Atrial fibrillation - causes, symptoms and treatment
Atrial fibrillation is manifested by scattered, chaotic contraction of the muscle tissue (myocardium) of the atria, at a speed of 350-600 pulse waves per minute. As a result, the atria do not contract fully, and the presence of blood in the ventricles weakens. Some blood is retained in the atria, which increases the risk of blood clots.
The presence of an outbreak of atrial fibrillation for more than 48 hours leads to a high risk of developing ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, thromboembolism of various organs and peripheral vessels, and severe cardiovascular failure.
What it is?
Atrial fibrillation is translated from Latin as “madness of the heart.” The term “atrial fibrillation” is a synonym, and the definition of the disease is as follows: atrial fibrillation is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, characterized by chaotic activity of the atria with their contraction at a frequency of 350-700 per minute.
This heart rhythm disorder is quite common and can occur at any age - in children, the elderly, middle-aged and young men and women. Up to 30% of cases of need for emergency care and hospitalization for rhythm disturbances are associated precisely with the consequences of atrial fibrillation. With age, the frequency of the disease increases: if up to 60 years of age it is observed in 1% of patients, then later the disease is registered in 6-10% of people.
With atrial fibrillation, contraction of the atria occurs in the form of their twitching, the atria seem to flutter, flickering ripples run through them, while individual groups of fibers work uncoordinated in relation to each other. The disease leads to a natural disruption of the activity of the right and left ventricles, which cannot throw a sufficient amount of blood into the aorta. Therefore, with atrial fibrillation, the patient often exhibits a pulse deficiency in large vessels and irregular heart rate. The final diagnosis can be made by ECG, which reflects the pathological electrical activity of the atria, and also reveals the random, inadequate nature of cardiac cycles.
Classification of atrial fibrillation
According to the duration of clinical manifestations.
The following forms of AF are distinguished:
- Paroxysmal (paroxysmal).
Single episodes of AF lasting no more than 48 hours in the case of cardioversion, or up to 7 days in the case of spontaneous restoration of rhythm. - Persistent form.
Episodes of atrial fibrillation lasting more than 7 days without spontaneous recovery, or atrial fibrillation amenable to cardioversion (medical or electrical) after 48 hours or more. - Permanent form (chronic).
Continuous AF not amenable to cardioversion, if the physician and patient decide to abandon attempts to restore sinus rhythm.
By heart rate
- Tachysystolic.
Atrial fibrillation with a ventricular rate of more than 90–100 beats. per minute - Normosystolic.
The AV node allows the ventricles to contract at a rate of 60–100 beats/min. - Bradysystolic.
Heart rate with this form of fibrillation does not reach 60 beats/min.
Causes
Various acute and chronic conditions can provoke heart rhythm disturbances such as atrial fibrillation.
Acute causes are:
- exposure to temperature factors – hyper- or hypothermia;
- operations;
- myocardial infarction;
- excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, nicotine;
- inflammatory heart diseases – pericarditis, myocarditis;
- taking drugs with arrhythmogenic effects;
- mechanical effects on the body - injuries, vibration;
- some other types of arrhythmias (WPW syndrome).
The impact of the factors mentioned above on a healthy heart will most likely not provoke atrial fibrillation - its occurrence is facilitated by structural and metabolic changes in the myocardium, as well as some types of non-cardiac pathology:
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart tumors;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- endocrine pathology, in particular;
- cardiac ischemia;
- acquired and some congenital heart defects;
- arterial hypertension;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (calculous cholecystitis, diaphragmatic hernia);
- pathology of the central nervous system;
- intoxication.
Mechanism of action
The mechanisms of action of antiarrhythmic drugs have not yet been clarified. However, many drugs have similar effects. Antiarrhythmic drugs change the flow of sodium, potassium and calcium ions across the cardiomyocyte membrane, resulting in a change in its electrical potential. The main electrophysiological effect is a change in the speed and duration of AP phases, the speed of electrical impulse conduction, refractoriness and automaticity of the heart muscle.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
It should be remembered that in 20-30% of cases, atrial fibrillation occurs without symptoms, without causing any sensations. The discovery of this form usually occurs by accident.
The main complaints of patients with atrial fibrillation include:
- the main complaint is sudden attacks of rapid irregular heartbeat or a feeling of constant irregular heartbeat, pulsation of the veins in the neck;
- squeezing pain in the heart area like angina pectoris;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- difficulty breathing (shortness of breath), especially during physical activity;
- dizziness, unsteadiness of gait;
- fainting states, fainting;
- increased sweating;
- rarely, an increase in urine (polyuria) with the release of natriuretic hormone.
With the development of a permanent form of the disease, patients cease to feel discomfort or interruptions in the functioning of the heart and adapt to living with this disease.
Complications
The most dangerous complications of MA:
- The development of thromboembolism due to thrombus formation in the chambers of the heart.
- Heart failure.
- The onset of sudden death due to cardiac arrest caused by blockage of its internal orifices.
- The development of cardioembolic stroke, which occurs due to stagnation of blood in the atria.
- Cardiogenic shock, which provokes a significant decrease in blood pressure, as a result of which the organs and tissues of the human body cease to receive the necessary nutrition, and irreversible processes begin in them.
- The formation of blood clots, which can travel through the bloodstream to any organ, including the brain, causing the death of brain tissue (stroke).
Atrial fibrillation seems to be a simple disease only at first glance. Patients with this diagnosis should remember that atrial fibrillation is a pathology, the danger of which is associated with complications that arise as a result of the lack of timely adequate treatment or the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
How to take medications and control your condition?
Each patient taking tablets for arrhythmia should be regularly monitored by a doctor. Timely examination allows you to assess the effectiveness of therapy, identify side effects in the early stages and take measures to eliminate them. During the examination, the doctor evaluates the following indicators:
- General condition and complaints of the patient.
- Blood pressure numbers.
- Pulse.
- Heart rate.
- Heart rhythm according to electrocardiogram or Holter monitoring results.
- State of the cardiovascular system according to ultrasound and echocardiography.
- General blood test, coagulogram, biochemical parameters, lipid profile.
- Electrolytes in the blood.
- Kidney and liver tests.
- Hormones.
Diagnostics
Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed based on:
- collection and analysis of anamnesis;
- detection of characteristic complaints of the patient himself;
- detection of certain specific changes in standard electrocardiogram recordings.
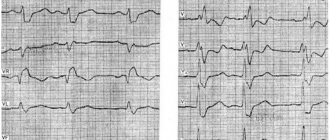
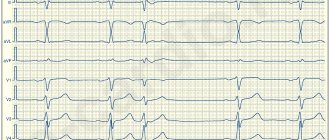
Electrocardiographic signs of the pathology in question are as follows:
- Multiple f waves are detected, confirming atrial fibrillation (flickering). This type of wave may differ in amplitude, shape and other characteristics;
- the recordings completely lack P waves, which are necessarily detected in normal sinus heart rhythm;
- while the QRS complexes are preserved, a chaotic violation of the RR intervals is observed.
In addition, when performing standard electrocardiography, doctors have the opportunity to determine the patient’s associated cardiac pathology that provokes rhythm disorders. Also, to establish an accurate diagnosis and detect all concomitant pathologies, doctors can use diagnostic techniques such as Holter monitoring, echocardiography, cardiac ultrasound, etc.
An example of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation on an ECG
Cost of drugs
Advertising:
Treatment with the drugs presented in the article is usually carried out in a hospital setting. Therefore, patients do not need to buy drugs. In some cases, therapy is possible on an outpatient basis. The table below shows comparative means for these medications.
| Drug name | approximate cost |
| Esmolol | 100-1500 rub. |
| Metoprolol | 100-300 rub. |
| Verapamil | 50-100 rub. |
| Diltiazem | 200-1000 rub. |
| Cordaron | 100-1000 rub. |
| Digoxin | 200-2000 rub. |
| Sotalol | 100-700 rub. |
The table shows that the final cost of drugs may vary. This is due to different dosages and release forms. In addition, the country of origin plays an important role. Foreign medicines are often much more expensive, but their therapeutic effectiveness is comparable to domestic medicines.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
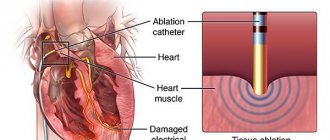
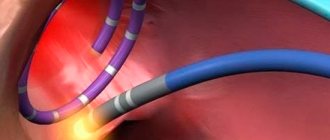
Today, several treatment methods are used for atrial fibrillation, aimed at restoring an adequate heart rhythm and preventing new attacks. Medicines and electrical cardioversion are used. If the effectiveness of these methods is weak, surgical treatment methods are used - catheter ablation or implantation of a pacemaker. An integrated approach to therapy helps prevent new attacks.
The following drugs are used for atrial fibrillation:
- Blood thinners - antiplatelet agents - prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Beta blockers (betaxolol, carvedilol, nebivalol, metoprolol, pindolol, propraolol, celiprolol, esmolol) and calcium blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) - they slow down the heart rate. These medications for atrial fibrillation prevent the ventricles from contracting too quickly, but do not regulate the heart rhythm.
- For antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulants are prescribed that do not prevent the formation of blood clots, but reduce the risk of this, and, consequently, the occurrence of strokes (heparin, fondaparinux, enoxaparin).
- Also, when atrial fibrillation is diagnosed, medications are used that prevent the formation of blood clots and strokes (warfarin, Pradaxa).
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone, dronedarone, ibutilide, procainamide, propafenone, sotalol, flecainide).
Regular blood tests are required to monitor the effects of medications. Only a doctor can choose the right pills for atrial fibrillation, since many of them have serious contraindications, as well as proarrhythmic activity, when taking the drug itself can unexpectedly provoke atrial fibrillation.
Before treating atrial fibrillation, the patient’s concomitant diseases should be taken into account. Sometimes medication is started in a hospital, where doctors can more easily monitor the body's response and heart rate. With this therapy, in 30-60% of cases the patient's condition improves, but over time the effectiveness of the drugs may decrease. In this regard, doctors often prescribe several antiarrhythmic drugs at once.
Calcium blockers
Advertising:
This group of medications includes Verapamil and Diltiazem. These drugs are familiar to people with various pathologies of the cardiac system. It is considered advisable to take them in the absence of symptoms of heart failure and at the same time there are contraindications to the use of beta blockers. However, when patients are diagnosed with cardiac asthma, calcium blockers are never prescribed to patients.
Cordaron
This drug is only suitable for temporary treatment. It is highly effective and has a pronounced effect. If it is used in a course of long-term therapy, the development of complications that affect the main systems of internal organs cannot be ruled out.
Cordarone is also prohibited for use by patients with individual iodine intolerance (in this case, it is replaced with a complete analogue - Sotalol), magnesium and potassium deficiency, and pathologies of the endocrine system.
Before prescribing, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, including the risks of electrolyte disturbances. It is recommended to start taking the drug with a minimum dose.
Cordarone is available in two dosage forms: tablets and solution for injection. The dosage is always selected individually. The initial dose of tablets is usually divided into several doses (600-800 mg) and gradually increased to a maximum of 10 g. The injection solution is usually used to achieve an immediate antiarrhythmic effect or when it is not possible to take a tablet.
Digoxin
This drug is used in long-term therapy. It is also used when there is an urgent need to control ventricular contractions and pulse. Digoxin is suitable for patients with heart failure due to its mechanism of action. the active components of the drug not only stop arrhythmic manifestations, but also effectively stimulate the work of the main muscle of the body, increasing the ejection fraction.
It should be noted that Digoxin is poorly excreted from the body. Therefore, general intoxication cannot be ruled out.
If a doctor prescribes a medication for long-term use, it is necessary to regularly monitor the quantitative indicators of the active substance in the blood. If it is critically high, the medicine is discontinued and symptomatic treatment is then prescribed.
Digoxin is administered intravenously by drip or bolus. The dosage is always selected individually and is determined not only by the course of the underlying disease, but also by the need to achieve a rapid therapeutic effect. If the patient has previously taken cardiac glycosides, start with a small dose of Digoxin.
Treatment of permanent atrial fibrillation
In this form, the patient is prescribed tablets that slow down the heart rate. The main ones here are the group of beta blockers and cardiac glycosides, for example, Concor 5 mg x 1 time per day, Coronal 5 mg x 1 time per day, Egilok 25 mg x 2 times per day, Betaloc ZOK 25-50 mg x 1 time per day etc. Of the cardiac glycosides, digoxin 0.025 mg is used, 1/2 tablet x 2 times a day - 5 days, break - 2 days (Sat, Sun).
It is necessary to prescribe anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, for example, cardiomagnyl 100 mg at lunch, or clopidogrel 75 mg at lunch, or warfarin 2.5-5 mg x 1 time per day (necessarily under the control of INR - a parameter of the blood coagulation system, 2.0-2.5 is usually recommended). These drugs prevent increased thrombosis and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Chronic heart failure should be treated with diuretics (indapamide 1.5 mg in the morning, veroshpiron 25 mg in the morning) and ACE inhibitors (Prestarium 5 mg in the morning, enalapril 5 mg x 2 times a day, lisinopril 5 mg in the morning), which have an organoprotective effect on the blood vessels and heart.
Lifestyle with atrial fibrillation
All heart diseases require leading a lifestyle that is traditionally characterized as healthy. Atrial fibrillation is no exception.
Standard recommendations include light physical activity for atrial fibrillation: morning exercises, daily walks in the fresh air. A person should maintain natural mobility and should not lie down all the time (except during periods of an arrhythmic attack).
A separate issue is the combination of the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and alcohol. People with heart disease should not abuse alcohol.
At the same time, it is known that in small quantities alcohol can have a positive effect, in particular: on the nervous system (calming effect), on the digestive system (stimulates digestion), on blood vessels (dilates blood vessels). In exceptional cases, a person suffering from atrial fibrillation can drink no more than 50 g of a drink with 40% alcohol and no more than 150 g of a drink with 12% alcohol per day.
Diet
The diet of such patients should be based on plant-based, low-fat foods, as well as whole grain porridges and water soups. Vegetable stews and casseroles, fresh salads seasoned with a small amount of any refined oil, boiled or steamed sea fish are shown.
You need to eat in small portions: overeating causes irritation of the vagus nerve, which has a depressing effect on the function of the sinus angle, where pathological impulses then arise.
Separately, I would like to say about any alcohol: it should be completely excluded from the nutrition system. Even in relatively healthy people, drinking alcohol can provoke an attack of arrhythmia, which can be very difficult to stop due to rapidly occurring degenerative changes in the heart.
What's the forecast?
The prognosis for life with atrial fibrillation is determined primarily by the causes of the disease. For example, for survivors of acute myocardial infarction and significant cardiosclerosis, the short-term prognosis for life can be favorable, but for health in the medium term unfavorable, since in a short period of time the patient develops chronic heart failure, which worsens the quality of life and shortens it duration.
However, with regular use of medications prescribed by a doctor, the prognosis for life and health undoubtedly improves. And patients with a permanent form of MA registered at a young age, with proper compensation, live with it for up to 20-40 years.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of the disease is determined by its type. We can talk about the development of tachysystolic, bradysystolic, constant and paroxysmal forms. Additionally, the specialist must check the patient’s psycho-emotional state, the condition of his heart valves and myocardium.
Peritonitis is an inflammation of organs in the abdominal cavity, accompanied by severe attacks of pain. Symptoms of the disease in adults do not go away on their own. Read more in the article: “peritonitis in adults: causes and symptoms.”
From a diagnostic point of view, the most difficult is the tachysystolic variant. In the case of this pathology, patients may complain of the following health problems:
- the occurrence of severe shortness of breath even after minor physical activity, and sometimes at rest;
- rapid heartbeat (up to 600 beats per minute);
- inability to do basic work;
- aching pain in the sternum area.
The listed symptoms may also appear in other forms of atrial fibrillation, but less pronounced. The frequency of attacks is largely determined by the patient's individual history. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathological process becomes chronic.
Advertising:
Atrial fibrillation is not always accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture. Quite often, people learn about their diagnosis by chance, for example, during an annual medical examination or when visiting a doctor for another issue. If the disease proceeds according to a typical scenario, the following disorders may appear:
- state of polyuria;
- panic attacks;
- unusual heartbeat that speeds up and slows down without a specific rhythm;
- tremor of the lower and/or upper extremities;
- dizziness, which often leads to loss of consciousness;
- constant feeling of weakness;
- pale skin;
- breathing problems even at rest;
- frequent changes in blood pressure.
In some cases, patients experience discomfort in the sternum, difficulty in inhaling air, and strong pulsation of blood vessels in the neck area. These signs may also indicate atrial fibrillation.
Complete disappearance of symptoms is possible in the absence of any treatment. If the doctor confirmed the diagnosis during the examination, you must always have medications on hand to stop the next attack and undergo a full course of treatment. When the patient’s profession is associated with emotional experiences or severe physical stress, the specialist usually recommends changing his occupation. Otherwise, work can only aggravate the course of the pathological process.