The average normal blood pressure is not ideal for everyone. Deviations from the notorious 120/80 can be either upward or downward. But if high blood pressure is considered clearly dangerous to health, hypotension does not always signal a threat. For some people it is familiar and is a variant of the norm. However, extremely low numbers are a reason to be wary. Especially if accompanied by dizziness, weakness and lightheadedness.
Physiological causes of low blood pressure
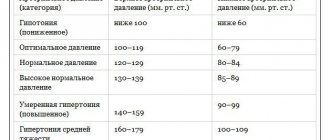
For an adult, blood pressure less than 95/65 mm is considered excessively low. But there are categories of people who feel comfortable with such indicators, and when the numbers increase to the ideal 120/80, they experience obvious signs of hypertension: headaches, arrhythmia and severe stress. At first glance, this is a paradox, but doctors recognize the existence of individual physiological norms that differ from the average.
- Slightly reduced blood pressure, for example, is typical for residents of high mountain regions, professional runners, and young women of fragile asthenic build. It is called compensatory. Usually this condition is not causing concern and does not lead to any health consequences.
- In some cases, vascular tone indicators decrease briefly with sudden changes in body position. These are orthostatic changes, also related to the norm. May be accompanied by momentary dizziness.
- Postprandial hypotension occurs after overeating. This is also a normal reaction of the body sending a large volume of blood to the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the appearance of weakness or drowsiness is possible.
Physiological fluctuations in blood pressure are typical for people during air travel, sudden deterioration of weather, and exposure to various radiations. Indicators return to normal when the situation stabilizes.
Causes of pressure, nausea, headache
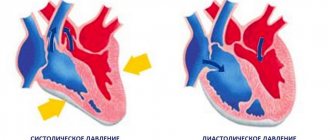
Acute headaches, nausea, weakness and deterioration in health, as well as various heart rhythm disturbances are symptoms that may indicate both high and low blood pressure. Normally, this figure is 120/80 mm. rt. Art., but in some people it remains at a higher or lower level. When measuring it, various factors are taken into account, but chronic hypertension or hypotension cannot be considered normal.
High blood pressure
Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure. It often occurs in a chronic form and can be diagnosed at any age. Blood pressure indicators with constant hypertension remain within the range of 140∕90 mm or more. rt. Art. Doctors recommend exercising with caution if you have this disease, avoiding stress, and regularly measuring your blood pressure at home.
Causes of hypertension
The main cause of hypertension is weakness of blood vessels and decreased elasticity of their walls. With a sharp increase in blood pressure, they cannot adapt to the load. This can happen in the warm season, during physical activity, under stress and nervous tension. In addition, chronic hypertension can be diagnosed, which manifests itself in both adults and children. Its causes may be:
- congenital or acquired diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- excess weight, which increases the load on the heart muscle;
- abnormal physical activity;
- age-related changes - in older people, blood vessels become less strong and elastic, and adapt less well to pressure changes;
- unhealthy diet, as well as frequent alcohol consumption;
- atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disease in which plaques and blood clots (often cholesterol) form on the inner wall of the arteries.
Attacks of hypertension can be associated with stressful situations, in which blood pressure increases and the heartbeat accelerates. Thus, severe fear causes a sharp increase in blood pressure, accompanied by pain in the heart area. Symptoms also often occur during intense physical activity, especially at high temperatures and insufficient ventilation.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
More than 20% of people in the world suffer from chronic hypertension. The danger of this disease is that at the first stage it can be asymptomatic. The clinical picture is noticeable during the next attack, but during periods of remission the disease does not manifest itself in any way. When blood pressure increases, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- acute headache, dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting, regardless of food intake;
- acceleration of heart rate, manifestation of various types of arrhythmia;
- redness of the skin in certain areas, often on the face;
- the appearance of small subcutaneous hemorrhages - they are associated with rupture of capillaries from increased blood pressure and can also be found on the mucous membranes;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of black dots or circles in the field of vision;
- fainting is possible.
The first symptoms of hypertension may remain unnoticed, but the load on the heart increases significantly. If you do not take this feature into account and continue to undergo intense physical activity, this can lead to dangerous consequences. A sharp increase in pressure is the main cause of vascular rupture and the development of hemorrhagic stroke with hemorrhage in the brain. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend regularly measuring blood pressure at home, even if there are no prerequisites for this. This simple procedure will allow you to recognize hypertension in the early stages and prevent dangerous consequences.
Lower blood pressure
Hypotension (low blood pressure) is an equally dangerous disorder. With this disease, blood does not move through the vessels intensively enough and does not reach areas distant from the heart. Thus, the blood supply to the lower arms and legs, internal organs and brain may be disrupted. It is important to monitor your health and take prescribed medications, since low blood pressure can cause ischemic stroke.
Causes of hypotension
Hypotension is diagnosed if, as a result of several measurements, blood pressure readings are 90∕60 mm. rt. Art. and less. It can be a chronic disease of the cardiovascular system and can also occur in healthy individuals under certain conditions. So, the causes of hypotension can be:
- deterioration of vascular tone, their constant expansion - the result of poisoning, allergic reactions and other disorders;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disease in which the regulation of vascular tone occurs, so their walls lose tone and elasticity;
- dehydration of the body due to insufficient fluid intake, especially in the heat, in case of poisoning or during sports – leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood;
- congenital and acquired diseases and heart defects, valve failure;
- systemic use of certain medications, including drugs against hypertension, which lead to a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
Separately, physiological hypotension is distinguished - a decrease in blood pressure, which is within normal limits. Thus, indicators may be underestimated as a compensatory response to environmental conditions. Residents of high mountain regions experience a mild degree of chronic hypotension, which is not harmful to health. It also develops in athletes who regularly engage in intense physical activity. An increase in the mass and volume of the heart and an increase in the volume of circulating blood lead to the fact that for proper blood circulation in normal mode, a low blood pressure is sufficient. In some healthy people, blood pressure is constantly slightly reduced, and this is considered normal. In other cases, hypotension is a pathology and requires timely treatment.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Hypotension can be asymptomatic only with a slight decrease in pressure. If the indicators are 90∕60 mm. rt. Art. and less, the clinical picture is clearly expressed. The disease manifests itself in attacks that sharply worsen health and can lead to fainting. The onset of an attack can be determined by the characteristic symptoms:
- aching headache that can spread over the entire surface of the head or pulsate in the temples;
- constant weakness, drowsiness, slow reaction to stimuli;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, with a sharp decrease in pressure to critical levels, their cyanosis may be observed;
- decrease in skin temperature on the distal parts of the extremities (hands and feet) due to their insufficient blood supply;
- nausea and vomiting;
- tendency to faint when the ambient temperature rises, during physical exertion, while dieting, and in other cases.
If you often have a headache and feel sick, and your blood pressure is constantly below the normal limit, you should consult a doctor for a more complete diagnosis. Hypotension is dangerous to health, since the rate of blood circulation in this disease is significantly reduced. The main risk is insufficient oxygen and nutrients to the brain cells, which causes fainting. Ischemic areas form in the brain tissue, which cannot function fully. Persistent hypotension can lead to the development of ischemic stroke - an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. This condition poses a threat to the patient’s life, so it is important to take care to prevent its occurrence.
Other reasons
Nausea, weakness, high or low blood pressure, and headache are symptoms of a number of diseases caused by circulatory failure. They pose varying degrees of danger to the patient, but equally require full diagnosis and proper treatment. It is difficult to recognize the disease and make a correct diagnosis at home. In addition, many dangerous pathologies in the initial stages are disguised as ordinary malaise and fatigue.
- Poisoning is a condition in which toxic substances enter the body or are formed as a result of metabolism. Food intoxication is the most common; poisoning with gases, alcohol and medications, and heavy metals is also identified. They are manifested by nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure due to dehydration, as well as acute headaches.
- Heart defects can be congenital or acquired. They represent insufficiency of the heart valve apparatus. This leads to a deterioration in the movement of blood through the vessels, insufficient blood supply to internal organs, and an increased risk of myocardial infarction.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disorder in which the walls of blood vessels become dense and inelastic. Plaques and blood clots form on their inner wall, preventing normal blood flow. Often the cause of atherosclerosis is a violation of cholesterol metabolism, and this element is deposited on the walls of blood vessels and in the internal organs.
Blood pressure, nausea, headache - these symptoms may indicate severe fatigue, nervous tension, and stress. They can also appear in a healthy person, especially during sudden changes in weather conditions. Also, this picture may be a sign of poor nutrition, a lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the diet.
Pathological factors of low pressure
If hypotension leads to insufficient blood circulation, hypoxia, heart rhythm disturbances, headaches and fainting, you need to sound the alarm. The critically low blood pressure limit is 85/55, which may be followed by loss of consciousness and vascular collapse. And regular attacks can lead to a stroke or heart attack.
Primary pathological hypotension is rare. Its cause is a special form of cardioneurosis, usually congenital. Secondary is not an independent disease, but a symptom of deeper health problems. The most common:
- Hypovitaminosis. Low blood pressure may be a sign of a lack of ascorbic acid, vitamins B12, A and E.
- Difficult pregnancy: with frequent attacks of toxicosis, dehydration, decreased hemoglobin levels.
- Inadequate nutrition: strict diets, fasting.
- Dystonia often causes a sharp drop in blood pressure, accompanied by tremor, dizziness, bradycardia, and loss of strength.
- Iron deficiency anemia: leads to hypoxia and systemic disorders, including a decrease in vascular tone.
- Diseases of internal organs: pancreatitis, hepatitis, stomach ulcer.
- Endocrine diseases. Hypotension is often accompanied by insufficiency of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Traumatic brain injuries. Damage to the central nervous system often manifests itself as a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
Vascular tone decreases in various acute conditions: massive blood loss, toxic shock, severe poisoning.
What is hypotension?
The term arterial hypotension (hypotension) defines a decrease in blood pressure. This is not a separate disease, but a syndrome that develops as a result of exposure to various provoking factors or against the background of diseases. A decrease in the indicator leads to a decrease in the volume and speed of blood flow in peripheral tissues. First of all, the cells of the nervous system, which are very sensitive to energy and oxygen starvation, are affected.
Low blood pressure - causes
Arterial hypotension develops due to exposure to a large number of pathological or physiological causes. The most common ones include:
- Poisoning of the body
– ingestion of various toxins from the outside with food, inhaled air, or intoxication due to the development of an infectious process.
- Violation of the regulatory influence of nervous system structures
on arterial vessels, leading to a sharp decrease in the tone of their walls - cerebral stroke, organic changes, infectious processes in the structures of the central nervous system, previous traumatic brain injuries, functional disorders of various origins.
- Dilatation of arteries against the background of decreased tone of the whole body
, which occurs against the background of physical and mental fatigue, lack of sleep, poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis (hypovitaminosis is an insufficient supply of one or more vitamins to the body).
- Decrease in circulating blood volume due to blood loss
(internal or external hemorrhage) or dehydration (loss of fluid due to uncontrollable diarrhea, vomiting, insufficient water intake).
- Severe allergic reactions
, accompanied by a pronounced decrease in arterial tone - anaphylactic shock.
- Changes in hormone levels in the blood
, which have a regulating effect on arterial tone, heart rate, blood pressure and other hemodynamic indicators - adrenaline, hormones of the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland influence the course of a large number of physiological processes in the body.
- Redistribution of fluid in the body
with a transition from the vascular bed to the intercellular substance of tissues, which leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood with arterial hypotension.
- Weakening of the contractile function of the heart
, provoked by pathological processes in the myocardium - infarction, myocardiopathy, myocarditis.
- Violation of the rhythm and frequency of heart contractions
, caused by various pathological factors and leading to a decrease in blood pressure.
A decrease in the level of systemic blood pressure is a consequence of pathological processes in other organs, in particular with diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, and anemia. Physiological arterial hypotension develops during the period of adaptation of the human body to a reduced concentration of oxygen in the inhaled air (stay in high mountain areas). Causes of low blood pressure in women include the effects of hormonal changes during menstruation, early pregnancy, and menopause (age-related decline in reproductive function).
Low blood pressure - symptoms?
Arterial hypotension is accompanied by a violation of the functional state of various organs and systems, which develops against the background of energy and oxygen starvation. Symptoms of low blood pressure include the following:
- General weakness
– a constant symptom of hypotension, the severity of which depends on the degree of decrease in blood pressure.
- Dizziness
– the result of oxygen starvation of neurocytes.
- Memory impairment, decreased mental performance
– low blood pressure affects a person’s higher nervous activity; signs usually appear with prolonged moderate hypotension, as well as against the background of the development of anemia.
- Paleness of the skin and visible mucous membranes
– the sign appears in cases where arterial hypotension develops sharply and is accompanied by a decrease in circulating blood volume (after bleeding).
- Headache
, which is predominantly localized in the temples, crown and can have varying severity.
With severe hypotension, a person loses consciousness, which is associated with oxygen starvation of the cerebral cortex. If systolic pressure is below 70 mm Hg. Art. acute renal failure develops, decompensation of the functions of all organs, which becomes the cause of death.
To understand why a particular patient has low blood pressure, a doctor (general practitioner, family doctor, cardiologist) must prescribe an additional objective examination. It includes various techniques, namely clinical blood tests, urine tests, ECG, X-rays, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging. Based on a thorough and reliable diagnosis, the correct treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms of Low Blood Pressure
The hypotonic state is characterized by:
- dizziness, dull headaches, squeezing the back of the head and temples;
- the appearance of dark circles before the eyes;
- muscle weakness, decreased sensitivity, numbness or tingling of the fingers;
- asthenia: irresistible drowsiness, apathy, absent-mindedness;
- excessive chilliness of the hands and feet.
During a sudden attack, most hypotensive patients feel lightheaded, may lose their balance, or faint. Another deterioration in health is provoked by severe stuffiness, physical fatigue, hunger, and dehydration.
Diagnostic methods
If you feel sick and have a headache, it is important to determine what pressure the patient has. This can be done at home using a tonometer. The most informative results are in dynamics, so it is better to take several measurements with a short interval. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions and modern equipment for full diagnostics. Experienced doctors will prescribe additional examinations that will make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and establish the cause of poor health.
- Blood tests are one of the first stages. Clinical analysis will help determine the level of hemoglobin, the number of red blood cells and other elements. Based on biochemical analysis, dysfunction of the heart and other organs can be suspected. Separately, the doctor can measure blood glucose levels and prescribe additional tests to determine the concentration of various vitamins and microelements.
- Dopplerography is an examination of blood vessels using ultrasound using a contrast agent. More often, this technique is prescribed when a violation of cerebral blood flow is suspected. Ultrasound of the vessels of the head is informative if chronic cerebral ischemia, thrombosis, or aneurysms are suspected.
- MRI, CT scan of the brain is the most accurate, informative diagnostic method for stroke, various brain tumors and other pathologies. Using a tomograph, you can get a complete three-dimensional picture and detect any disorders of the brain. The technique is complex and requires highly qualified specialists, but is available at the Clinical Brain Institute.
Pressure surges, nausea, headache - these signs may indicate a stroke. At home, you can carry out its initial diagnosis, but even if there is no positive response to the tests, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The patient should be asked to smile, raise both hands in front of him, and repeat a simple sentence. In this way, it is possible to determine disturbances in coordination of movements, facial expressions and speech, characteristic of damage to certain areas of the brain. Further treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting, aimed at restoring lost functions.
Treatment methods
The treatment method for high or low blood pressure, nausea, and headache depends on the exact diagnosis. It is prescribed only based on diagnostic results and often involves taking specific medications. It is important to understand that independent selection of medications can aggravate the situation and lead to undesirable consequences.
- Drug treatment is the main stage of therapy. The doctor selects medications to correct blood pressure for hyper- or hypotension and describes in detail the regimen for taking them. You may also need a course of vitamins, and for chronic hypertension, diuretics.
- Diet is a necessary condition for high or low blood pressure, as well as for atherosclerosis. The patient needs to give up fried foods and sweets, limit the intake of salt and fast carbohydrates.
- Work and rest schedule is one of the main points. It is important to ensure a good night's sleep and make time for light physical activity. These conditions will help stabilize blood pressure and improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Clinically, the Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders that are accompanied by headache, nausea, blood pressure, and general deterioration of well-being. Experienced specialists, modern equipment, highly qualified personnel are the main advantages of the center. Here you can undergo treatment in a hospital setting, under round-the-clock supervision by doctors, and also receive recommendations for maintaining health at home.