Arrhythmia - symptoms and treatment
First aid for an arrhythmia attack
First aid measures depend on the specific arrhythmia, and its type can only be determined by a doctor. Therefore, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help.
Is it possible to cure arrhythmia?
Cardiac arrhythmias vary greatly in prognosis. Some are completely harmless, and some are dangerous. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias is not always required. First, treatment is appropriate when arrhythmia reduces quality of life. Secondly, it makes sense to treat those arrhythmias that worsen the prognosis, that is, they can lead to premature death or other complications (and the reality of such complications must be proven in clinical studies). Accordingly, asymptomatic cardiac arrhythmias that do not lead to any sensations are not treated in most cases.
In addition, the doctor must try to establish what caused the arrhythmia, and then prove the connection between the suspected causative factor and the arrhythmia itself.
When the decision about the need to treat a particular cardiac arrhythmia is made, the question arises of how to treat it.
Surgery
For many decades, the doctor had no other treatment options for heart rhythm disorders other than medication. Rare exceptions include electrical shock therapy, which delivers a shock using an external defibrillator in a critical situation to eliminate a life-threatening arrhythmia, and transesophageal electrical stimulation of the heart to eliminate some supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
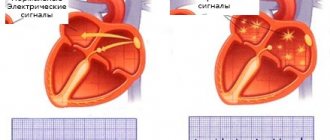
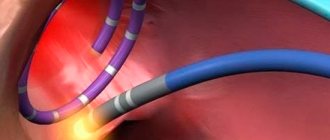
Since the 90s of the last century, and in Russia since the 2000s, a new treatment method has appeared that is effective for many cardiac arrhythmias - radiofrequency ablation (RFA). The method allows in many cases to permanently relieve the patient of the need to take medications to treat arrhythmias. The essence of the method is a local radiofrequency effect on the source of arrhythmia or on the pathological path of electrical impulse circulation in the heart. The procedure is carried out using a catheter passed to a specific area in the heart through a puncture in a vessel (usually in the thigh). Due to the effect through the tip of the catheter, local heating of the heart muscle area occurs up to 70 °C. As a result, in this place there is a local death of cells involved in the unwanted generation of impulses or in their unwanted conduction. Thus, the conditions for the occurrence and maintenance of certain cardiac arrhythmias, for example, ventricular tachycardia, disappear.
Almost all supraventricular tachyarrhythmias can be treated with RFA: atrioventricular nodal tachycardia, tachycardias involving accessory pathways, atrial flutter, focal atrial tachycardia, and, with less success, atrial fibrillation.[9] In addition, this method treats many types of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular extrasystoles, if it is very frequent (tens of thousands of extrasystoles per day) and comes from one focus.[10]
Another high-tech treatment for potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias is implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator.[10] This device is capable of eliminating already developed ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation in two ways: by electrical stimulation of the ventricles at a rhythm exceeding the tachycardia rhythm, or by applying a fairly powerful electrical discharge, which is quite painful, but saves lives. Thus, a cardioverter-defibrillator is used in cases where there is a real risk of sudden death due to ventricular arrhythmias.[13]
Electrocardioversion
Electrical cardioversion (defibrillation) is used when the arrhythmia sharply worsens the patient's condition and is accompanied by a significant drop in blood pressure. It is also sometimes performed routinely to restore sinus rhythm if atrial fibrillation persists.
Pharmacotherapy
However, in many cases, cardiac arrhythmias are treated with medications. Most often, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed in the case of atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), in which case the effectiveness of RFA is not so high. Another situation in which antiarrhythmic drugs are often used is frequent premature beats (thousands or tens of thousands of untimely heartbeats per day) accompanied by symptoms. Less commonly, the drug method is used to treat other arrhythmias - for example, ventricular tachycardia, supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Unfortunately, few antiarrhythmic drugs are registered in Russia compared to Europe or the USA. Available in our country are “Novocainamide” (still used for intravenous administration in the emergency treatment of paroxysms of atrial fibrillation and rarely ventricular tachycardia), “Lidocaine” (for intravenous administration for ventricular tachycardia), “Etatsizin”, “Allapinin” and “Propafenone”. " These drugs exist in the form of tablets and are prescribed for long-term use in order to prevent the occurrence of a wide range of ari in the form of tablets and solution is also used to eliminate paroxysms of atrial fibrillation - a universal antiarrhythmic drug, but is used mainly as a backup antiarrhythmic. But it can be prescribed for organic damage to the heart (previous myocardial infarction, low cardiac contractility, severe left ventricular hypertrophy, etc.), while Etatsizin, Propafenone and Allapinin cannot be used in these conditions.[11]
Sotalol is an antiarrhythmic drug to prevent attacks of atrial fibrillation, as well as ventricular arrhythmias. Available in tablets.
Another class of drugs for arrhythmia are calcium antagonists - Verapamil and Diltiazem. They are used for some supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, both for long-term use in tablets and to eliminate developed attacks of arrhythmias with a high heart rate.
Beta-blockers form an independent class of antiarrhythmic drugs, although their direct antiarrhythmic activity is low. Their main effect is their ability to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death, mainly in people with low cardiac contractility and associated heart failure.[11] The most studied in this regard are Metoprolol succinate, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol and Nebivolol.
In the treatment of atrial fibrillation and flutter, the most important place is occupied by antithrombotic drugs, which reduce blood clotting and thereby reduce the risk of blood clots (in these cardiac arrhythmias it is increased). These are Warfarin, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban. Accordingly, taking these medications reduces the risk of stroke associated with thromboembolism.
Lifestyle
Some arrhythmias are provoked by stress, abuse of coffee and caffeine-containing drinks, smoking, lack of sleep, physical activity and taking certain medications. Therefore, the doctor first of all looks for a cause-and-effect relationship between lifestyle factors and the occurrence of arrhythmia. Sometimes the patient himself notices this connection. In such cases, if you eliminate the provoking factor, you can get rid of the arrhythmia. However, it is not always possible to detect such a connection.
Folk remedies
If you suspect an arrhythmia, you should consult a doctor, get diagnosed and adhere to the prescribed treatment. Traditional methods of therapy are not scientifically substantiated and can be hazardous to health. Without adequate treatment, arrhythmia can cause serious complications: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia
Risk factors for developing cardiac arrhythmia:
- various CVDs: ischemic heart disease (myocardial infarction, angina pectoris), arterial hypertension, heart defects, myocarditis, atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, etc.;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, in particular thyrotoxicosis;
- diseases of internal organs;
- brain diseases, traumatic brain injuries;
- metabolic disorders;
- blood diseases;
- infections of various types;
- mature and old age;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- taking certain medications, narcotic substances;
- mental, emotional and physical overload;
- passion for caffeinated drinks (energy drinks).
Cardiac arrhythmias of unknown origin are usually called idiopathic arrhythmias .
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia
Treatment begins with eliminating the causes of cardiac arrhythmia - treatment of underlying and concomitant diseases, correction of the psycho-emotional state, and lifestyle changes.
Pharmacotherapy in the treatment of extrasystoles, the treatment of sinus tachycardia and numerous other types of cardiac arrhythmias involves the use of drugs such as:
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- beta blockers;
- anticoagulant drugs (for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter - if indicated);
The selection of an antiarrhythmic drug is carried out only by a specialist, since uncontrolled use of these drugs can lead to life-threatening conditions!
If drug treatment of cardiac arrhythmia is inappropriate, electrical pulse therapy (cardioversion) and surgical treatment methods are used to normalize the heart rhythm:
- cardioversion - administration of a short-acting intravenous anesthetic to the patient and short-term exposure to an electric current discharge in the heart area;
- radiofrequency catheter ablation - removal (by cauterization) of additional pathological pathways and pathological foci of arrhythmia;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator (a device that combines the functions of a direct current defibrillator and an electronic rhythm synchronizer) into the chest;
- implantation of an electric pacemaker, etc.
Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmia and heart block at MedicCity has a number of advantages. High-precision diagnostics of cardiac arrhythmia at the MedicCity clinic allows us to identify the disease at an early stage of development. The antiarrhythmic treatment prescribed by our qualified cardiologists will improve your well-being, avoid complications and maintain your health! We diagnose and treat a wide range of cardiovascular diseases using the most modern techniques.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia. Diagnosis of blockades
Diagnosis begins with a history and physical examination of the patient.
From laboratory and instrumental studies the following are usually prescribed:
- Blood tests (general and biochemical);
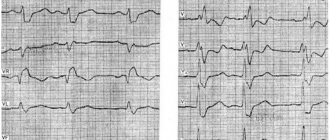
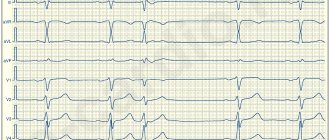
- standard electrocardiography;
- Holter monitoring ECG;
- Echo-CG (ultrasound of the heart);
In some cases, an invasive electrophysiological study (used, for example, to determine indications for radiofrequency ablation, determine indications for implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator).
1 Ultrasound of the heart for arrhythmias
2 ECGs for arrhythmias
3 ECHO-kg for arrhythmias