cinnarizine.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is designed to combat movement disorders.
The main goal of physical education is to increase the range of motion, as well as strengthen the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In addition, simple exercises and proper breathing can activate the brain.
Massage
Massages are used that are aimed at strengthening tissues and improving the functioning of the nervous system. The massage must be performed by a medical professional in strict accordance with the instructions of the attending physician. Massage is carried out several times a week. Performing this type of treatment on your own is unacceptable, as there is a high risk of aggravating the situation.
Working with a speech therapist
Individual sessions with a speech therapist are conducted in the first stages of recovery . Further, group attendance at classes is possible. According to psychologists, this is the most effective measure to return to normal life.
- How to avoid stroke in women: prevention with drugs and folk remedies
The speech therapist selects programs individually, depending on the characteristics of the stroke and recovery of each patient
Physiotherapy
The main goal of physiotherapy is to prevent recurrence of stroke , reduce pain, improve blood circulation, increase immunity, and therefore the result of treatment. Additionally, the passage of nerve impulses improves, sleep normalizes and swelling is eliminated.
Depending on individual cases, patients are offered various types of physiotherapy. Among them:
- electrophoresis;
- vibration therapy;
- manual therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- heat therapy;
- acupuncture.
Psychotherapy
Many patients, realizing their helplessness after a stroke, refuse to recover and move on with their lives. Therefore, communication with a psychotherapist is important. He will help you find the strength to live, sort out problems, and also find motivation to improve your condition.
Important! As practice shows, in 83% of cases, after communicating with a psychotherapist, the patient developed a desire to live.
What types of hematomas occur in hemorrhagic stroke?
Types of hematomas in cerebral hemorrhage or hemorrhagic stroke:
- Parenchymatous with the distribution of blood directly inside or under the membrane of the brain, with the formation of hematomas and with saturation of the nerve brain tissue. With such a hemorrhagic stroke, severe neurological deficits can form.
- Intraventricular with the effusion of blood into the ventricles of the brain, with tissue penetration and the formation of a hematoma. With this type, death especially often occurs within 3-5 days.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhages in the area between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain.
- Mixed types of strokes, in which focal hemorrhages appear in different parts of the brain.
There is also a classification based on the volume of blood that forms hematomas: small - up to 20 ml, medium - in the range of 20-50 ml, large - from 50 and above.
Period of return to normal life
Rehabilitation after hemorrhagic stroke is carried out according to plan in medical institutions of various specialties:
- For 1 month, patients are treated in the neurological or neurovascular department of the hospital.
- Then they receive rehabilitation treatment in the rehabilitation department for another 1 month.
After this, doctors evaluate how successful the treatment was. Depending on the preliminary results, the patient is offered different programs for further recovery.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke
With hemorrhoidal stroke, symptoms most often appear suddenly, mainly during the daytime and during very heavy physical activity. The following symptoms are typical:
- convulsions;
- Strong headache;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- serious depression of a person's consciousness, similar to or leading to a coma
In addition, general symptoms of a stroke appear:
- decreased facial expressions and muscle strength affecting any part of the body;
- the occurrence of speech disorders and problems with visual perception;
- loss of coordination of movement with impaired ability to move.
During an attack, the patient's skin becomes cold and sometimes acquires a purplish-bluish tint. Breathing becomes more frequent, noisy, with wheezing. Sometimes, on the affected side, the pupil dilates, diverges, or chaotic movements of the eyeballs occur.
An important indicator of the severity of the patient’s current condition is comatose status with loss of consciousness, which can last several days. This makes the prognosis very unfavorable.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage most often results from rupture of a cerebral aneurysm. As a result, the patient experiences severe headaches localized in the back of the head and forehead. Then it spreads to the rest of the head. Later, other symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke appear.
In case of extensive cerebral hemorrhage, neurosurgical microtechnical operations are performed. In this case, removal of the hematoma leads to a decrease in pressure on the brain tissue and prevents the development of brain edema. But surgery is performed strictly for medical reasons.
In case of an aneurysm, surgery is performed to stop bleeding, and the patient is prescribed hemostatic drugs. Often with subarachnoid lesions, narrowing of the vessel occurs and the development of ischemic stroke. In this case, calcium channel blockers are necessarily prescribed to prevent narrowing and spasm of the vascular walls.
In the first 3 weeks after the attack, the patient’s condition remains the most severe due to progressive cerebral edema, as well as a gradual increase in cerebral symptoms. If there are any chronic pathologies in the body, aggravated by a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient may die. A month later, the patient begins to experience regression of cerebral symptoms and blood pressure stabilizes.
This is interesting! It is recommended to always have glycine in your home medicine cabinet. Many qualified doctors classify this drug as a neuroprotector or a substance that protects brain tissue.
If unpleasant weakness in the limbs or speech disorder occurs, you should immediately put 5 glycine tablets under your tongue. To some extent, such prevention can prevent acute brain damage and the development of hemorrhagic lesions.
Many people are interested in the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Two such lesions have almost identical symptoms, but have different reasons for the development of such a serious pathology. With ischemic stroke, the prognosis is favorable and mainly depends on the degree of brain damage that has occurred.
The following symptoms are characteristic of each type of this disease:
- suppression of speech ability;
- partial or complete paralysis of the body and limbs;
- impairment of visual sensitivity or its complete loss;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- complete loss of hearing in a hemorrhagic condition;
- • serious inhibition of the functions of the cerebral cortex;
- • increased blood pressure.
The consequences of a stroke mainly depend on the location and extent of the existing lesion. A hemorrhagic attack has an acute onset and progresses rapidly. The onset of coma in this case is possible within the first few minutes or hours. With ischemic stroke, the symptoms are less severe.
Damage to the left hemisphere leads to paralysis of the right side of the body. Hemorrhage in the cerebellar area deprives the patient of sensitivity, the ability to swallow, see and speak. Often the consequence of a hemorrhagic stroke is the gradual development of dementia or dementia.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Recovery time after hemorrhagic stroke
The rehabilitation performed after such a brain injury consists of several stages:
- early period, lasting about six months after the attack;
- later recovery, lasting from six months to 1 year;
- the stage of final recovery, which in its duration occupies the entire subsequent time.
A year after the attack, residual effects begin. The best results during rehabilitation can be obtained in the first year; for this reason, recovery should not be delayed.
Effective results are obtained by strictly observing the following important principles:
- taking action at an early stage of ongoing treatment in a hospital;
- daily implementation by the patient of appropriate recommendations without any delays;
- prescribing special physical activity with appropriate intensity and gradual complication of exercises.
In addition, it is very important to take comprehensive measures: prescribing physiotherapy, drug treatment and the necessary correction of the patient’s psychological state. During this period, a recovering person must protect himself from unnecessary stressful situations, and also be surrounded by the care and love of family and friends.
Short-term complications of concussion
Some patients who have suffered a concussion may experience so-called post-stress disorders:
- persistent headaches lasting 7-14 days, the intensity of which decreases when taking analgesics or painkillers of other groups;
- attacks of dizziness, difficulty concentrating, difficulty performing any normal activities (reading, writing, etc.);
- periodic vomiting for no apparent reason, feeling of nausea.
Most often, the side effects of a concussion disappear after some time without treatment; if they bother the patient for several months, you should visit a doctor and get an appointment for a consultation with a neurologist or a brain tomography (magnetic resonance, computer) to clarify the diagnosis.
Rehabilitation objectives
The main objectives of the ongoing rehabilitation are:
- Work on restoring lost everyday and physiological functions of a person suffering from a stroke. Restoring full range of motion, the ability to independently care for oneself and perform simple household chores.
- Restoration of lost professional ability to work with a return to the previous place of activity or assistance in retraining.
- Maintaining the necessary social activity of a person, first of all, restoring his contact with loved ones and the ability to make new acquaintances;
It is very important to prevent a possible relapse and correct the patient’s current lifestyle.
Recovery points after hemorrhagic stroke
Complications for the patient mainly depend on the location of the hemorrhage that occurs, as well as its volume. Today there are the following groups of possible threatening consequences:
- Motor disorders. The appearance of severe weakness and paresis in a person, the patient’s inability to accept and maintain a sitting position. This may be paralysis of one side of the body, high muscle tone or spasms that occur, which seriously complicates self-care, requires mandatory assistance and causes a lot of inconvenience to the person.
- Impaired sensitivity is, for example, numbness of the limbs, a feeling of “insects under the skin” and burning, the inability to control the hands, leading to various everyday problems.
- The appearance of speech pathologies after a stroke is confusion of speech and the inability to correctly pronounce individual sounds or loss of the ability to maintain a conversation. There may be loss of skills such as recognizing the meaning of words, counting, reading, telling time by a clock, and understanding calendar periodicity.
- Problems with swallowing when eating food and various liquids, and in some cases, complete loss of the ability to eat independently.
- Disorders of the excretory system: the appearance of urinary and stool incontinence, problems with the intestines and urinary system that arise on an ongoing basis.
The patient often develops acute and chronic psychological and mental disorders in the form of depression, excessive emotional temper or apathy. Sometimes partial amnesia occurs: the inability to recognize familiar people or objects, the understanding of performing simple everyday actions disappears.
Types of rehabilitation after hemorrhagic stroke
The necessary medicinal and motor rehabilitation is carried out for the following purposes:
- significant reduction in the risk of recurrence of hemorrhagic stroke;
- gradual return to normal lifestyle;
- return of lost ability to work;
- the patient performs basic skills and actions;
- preserving the patient’s identity through the provision of social and psychological assistance.
Drug treatment
In the human brain, dead neurons are replaced with elements with high activity. But due to the increasing load, additional energy is necessarily required. Neurons that remain alive after damage restore lost functions over time.
Prescribed medications provide additional nutrition and significantly improve recovery processes in the brain. Additional courses of essential drug therapy are recommended once every three months throughout the year.
Drugs that are administered to the patient by injection during treatment:
- nootropics, which include piracetam, Actovegin and other drugs;
- medications to stimulate the necessary impulses in brain cells, for example, proserin or neuromidin;
- selected B vitamins that improve cell metabolism.
Taking the prescribed medications should continue even after completion of the prescribed treatment in the hospital. At home, tablets are taken with food.
Chronically high blood pressure is corrected with medication. If necessary, the doctor prescribes suitable medications for blood pressure, calcium channel blockers in vascular cells, or drugs to lower blood sugar levels.
Motor recovery
It is necessary to restore lost movement already at the stage of inpatient treatment after primary care has been provided. It is imperative to provide physical activity to the limbs to improve blood circulation, which helps in reducing tone and prevents the appearance of congestion in the blood vessels, and also protects the patient from the occurrence of pneumonia due to a recumbent lifestyle.
The position of the limbs in a supine state, if necessary, is corrected using a splint or special weights. Such patients must turn over every 2 hours to prevent the appearance of bedsores on the skin; in addition, this is recommended to stabilize blood pressure.
A few days after the attack, passive gymnastics begins, during which the person is assisted in smooth movement of various parts of the body. Procedures are carried out only if the person does not experience pain. If the condition improves, you should help the patient learn to take a sitting position, and then help him restore an upright position. Before walking, leg training is performed in order to regain the lost sense of position in space. Then the patient needs to begin to move around using supports, walkers and canes.
Movement restoration techniques
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the rehabilitation of lost motor ability. In this case, suitable exercises are developed for different muscle groups, classes are conducted using special simulators, and a device is used to reduce high muscle tone.
Prescribing a special massage is very useful. First, the limbs are stroked with a sufficiently high muscle tone, and then other muscle groups are rubbed. The use of a warm heating pad before the session significantly improves the effect. The massage procedure can take 20 minutes and mainly depends on the current condition of the patient.
Effective methods of physiotherapy include oxygen baths, electrophoresis of blood vessels in the neck, and electrical stimulation of muscles that have lost their functions as a result of a stroke.
Speech restoration
The return of speech is possible even after an attack that occurred more than a year ago. Conversation after a stroke should be slow and words pronounced clearly. At the same time, there is no need to rush to answer and ask difficult questions.
Working with a speech therapist helps a lot in restoring muscle functionality. Practicing in front of a mirror can also be very useful. In the process of noticeable improvements, it is possible to complicate tasks and stimulate a person to pronounce more complex spoken phrases.
Restoring breathing and swallowing
Nutrition of patients in a hospital is most often performed using a special feeding tube. Then comes the time to independently master the skill of eating food. Proper preparation of foods greatly simplifies the rehabilitation of a patient seriously affected by a stroke. Cooked food should be warm, not hard and have a soft texture. Flavorful foods trigger saliva production.
Patients should absolutely not be rushed during the process of eating; this process can take half an hour or more. You may need help holding a utensil or spoon. Restoration of the functions of the swallowing muscles occurs with regular repetition of the nutritional process.
Psychological recovery
Many patients develop depression and serious behavioral problems after a severe hemorrhagic stroke. Properly selected drug therapy helps in restoring thinking: courses of nootropic drugs that stimulate neurometabolic functions
Correcting the current state of the psyche is possible with regular work with a psychologist and psychotherapist. A good effect is achieved in group and individual psychotherapy sessions with an appropriate specialist. In this case, support from relatives and friends is of great importance, restoring a person’s joy of life and self-confidence.
Typically, the prognosis after this disease is unfavorable due to severe damage to brain function and its gradual progressive swelling, often leading to death. In some cases, death may occur due to another hemorrhage that occurs in another part of the brain. Even if the patient survives, the consequences often lead to disability, and recovery from a hemorrhagic stroke becomes an extremely difficult and lengthy process.
Full recovery after a stroke is almost impossible, but still, partial return of lost functions with due persistence, good care and the necessary care becomes possible.
For this purpose, doctors, nurses, physical therapy instructors, caregivers and nannies take part in the rehabilitation process. This often takes months and years. Rehabilitation procedures are carried out in special departments of hospitals and sanatoriums, where highly qualified specialists closely monitor the patient’s recovery.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
What is subarachnoid hemorrhage
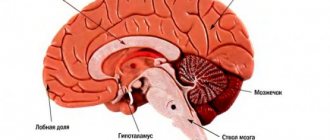
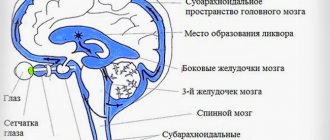
The brain is protected by the pia mater, dura mater and arachnoid membrane.
In direct contact with the convolutions is the arachnoid membrane, followed by the pia mater. The dura mater is located between the brain and the bones of the skull. Normally, the space between these structures is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the space of the brain between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. In simple words, blood accumulates in the subarachnoid space of the brain and compresses the surrounding structures.
The pathology is considered one of the types of hemorrhagic stroke and threatens with serious consequences for a person - a sharp increase in intracranial pressure, cerebral edema, so urgent medical attention is needed. Brain bleeding develops as a result of impaired cerebral circulation.
Kinds
Experts classify subarachnoid hemorrhage depending on the cause of SAH:
- spontaneous hemorrhage. Occurs as a result of a sudden increase in intra-arterial pressure during nervous tension, severe coughing, at the time of childbirth, when lifting heavy objects and straining during defecation. But pathology does not develop out of the blue. It is preceded by existing diseases, for example, vasculitis, aneurysm, thrombosis of cerebral veins, impaired circulation, hypertension, etc.,
- traumatic hemorrhage. Diagnosed less frequently. The disease develops as a result of mechanical impact on the head - severe bruise, fracture of the skull bones, rupture of internal tissues, concussion, traumatic brain injury, when vessels in the subarachnoid space rupture due to injury.
In addition, SAH is divided into several forms depending on where the blood has accumulated:
- isolated. The blood flows under the arachnoid membrane, therefore it does not compress the intracerebral structures and brain substance,
- subarachnoid-parenchymal. After getting under the arachnoid membrane, the blood is cut into the substance of the brain,
- subarachnoid-ventricular. After entering the arachnoid membrane, the blood enters the ventricles of the brain,
- subarachnoid-parenchymal-ventricular. Blood spreads throughout all structures of the brain. Unfortunately, this form has an increased risk of death.
Causes
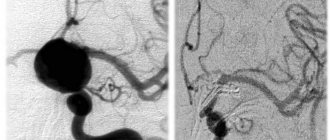
Based on practice, bleeding occurs due to a rupture of an aneurysm, less often the cause of pathology is an atherosclerotic or mycotic aneurysm. Typically, an aneurysm of the middle, anterior cerebral, communicating or carotid artery ruptures. SAH usually occurs after age 50, when a congenital or acquired aneurysm thins and ruptures. The walls of the brain artery protrude, the lumen gradually increases, and the artery bursts. Blood from the damaged artery flows into the subarachnoid space and increases intracranial pressure.
In addition to an aneurysm, the triggering mechanism for subarachnoid bleeding can be:
- abnormal connection of veins and arteries into a common structure without connecting capillaries,
- malignant brain tumors,
- congenital diseases of the connective tissues of the brain,
- degeneration of vascular walls as a result of inflammation,
- complications of brain and spinal cord infections,
- blood flow diseases, for example, impaired blood clotting or increased fragility of blood vessels,
- acute head injuries, traumatic brain injury,
- uncontrolled surges in blood pressure (hypertension, eclampsia),
- exceeding the norm of injections of osmotic diuretics, due to which the amount of circulating blood increases and the walls of blood vessels rupture under pressure.
A very rare but possible cause of SAH may be a complication of acute pancreatitis, in which pancreatic enzymes enter the blood and fill the subarachnoid space of the brain.
The risk group includes patients with hypertension, cocaine addicts, people with autoimmune and degenerative lesions of the cerebral vessels, as well as people who uncontrollably take anticoagulants.
Symptoms and signs
The pathology develops suddenly and rapidly, before which the clinical picture of the disease is invisible.
Symptoms of subarachnoid bleeding appear progressively and the patient’s well-being worsens literally every minute. At the moment of rupture of the vessel and the release of blood, the clinical picture is as follows:
- a headache appears immediately. It is so acute that a person cannot be distracted by other activities. The pain becomes maximum after two hours,
- fainting occurs at any moment, and at the moment of rupture of the vessel the patient loses consciousness,
- seizures and convulsions of the limbs occur,
- it feels like someone is hitting the head with a heavy object,
- floaters and dark circles flash before the eyes,
- within two hours the patient becomes concerned about his condition, and neurological symptoms intensify. The patient becomes emotional - shows fear, panic, aggression.
If first aid is not provided within the first hours, the patient's condition will worsen. At the moment of blood flow from the vessels and mixing of blood with brain matter, neurological signs intensify:
- severe nausea with urge to vomit,
- breathing and heart rate increase,
- the pupil dilates on the side of the hemorrhage,
- facial features lose symmetry,
- urination is impaired, the patient does not control the urge,
- visual acuity decreases, the picture before the eyes blurs, the patient cannot look at bright light, the eyes hurt,
- a jump in temperature with further fever indicates brain damage,
If the patient faints for more than 10 minutes and the frequency of loss of consciousness increases, this means that the ventricles of the brain are filling with blood. During the hemorrhagic stage, the patient is inhibited, does not speak or answer questions, and does not respond to touch.
The very next day, subarachnoid hemorrhage causes meningitis syndrome - the muscles of the back of the head and neck become harder, the muscles of the front surface of the lower leg become tense, the patient draws his legs under him and throws his head back.
In the post-hemorrhagic period, nervous functions are restored, but partial paralysis occurs, coupled with speech and swallowing disorders. The patient falls into a coma and his neurological functions are again depressed.
Which doctor treats subarachnoid hemorrhage?
First of all, if symptoms develop, you need to call an ambulance. Subsequently, after hospitalization, a neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Diagnostics
After admission to the hospital, a comprehensive examination is carried out. The first signs of subarachnoid hemorrhage are similar to complications of meningitis, influenza, epilepsy, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, therefore, to confirm the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
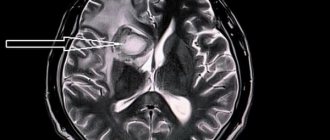
- Brain MRI. Visualizes the location and size of the hemorrhage focus. In real time, areas of blood loss and parenchymal compaction are shown on the computer monitor. The images show which parts of the brain are affected, which vessel burst, whether the brain stem is affected,
- CT scan of the brain. Based on the results, the stage of hemorrhage is diagnosed. The first stage - there is no blood, the second stage - blood clots less than one millimeter, the third stage - blood clots more than one millimeter, the fourth stage - blood has entered the ventricles,
- cerebrospinal fluid puncture. Through a puncture in the lower back, cerebrospinal fluid is taken from the spinal canal to assess its composition. If blood is detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, then subarachnoid-ventricular or isolated hemorrhage is diagnosed. A study of the cerebrospinal fluid is carried out 12 hours after the development of the first symptoms, since only during this time will blood penetrate from the ventricles of the brain into the spinal space,
- Vascular ultrasound or cerebral angiography. It is carried out before surgery to clarify the etiology of parenchymal hemorrhage.
The neurologist checks reflexes, measures blood pressure and temperature. It is worth noting that diagnosing SAH is often difficult, because the patient is admitted to the hospital in an unconscious or coma state.
In some cases, the diagnosis is supplemented by an examination of the fundus to determine swelling of the optic nerve, an EEG to detect epileptic exacerbations, and an X-ray of the skull in case of the traumatic nature of the development of the disease.
Treatment methods
During the first minutes of an attack, you need to lay the person on a flat surface, place a pillow under the head and turn the head to the side. You should unbutton the buttons on your shirt and open the window for fresh air. Call an ambulance immediately. The patient should not be given any medications. Due to the risk of complications and death, subarachnoid hemorrhage is treated as an inpatient in the intensive care unit.
Complex therapy includes:
- actions on cardiovascular and respiratory stimulation. Often the patient is connected to a ventilator,
- intravenous injections of diuretics to reduce fluid and prevent brain swelling,
- intravenous injections of insulin or glucose if hypo- or hyperglycemia is detected,
- magnesium injections for fever,
- taking painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve neurological symptoms,
- taking sedatives with severe psychomotor agitation,
- taking antihypertensive drugs to normalize blood pressure,
- taking anticonvulsants to relieve seizures,
- taking vitamin K to stop bleeding,
- taking calcium antagonists to prevent vasospasm,
- taking antioxidants to improve brain nutrition.
Medicines stabilize respiratory function, the function of the cardiovascular system, prevent cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure, prevent vascular spasm and relieve pronounced neurological symptoms.
Surgical intervention
The operation is performed urgently if, according to MRI results, there is more than 60 ml of blood in the brain structures. The maximum result is achieved when the accumulated blood is removed within 72 hours after the onset of SAH. To eliminate compression of the meninges and saturate the brain matter, drainage is performed.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia through burr holes. The pooled blood is removed and a drain is placed to suck out the new blood. To eliminate the consequences of subarachnoid hemorrhage, different surgical techniques are used:
- if MRI images reveal a ruptured aneurysm, then a clip is applied to the damaged vessel and it is turned off from the blood supply,
- when the lumen of the vessels narrows by more than a third, a stent is installed,
- no later than 6 hours after hemorrhage, endovascular intervention is performed. Through percutaneous puncture, the aneurysm is embolized with thin coils. The coils “lock” the damaged vessel and blood stops flowing to the brain.
It is worth noting that surgical intervention is prohibited if the patient is in a coma and his consciousness is depressed, he has no reaction to neurological stimuli, and cerebral ischemia is recorded. If this clinic is present, the operation is postponed until the patient’s condition has stabilized and the activity of the central nervous system has normalized.
results
Further recovery depends on the degree of hemorrhage. The more brain structures are filled with blood, the longer and more difficult the rehabilitation. The first rehabilitation period, during which basic skills are restored, lasts six months. The second rehabilitation period lasts for a year. During this period, the consequences of neurological disorders are eliminated, and the patient restores the possibilities of household services and social activity. In many cases, residual effects of SAH remain.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
To restore body functions, begin physiotherapeutic treatment. The neurologist prescribes a course of electrophoresis of the cervical-collar area, magnetic therapy, or electrical myostimulation of your choice to restore sensitivity and normalize motor activity. Areas subject to muscle spasms are treated with acupuncture, due to which sensitivity in the arms and legs returns. In the late rehabilitation period, ozokerite applications, oxygen and pine baths are useful.
A little later, the therapy is supplemented with physical therapy and massage. The doctor individually selects a set of exercises for each patient. Exercise therapy restores muscle tone, helps restore walking skills, improves coordination and balance, and prevents the development of contractures during prolonged immobility. Exercises should be performed slowly and smoothly, under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor.
Massage of the affected limbs is done from the first days of rehabilitation. To eliminate increased muscle contraction, stroking techniques are used; to increase muscle tone, rubbing and stroking techniques are used. The intensity increases gradually and after a few months intensive massaging begins. Typically, massage is done in a course of 10-15 sessions with breaks of several months.
If SAH has resulted in speech disorders, classes are held with a speech therapist. The doctor strengthens the muscles of the tongue, teaches you to pronounce syllables and words again.
Lifestyle with subarachnoid hemorrhage
Unfortunately, in most cases, SAH leads to disability. Patients need to monitor blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and carbohydrate metabolism. You cannot smoke or drink alcohol - restoring neural connections is incompatible with bad habits. Also engage in strenuous and active sports, so as not to lead to repeated hemorrhage when exposed to physical activity.
It is important to stabilize your diet, eat more vegetables and fruits to provide the body with nutrients. Experts recommend reducing the consumption of salt and spices. To make swallowing easier, food should be liquid, ground, and soft.