When examining heart rate, a qualified specialist is most likely able to determine the diagnosis, assess the general condition of the patient’s body and give recommendations for symptomatic treatment. High pulse is a violation of the standard heart rate in a given period of time, associated with a number of diseases, the treatment of which will lead it to standard values.
What is cardiac tachycardia?
A healthy heart works in a constant rhythm, and normally a person does not feel its beating.
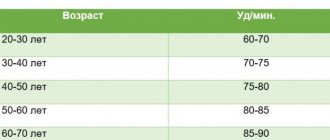
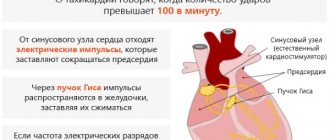
But if the normal heartbeat is disrupted, discomfort in the chest, anxiety, dizziness and pulsation in the area of large vessels appear. During the cardiac cycle, i.e. rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle, the vessels are first filled with blood, and then their blood supply decreases. The vibration of the vascular walls during this cycle is called the pulse. Normally, the heart beats 60-90 times per minute. If the heart rate is more than 90 beats per minute, it is tachycardia, less than 60 is bradycardia.
How to measure pulse?
It is recommended to measure your pulse in the morning immediately after waking up in a lying position. It is better to do this on the wrist, feeling the artery with the middle and index fingers. You need to count the number of hits in 15 seconds and multiply the indicator by 4.
The heart rate in healthy people depends on many factors:
- gender: on average, women's heart beats slightly faster than men's;
- age: with age, the pulse gradually slows down, but after 50-55 years it increases again, especially in women with the onset of menopause;
- environment: poor environmental conditions affect heart rate;
- time of day: during night sleep the pulse slows down, and at 11 o’clock in the day it accelerates to maximum values;
- lifestyle: tachycardia is observed in people who smoke, as well as in people who regularly drink alcohol, with improper work and rest schedules, and lack of sleep;
- Diet: Some foods and drinks, as well as medications, speed up your heart rate.
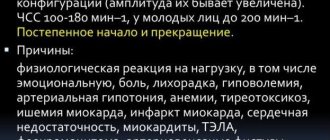
An increase in heart rate can be observed in a completely healthy person after active sports, heavy physical work, with a lack of oxygen, heat, during stressful situations, after drinking a large amount of strong coffee or alcohol (Fig. 1). The heart beats faster in response to external factors. In this case, tachycardia is a reaction to the release of adrenaline into the blood or nervous excitement. Usually the pulse returns to normal after a fairly short rest.
Figure 1. How coffee and alcohol affect heart rate. Source: MedPortal
Another manifestation of the protective function of tachycardia is a rapid pulse in patients with internal bleeding or significant blood loss due to injury. An increase in heart rate allows you to avoid hypoxia and saturate the myocardium with oxygen in conditions of decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood.
Children's pulse
In children, the heart rate is noticeably different, since the growing body has a high need for oxygen and nutrients. An accelerated metabolism leads to an increased heart rate at rest. In newborns, the heart beats at a frequency of 120-140 beats per minute, the most frequent pulse in six-month-old babies is 130-135. With age, the heart rate gradually slows down, and in 15-year-old teenagers it is already approaching the norm for adults.
Is a pulse of 68 beats normal for an athlete, and how can you measure it yourself?
69 beats per minute, the athlete's heart has just warmed up. Yes Yes exactly. Professional skiers, runners and swimmers are able to warm up at a heart rate of 69 beats per minute. At the same time, they can bring the pulse rate to 190-210 beats and work at it for a long/short time. And then recover in 1 minute to 120-110 beats.
This indicates their increased training and cyclical load on the heart. During training of professional athletes, amateur runners, and fitness girls, it is important to measure the pulse. For what? - so as not to drive a person’s heart, leading him to overwork or even loss of consciousness from heavy workload.
How can I do that?
- Using the old and familiar method: Counting with your hand while holding your neck. Find the pulse in the area of the neck artery. Count it within 6 seconds. Then multiply the resulting figure by 10. This way you can more accurately determine your heart rate immediately after exercise.
- Wear a heart rate monitor. This is the sensor that comes with sports watches. Dressed in the chest area. Heart rate readings are displayed on the watch screen.
- Using a pressure apparatus. The electronic device will show you your blood pressure and pulse.
We hope that our article was informative and useful for you..
Remember, a heart rate of 74 is normal and a heart rate of 79 beats per minute is normal. After all, everything depends on the characteristics of our body. From the genetics of our parents. We are able to influence and develop our heart muscle through proper physical activity. Modern technologies (pulse monitors, pressure machines, watches) give us the opportunity to measure our pulse anywhere, track its dynamics and statistics during work. We just have to use it and not overstrain our hearts.
Add AN to your sources so as not to miss important events - Yandex News
- Cosmonaut Shkaplerov spoke about the chaos on the Russian segment of the ISS after filming the film
- Late pregnancy. Until what age can you give birth?
- What heart rate is considered normal?
- Pathologist Marina Kulikova: “With Covid, the patient simply stops breathing because he does not have such an opportunity”
- Sohu: Ukraine turned into “the poorest and most unfortunate country in Europe” after exchanging Russia for the USA
- Priest of the Orthodox Church: “Sobchak needs to be begged for”
Become a member of the CLAN and every Tuesday you will receive the latest issue of “Arguments of the Week” with a discount of more than 70%, along with exclusive materials not included in the newspaper. Get premium access to a library of the most interesting and popular books, as well as an archive of more than 700 published issues for FREE. In addition, you will have the opportunity to benefit from free legal advice from our experts for a whole year.
- Enter your email address, then select any convenient payment method for your annual subscription
- Scan the QR. In the Sberbank Online application that opens, enter the annual subscription cost (490 rubles). Then send the confirmation code by email
Or
Causes
The causes of pathological tachycardia are divided into cardiac ones, i.e. associated with dysfunctions of the cardiovascular system, and extracardiac - caused by diseases of other organs and systems of the body.
Extracardiac causes:
- physical inactivity,
- heat,
- diseases of the endocrine system - hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, low blood sugar,
- anemia - drop in hemoglobin level,
- low blood pressure,
- chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, pneumonia,
- states of shock,
- adrenal tumors,
- lack of weight, strict diets,
- intoxication with certain drugs,
- problems with the nervous system,
- abdominal obesity,
- apnea,
- some diseases of internal organs.
Heart pathologies:
- myocardial infarction and its complications,
- hypertonic disease,
- cardiomyopathy,
- various congenital and acquired heart defects.
Risk factors for developing tachycardia:
- diabetes mellitus and thyroid diseases;
- alcoholism;
- genetic predisposition;
- high blood pressure;
- elderly age.
Tachycardia in pregnant women
An increase in heart rate of 20-30 beats per minute often occurs in women at different stages of pregnancy. This may be due to:
- hormonal changes;
- an increase in the amount of circulating blood;
- pressure from the enlarged uterus on the heart and blood vessels.
In the absence of a history of heart disease, this condition is considered normal and goes away after childbirth. Women with excess weight, endocrine and cardiovascular diseases, and bronchial asthma require increased attention.
Classification of tachycardia
The classification of tachycardia is based on determining the primary sources of rapid heart rate.
Sinus tachycardia
This type of tachycardia is diagnosed when the heart rate is in the range of 100-200 beats per minute. This disorder is a physiological response to irritation of the sympathetic nervous system: stress, physical activity, pain, etc.
Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a gradual onset and smooth normalization of the pulse. A prolonged attack can cause dizziness, decreased blood pressure, and a decrease in the amount of urine produced.
This is the most common type of tachycardia and does not require special treatment. In most cases, the heart rate returns to normal after the cause of the increased heart rate is eliminated.
Ventricular tachycardia
The pathology is based on an increase in the number of contractions of the ventricles and acceleration of the heart rate due to disturbances in the structure of the myocardium or the conduction system of the ventricles. As a result, the electrical impulse is interrupted in the ventricles and circulates in a vicious circle.
The pulse during an attack of ventricular tachycardia increases to 140-220 beats per minute, which can lead to disruption of blood supply to the brain, a sharp drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
This is the most dangerous type of tachycardia and can lead to ventricular fibrillation, a condition in which the heart can beat more than 300 times per minute.
Ventricular tachycardia can lead to circulatory arrest and clinical death.
In the vast majority of cases, the cause of ventricular arrhythmia is coronary heart disease. Sometimes an attack occurs while taking certain medications: cardiac glycosides, psychotropic drugs, anesthetics.
Atrial tachycardia
This type of tachycardia develops in limited areas of the atria. In the general structure of arrhythmias, atrial tachycardias account for 10-15% of cases.
Risk factors for atrial tachycardia:
- hypertonic disease;
- cardiac ischemia;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- chronic bronchitis.
Atrial tachycardia can occur against the background of endocrine disorders, alcohol abuse, and obesity.
Atrioventricular tachycardia
This type of arrhythmia is not associated with pathologies and is more common in adolescents and young adults during physical and emotional stress. In adults, rapid heartbeat appears against the background of heart disease and sclerotic changes in the heart muscle.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
This type of arrhythmia is characterized by attacks of rapid heartbeat with a frequency of up to 220 beats per minute and above. Various forms of paroxysmal tachycardia are diagnosed in 20-30% of patients with arrhythmia.
Normally, electrical impulses are generated in the sinus node, the natural pacemaker of the heart muscle. In paroxysmal tachycardia, they are generated in the ventricles, atria or atrioventricular junction. The attacks begin suddenly and end just as abruptly, repeating regularly at approximately equal intervals.
Attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia impede blood circulation, and the heart works with increased load. Prolonged attacks lead to weakness and fainting.
Arterial tachycardia
Tachycardia of this type is not a separate form of heart rhythm disturbance; it is considered as a symptom of various pathologies. Most often, arterial tachycardia is associated with hypertension and other vascular diseases. Usually detected in older people.
With hypertension, rapid heartbeat is accompanied by shortness of breath, tinnitus, dizziness, and general weakness. A person may not feel a strong pulsation, and a heart rate above 100 beats per minute is determined only by a doctor when measuring blood pressure if a hypertensive crisis is suspected.
Orthostatic tachycardia
With a steady acceleration of the pulse (more than 30 beats per minute in adults and 40 beats in children) when changing from a lying position to a standing position, they speak of orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. This condition is not a separate disease; this term refers to a large number of characteristic symptoms. Treatment is required only for regular attacks accompanied by nausea, dizziness and chest discomfort.
Consequences of increased heart rate
A pulse of 130 beats or more - is this normal or is it still dangerous?
The doctor will definitely notify him of the consequences of this condition.
Prolonged tachycardia can lead to the development of complex diseases, such as:
- arrhythmic shock;
- stroke;
- cerebral ischemia;
- thromboembolism;
- cardiac asthma;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- decreased immunity;
- acute ventricular failure.
An accelerated heart rate of 130 beats indicates certain risks, such as heart overload.
Which will sooner or later lead to its wear. The condition is accompanied by insufficient blood circulation and oxygen starvation, which will cause other organs and the brain to suffer.
Why is tachycardia dangerous?
Tachycardia poses a health hazard if it is caused by dysfunction of the cardiovascular system or other diseases of the internal organs. A rapid heartbeat prevents the heart ventricles from filling with blood, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure and a deterioration in the blood supply to internal organs. In addition, a heart working hard requires much more oxygen. This condition threatens to develop into acute heart failure and lead to heart attack and coronary artery disease.
Clinical picture of tachycordia
In order to promptly diagnose an attack of tachycardia, it is important to know the first and characteristic signs of this condition.
They are the following manifestations:
- darkness in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- prostration;
- lightheadedness or fainting.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing tachycardia is an electrocardiogram. Based on the nature of the ECG, the doctor determines the type of pathology and the degree of its severity (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. ECG picture in the presence of tachycardia. Source: MedPortal
To clarify the main diagnosis, daily Holter ECG monitoring, cardiac MRI, echocardiography and other hardware and laboratory tests are prescribed.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of rapid heartbeat and is carried out comprehensively. First of all, factors that cause tachycardia are excluded: it is forbidden to drink strong coffee, tea, alcoholic beverages, eat chocolate, or smoke. It is recommended to normalize your emotional state and avoid excessive physical activity.
The complex of treatment of the underlying disease includes sedatives and additional drugs that normalize the functioning of the heart muscle.
Photo: v_l / freepik.com
If tachycardia is caused by structural changes in the heart or a disruption in the production of hormones and does not respond to drug treatment, the patient may be offered surgery: radiofrequency catheter ablation, installation of a pacemaker, removal of tumors if present. In any case, the treatment regimen is prescribed by a cardiologist after consultation with other specialists.
Important! Medicines that correct heart rhythm should not be taken without a doctor’s prescription; incorrect selection of therapy can only worsen the disease.
Heart rate is normal
They are used by specialists to determine the level’s compliance and its relationship to standard indicators.
| Person's age (in years) | Rest value (lowest) | The highest allowed value at rest | Conditional norm at rest |
| Up to 12 months | 105 | 165 | 133 |
| Up to 2 years | 95 | 155 | 125 |
| From 2 to 5 | 85 | 125 | 105 |
| From 6 to 8 | 80 | 120 | 100 |
| From 8 to 10 | 70 | 110 | 90 |
| From 11 to 12 | 65 | 105 | 85 |
| From 13 to 15 | 60 | 90 | 80 |
| From 16 to 50 | 62 | 85 | 72 |
| From 51 to 59 | 65 | 86 | 75 |
| From 60 to 80 | 70 | 90 | 80 |
PCSS
are directly combined with the general condition of the body and the slightest deviations should attract the attention of both the patient and specialists.
Numbness, or paresthesia, of the lower leg, from the ankle to the kneecap, is common. The pathology can affect the left leg, the right leg, as well as both limbs - each type of phenomenon has its own causes and treatment features. Read more in the article: “numbness of the leg from the knee to the foot.”
The first signs of a high frequency pulse are an alarming symptom, indicating the onset of a disease or a complicated course of an existing disease.
Unequal time intervals or different pulse depths indicate disruption of the heart muscle (arrhythmia).
Prognosis and prevention
If you follow all medical recommendations and switch to a healthy lifestyle, the prognosis is favorable. The success of therapy depends on the time of contacting a doctor and the adequacy of treatment of the underlying disease.
In order to reduce the risk of developing tachycardia, you should:
- eat varied and regularly, include vegetables, fruits, fish, dairy and seafood in your diet,
- regularly do exercises, cardio exercises,
- avoid stress,
- do not abuse coffee and alcohol, stop smoking.
Photo: DCStudio / freepik.com
Sources
- Utsumueva M.D., Mironov N.Yu., Shlevkov N.B., Kiktev V.G., Gupalo E.M., Kashtanova S.Yu., Mironova N.A., Golitsyn S.P. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in a patient with dilated cardiomyopathy and concomitant cardiac conduction disorders. Clinical case and discussion of the problem. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention. 2020;19(3):2368.
- Salami Kh.F., Shlevkov N.B., Sokolov S.F. Possibilities and limitations of standard electrocardiography for the differential diagnosis of tachycardias with widened QRS complexes. Almanac of Clinical Medicine. 2019;47(4):350-360.