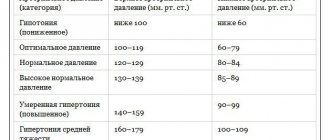
© Author: Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Often, it is possible to determine whether a patient has a particular pathology of the heart muscle based on the doctor’s ability to use his hands to pick up sound vibrations created by heart contractions and conducted to the anterior chest wall. This technique is called palpation, or palpation of the heart.
In order to determine the presence of a particular pathology in a patient, several aspects should be highlighted during palpation of the heart. These include the apical impulse, cardiac impulse, as well as the determination of pulsation and trembling of the heart.
Why is heart palpation needed?
There are no clear indications for this physical examination, because it is advisable for each patient to perform a chest examination and palpation of the heart, along with auscultation of the heart and lungs during the initial consultation with a therapist or cardiologist.
These methods suggest hypertrophy of the left or right ventricles, since an increase in the size of the heart chambers leads to expansion of the heart, as a result of which its projection onto the anterior surface of the chest, determined using the hands, also expands. In addition, it is possible to suspect pulmonary hypertension and an aneurysm of the ascending aorta.
After receiving data that differs from the norm, it is necessary to clarify the disease that caused hypertrophy or pulmonary hypertension using further instrumental methods - ECG, ultrasound of the heart, coronary angiography (CAG), etc.
What is a cardiac impulse?
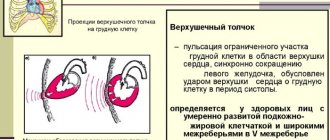
The shaking of the anterior chest wall caused by the contraction of the heart is called a cardiac impulse. It occurs synchronously with ventricular systole.
In the tension phase, the shape and size of the heart changes, which makes it possible for the surface of the ventricles to come into contact with the chest wall. The study of the cardiac impulse is carried out using inspection, palpation, and a sound signal.
The technique and characteristics of palpation of the heart are normal
Figure: sequence of heart palpation
Palpation of the apex beat is carried out as follows. The patient can stand, sit or lie, while the doctor, after a preliminary examination of the heart area (sternum, left half of the chest), places the hand of the working hand with the base of the palm perpendicular to the left edge of the sternum, and with the fingertips in the fifth intercostal space along the midclavicular line, approximately under the left nipple. At this moment, the woman should hold her left mammary gland with her hand.
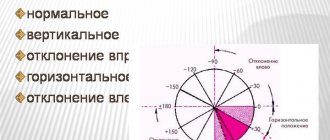
Next, the characteristics of the apical impulse are assessed - the strength, localization and area (width) of the apical impulse. Normally, the impulse is located in the fifth intercostal space medially from the left midclavicular line by 1-2 cm and is 1.5-2 cm wide. Under the fingers, the impulse is felt as rhythmic vibrations caused by impacts of the apex of the left ventricle against the chest wall.
The cardiac impulse is formed by the boundaries of absolute dullness of the heart. The latter concept, in turn, includes the area of the heart that is not covered by the lungs and is directly adjacent to the anterior chest wall. Due to the anatomical position of the cardiac axis in the thoracic cavity, this area is formed mainly by the right ventricle. Thus, the cardiac impulse gives an idea mainly about the presence or absence of right ventricular hypertrophy. The search for the cardiac impulse is carried out in the third, fourth and fifth intercostal spaces to the left of the sternum, but normally it should not be detected.
The pulsation of the heart, or rather, the large great vessels, is determined in the second intercostal space to the right and left of the sternum, as well as in the jugular notch above the sternum. Normally, pulsation can be detected in the jugular notch, and it is due to the blood supply to the aorta. Normally, heart pulsation on the right is not detected if there is no pathology of the thoracic aorta. On the left, pulsation is also not detected if there is no pathology of the pulmonary artery.
Heart tremors are not normally detected. With pathology of the heart valves, cardiac tremors are felt as vibrations of the anterior wall of the chest cavity in the projection of the heart and are caused by sound effects caused by significant obstacles to the flow of blood through the cardiac chambers.
Epigastric pulsation is determined by palpating the abdominal area between the ribs closer to the xiphoid process of the sternum with your fingers. It is due to the fact that rhythmic contractions of the heart are transmitted to the abdominal aorta and is not normally detected.
Palpation of the heart in children
In children, the technique for palpation of the heart does not differ from palpation in adults. Normally, in a child, the localization of the apical impulse is determined in the 4th intercostal space, 0.5-2 cm medially from the midclavicular line on the left, depending on age - 2 cm in a child under two years old, 1 cm - up to seven years, 0.5 cm - after seven years. Deviations from the norm in the characteristics obtained by palpation of the heart may be due to the same diseases as in adults.
Contraindications?
Due to the fact that cardiac palpation is a safe method of examination, there are no contraindications for its implementation, and it can be performed on any patient with any degree of severity of the general condition.
4. The danger of arrhythmia and measures in case of interruptions in heart rhythm
An abnormal heart rhythm may not be accompanied by pain or other unpleasant sensations other than “fluttering in the chest” or the feeling of your own uneven heartbeats. However, it is extremely dangerous to treat sudden changes in heart rate as a normal ailment that will “go away on its own.” The insidiousness of cardiac disorders is that the gradual wear and tear of the heart can at some point lead to a sudden life-threatening condition requiring emergency medical attention. It could be:
- ischemic stroke;
- acute heart failure;
- heart block (complete stop of heart contractions);
- myocardial infarction.
Any systematic or persistent heart rhythm disturbances should be a reason to contact a cardiologist and conduct a thorough diagnosis. This is necessary to identify the causes of arrhythmia and take measures to eliminate factors affecting heart rhythm.
Diagnostics may include:
- echocardiography;
- ECG;
- daily monitoring;
- MRI, including duplex scanning;
- functional diagnostics with load.
Further treatment
depends on the diagnosis and the factors that led to interruptions in heart rhythm. Sometimes it is enough to give up bad habits, move more, spend time in the fresh air, optimize your work and rest schedule, lose excess weight, and reduce the fat content in your diet.
If the cause of arrhythmia is heart disease or diseases of other organs and systems, then appropriate therapy is prescribed. Surgical, sanatorium-resort and inpatient treatment can also be used. Sometimes it is necessary to strictly follow a number of rules and restrictions throughout your life to maintain proper heart function and reduce the risk of developing more severe conditions.
What diseases can be suspected by palpation of the heart?
Palpation of the apex and cardiac impulse, which differs in characteristics from the norm, as well as the determination of pathological tremors and pulsations of the heart, can be caused by the following diseases:
- Congenital and acquired heart defects, which cause disruption of the normal architecture of the heart and sooner or later lead to the formation of myocardial hypertrophy, Long-term arterial hypertension, which is especially difficult to treat and reaches high blood pressure numbers (180-200 mm Hg),
- Aneurysm of the thoracic aorta,
- Pericarditis, especially with the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the cavity of the pericardium,
- Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, adhesions in the pleural cavity, adhesive pericarditis,
- Diseases of the abdominal cavity with an increase in its volume - ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity), tumor formations, late pregnancy, severe bloating.
For example, if a negative apical impulse is detected in a person being studied, which looks like a retraction of the intercostal space in the area of the impulse, the doctor should certainly think about adhesive pericarditis, in which the pericardial layers “solder” to the inner surface of the chest. With each contraction of the heart, the intercostal muscles are pulled into the chest cavity due to the formed adhesions.
Determination algorithm
The heartbeat is palpated as follows:
- The doctor's hand is placed on the precordial area, the fingers are at the level of the apical impulse, and the palm is at the right edge of the sternum, then palpation is performed. This is how the precordial region is assessed.
- Having assessed the condition at this level, the doctor’s hand moves to the third rib and palpation is also carried out here.
Thus, the doctor, with an existing cardiac impulse, distinguishes between the vibration of the lower part of the sternum, the pulse at the edges of the sternum and the epigastric pulsation.
Interpretation of results
What can palpation of the apex beat tell you? For an experienced doctor who has the skills to physically examine a patient and has discovered, for example, a weakened apical impulse, it will not be difficult to associate this symptom with the presence of effusion pericarditis , characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the heart sac, or pericardium. In this case, the vibrations caused by heart beats are simply not able to pass through the layer of fluid and are felt as a push of weak force.
In the case when a doctor diagnoses a diffuse apical impulse, he may think about the presence of left or right ventricular hypertrophy . Moreover, an increase in myocardial mass is likely if there is a displacement of the impulse to the right or left. Thus, with left ventricular hypertrophy, the impulse shifts to the left. This is due to the fact that the heart, increasing in mass, must find a place for itself in the chest cavity and it will shift to the left side. Accordingly, the apex of the heart, creating a push, will be determined on the left.
Thus, palpation of the heart, when performed by an experienced doctor, can bring undoubted benefit to the patient, since during a routine examination the doctor is able to suspect any disease and promptly refer the patient for further examination using instrumental diagnostic methods.
1. Heart rhythm disturbances
Normal heart function is, as a rule, subjectively imperceptible. Only when you are scared, rise sharply or jog do you feel a palpitation. If there are objective reasons for changes in heart rate, then this is a harmless and transient physiological reaction to internal and external changes. Unfortunately, interruptions in heart rhythm
can occur for no apparent reason, and the average age of onset of cardiac dysfunction is steadily decreasing.
Evolutionarily, it so happened that the work of the heart becomes noticeable to the person himself only when cardiac arrhythmias occur. Even a single freezing of the heart or its too strong contraction is felt as an interruption or a jolt. Arrhythmia
It can be an independent cardiac disease (congenital or acquired), accompany other diseases, or represent a reaction to external factors or internal conditions.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
So that there is no confusion
As you can see, there are many options, and determining on your own whether heart failure is dangerous is quite problematic. Cardiologists agree on one thing: if you periodically feel heart beats and pauses following them, it is better not to guess, but to go for a consultation with a specialist. This is also important because not everything that is perceived as cardiac arrest is actually extrasystoles. For example, many people often confuse heart pain (which almost always indicates a problem that requires treatment) or intercostal neuralgia with interruptions.
A banal ECG will help eliminate confusion - with frequent extrasystoles, such an examination will be enough to detect them. If fading occurs less frequently or, for example, only in the evening, it makes sense to conduct 24-hour Holter monitoring. A compact device that is attached to the body and records the heart rhythm will give answers to all questions.
Symptoms of extrasystole
If strong heartbeats are observed in a practically healthy person and are associated with stress or drinking strong coffee, the unpleasant sensations are mild, without pain or burning. In chronic pathologies, the patient describes the following symptoms:
- inside the heart turns around its axis;
- flutter;
- interruptions;
- sweating;
- heat;
- weakness in the limbs;
- dyspnea.
When tremors occur, a person feels anxious, and there is a desire to go out into the air and take a deep breath. If the attack occurs in several stages, your hands begin to tremble and you feel dizzy.
A complication of extrasystole is its degeneration into more severe health problems: arrhythmia, constant tachycardia, cerebrovascular insufficiency. With constant attacks, the atrium muscles do not receive enough blood and oxygen, and necrosis of certain areas occurs. If left untreated, the patient faces a heart attack or death.
Treatment of heart beats
If sharp tremors in the heart area are caused by a lack of potassium and sodium, the doctor adjusts the diet, recommends taking vitamin complexes, and saline-based injections. The specialist calculates the amount of salt and prescribes a course of therapy with Narzan mineral water. In case of incomplete absorption of nutrients, an examination of the digestive system and consultation with a gastroenterologist is required.
The presence of psychogenic factors must be treated using different methods:
- Eliminate bad habits, stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Take natural herbs to relieve tension, stress, and improve sleep. Instead of tea and coffee, you can drink a decoction of motherwort, mint, chamomile, or peony infusion.
- For frequent attacks of extrasystole (more than 200 beats per day), it is necessary to select sedative medications to normalize the functioning of the nervous system: Persen, Sedofyton, Novo-Passit.
Often the cause of tremors is cervical osteochondrosis. His treatment is carried out by a neurologist together with a cardiologist. The therapeutic course includes therapeutic massage, physiotherapy, taking anti-inflammatory drugs: Movalis, Diclofenac, Nimesulide. Muscle relaxants help relieve tension and reduce discomfort in the heart area: Mydocalm, Sirdalud, Tizalud.
Prevention of tremors in the heart is to prevent diseases that can disrupt its functioning: colds, flu, sore throat, internal infections. Moderate cardio exercises are recommended, which strengthen the heart muscle well and stimulate its stable functioning. Proper nutrition and a nutritious diet maintain electrolyte balance and prevent complications due to stress.
FacebookvKontakteTwitterWhatsApp
Causes of heart beats
In most cases, the sensation of tremors in the heart area in patients under 50 years of age provokes a disruption of the heart rhythm caused by psychogenic factors. This group includes uncontrolled use of many medications, drugs, and alcohol. Common causes of such extrasystole:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- osteochondrosis in the cervical spine;
- stressful conditions;
- depression;
- neuroses;
- working in unfavorable conditions;
- living in a region with a polluted environment.
Rare attacks occur in women during periods of hormonal imbalance: menstruation, pregnancy, taking contraceptive medications. This is a common problem among people who overindulge in coffee, strong tea, or energy drinks.
Organic causes of unpleasant tremors occur when the myocardial muscle is inflamed or damaged, which is caused by the following health problems:
- previous heart attack;
- chronic ischemia;
- infectious pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- any vices;
- congenital deficiency.
For some people, the problem appears when the heart muscle is depleted, which is caused by hard work, physical activity: athletes, hot shop workers, miners. It becomes a complication of a sore throat, pneumonia, or purulent otitis media.
The toxic form of the pathology is distinguished separately. It appears with long-term use of medications that a person has to take constantly: sedatives, diuretics to lower blood pressure, glucocorticoids. Tremors in the heart area are provoked by the use of Euphyllin and Furosemide. Their components wash away sodium and potassium ions, which extinguishes conductive signals and weakens muscles.