Ethanol is a poison that affects almost all organs of the drinker. Nerve tissue is most susceptible to damage. The second target is the heart. Long-term alcohol abuse leads to the formation of specific changes in the heart muscle - alcoholic cardiomyopathy (AC).
Alcohol and the heart - these two concepts are incompatible. Damages to blood vessels and muscle tissue carry serious complications, which without treatment can cause death. One of the tasks facing doctors at the Verimed clinic is the timely detection and treatment of cardiac pathologies.
How alcohol affects the heart:
A more accurate and complete medical name for cardiopathic ethanol damage is myocardial dystrophy. That is, with alcoholic lesions we are not talking about inflammatory processes in the myocardium, but about pathologies of cellular metabolism. Metabolic disorders lead to deterioration in nutrition of the cardiac muscular system and coronary vessels that supply blood to the entire organ. Increasing metabolic abnormalities form serious enzymatic failures.
The cause of these pathological disorders is:
- A sharp decrease in the production of substances - energy sources for the work of heart cells (cardiocytes). The most significant in this process is adenosine triphosphoric acid - ATP. A decrease in its quantity leads to dystrophic changes in muscle fibers.
- Destruction of vitamin complexes, in particular thiamine. As a result of hypovitaminosis, energy problems develop.
Obvious clinical manifestations of the disease are preceded by a latent period. It is possible to recognize upcoming changes at an early stage of AK only with the help of laboratory diagnostics. Latent heart failure is aggravated by additional nicotine intoxication, because most people suffering from alcoholism also smoke. Under the influence of toxins, a deficiency of proteins and vital vitamins gradually develops.
Over time, the clinical picture of alcoholic cardiomyopathy develops. It manifests itself:
The development of hypertension with periodic crises and constant increases in blood pressure.- Transient circulatory disorders causing angina pain.
- Deterioration of myocardial nutrition, causing manifestations of coronary heart disease (CHD). In this case, we are talking about a constant, chronic deficiency of substances necessary for normal cardiac activity. The main complication of this pathology can be myocardial infarction.
Content:
- How alcohol affects the heart
- What happens to the heart when taking high doses of alcohol?
- Screening for people with heart problems caused by alcohol
- Heart treatment for alcoholism
There is no need to believe that alcohol has a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Talk about the need to drink a certain amount of vodka or good red wine every day is a banal myth. Most often they are invented by people who want to drink but have serious illnesses. Alcohol and the heart are incompatible concepts. As a result of drinking, nervous tissue is invariably damaged. Following this, ethanol attacks the heart muscle. Then the addict develops alcoholic cardiomyopathy. If left untreated, it can be fatal. Is it possible, knowing about such consequences, to talk about benefits?
Consequences of ignoring the problem
Hangover syndrome does not tolerate neglect. As soon as alcohol enters the body, the heart increases in size, and as a result, the person’s weight increases. Heart pain may increase each time you drink alcohol. In a normal state, a person will not feel discomfort, but as soon as he drinks alcohol, the pain in the heart intensifies.
A hangover is the first call to quit drinking. Otherwise, the patient experiences deformation , various disorders arise, irritability prone to aggression, paranoia, epilepsy, volitional character traits are deformed, and much more.
An hour-long feast with drinking alcoholic beverages is not worth ruining human life. Think about it!
If you cannot cope with a hangover, then call a narcologist to your home! An experienced doctor will quickly help you get rid of all symptoms.
How alcohol affects the heart
Drinking alcohol in high doses causes the development of myocardial dystrophy. This is a pathology in which metabolic processes in the heart muscle are disrupted. As a result of the disease, the load on the organ increases significantly, and it ceases to cope with it.
There are two main causes of myocardial dystrophy. This:
- a rapid decrease in the production of cardiocytes - substances that provide heart cells with energy;
- decrease in thiamine levels.
Both factors are associated with drinking. The difficulty is that it is almost impossible to recognize the development of disorders in the early stages, when life-threatening complications can still be avoided. The alcoholic feels good for a long time. When he gets to a specialized clinic, it turns out that his heart is working at the limit of its capabilities.
Progressive myocardial dystrophy leads to:
- hypertension, hypertensive crisis;
- angina pectoris;
- pain in the chest area;
- poor quality myocardial nutrition;
- ischemic disease.
The effect of alcohol on the heart is so harmful that the organ cannot function fully. This is why alcoholics often die due to stroke, hypertensive crisis, or heart attack.
Cardiovascular health: how to take care of it
The heart has no days off or holidays. The organ works smoothly in any circumstances, and always needs all possible support. Regardless of whether there are obvious heart problems or they are not yet felt, you need to take care of the main engine constantly.
Give up alcohol and cigarettes forever. The most destructive effect of alcohol on the heart and blood vessels occurs as a result of a combination of these two bad habits. Nicotine excessively constricts blood vessels, creating oxygen starvation; alcohol, on the contrary, dilates blood arteries, making them fragile. If an alcoholic smokes more than 3 cigarettes a day, the likelihood of a stroke or heart attack increases 3 times than if he simply abused alcohol. But both habits are deadly separately.
Watch your weight. Overweight people are always at risk. Fat that envelops internal organs is the most dangerous: unlike subcutaneous fat, it is almost impossible to eliminate. In such cases, myocardial dysfunction occurs much more often. Running, walking, swimming and cycling can help you lose weight, but the permissible load should only be determined by a specialist.
Review your diet:
- Replace pork and lard with beef and poultry.
- Drink no more than 1.5 liters of clean water per day so as not to cause swelling.
- Remove canned food from your diet and do not exceed the daily salt intake - 5 grams.
- Limit your coffee intake or eliminate it completely.
- Apples, dark grapes, plums, strawberries, garlic, flax seeds, grape seeds, arugula, onions, asparagus, nuts, honey and fatty fish are those foods that are good for blood vessels and the heart, which should be included in the diet regularly or as often as possible .
The harm of alcohol and its harmful effects on the heart and blood vessels is difficult to exaggerate. But there is no benefit, even conditional, from alcoholic drinks. And if a young body can somehow resist the threat, then after 40 years the consequences of drinking alcohol can cost one’s life.
What happens to the heart when taking high doses of alcohol?
As soon as the heart muscle is exposed to the negative influence of large amounts of alcohol, the following pathological changes are observed:
- the myocardium begins to contract poorly;
- heart rhythm is disturbed (usually towards tachycardia);
- blood oxygen saturation decreases (hence severe shortness of breath);
- The minute volume of blood decreases, due to which the atria and ventricles do not receive important nutrients and oxygen.
Drinking heart patients often develop edema. They suffer from an unpleasant feeling of lack of air. If you ignore all these symptoms, dangerous complications cannot be avoided in the near future.
Diagnostics and additional research methods
The diagnosis of alcoholic cardiomyopathy is based on:
- inspection data;
- survey;
- listening to the heart.
A patient with suspected AK should definitely undergo electrocardiography. Characteristic changes clearly appear in the recording. Heart ultrasound provides a large amount of information.
The necessary examination is radiography (or Rg-scopy). The radiologist notes a specific syndrome - myopathic configuration. A characteristic feature of this syndrome is an increase in cardiac dimensions during the period of binge drinking and a decrease during the period of calm (remission). In the “language” of radiologists, this feature received the figurative name of the “sliding harmonic” symptom.
Histological analysis of the myocardium determines the presence of fatty impregnation of muscle tissue, accumulation of glycogen and swelling of cardiocyte elements. From a prognostic point of view, alcoholic cardiomyopathy can undergo reverse development if the patient maintains a sober lifestyle.
Screening for people with heart problems caused by alcohol
Patients who have cardiovascular diseases or are prone to developing them and who drink alcohol frequently and in large quantities should definitely be examined.
It is good if diagnostic procedures are suitable at the stage of preparation for coding in a narcology clinic. Then the doctor will be able to tell which option of anti-alcohol therapy is most appropriate, and the cardiologist will prescribe an effective treatment program for the identified cardiac disorders. When identifying alcoholic cardiomyopathy, the following diagnostic measures are used:
- Examination and interview of the addict. The doctor finds out how long ago and what kind of alcoholic compounds the patient has been taking, whether he was previously coded, and whether he underwent therapy for cardiac pathology.
- Study of percussion and auscultation patterns. The specialist listens to heart sounds and taps the chest area. Particular attention is paid to noise and rhythm.
- Carrying out ECG and ultrasound. These diagnostic methods are highly accurate, safe and effective. Based on their results, the cardiologist can easily make the correct diagnosis.
It is very important that a person undergoing diagnosis and planning treatment for heart disease observe the law of sobriety. It is unacceptable to go to doctors during the day and get drunk in the evening.
How to avoid becoming an alcoholic?
If you do not have signs of alcoholism, but you drink alcohol often and in large quantities, decide to reduce the amount of alcohol and reasons for drinking. Do not let the situation get out of control if you value your family, work, and your health.
- Avoid companies where large amounts of alcohol are consumed.
- Control the amount of alcohol you drink.
- Do not hesitate to refuse if you are offered a drink.
- Learn to relax in other (non-alcoholic) ways: engage in sports, creativity, tourism or other enjoyable activities.
If you or someone close to you has signs of alcoholism, consult a doctor immediately!
It is very difficult to cope with the disease without the help of a doctor. Remember: to cope with this serious illness, modern treatment methods and the active desire of the patient himself to get rid of the disease are necessary!
Heart treatment for alcoholism
To support the functioning of the main organ, alcoholic patients with heart disease are prescribed medications for:
- pain relief;
- reducing the voltage level;
- elimination of degenerative and dystrophic processes in the myocardium;
- normalization of heart rate;
- strengthening the whole body, stimulating the immune system.
It is very important to improve your heart function during the pre-coding phase. But even after coding, cardiotherapy does not stop. The patient consults a cardiologist for as long as necessary.
Take care of your heart - don't drink alcohol. On holidays, if necessary, use only high-quality alcohol and in small quantities. Any drinking is a blow to your heart. It is impossible to predict in advance how strong it will be. It's important to remember this.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
How does alcoholism develop?
There are three stages of alcoholism.
The first is the stage of mental dependence.
At this stage, it becomes habitual for a person to drink alcohol in order to forget about troubles and adversities, facilitate contact with others, and relax. A person is constantly looking for a reason, appropriate company, to drink. Control over the amount of alcohol consumed is lost: once a person starts drinking, he cannot stop and reaches a state of severe intoxication. In addition, at this stage, a person’s threshold of sensitivity to alcohol decreases, that is, in order to achieve the desired level of intoxication, he needs a dose 2-3 times larger than before. The gag reflex, which is the body’s defense mechanism during alcohol poisoning, disappears. When a person gets drunk, he loses control of himself, often commits reckless acts, and later cannot remember what happened to him the day before. After alcohol abuse, sleep deteriorates, after drinking, the mood deteriorates, sweating, palpitations, and sometimes hand trembling are noted.
The second is the stage of physical dependence.
Regular alcohol abuse leads to changes in the biochemical processes of the body, as a result of which the regular intake of alcohol into the body becomes necessary for its normal functioning. At this stage, signs of an alcoholic hangover appear and become established. A person, being in a state of hangover, experiences many unpleasant sensations - headache, nausea, sweating, palpitations, anxiety, trembling fingers. In order to alleviate the condition, a person drinks alcohol again - gets a hangover.
From the moment a hangover appears, a person is terminally ill. The only measure that can help stop the disease is a complete abstinence from drinking alcohol in any form.
This can be repeated for several days - 3 days or more. Binges occur. In the absence of alcohol entering the body, a person experiences mental disorders, headache, thirst, loss of appetite, muscle tremors, irritability, and aggression.
The third is the stage of personality degradation.
A person becomes indifferent to family and friends, neglects the most basic rules of morality and ethics, and is indifferent to his behavior. His memory is deteriorating and his intelligence is decreasing. At this stage, people begin to drink “whatever”, as long as the liquid contains alcohol. Drunkenness is constant (daily) in nature or is expressed in binges that stop due to a sharp deterioration in physical condition and often require medical care, without which a person can die. At this stage, the changes that have occurred in the internal organs are irreversible. Alcohol completely destroyed their normal functions.
What explains the special sensitivity of the liver to alcohol?
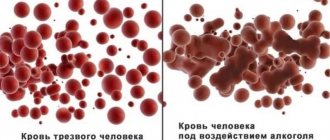
Approximately 10% of ethanol entering the body is excreted unchanged in biological fluids (urine and sweat). The remaining 90%, after absorption in the stomach and intestines, is neutralized by liver cells (hepatocytes) to CO2 and H2O. As a result, the metabolic load on the liver and its enzyme systems increases. The stages of ethanol conversion can be represented as a diagram: ethanol – acetaldehyde – acetic acid – acetyl coenzyme A – CO2 and H2O. The metabolism of alcohol involves cytoplasmic dehydrogenases, as well as catalase, thiokinase and ribosomal alcohol oxidase. The rate of metabolic decomposition of ethanol is determined mainly by the activity of dehydrogenases and remains at a constant level all the time, regardless of the concentration of incoming alcohol.
Liver damage occurs after a year of systematic alcohol abuse. Due to the constant activation of enzymes involved in the processing of ethyl alcohol in hepatocytes, the synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol is disrupted, the amount of intracellular fat increases, and membrane structures are damaged. All this leads to fatty degeneration of the liver, the so-called fatty degeneration. Deposits of 5-50% fat on a dry basis are reversible and do not lead to the death of hepatocytes. The stage of reversible changes lasts 3-5 years.
Without proper treatment for alcoholism, liver cell death occurs as a result of prolonged alcohol intoxication and inflammation and leads to fibrosis (overgrowth of connective tissue), which turns into cirrhosis. At the stage of cirrhosis, changes in the liver become irreversibly progressive and end with the shutdown of its basic vital functions.
By the way, the total number of functional “responsibilities” of the liver is quite impressive - about 500. The liver synthesizes and secretes bile into the intestine to emulsify fats, neutralizes a lot of endo- and exotoxins, and participates in the biosynthesis of many essential compounds.
The clinical picture also changes as alcoholic liver damage progresses. At the initial stage, asthenic syndrome predominates - increased fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness, general weakness. At the stage of cirrhosis, the following symptoms join them:
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Weight loss.
- Dry skin, the appearance of cirrhotic blood networks in the form of spiders on the abdomen.
- The appearance of hematomas on the body even with minimal physical impact.
- Poor wound healing.
- Brittle bones and frequent fractures.
- Muscle pain.
- Almost constant bitterness in the mouth.
With further progression of cirrhosis, yellowness of the skin, sclera, and dark urine color occurs due to impaired bilirubin metabolism.
If you want to avoid such detrimental consequences for your health and life, it is best to completely abstain from drinking alcohol, and especially from drinking it on a regular basis. Timely and well-organized treatment of alcoholism will help the liver recover within a few weeks, since its regenerative potential is truly enormous. There is also compulsory treatment for alcoholism.
What are the features of the effect of ethanol on the nervous system?
Alcohol (translated from Arabic as “soul of wine”) has a specific effect on nerve cells called neurons. Each neuron has two types of processes:
- Dendrites are short and numerous processes that perceive irritation from receptors and transmit them to the nerve cell.
- An axon is one longer process, up to 1 meter long, that transmits an already analyzed and transformed signal to other neurons or cells of the “supervised” organ.
Due to its ability to dissolve in water and fat, alcohol not only easily penetrates neurons, but is also integrated into their phospholipid membranes, changing the functioning of receptors and ion channels. It is thanks to this property that alcohol is a mentally active substance that affects the formation and transmission of nerve impulses.
Signal transmission is realized with the help of biologically active substances called neurotransmitters and released into the synaptic cleft between the membranes of the processes. Each mediator has its own sphere of action, providing processes of excitation or inhibition, the formation of dependence, and the characteristics of mental and autonomic responses. Neurotransmitters include substances such as dopamine, adrenaline, norepinephrine, serotonin, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, etc.
The release of neurotransmitters upon intake of ethanol occurs in stages:
- First, dopamine receptors are turned on, which are the most sensitive to the effects of alcohol and activate the process of producing the neurotransmitter dopamine, the so-called “hormone of joy.” It is responsible for positive emotions of pleasure, euphoria, as well as motor activity and improved mood. This effect is observed when consuming safe doses of ethyl alcohol - 20-40 g in its pure form. Unfortunately, they often don’t stop there and continue with further libations.
- At a dose of 40-80 g of pure ethanol, the main inhibitory system of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is included in the process. This manifests itself in a relaxing, anti-stress and calming effect, which subsequently turns into a depressive state.
- With a dose of 80-100 g of alcohol, which is contained in the previously popular folk “chekushka” (250 ml of 40% vodka or half a 0.5 liter bottle), a cascade of all mediators is launched, which, depending on the individual characteristics of the psyche, can have a different character. Some begin to show aggression, others - tearfulness and depression, others - causticism, others - sexual aspirations, others begin to cut the truth, etc. It is often said that what is on the tongue of a drunk is what is on the mind of a sober person. It is believed that in this state the hypertrophied essence of the individual is revealed. In fact, this is the perverted functioning of the mediator systems under the influence of a powerful psychoactive substance, which is alcohol.
- The entire process of alcohol intoxication ends with rapidly developing depression of the central nervous system and deep sleep, which can dump a heavily drunk person in any place, often not suitable for this.
If alcohol consumption is regular, especially in medium and large doses, then the constant activation of the dopamine and GABA neurotransmitter systems leads to the development of two types of addiction:
- Dopamine-like, similar to amphetamine addiction. With this type of addiction, without the usual morning dose of alcohol, dopamine receptors are not activated, you cannot cheer yourself up, your mood does not improve, things don’t go well and everything falls out of hand. In general, without alcohol, it is impossible to return positive emotions and perceive the surrounding reality without depression, and this is already alcohol addiction. Withdrawal syndrome in this type of addiction is manifested by weakness, lethargy and depression.
- GABA type. When this inhibitory system fails, the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate is activated. This leads to excessive motor activity, imprecision of movements, inadequate emotions and inability to concentrate - thoughts literally scatter in different directions, and it is impossible to stop at any one. The hangover syndrome in this case, after giving up alcohol, manifests itself as a sharply increased activity of all nervous processes, up to the development of various types of alcoholic psychoses, 80% of which are due to delirium tremens, otherwise alcoholic delirium.
It is very difficult to get rid of alcohol addiction, because... The brain of an alcoholic is severely damaged by intermediate products of ethanol oxidation, in particular acetate aldehyde. Alcohol metabolism is regulated by dehydrogenase enzymes:
- Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes ethanol to particularly toxic acetaldehyde (acetic aldehyde).
- Acetaldehyde is converted to acetic acid by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase.
The body’s individual response to ethanol depends on the balance of these enzymes:
- If both enzymes work actively and in a balanced manner, then the effect of intoxication, even with large doses, is mild, and hangover syndrome is rarely observed. A person can drink a lot and be “like a cucumber.” But this is for the time being, sooner or later the enzyme systems will begin to function inadequately, and the reaction to ethyl alcohol will change.
- If the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is high, and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (AADH) is low. This is the most typical situation. Manifested by the accumulation of acetaldehyde, severe intoxication and severe hangover syndrome. With severe AADH deficiency, a hangover appears almost immediately even after a small dose of alcohol. This dehydrogenase phenotype creates convinced abstainers, because For them, drinking even minimal amounts of alcohol causes severe headaches.
- If the ADH does not work well. This is the case when a person “joyfully” gets drunk even from a small portion of alcohol with rapid addiction and the formation of dopamine-type alcohol dependence. This option is the most dangerous in terms of the development of alcoholism. Instantly intoxicated people are at increased risk of quickly becoming a heavy alcoholic.
One of the clinical signs of the development of alcoholic illness is sleep disturbances and memory loss after alcohol. Moreover, memory lapses first concern individual episodes (palimpsests). They are characteristic of the first stage of alcoholism and can occur even in healthy people after heavy drinking. Longer memory loss during alcohol intoxication, affecting a many-hour period of time when a person remembers practically nothing about his actions, develops at stages 2-3 of alcoholism.
Another feature of neuropsychic disorders characteristic of alcoholism is alcoholic insomnia, especially after binge drinking. An alcoholic's sleep is short and disturbing, accompanied by nightmarish and rather realistic dreams. Without qualified help, insomnia after binge drinking turns into delirium tremens, when visions begin to haunt the patient in reality, increasing fear and anxiety, causing panic and aggression. The consequences of delirium tremens can end very sadly - in his desire to protect himself from illusory enemies, a person can attack others and even attempt suicide in horror. All this is accompanied by autonomic disorders - tremors of the limbs, tachycardia, pressure surges, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that alcohol is a psychotropic substance that is easily integrated into the metabolism; when used systematically, it has a destructive effect on nerve cells, distorts neurotransmitter systems, leads to inadequate mental reactions, the formation of addiction and personality degradation.
Heart failure from alcohol
Heart failure is a widespread disease. Heart failure is a condition where, as a result of damage to the heart, the heart muscle weakens and cannot satisfactorily perform its pumping function. As a result, the body's supply of oxygen and nutrients is disrupted.
Causes of heart failure
Heart failure most often develops as a result of coronary heart disease (myocardial infarction, angina pectoris). Arterial hypertension, valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathies also lead to heart failure.
How does chronic heart failure manifest?
The most common symptoms are shortness of breath and weakness. Initially, everyday physical activity is not accompanied by weakness, shortness of breath or palpitations. Then it is somewhat limited, but at rest there are no complaints. Everyday stress may cause weakness, shortness of breath, or palpitations. Over time, as the disease progresses, complaints appear with little physical activity and at rest.
In heart failure, edema develops in the body due to water and sodium retention. They appear first in the ankle area and disappear after rest or towards the end of the day, and then may spread and do not disappear after a night's rest.
Drug therapy for heart failure
Only a doctor after examination can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Different groups of drugs are used to treat heart failure. Regular and correct use of medications will help improve the health of patients. You need to know the names and dosages of the medications you are taking and strictly follow your doctor's instructions. Non-drug treatment methods are of particular importance in improving the health of patients.
Weight monitoring
Patients are advised to weigh themselves regularly (it is better to weigh themselves during some daily activities, for example, after the morning toilet), and in the event of a sudden unexplained weight gain of more than 2 kg in three days, inform the doctor or increase the dose of the diuretic.
Diet
Salt restriction (2-5 g/day) is more important in severe heart failure. Salt substitutes should be used with caution, as they may contain potassium and in large quantities, especially when taking ACE inhibitors simultaneously, cause hyperkalemia.
Liquid
In patients with severe heart failure, regardless of the presence of hyponatremia, free fluid restriction to 0.6 l/day is indicated. Vitamins A1, B1, B2, C, PP are added. Meals are fractional (for the whole day, bread 150 g, sugar 40 g, butter 10 g).
It is acceptable to drink alcohol in moderate doses (a bottle of beer or 1-2 glasses of wine per day). If alcoholic cardiomyopathy is suspected, alcohol is excluded.
In obese patients, treatment of heart failure includes weight loss. We speak of being overweight if the body mass index (BMI) = weight (kg)/height (m2) is 25-30; if it exceeds 30, obesity is diagnosed.
Pathological weight loss
Pathological weight loss is observed in approximately 50% of patients with heart failure. The decrease in fat and lean body mass that accompanies such weight loss is called cardiac cachexia. This condition is an important predictor of reduced life expectancy. Pathological weight loss should be suspected if:
- body weight is less than 90% of ideal
and/or
- there is a documented unintentional weight loss of more than 5 kg, or 75% of baseline (measured in the absence of edema) over 6 months and/or
- BMI is less than 22 kg/m2.
The goal of treatment is to achieve weight gain not through edema, but preferably through muscle mass through adequate physical activity. If weight loss is caused by nausea, shortness of breath or a feeling of fullness in the stomach, frequent small meals are recommended.
Smoking
Quitting smoking is desirable in all cases. The use of auxiliary products, in particular nicotine patches, chewing gum, etc., should be strongly encouraged.
Staying in high mountains, places with a hot or humid climate is contraindicated. Short flights are preferable to long trips by other means of transport. In case of severe heart failure, long flights are fraught with complications (possible dehydration, sudden swelling of the legs, deep vein thrombosis), which patients should be warned about. Possible consequences of changes in diet during travel in the form of acute gastroenteritis. If water and salt are lost in hot and humid climates, the dose of diuretics and vasodilators must be adjusted accordingly.
Sex life
It is impossible to give unambiguous recommendations on sex life. If necessary, it is recommended to take nitrates under the tongue before sexual intercourse and abstain from particularly violent emotions. In functional class II, the risk of decompensation provoked by sexual activity is average, and in functional class III-IV it is high. Little is known about the effect of heart failure treatment on sexual function.
Immunization
There are no reliable data on the effects of immunization in heart failure. Immunization against pneumococcal disease and influenza reduces the risk of respiratory infections that can worsen heart failure. Immunization against influenza is widely used.
In case of acute heart failure or destabilization of chronic heart failure, rest is necessary, including bed rest. To prevent the undesirable consequences of bed rest, including venous thrombosis, passive exercises are performed. As the condition improves, they move on to breathing exercises and gradually increase activity.
Exercise stress
If the patient's condition is stable, then moderate physical activity, which prevents muscle detraining, should be encouraged. For patients with severe functional impairments, short training sessions (15-20 minutes) 3-5 times a week are recommended. The intensity of training is selected so that the heart rate reaches 60-80% of a predetermined maximum value. Preference is given to walking at an average pace (60-80 steps per minute).
The doctor must talk with the patient so that the patient can actively participate in treatment. The patient must know and understand:
- improvement may be slow and incomplete even after weeks, and with some drugs, months of treatment;
- doses of ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers and beta-blockers should be gradually increased to a certain level, although this will not bring direct improvement;
- in case of dehydration (at rest, with profuse sweating in hot climates), the dose of diuretics should be reduced;
- when blood pressure decreases, it is necessary to reduce the dose of diuretics, and, if necessary, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers and beta-blockers;
- ACE inhibitors may cause cough and taste disturbances;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should not be taken simultaneously with ACE inhibitors;
- if shortness of breath suddenly appears or as a preventive measure in certain situations, you can take nitrates - in the form of tablets under the tongue or an aerosol.
Treatment of heart failure has several goals. First, eliminating the symptoms characteristic of this disease. Secondly, and no less important, is to protect organs from damage: heart, kidneys, lungs, brain, liver, blood vessels. The third goal is to improve the patient's quality of life. This means that treatment for heart failure should provide the patient with the opportunity to live the same full life as his healthy peers.
What is the effect of alcohol on the pancreas?
A healthy pancreas and alcohol are incompatible concepts. The main complication of excessive consumption of alcohol-containing drinks on the pancreas (P) is alcoholic pancreatitis - an inflammatory disease. It develops against the background of toxic damage to the pancreas by alcohol breakdown products and has a complex pathogenesis. Under the influence of toxins, gland cells secrete a large number of enzymes, which begin to digest their own tissues with the formation of areas of necrosis and pseudocysts filled with liquid necrotic contents. Swelling and enlargement of the gland occurs, causing stretching of its shell and compression of neighboring organs. All this is accompanied by severe pain.
Further development of the inflammatory process is accompanied by fatty fibrosis (proliferation of connective and adipose tissue), deformation of the ducts and stagnation of secreted contents. Replacement of normal tissue leads to further disruption of the endocrine and exocrine functions of the pancreas up to the development of diabetes mellitus, and in some cases to a fulminant form of pancreatic necrosis with high mortality. A factor that sharply increases the harmful effects of alcohol in pancreatitis is smoking, which causes vasospasm and ischemia in the organ.
If there is already a history of diseases of the pancreas and alcohol is not excluded from consumption, then the symptoms only intensify, and the disease becomes irreversible, practically untreatable. The combination of pancreatitis and alcohol is not permissible, otherwise the risk of death increases sharply.
Symptoms of alcoholic pancreatitis:
- Intense pain in the epigastrium, often becoming girdling in nature and radiating to the right arm and back. They can be sharp or aching, worsening when lying on your back and after eating. Hence the fear of eating, which, together with poor absorption of nutrients, can lead to a sharp weight loss for the patient.
- Flatulence, belching.
- Nausea and vomiting.
How to treat alcoholic pancreatitis? This question can be answered specifically - treatment will be effective only if you completely abstain from alcohol. For acute pancreatitis, fasting for several days is recommended; for chronic pancreatitis, diet No. 5 is recommended; smoking is strictly prohibited. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. Conservative therapy uses enzyme replacement, painkillers and antiemetics, and fat-soluble vitamins. Surgical intervention is performed to excise cysts, necrotic areas, abscesses, and close fistulas. It is justified only for health reasons, as it sharply increases the likelihood of developing diabetes.