A high pulse wave velocity in patients with COVID-19 may serve as a marker of a higher risk of death, a study by European scientists has shown. This indicator reflects the condition of the blood vessels. Pulse wave speed is usually higher in older people and hypertensive patients, plus it increases in a state of acute inflammation associated with coronavirus infection. It is likely that measuring this parameter in patients with COVID-19 may become an additional diagnostic measure that doctors will resort to in special cases, experts believe.
What should an adult’s pulse be like: normal and pathological
What is the pulse like? What do its values depend on? Is the pulse always equal to the heart rate?
Physician, cardiologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina, helped us find answers to these and other questions.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what is a pulse and what does its frequency depend on?
The pulse is a rhythmic oscillation of the walls of the arteries, associated with the entry of a certain amount of blood into them during the contraction of the heart and a change in pressure.
Heart rate is affected by:
— level of physical activity (rest, exercise);
— condition of the heart muscle and valves;
- blood pressure value;
— work of the neuroendocrine system;
- level of basal metabolism (one of the criteria is body temperature).
BECAUSE THE PULSE MAY BE IRRHYTHMIC, IT IS RECOMMENDED IN ALL CASES TO COUNT IT FOR NO LESS THAN 60 SECONDS
A situational increase in heart rate is possible when taking certain substances (both medicinal and toxic), and this also happens in a person in a positive and negative emotional state (joy, fear, anger, etc.).
— How to measure the pulse correctly?
Mainly by palpation (feeling) of the vessel. The pulse can be counted in the radial, carotid, temporal, and femoral arteries. But in practice, the radial artery is most often used.
The wrist of one hand or another is covered with the fingers in the area of the wrist joint, the artery is felt, pressed with 2-3 fingers, and the pulse is counted.
Read the material on the topic: What should a child’s blood pressure be?
Usually the pulse is counted for 1 minute. In the literature you can find measurement methods where the pulse is calculated for 15 seconds and then multiplied by 4, or for 30 seconds and then multiplied by 2. However, due to the fact that the pulse can be irregular, it is recommended in all cases to count it at least than within 60 seconds.
— In Chinese medicine, there is a diagnostic method based on the pulse. In fact, what can the pulse tell you?
Indirectly, the pulse can be used to judge the heart rhythm (and its disturbance), the state of the myocardium, heart valves, blood vessels and vascular wall, the level of basal metabolism, the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, and the emotional state of a person.
Read material on the topic: Heart, why don’t you want peace? What causes tachycardia?
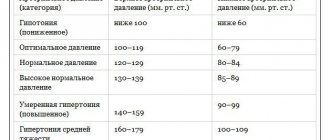
— What should be the normal heart rate of an adult?
According to various sources, normal levels in adults range from 60-80, 60-90 beats per minute. The number of pulse beats is equal to the heart rate (HR), i.e. Normally, there should be no so-called pulse deficit (a situation when its frequency is less than heart rate. This occurs, for example, with atrial fibrillation). In addition, the normal pulse is rhythmic, symmetrical, with satisfactory filling and tension.
— What affects a person’s pulse? What factors does it depend on?
There are several factors. The symmetry of the pulse is affected by a decrease in the lumen of one of the arteries, its incorrect location (the radial one itself, or the overlying ones, the radial branch of which is), compression of the artery (for example, an aortic aneurysm, a neoplasm, enlarged lymph nodes).
NORMALLY IN ADULTS, THE PULSE VALUES WITHIN 60-80, 60-90 BLOCKS PER MINUTE
Pulse is also influenced by heart rate; the adequacy of the contractility of the heart and the amount of blood ejected into the aorta during contraction of the left ventricle; condition of the artery wall; operation of the valve apparatus.
- For what reasons can the pulse decrease?
If this means a decrease in heart rate, then normally this is possible during intense sports training, in a state of sleep.
A rarer, slower pulse, as an indicator of pathology, may occur with certain disorders of the rhythm and conductivity of the heart, aortic valve stenosis, a disorder of the autonomic nervous system, poisoning, and certain infectious diseases (typhoid fever, brucellosis).
Read the material on the topic: Is there a diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia?
Taking certain medications (beta blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs) can reduce your heart rate.
- If the pulse is low, does this mean that the person has low blood pressure?
If by low heart rate we mean rare, then such a relationship does not always happen. There are situations when the pulse is low and the blood pressure is high.
Read the material on the topic: For what reasons can blood pressure be low?
— Under what conditions can the pulse be high?
If a high pulse is understood as its increase, then the cause may be physical activity, stress, consumption of caffeine-containing drinks, or a number of medications (for example, aminophylline, nifedipine, cordiamine, salbutamol, atropine).
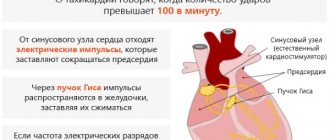
A frequent pulse can occur in various pathologies: diseases of the cardiovascular system (rhythm and conduction disorders; damage to the myocardium and pericardium, valvular apparatus; heart failure), dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system with a predominance of the influence of its sympathetic department, most infectious diseases, diseases of the endocrine system ( thyrotoxicosis), bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolism, shock and a number of others.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, is a high pulse always accompanied by an increase in blood pressure or is this not necessary?
No, this doesn't always happen.
Read related material: The Ultimate Guide to High Blood Pressure: Frequently Asked Questions
— What heart rate indicators require urgent medical attention?
Pulse parameters in themselves are not always a reason to urgently consult a doctor. However, if a decrease or increase in heart rate is accompanied by any symptoms (for example, with a low pulse, dizziness and loss of consciousness are noted), then you should immediately consult a doctor.
— How to provide first aid at home to a person who has a high or low pulse?
It is necessary to clarify whether such conditions have occurred before, what they were associated with, how they were tolerated; What diseases does he suffer from and have suffered in the past?
You should definitely ask about the person's medications: it is possible that he forgot to take a medicine (for example, a beta blocker), which is why his pulse quickened. Taking the drug in this case can be first aid.
AN IMMEDIATE CALL OF AN AMBULANCE IS NECESSARY IF THE CONDITION OF HIGH OR RARE PULSE HAS DEVELOPED FOR THE FIRST TIME, ESPECIALLY IF THE PERSON HAS PREVIOUSLY HAD SOME DISEASES
If you have a tonometer and thermometer, measure your blood pressure and body temperature. Reducing high numbers for both indicators can also have a positive effect on your heart rate.
In case of stress or autonomic dysfunction, it is necessary to try to calm the patient. Taking one of the drugs such as valocordin, corvalol, valerian, motherwort may help.
If the pulse is low, it is better if the person lies down. Of course, you need to lie down even if your pulse is high, if this condition is accompanied by general weakness, a feeling of lightheadedness, or dizziness.
If a low pulse is accompanied by low blood pressure, you can drink tea or coffee.
If there are no positive changes, you must call an ambulance. In addition, an immediate call is also needed in the case of an increase or decrease in heart rate that develops for the first time (and especially suddenly); progressive deterioration of health, especially in a person who has had certain diseases previously (for example, heart rhythm disturbances, myocardial infarction or stroke, gastrointestinal bleeding, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolism).
Subscribe to our materials on social networks: VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, Facebook
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
In 2007 she graduated from the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko.
From 2007 to 2008 she completed an internship in therapy, in 2010 she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, and in 2017 – in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has been working as a general practitioner, and since 2021, as a cardiologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Reception is conducted at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Heart rate table by age
Normal heart rate depends on many factors: age, gender, activity (physical or emotional) or rest, level of physical fitness or the presence of diseases. Pulse rate is measured in beats per minute, and the rate of this indicator is determined by age.
Normal heart rate values for children:
| Child's age | max and min indicators | Average value |
| 0 – 1 month | 110 – 170 | 140 |
| 1 – 12 months | 102 – 162 | 132 |
| 1 – 2 years | 94 – 155 | 124 |
| 4 – 6 years | 86 – 126 | 106 |
| 6 – 8 years | 78 — 118 | 98 |
| 8 – 10 years | 68 – 108 | 88 |
| 10 – 12 years | 60 – 100 | 80 |
| 12 – 15 years | 55 – 95 | 75 |
Normal heart rates for adults:
| Age | max and min indicators | Average value |
| Up to 50 years | 60 – 80 | 70 |
| 50 – 60 years | 65 – 85 | 75 |
| 60 – 80 years | 70 – 90 | 80 |
How to properly examine the pulse?
The arterial pulse is most easily measured with a finger, while the venous and capillary pulse cannot be determined by palpation and are measured using special techniques. In some cases, to study the arterial pulse, the patient is prescribed the following instrumental methods:
- sphymography;
- sphygmomanometry;
- ECG or Holter ECG;
- Pulse symmetry.
Pulse counting can be done by yourself, a loved one, or a doctor. Remember, the person who is taking the pulse must be relaxed and emotionally calm, his hand must be in a comfortable position!
Video: How to measure pulse
Most often, the measurement is performed by palpating the radial artery at the wrist. To do this, press the artery with two or four fingers so that the fingertips feel the vibrations of the arterial walls. After this, they note the time (it is better to do this with a stopwatch) and begin to count the pulse. The number of vibrations of the arterial walls can be calculated in 1 minute, and if the pulse is rhythmic, then the measurement can be accelerated by counting the frequency of beats in 30 seconds and multiplying the result by 2.
Sometimes the pulse is measured in other arteries:
- ulnar - on the bend of the elbow or in the center of the wrist;
- carotid - on the neck on the side of the thyroid cartilage and closer to the chin;
- axillary - at the level of the edge of the first rib;
- femoral - on the inner side of the thigh (closer to the pubic symphysis);
- temporal - on the temple just above the cheekbone.
Pulse form
The shape of the pulse reflects the rate of change in pressure between contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. Depending on these indicators, doctors distinguish the following forms of pulse fluctuations:
- rapid pulse - is a sign of aortic insufficiency or thyrotoxicosis, occurs due to the fact that a lot of blood is pushed out of the ventricles and the pressure during diastole decreases sharply;
- slow pulse - occurs with mitral regurgitation or narrowing of the aortic walls, manifested by small pressure drops;
- dicrotic pulse - appears when the tone of peripheral vessels deteriorates and is manifested by the passage of an additional wave of oscillations through the vessels.
Why measure your pulse?
Pulse is one of the important parameters of the quality of physiological processes, reflecting the state of health, level of physical fitness or the presence of diseases of the heart, blood vessels and other systems and organs. The indicators given in the tables above are the normal heart rate for healthy people at rest. It should be remembered that any changes in the body can provoke deviations from the norm in different directions. For example, during pregnancy or menopause, hormonal changes occur that can affect the pulse rate. A person's heart rate can change under the influence of many factors.
Rapid pulse - tachycardia - can occur in the following physiological conditions or pathologies:
- emotional outburst or stressful situation;
- pregnancy;
- menopause;
- hot weather or stuffy room;
- overwork;
- high level of physical fitness;
- consumption of products containing caffeine;
- taking certain medications;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- severe pain;
- diseases of the endocrine and nervous system, blood vessels and heart, high temperature in some infections, neoplasms, anemia, bleeding, etc.
Physiological or pathological slowing of the pulse - bradycardia - can be provoked by the following factors:
- dream;
- high fitness of the heart muscle (in athletes, active people);
- age-related changes;
- intoxication;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- myocardial infarction;
- inflammatory processes in the tissues of the heart;
- organic heart lesions;
- peptic ulcer;
- hypothyroidism;
- taking certain medications.
Heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heart contractions per unit of time. It reflects the frequency of contractions of the ventricles of the heart in one minute and normally ranges from 60 to 80 beats (in an adult and healthy person). This indicator is often confused with the pulse, while this parameter of the cardiovascular system displays the number of oscillations of the vessel walls in response to heart contractions. Typically, both heart rate and pulse are approximately the same.