Causes of respiratory arrhythmia
In children and young people during the period of growth and development of internal organs and systems, disruptions in the nervous mechanisms of regulation of cardiac activity often occur. For example, the vagus nerve, which is part of the autonomic nervous system, when excited, leads to a decrease in heart rate. A decreased tone during deep inhalation causes an increase in heart rate; an increased tone during exhalation causes a slower pulse.
In adults, respiratory arrhythmia is a consequence of:
- smoking;
- taking certain medications;
- pathological heart rhythm disturbances;
- infections;
- organic heart lesions (during the rehabilitation period after myocardial infarction, valvular defects, rheumatic myocarditis).
Diagnosis and treatment
The examination begins with an examination and collection of anamnesis, identifying the causes of rhythm disturbances and electrical conductivity of the heart. The main diagnostic methods are:
- electrocardiographic study;
- echocardiography;
- ultrasonography.
The doctor may also prescribe additional hardware and laboratory tests:
- angiography;
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring;
- orthostatic test;
- biochemical and general blood tests;
- consultation with a neurologist, endocrinologist, nutritionist.
The treatment tactics for respiratory arrhythmia are determined by the severity of symptoms, the state of the cardiovascular system, the patient’s age, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases. If the cause of the illness is organic heart damage, the doctor prescribes appropriate drug therapy. In case of arrhythmia against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, stress, emotional overstrain, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Make an appointment (video consultation available)
Your message has been sent
Thank you for contacting Multidisciplinary Medical!
Your message will be processed shortly and we will contact you to clarify the details.
Be healthy!
Join us on social networks!
Current news, promotions, useful information.
How to find us
OUR ADDRESS
Moscow, st. Shchukinskaya, 2
Shchukinskaya, Streshnevo, Sokol
TELEPHONE
+7
Symptoms of respiratory arrhythmia
The main sign of respiratory arrhythmia is the following: during deep breathing, when exhaling, the heartbeat slows down, and when inhaling, it increases. Sinus rhythm increases during emotional stress and physical activity.
Some patients with respiratory arrhythmia experience:
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- nausea.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Symptoms
The main indicator of arrhythmia is a disturbance in the heart rhythm associated with the act of breathing: a slower heartbeat when exhaling, an increase in heart rate when inhaling. As a rule, this pathology does not have symptoms that threaten the life and health of the patient. However, with respiratory arrhythmia, signs may be observed indicating increased excitability of the parasympathetic nervous system, namely:
- darkening of the eyes, weakness – even to the point of fainting;
- sweating, asthenia;
- intolerance to heat or stuffy rooms.
Arrhythmia provokes:
- cardiopalmus;
- dizziness, nausea;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart - “stopping” or “fading”.
Diagnosis of respiratory arrhythmia
Since in most cases, respiratory arrhythmia does not cause any discomfort, it is usually discovered during a medical examination for other diseases. The doctor draws attention to the fact that with deep breathing, the pulse rate changes.
To confirm the diagnosis of respiratory arrhythmia, methods are used:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- Holter monitoring;
- orthostatic test.
Sinus arrhythmia
The human heart must continuously beat in the correct rhythm so that all organs receive a sufficient amount of blood. Even minor malfunctions in the functioning of the cardiac muscle pump can provoke severe disruptions in vital activity. Sinus arrhythmia is a common functional disorder of the cardiovascular system. The disease is diagnosed in patients of any age.
What is sinus arrhythmia?
The term arrhythmia combines a wide range of functional pathologies of the heart that affect the functioning of the myocardium. Doctors classify rhythm disturbances according to the place of occurrence and the nature of the course. Thus, pronounced sinus arrhythmia occurs when the main conduction node of the myocardium is damaged or disrupted. This form of the disease is considered the most benign.
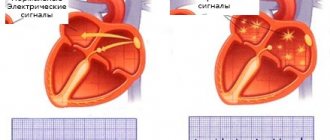
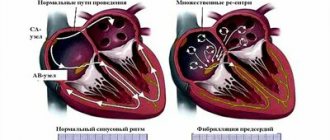
To better understand the nature of the rhythm disorder, it is necessary to have an understanding of the work of the heart. The muscular layer (myocardium) is the main part of the organ responsible for the redistribution of blood in the body. It is thanks to the myocardium that each cell receives a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients on time. The strict rhythm of heart activity, including a contraction phase (systole) and a rest phase (diastole), allows the chambers of the atria and ventricles to fill with blood before a new heartbeat. The rhythm of contractions is regulated by the conductive components of the myocardium - the sinus node, atrioventricular node, His bundle and smaller fibers.
The sinus node occupies a dominant position in the regulation of myocardial function. It is here that electrical impulses are generated, stimulating the contraction of muscle fibers and the release of blood into the vessels. Secondary conducting nodes and fibers are responsible for the gradual spread of the impulse throughout all parts of the myocardium. In this case, the main node generates impulses with a certain frequency - from 60 to 100 beats per minute, which determines the mode of operation of the heart at rest. Sinus arrhythmia is characterized by disruption of the main node of the myocardium.
8
24/7
Main types of pathology:
- Sinus tachycardia is the occurrence of too rapid heartbeats (more than 100 beats per minute). The danger is that this mode of myocardial operation does not allow the parts of the heart to fill with blood before contractions, resulting in hemodynamic disorders.
- Sinus bradycardia is a pathological decrease in the frequency of contractions (less than 60 beats per minute). In this case, the organs do not receive sufficient blood supply.
It should be noted that sinus arrhythmia affects only the frequency of myocardial contractions, while the sequence of operation of the organ does not change. Tachycardia and bradycardia can also occur when cardiac functions are preserved, when the body requires adaptation to certain conditions. Active muscle work requires increased blood supply, and during sleep the need for this mode of heart contraction decreases. The pathological form of rhythm change is characterized by a lack of adaptation.
Causes
The etiology of the sinus form of rhythm disorder is almost no different from the causes of any arrhythmia. The disease may be a consequence of other pathologies of the heart and blood vessels that affect the functioning of the sinus node.
Possible reasons:
- Damage to the muscular lining of the heart due to myocardial infarction, injury or infection.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the myocardium.
- Valve malfunction.
- Blood loss.
- Low or high blood pressure.
- Side effects of drugs that affect the heart.
- Respiratory failure.
- Pathology of the thyroid gland.
- Anemia.
- Abuse of caffeine and alcoholic beverages.
- Disruption of the sympathoadrenal system.
Doctors are not always able to determine the exact cause of the disease. In children and adolescents, sinus arrhythmia can occur without any clinical prerequisites, however, at this age, rare attacks of arrhythmia are not considered dangerous. The most severe forms of pathology occur against the background of organic damage to the myocardium.
Symptoms
Signs of rhythm disturbance may vary depending on the frequency of attacks and the etiology of the disease. In most patients, sinus arrhythmia is asymptomatic. In severe cases of the disease, signs may appear indicating a violation of the blood supply to organs.
Symptoms and signs:
- Pain and discomfort in the heart area.
- Increased sweating.
- Breathing disorders, shortness of breath.
- Sensation of pulsation in temples.
- Dizziness and nausea.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Anxiety and fear.
It should be taken into account that other chronic heart diseases, against the background of which arrhythmia occurs, can aggravate the course of arrhythmia. Heart failure and coronary artery disease will significantly increase neurological symptoms.
8
24/7
Diagnostic methods
Sinus node arrhythmia often requires the use of more thorough diagnostic methods, since attacks can occur relatively rarely. You can only detect changes in your heart rate manually or using an electronic device. However, this is not enough to make a diagnosis, so you need to contact a cardiologist. During the appointment, the doctor will review the patient's medical history, conduct a physical examination, and interview the patient to identify complaints. An important task is to exclude the psychogenic form of rhythm disturbance.
Basic methods of instrumental diagnostics:
- Electrocardiography is the recording of the electrical activity of the heart. Special electrodes connected to a cardiogram recording device are placed on the patient's body. Based on the results of this method, one can judge any dysfunction of the organ, characterized by slow impulse conduction and inconsistent contractions.
- Echocardiography is a visual study of the heart using ultrasound. During the examination, the doctor can observe the functioning of the organ on the screen. EchoCG is an excellent way to basicly diagnose arrhythmia and assess the severity of the condition.
- Long-term recording of a cardiogram using a portable device. The patient is instructed to keep a diary of how he feels so that the cardiogram can be studied during an attack. This is the best way to diagnose a latent form of arrhythmia.
- Stress test - obtaining a cardiogram during palpitations. Thus, attacks of the disease can sometimes occur only under conditions of high stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Angiography with contrast is a scan of the blood vessels of the heart to detect blockages, narrowing and other causes of coronary artery disease or heart attack.
- MRI and CT scans provide highly accurate images of the heart.
- Blood analysis. The cardiologist will primarily be interested in parameters such as electrolyte balance, thyroid hormone concentrations, and the presence of enzymes indicating a recent myocardial infarction.
Comprehensive diagnostics should include functional cardiac testing and imaging. Even if a rhythm disorder is detected by one test, other tests may be needed to find the cause of the disorder.
Drug treatment and prevention
Sinus arrhythmia does not always require treatment. First, the doctor must make sure that the change in rhythm is actually provoked by functional or structural pathologies of the cardiovascular or nervous system. If attacks occur against the background of neuroses, thyroid diseases, lack of electrolytes and other secondary causes, appropriate treatment of the primary condition will be required.
If necessary, a drug treatment regimen is prescribed aimed at preventing the development of attacks and preventing complications. As a rule, doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Direct antiarrhythmic drugs as symptomatic treatment.
- Indirect antiarrhythmic drugs, including cardiac glycosides and beta blockers.
- Blood thinners for stroke prevention.
It must be taken into account that sinus arrhythmia, the treatment of which can be lengthy and ineffective, is highly preventable. Methods to prevent illness include:
- Eliminating fatty foods, alcohol and coffee from the diet.
- Increase physical activity.
- To give up smoking.
- Reducing body weight.
- Coping with stress and anxiety.
- Timely treatment of primary cardiovascular, neurological and metabolic diseases.
- Screening diagnostics of the heart and blood vessels to identify asymptomatic pathologies.
These same methods can be useful if the disease has already been diagnosed.
Surgical interventions
Treatment of sinus arrhythmia may include surgical methods in case of severe disease. As a rule, this is a rhythm disorder due to primary heart pathologies and the ineffectiveness of drug treatment.
Possible surgery options:
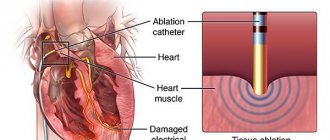
- Radiofrequency ablation is the removal of a problem area in the heart using an electrical current.
- Open surgery on the heart and blood vessels to correct structural pathologies.
- Implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
As a rule, surgical treatments are more reliable.
Thus, a rhythm disorder associated with malfunction of the sinus node in most cases has a benign course. However, if unpleasant symptoms appear, you should not delay contacting a doctor.
8
24/7
Prevention of respiratory arrhythmia of the heart
To normalize heart function, you need to:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- perform breathing exercises regularly;
- eliminate stress;
- Healthy food;
- move more, take walks in the fresh air;
- sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- maintain a daily routine;
- strengthen the immune system.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Symptoms and complications of sinus arrhythmia
Physiological arrhythmia usually does not cause any discomfort.
Pathological sinus arrhythmia can manifest itself in different ways. It most often occurs in three forms: sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia and extrasystole.
Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a heart rate below 60 beats per minute at rest. Patients with bradycardia complain of attacks of weakness, dizziness, and pain in the heart area. Periodically they experience fainting. These symptoms can be observed either all together or separately - each patient has individual manifestations.
Rare heartbeats lead to the fact that an insufficient amount of blood reaches the organs and tissues, they lack oxygen and nutrients, and this negatively affects their vital functions. Frequent complications of sinus bradycardia include strokes, heart failure, and myocardial infarction. This condition can even cause cardiac arrest (called sudden cardiac death).
Sinus tachycardia is an increase in heart rate, usually up to 120, sometimes up to 150 beats per minute. Its signs are a feeling of rapid heartbeat, squeezing pain in the chest (sometimes), attacks of weakness and dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
With sinus tachycardia, the heart fills with less blood than necessary. Blood pressure decreases, organs, and first of all, the heart muscle itself, are insufficiently supplied with blood. Sinus tachycardia is often complicated by the development of myocardial infarction and heart failure.
Pathological sinus extrasystole usually manifests itself as a feeling of a sinking heart followed by a strong shock in the chest, or attacks of increased heartbeat. They may be accompanied by pain in the heart area, pale skin, a feeling of anxiety, and lack of air.
Sometimes all these violations are not felt by a person at all.