Reasons for appearance
A pulse of 180 beats per minute or more is the first sign that you need to urgently call an ambulance.
There can be many reasons for high numbers:
- severe sinus tachycardia;
- atrial flutter;
- supraventricular tachycardia;
- paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia.
If you call an ambulance urgently, you can record an ECG during an attack, which will subsequently help to correctly diagnose and select effective treatment.
In healthy people, all of the above cardiac arrhythmias are rare.
But often high levels can be the causes of heart disease:
- ischemic disease, previous heart attack;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- heart disease;
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome;
- CLC syndrome;
- chronic heart failure.
No lung ailments, problems with the thyroid gland, anemia or fever provoke a rapid pulse, but there are exceptions - supraventricular arrhythmia and thyrotoxicosis.
It is considered normal if the heart beats faster when:
- physical activity;
- waking up in the morning;
- sudden change in body position;
- strong emotional shocks;
- increased blood circulation in the organs of the digestive system after eating.
There are also a number of specific factors that contribute to heart palpitations:
- if you had a nightmare at night;
- for insomnia;
- after using drugs or aphrodisiacs;
- during therapy with antidepressants or drugs that stimulate sexual activity;
- constant stress and overwork;
- alcohol abuse;
- high pressure;
- acute viral respiratory diseases;
- overweight.
A person can have a pulse of 200 beats per minute even in a state of complete rest, which indicates:
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- nervous system disorder, mental imbalance;
- poisoning: toxins, poisons, alcohol, nicotine;
- flu and colds at high temperatures;
- infectious or cold pathologies;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- bleeding.
It is considered normal for children if the heart beats rapidly. In newborns, the pulse can reach 170 beats per minute and this is considered normal.
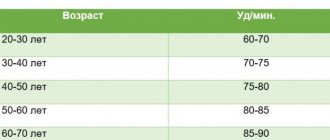
To understand whether the pulse is rapid or not, you need to know the norm, because it differs depending on age. The standards are described in the table below.
| Age | Pulse (minimum-maximum) |
| From the first hours to 1 month of life | 110-170 |
| 1-12 months | 102-162 |
| 1-3 years | 94-154 |
| 4-6 years | 86-126 |
| 6-8 years | 78-118 |
| 8-10 years | 68-108 |
| 10-12 years | 60-100 |
| 12-15 | 55-95 |
| 15-50 | 60-80 |
| 50-60 | 64-84 |
| 60-80 | 69-89 |
Forecast
Short-term attacks of increased heart rate up to 170 per minute are not dangerous to health. The likelihood of complications arises in the following situations:
- severe heart disease;
- the first month after myocardial infarction;
- unstable angina, increased frequency of attacks, increased need for nitroglycerin;
- drop in blood pressure and fainting during an attack.
In all these cases, the patient should be a candidate for RFA surgery, which will help completely get rid of palpitations.
Possible diseases
There are several types of rapid pulse. All types, features and symptoms are described in the table.
| Type of tachycardia | Features, symptoms |
| Nodal or sinus | This is a sign of a physiological increase in heart rate. It appears during emotional arousal or against the background of a stressful situation. The number of heart contractions can be within 100 beats or a little more. The general condition is not disturbed in any way, the pulse slows down once the provoking factor is eliminated. |
| Supraventricular | The pulse increases sharply to 200 beats per minute. To determine its quantity, simply place your hand on one of the large vessels. This condition can cause discomfort in the chest area, fear and anxiety appear. |
| Ventricular | This type of tachycardia occurs only in an emergency situation, when disturbances in the functions of the myocardial muscles are observed. The pulse can increase to 250 beats. It is difficult for the heart to maintain such a rhythm; if timely assistance is not provided, the result can be death. |
More often, the pulse increases due to disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, hormonal and endocrine ailments.
Tachycardia manifests itself due to:
- Cardiac pathologies: myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, myocardial dystrophy, changes in the structure of the heart valves, hypertension, coronary artery disease.
- Thyroid diseases: hypothyroidism, myxedema, amenorrhea.
- Hormonal changes: menopause, malignant and benign formations.
What happens in the heart
Most often, such a pulse occurs in paroxysms and reflects the development of supraventricular tachycardia. What kind of rhythm disturbance is this:
- with supraventricular tachycardia, the heart rate ranges from 140 to 220 per minute (usually in the range of 160 to 180 per minute);
- the source of electrical signals is not the usual sinus node, but a cluster of cells between the atria and ventricles; therefore, the atria are excited retrogradely (from bottom to top), and their contractility is impaired;
- due to the “bifurcation” of the atrioventricular node into 2 paths, with this arrhythmia the impulse quickly circulates through the resulting loop, constantly stimulating the ventricles with a frequency of 140 per minute and higher;
- little blood enters the ventricles, and just as little of it is thrown into the aorta, so the body experiences a pronounced lack of blood circulation.
Another reason why the pulse can be in the range of 140 – 150 or more is the tachysystolic form of atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation. With this disorder, the muscle fibers of the atria contract irregularly, as if twitching, with a very high frequency (up to 450 per minute). Only a portion of these signals are carried to the ventricles.
The tachysystolic form is said to occur when the number of heart contractions during atrial fibrillation exceeds 100 per minute.
When it increases to 140 per minute, a pulse deficit often occurs. This is a discrepancy between heartbeats and palpable pulse waves, since some of them are “empty”; very little blood is thrown into the aorta at this time.
Therefore, if the pulse is 150 beats per minute or higher, and it is rhythmic, we are most likely talking about supraventricular tachycardia.
Such a pulse during exercise can normally be observed in young people and children. However, prolonged sinus tachycardia up to 170 per minute can adversely affect the heart muscle. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a sports training regimen individually, with gradual adaptation of the body.
Diagnostics
Based on the collected history and symptoms, the family doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis of a patient with a rapid pulse.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination, including the following studies:
- ECG (electrocardiogram). This technique helps determine the electrical activity of the heart muscles. And the biological potential is recorded by electrodes. All received data is displayed in the form of a graph on the monitor or printed on paper. This study allows you to determine the frequency of contractions, the conductivity of the heart muscle, the size of the atria, and the degree of blood supply. The price of the examination is within 500 rubles.
- Ultrasound of the heart . This study shows deviations in the structure of the organ and its functional features. Shows the mass of the ventricles, the size of the heart, myocardial contractility, blood pressure in the vessels, the condition of the valves, the structure of the arteries of the lung and aorta, and the presence of foreign objects. The cost of the study is about 3000 rubles.
- General blood analysis. With its help, it is possible to count the number of blood cells and allows you to identify leukopenia, anemia or leukemia. The test can be done free of charge at the clinic.
- Test for thyroid hormone – thyroxine. Helps exclude pathologies such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. If the level of the hormone is below normal, then weakness and depression are observed, and if it is above normal, it causes rapid pulse, shortness of breath, and excessive sweating. The cost of the study is from 300 rubles.
- Analysis of urine. Helps determine the hormonal cause of increased heart rate. With tachycardia and pheormomocytoma, a symptom is combined that manifests itself in the form of improper processing of adrenaline. The test can be done free of charge at your local clinic.
When to see a doctor
A pulse of 190 beats per minute is the first signal to urgently visit a doctor. Often this symptom is a consequence of a serious heart condition. The sooner first aid is provided and the cause is determined, the easier the treatment will be and the complications will not appear.
Whatever the reason for the rapid beating of the heart, a doctor must establish it, because with tachycardia the heart works beyond its capabilities, which will ultimately provoke the development of a serious illness, even if there was none at the first attack.
Initially, you need to visit a general practitioner or family doctor, and after collecting an anamnesis, he will refer you for a consultation with specialized specialists: a cardiologist, an endocrinologist.
Symptoms
The development of a rapid pulse up to 180 - 200 per minute is usually well felt by a person. The paroxysm begins suddenly. The following symptoms arise and intensify:
- dizziness, “veil” before the eyes;
- shortness of breath, lack of air;
- interruptions in the functioning of the heart, any tremors or other unpleasant sensations;
- pressing pain, heaviness behind the sternum;
- severe weakness, nausea, decreased blood pressure.
If the arrhythmia continues, loss of consciousness, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, thread-like pulse, coldness of the extremities are possible, that is, arrhythmogenic shock develops. Such cases require treatment of the patient in the intensive care unit.
Prevention
To reduce a rapid heart rate, it is necessary to take preventive measures aimed at improving heart function:
- You should definitely give up drinking coffee, sparkling water, strong black tea, and chocolate. These foods cause your heart to beat faster.
- Give up bad habits: drinking alcohol, smoking.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and exercise daily.
- Read the instructions for the medications. One of the side effects of many medications is increased heart rate.
Treatment methods
If the pulse suddenly increases sharply, then it is necessary to urgently perform several manipulations:
- stop any physical activity;
- take a horizontal position;
- unfasten tight clothing, ensuring a flow of fresh air to the body;
- Call the ambulance team.
You can also try to do vagal tests yourself:
- deep breath with straining;
- Wash with cold water, while holding your breath.
Until the ambulance arrives, you can alleviate the condition of a patient with tachycardia by giving him 20-30 drops of Corvalol or Valocordin.
There are several treatment options for arrhythmia:
- taking medications to help prevent the development of an attack;
- surgical intervention for serious life-threatening illnesses.
Medications
Drug treatment should be selected only after the type of tachycardia is determined. So, for example, if a person has sinus tachycardia, then it is provoked by physical causes and it is not necessary to take medications for it, just calm down and rest. If the pulse does not normalize and blood pressure is normal.
Then you can take the following medications:
- Diazepam. It is a tranquilizer from the benzodiazepine group, which has anticonvulsant, hypnotic and muscle relaxant effects. The drug has a calming effect and reduces the heart rate. The drug has a number of contraindications, so only the attending physician should select the dosage and course. The price of the drug is 200 rubles.
- Phenobarbital. This drug has a hypnotic effect and helps relieve nervous system disorders, which often provoke a rapid heartbeat. The drug also reduces muscle tone, relieves cramps, calms, affects metabolic processes, relieves pain, and lowers blood pressure. Take the medicine 50 mg 2 times a day. The course is selected individually. The price of the drug is 100 rubles.
But ventricular tachycardia can be a pre-infarction condition. In this case, a rapid heartbeat is accompanied by high blood pressure.
- Verapamil. This is a selective or as it is also called a slow calcium channel blocker. The drug has antiarrhythmic, antianginal and antihypertensive effects. The medicine reduces the myocardial oxygen demand, causes stable vasodilation, increasing blood flow, and reduces the muscle tone of the peripheral arteries. The drug effectively helps with angina and arrhythmia. The dose and course are selected only by a specialist, the standard dosage is up to 60 mg 3 times a day. Price from 50 rub.
- Corinfar. This is a calcium channel blocker, which is prescribed for arterial hypertension, dilates peripheral vessels, increases myocardial tone, increases renal blood flow, and lowers blood pressure. Take the drug 10 mg 3 times a day, the course is selected individually. The price of the drug is from 200 rubles.
For proper functioning of the heart and blood vessels, minerals and vitamins are necessary. If little of them enters the body, then a disturbance in the heart rhythm occurs, including tachycardia. That is why, if you have an increased heart rate, you should take a premix of vitamins and minerals along with your medications.
The complex must contain the following components:
- Vitamins A, C, E, B1 and 6 and others. With their help, it is possible to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, improve metabolic processes, and protect heart tissue from damage.
- Magnesium. Prevents the formation of blood clots, improves heart metabolism.
- Calcium. Normalizes heart contraction.
- Selenium. Protects the heart from adverse effects.
- Phosphorus and potassium. Help transmit nerve impulses.
Effective vitamin premixes for problems with heart rhythm are: Direct, Asparkam, Cardio Forte.
Traditional methods
A pulse of 170 beats per minute is a serious strain on the heart. If such jumps are constant, then complications cannot be avoided.
You can help your heart using folk methods:
- Drink ½ tbsp. Calendula tinctures up to 4 times a day. To prepare you will need to take 1 tbsp. l. calendula flowers and pour 2 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 2 hours.
- You can relieve an attack of rapid heartbeat with an infusion of blue cornflower flowers. 1 tbsp. l. pour 500 ml of dry raw materials. boiling water, infuse and drink 100 ml 3 times a day.
- If your heart beats frequently, you should consume figs in any form. You also need to consume honey and black currants as much as possible. You can replace sugar with honey, and make fruit drinks, tea, puree, jam, and jelly from currants.
- Rosehip tea will help support heart function. You will need to take 2 tbsp. l. fruits, pour 2 tbsp. boiling water, leave in a thermos for 1 hour, drink instead of water. But do not abuse it, the course should not exceed 14 days, otherwise the tea will be harmful - it will wash out vitamins from the body.
- Hawthorn tincture. For increased heart rate, it is recommended to take 20 drops, adding ½ tbsp. water. Take up to 3 times a day. Treatment continues for 3 weeks.
- Infusion of calendula and motherwort. You will need to take 1 tbsp. l. dry collection and pour 1 tbsp. water, leave for 2-3 hours, strain and take after lunch. Continue treatment for 3 weeks.
- The pulse often rises to 220 beats per minute, heart problems are observed, and medications do not help, then you can drink healthy fortified juice every morning. You need to take and squeeze out ½ tbsp. chokeberry juice, add 1 tbsp. carrot juice, juice from 1 lemon, drink in small sips in the morning. The course is 2 weeks, after which you take a break of at least 1 week and you can repeat the course.
Each organism is individual, so an effective medicine may not always help in a particular case, and most medicines have many contraindications. Therefore, only a specialist should prescribe treatment.
Other methods
There are many reflex techniques that help calm heart palpitations. Almost all of them are aimed at increasing the tone of the vagus nerve. Here are some effective and proven techniques.
Helping to calm the pulse:
- hold your breath at the height of inspiration for up to 10 seconds, accompanied by straining;
- Press your fingers on your eyes in the area of the supraorbital arches for 5 seconds;
- Place your face in a bowl of cold water and hold your breath for 20 seconds;
- strain the muscles of the abdomen and limbs for 15 seconds, be sure to maintain intervals between tension of 1-2 minutes;
- sharp contraction of the eyes helps slow down the pulse;
- You can remove rapid heartbeat by coughing or gagging;
- massage of the common carotid artery, located in the neck, helps to calm a rapid pulse.
If medications and reflex techniques do not help relieve tachycardia, then electrical defibrillation may be performed.
Treatment
If your heart rate suddenly increases to 140 - 170 per minute or more, you can try to help yourself, but then still call an ambulance, especially if the paroxysm occurs for the first time.
For a pulse with a heart rate exceeding 140 beats, the following is used for treatment:
- Home remedies.
- Medicines.
- Surgery.
Home Remedies
If the attack was not accompanied by fainting or a drop in blood pressure, vagal tests can be used to stop it:
- inhale and strain, as during bowel movements;
- wash with cold water;
- Drink a glass of cold water in small sips.
In young children, it is permissible to use carotid sinus massage, that is, gently rubbing the area of the carotid artery for several seconds. If the child is right-handed, the maneuver should be performed on the right, if left-handed, then on the left, that is, from the side of the non-dominant hemisphere.
Medicines
Ambulance doctors who arrive at the scene can administer medications from the following:
- adenosine;
- verapamil or diltiazem;
- amiodarone.
When paroxysm of atrial fibrillation develops, medications (amiodarone, flecainide, propafenone) or electrical restoration of sinus rhythm are used to stop it. Atrial fibrillation, even paroxysmal, increases the risk of stroke, so anticoagulant therapy is recommended for this disease - from traditional warfarin to the newer dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban.
In the future, many patients who have suffered an attack of increased heart rate are offered treatment with beta blockers or calcium antagonists.
Surgery
Before the advent of percutaneous radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFA), the only treatment for severe paroxysmal tachycardias was open cardiac surgery. Now they are practically not carried out, and RFA is considered the first treatment for recurrent attacks of rapid pulse, accompanied by unfavorable symptoms. In many cases, the intervention is performed under local anesthesia and requires only 1 to 3 days of hospitalization.
RFA is used to treat arrhythmias accompanied by an increase in heart rate of more than 140 per minute - atrial, AV nodal tachycardia, flutter and, in some cases, atrial fibrillation.
Candidates for surgery are people whose frequent palpitations cause dizziness and other symptoms and do not respond to drug therapy. Surgery is also performed for symptomatic WPW syndrome.
The effectiveness of RFA is often higher than with long-term medication. In this case, the patient no longer has to spend money on purchasing them, and, naturally, does not experience side effects. RFA is also more effective for the prevention of severe paroxysms, when palpitations can only be relieved by defibrillation (electric shock using a special device).
In the treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, which is the most common cause of increased heart rate to 160 - 190 at rest, the effectiveness of RFA reaches 90%. The surgical technique is well developed, and intervention should never be refused if doctors offer it.
Possible complications
A rapid pulse is a sharp or gradual increase in the number of vibrations in the walls of blood vessels, which indicates a lack of oxygen in the cells. The heart tries to increase blood flow, so it works hard. Gradually, the myocardium can no longer contract qualitatively and conduct impulses.
This condition can cause serious complications in the cardiovascular system, lead to a heart attack, or even cause cardiac arrest. Sudden changes in heart rate can lead to brain hypoxia and cause fainting.
Pathological tachycardia can provoke:
- vascular thrombosis;
- persistent arrhythmia;
- cardiac ac src=»https://healthperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/puls-180-190-200-210-220-udarov-v-minutu-1264.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=”631″ height=”407″[/img]
- cardiac ischemia.
If you find out the cause of your rapid pulse in a timely manner, you can avoid serious complications. Timely treatment is the key to a healthy and fulfilling life.
The pulse rises to 190 beats per minute for no apparent reason - this is a serious problem that requires the intervention of a specialist.
If the cause is stress or serious physical exertion, then rest will help normalize the rhythm, and if the cause is illness, then only complex treatment will solve the problem. Urgent care will help avoid complications, one of which could be a heart attack or even death.