General rules:
- For most studies, it is recommended to donate blood in the morning, from 8 to 11 o’clock, on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and blood collection, you can drink water as usual), on the eve of the study, have a light dinner with limited intake of fatty foods. food. For tests for infections and emergency studies, it is acceptable to donate blood 4-6 hours after the last meal.
- ATTENTION! Special preparation rules for a number of tests: strictly on an empty stomach, after a 12-14 hour fast, you should donate blood for gastrin-17, lipid profile (total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoprotein (a), apolipo -proten A1, apolipoprotein B), glucose tolerance test.
- On the eve of the study (within 24 hours), avoid alcohol, intense physical activity, and taking medications (in consultation with your doctor).
- 1-2 hours before donating blood, refrain from smoking, do not drink juice, tea, coffee, you can drink still water. Avoid physical stress (running, quickly climbing stairs), emotional excitement. It is recommended to rest and calm down 15 minutes before donating blood.
- You should not donate blood for laboratory testing immediately after physiotherapeutic procedures, instrumental examination, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, massage and other medical procedures.
- When monitoring laboratory parameters over time, it is recommended to conduct repeated tests under the same conditions - in the same laboratory, donate blood at the same time of day, etc.
- Blood for research must be donated before starting to take medications or no earlier than 10–14 days after their discontinuation. To assess the control of the effectiveness of treatment with any drugs, a study should be conducted 7-14 days after the last dose of the drug.
If you are taking medications, be sure to notify your doctor.
General rules apply to all tests, but some tests require special preparation and additional restrictions. It is very important to strictly follow the recommendations below, since only in this case will reliable research results be obtained.
General rules for preparing for sputum tests
- The patient collects sputum independently through deep coughing.
- Sputum collection is recommended to be carried out in the morning.
- Before collecting sputum, it is recommended to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth and throat with boiled water.
- Smears (scrapings) from the surface of the cervix (external uterine pharynx) and cervical canal for atopy.
- It is advisable to take smears no earlier than on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
- You cannot obtain smears within 24 hours after sexual intercourse, the use of lubricants, vinegar or Lugol's solution, tampons or spermicides, douching, insertion of medications, suppositories, creams into the vagina, including gels for ultrasound examination.
- In case of acute infection, it is advisable to obtain material for the purpose of examination and identification of the etiological agent; after treatment, but not earlier than 2 months, cytological control is necessary.
General urine analysis
On the eve of submitting urine for analysis, it is not recommended to eat fruits and vegetables that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots, etc.), not to take diuretics, and to avoid significant physical activity.
Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the genitals. Women are not recommended to take tests during menstruation.
To properly collect the material, release a small amount of urine (the first 1-2 seconds) into the toilet, and then, without interrupting urination, place a container to collect urine. To donate, you need to collect approximately 50 ml.
The material must be delivered to the laboratory in the morning of the same day. You should not store urine for a long time, because... this leads to a change in its physical properties, the proliferation of bacteria and the destruction of sediment elements.
General rules for preparing for hair analysis
Scalp hair is the most preferred biomaterial for research. Hair from other areas of the body should only be used if there is no hair on the head.
- Stop using hair treatments 2 weeks before submitting your hair for analysis. Dyed, bleached, permed hair is not suitable for research. You must wait until enough hair has grown back to collect a hair sample.
- Hair should be clean and dry (it is advisable to wash your hair no later than 24 hours before collecting hair). Before the study, it is not allowed to apply any cosmetic or medicinal products (creams, oils, gels, etc.) to the hair.
- Avoid professional contact of hair with external contaminants (welding, mining) between shampooing and hair collection.
- Before collecting hair, thoroughly wash and dry your hands and scissors.
Biochemistry
Urea
1-2 days before the study, you must follow a diet: stop eating foods rich in purines - liver, kidneys, and also limit meat, fish, coffee, tea in your diet as much as possible. Intense physical activity is contraindicated.
Cholesterol, lipoproteins
Two weeks before the study, it is necessary to discontinue drugs that lower blood lipid levels, unless the goal is to determine the lipid-lowering effect of therapy with these drugs.
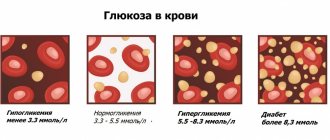
Glucose
When donating blood for glucose (in addition to the basic requirements for preparing for tests), you should not brush your teeth, chew gum, or drink tea/coffee (even unsweetened). A morning cup of coffee will dramatically change your glucose levels. Contraceptives, diuretics and other medications also have an effect.
Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out only if there are preliminary results of determining glucose on an empty stomach, without load. The glucose content in blood plasma is determined on an empty stomach and 2 hours after a glucose load.
It is necessary to follow a normal diet (with a carbohydrate content of more than 125-150 g per day) and adhere to the usual physical activity for three days before the study. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach after an overnight fast for 12-16 hours (during this time you should not smoke or drink alcohol).
During the study, the patient should lie or sit quietly, not smoke, not be overcooled, and not engage in physical activity.
It is not recommended to conduct research after and during stress, after operations and childbirth, during inflammatory processes, alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis, during menstruation, and in gastrointestinal diseases with impaired glucose absorption.
Before the test, it is necessary to exclude medical procedures and medications (adrenaline, glucocorticoids, contraceptives, caffeine, thiazide diuretics, psychotropic drugs and antidepressants).
Discontinuation of medications is carried out only after preliminary consultation of the patient with a doctor.
for CHILDREN UNDER 14 YEARS OLD .
PREGNANT women are recommended to carry out a glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks, this allows identifying women with gestational diabetes with an accuracy of 98%.
Haptoglobin
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude the use of drugs: dapsone, methyldopa, sulfasalazine, estrogens, oral contraceptives, tamoxifen, androgens.
Alpha-2-macroglobulin
You must abstain from meat for three days before the test.
FibroTest, FibroMax, SteatoScreen
Blood sampling is carried out strictly on an empty stomach in the morning. It is not recommended to take ascorbic acid 1-2 days before the test; it is also necessary to exclude medications and foods that cause artificial coloration of the serum (carrots, oranges).
To conduct a FibroMax study, you must indicate your exact weight and height.
Bacteriological studies:
Discharge from the eyes
The material is taken from the affected areas at the height of the inflammatory process in compliance with the rules of asepsis. At least 5-6 hours before the study, all medications and procedures are canceled. The doctor takes the material with a separate swab for each eye.
Conjunctiva
If there is abundant purulent discharge, use a sterile dry cotton swab to take pus from the inner surface of the lower eyelid moving towards the inner corner of the palpebral fissure. It is necessary to ensure that the eyelashes do not touch the tampon (hold the eyelids with your hands).
Edge of the eyelids
Crusts of pus are removed with tweezers. The material is taken from the sore at the base of the eyelashes.
Cornea
The material for research is taken after anesthesia with a sterile dry cotton swab.
Nasal discharge
The material from the nasal cavity is taken with a dry sterile cotton swab, which is inserted deep into the nasal cavity. A separate swab is used for each nasal passage.
Nasopharyngeal discharge
Material from the nasopharynx is taken with a sterile posterior pharyngeal cotton swab, which is inserted through the nasal opening into the nasopharynx. If a cough begins, the tampon is not removed until it is over. To test for diphtheria, films and mucus from the nose and throat are examined simultaneously.
Oral material
Material from the oral cavity is taken on an empty stomach or 2 hours after a meal with a sterile cotton swab from the mucous membrane or its affected areas at the exits of the ducts of the salivary glands, the surface of the tongue, and from ulcers. If there is a film, remove it with sterile tweezers.
Ear material
The doctor takes the material for inflammation of the middle ear. The skin of adjacent areas is treated with an antiseptic solution.
Hormones
Blood for hormonal studies must be donated on an empty stomach in the morning. If this is not possible, blood can be donated for some hormones 4-5 hours after the last meal in the daytime/evening hours (except for those studies for which blood must be donated strictly in the morning). 1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from the diet; the last meal should not be large. 1 day before the study, psycho-emotional and physical comfort (calm state without overheating and hypothermia) is necessary.
Thyroid hormones
During the initial check of thyroid hormone levels, discontinue medications that affect thyroid function 2-4 weeks before the test (after consultation with your doctor). When monitoring treatment, exclude taking medications on the day of the study and be sure to note this on the referral form (also note information about taking other medications - aspirin, tranquilizers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives).
Sex hormones
In women of reproductive age, the results of hormonal studies are influenced by physiological factors associated with the phase of the menstrual cycle. When examining sex hormones, indicate the phase of the menstrual cycle. Hormones of the reproductive system must be taken strictly on the days of the cycle:
- LH, FSH – 3-5 days of the cycle;
- Estradiol – 5-7 or 21-23 days of the cycle;
- Progesterone – 21-23 days of the cycle;
- 17-OH-progesterone, DHA sulfate, testosterone – days 7-9;
- Prolactin - donate blood in the morning at rest; before the study, exclude palpation of the mammary glands.
Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH/MIS), Inhibin B
For women, the study is carried out on days 3-5 of the menstrual cycle. 3 days before taking blood, avoid intense sports training. The study should not be performed during any acute illness. Do not smoke 1 hour before taking blood.
Adrenaline and norepinephrine
8 days before the study, exclude medications: salicylates, β-blockers. 1 day before the test, you must refrain from heavy physical activity, exclude alcohol, coffee, tea, B vitamins, and bananas.
Renin, angiotensin
Before the study, exclude the use of estrogens (1-2 months before), diuretics (3 weeks before), and antihypertensive drugs (one week before). Blood collection should be carried out in a sitting or standing position.
Aldosterone
In consultation with your doctor, 8 days before the study, discontinue antihypertensive drugs, β-blockers, laxatives, corticosteroids, diuretics, and antidepressants. 3 weeks before the study, discontinue aldosterone antagonists.
ACTH, cortisol
Due to the fact that ACTH and cortisol are stress hormones, you need to calm down and relax for 20 minutes before donating blood. Any stress causes an unmotivated release of these hormones into the blood, which will lead to an increase in this indicator. The level of these hormones changes cyclically throughout the day, so the most informative results are studies conducted in the morning before 9 o’clock.
Insulin, C-peptide
Donate blood strictly in the morning.
Gastrin 17, Gastrin-17 stimulated, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, H. Pylori IgG
Blood must be donated for testing on an empty stomach after a 12-hour fast. 1 week before the study, refrain from taking medications that affect gastric secretion: Pepcedin, Zantac, Nizax, Ranimex, Esofex, Losec, Somac, Ranixal, Ranil. 1 day before the study, refrain from taking medications that neutralize hydrochloric acid secreted by the stomach: Alsucral, Balancid, Prepulsid, Metropam, Librax, Gaviscon. If you have difficulty stopping medications, be sure to inform your doctor. 3 hours before donating blood, refrain from smoking.
PCR studies:
General recommendations for collecting biomaterial for PCR research
1. Various microorganisms have their own characteristics of localization, routes of distribution and excretion, which should be taken into account when choosing the place for taking biomaterial.
2. The collection of biomaterial, if possible, should be carried out during an exacerbation of infection. A few days before the study, you must stop taking chemotherapy. Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment should be carried out no earlier than 3-4 weeks after the end of therapy.
3. The volume of the selected biomaterial should not be excessive, since substances that can cause PCR inhibition or contribute to DNA degradation during storage and transportation get into the sample along with the pathogen. When taking smears and scrapings, it is enough to obtain material in the volume of a “match head”.
4. To take samples, you must use only disposable instruments and sterile plastic containers (or tubes with transport medium) with a tight-fitting lid.
Recommendations for women on preparing for a smear test for PCR, RIF, culture for flora, mycoplasma, trichomonas, fungal infection.
- Such studies cannot be carried out while taking any antibacterial drugs.
- These studies are not carried out during menstruation and for 1-2 days after its end.
- 2-3 days before your visit to the clinic, you should stop using any vaginal tablets, balls, suppositories - both medicinal and contraceptive (Pharmatex, Pantex-Oval, Klion D, Polygynax and others).
- The night before and in the morning on the day of taking a smear, you should not wash yourself or douche.
- IMPORTANT! You cannot take smears for PCR after colposcopic tests.
Urethral material
Before taking the material, the patient is advised to refrain from urinating for 1.5-2 hours. Immediately before taking the material, the external opening of the urethra must be treated with a swab moistened with sterile saline. In the presence of purulent discharge, it is recommended to take a scraping after 15-20 minutes. after urination, if there is no discharge, it is necessary to massage the urethra using a probe to collect material. In women, before inserting a probe into the urethra, it is massaged on the pubic joint. In women, the probe is inserted into the urethra to a depth of 1.0-1.5 cm, in men - to 3-4 cm, and then several careful rotational movements are made. In children, material for research is taken only from the external opening of the urethra. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or placed in a test tube with a transport medium and thoroughly washed, the test tube is closed and labeled, after which the material is delivered to the laboratory.
Material from the cervical canal
Before taking the material, it is necessary to remove the mucus with a cotton swab and then treat the cervix with sterile saline solution. The probe is inserted into the cervical canal to a depth of 0.5-1.5 cm, the material is collected with careful rotational movements. If there are erosions of the cervical canal, they must be treated with sterile saline; the material should be taken at the border of healthy and altered tissue. When removing the probe, it is necessary to completely avoid its contact with the walls of the vagina. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or placed in a test tube with a transport medium and thoroughly washed, the test tube is closed and labeled, after which the material is delivered to the laboratory.
Vaginal material
The material must be taken before performing a manual examination. Before manipulation, the mirror can be moistened with hot water; the use of antiseptics for treating the mirror is contraindicated. If there is excess mucus or excessive discharge, remove it with a sterile cotton swab. Vaginal discharge is collected with a sterile disposable probe from the posterior inferior fornix or from pathologically altered areas of the mucosa. In girls, the material must be taken from the mucous membrane of the vaginal vestibule, in some cases - from the posterior vaginal fornix through the hymenal rings. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or placed in a test tube with a transport medium and thoroughly washed, the test tube is closed and labeled, after which the material is delivered to the laboratory.
Prostate secretion
Before taking prostate secretions, the head of the penis is treated with a sterile cotton swab moistened with saline solution. After preliminary massage of the prostate through the rectum, the doctor performs a pressure massage with several vigorous movements from the base to the tip of the penis. Then 0.5-1 ml of prostatic secretion is squeezed out from the cavernous part, which is collected in a dry sterile container. The material must be delivered to the laboratory within 1-3 hours; transportation must be carried out only in a cooler bag.
Material from the conjunctiva of the eyes
If there is abundant purulent discharge, it is removed with a sterile cotton swab moistened with saline solution. A scraping is taken from the inner surface of the lower eyelid moving towards the inner corner of the palpebral fissure. When taking a scraping, you must hold the eyelid with your hands so that when you blink, the eyelashes do not touch the probe. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or the probe is placed in a test tube with a transport medium and washed thoroughly, the test tube is closed, labeled and delivered to the laboratory.
Material from the back of the throat
The material is taken on an empty stomach or no earlier than 2-4 hours after a meal. A disposable probe is inserted behind the soft palate into the nasopharynx and passed along the back wall of the pharynx. If the purpose of the study is the tonsils, the probe is inserted into the lacunae of the tonsils and rotated there. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or placed in a test tube with transport medium and washed thoroughly. The tube is capped, labeled and delivered to the laboratory.
Material from the nasopharynx
The material is taken on an empty stomach or no earlier than 2-4 hours after a meal. When taking material, good lighting is necessary, the patient sits against the light source, the root of the tongue is pressed with a spatula, the material is taken with a sterile probe, without touching the tongue, mucous membranes of the cheeks and teeth. After taking the material, the probe is transferred to the probe packaging, or placed in a test tube with a transport medium and washed thoroughly, the test tube is closed, labeled and delivered to the laboratory.
Material from periodontal pockets
Smears from the periodontal pocket are collected in a sterile test tube (Eppendorf type) with saline solution. In this case, the test tubes can be stored in the refrigerator (+4... 6°C) for no more than 12 hours, and they are transported in a cooler bag. You can also take smears with rigid urethral probes. In this case, after taking the material, the probe is placed in its disposable packaging, and in this form it is delivered to the laboratory.
Saliva
12 hours before taking (collecting) saliva, the intake of food, alcohol and medications is excluded. Immediately before collecting saliva, it is necessary to avoid the use of toothpaste and remove dentures. Before collecting saliva, you need to brush your teeth without toothpaste, then rinse your mouth well without using irritants. Saliva is spat out or sucked out from the bottom of the mouth with a disposable syringe and transferred to a test tube (Eppendorf type). Saliva can be stored in the refrigerator (+4...6°C) for no more than 12 hours; transportation is carried out without refrigeration.
Rectal smears for the intestinal group
A sterile disposable probe is inserted into the rectum, the material is collected with rotational movements, the probe is removed and placed in a sterile tube, which is delivered to the laboratory.
Sputum
After thorough oral hygiene (brushing teeth and rinsing with boiled water), the morning portion of sputum is collected in a sterile container. Sputum of a mucous or mucopurulent nature, as well as sputum containing dense whitish inclusions, and sputum colored yellowish, gray or brown, are of diagnostic value. The volume of sputum sufficient for examination is 3-5 ml. To increase the information content, it is possible to repeat (up to 3 times) sputum examination, which increases the number of positive findings.
If sputum is produced irregularly or in scanty quantities, expectorants or irritant inhalations should be used the night before and early in the morning on the day of sputum collection. Preparation of smears from material obtained in this way must be done on the day of collection. In the absence of sputum, the impossibility of aerosol inhalation or its failure to test for mycobacteria, bronchial or gastric lavage water should be examined.
Gastric lavage water
They are studied mainly in young children who cough up sputum poorly and often swallow it. To avoid mixing of swallowed sputum with food, gastric lavage should be taken on an empty stomach. The last meal should be at least 12 hours before taking gastric lavage. Before taking the material to neutralize the stomach contents, the patient drinks 100-150 ml of a solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per 1 glass of water) in sterile distilled water, after which a sterile gastric tube is inserted into the stomach and the stomach contents are collected in a sterile bottle. The material is immediately delivered to the laboratory and processed, which eliminates the possible destructive effect of gastric enzymes on the pathogen.
Blood tests for infections
1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from your diet. 2 days before donating blood for viral hepatitis, exclude citrus fruits, orange fruits and vegetables from the diet. The results of tests for the presence of infections depend on the period of infection and the state of the immune system, so a negative result does not completely rule out infection. At an early stage of the disease, seroconversion occurs (absence of antibodies during the acute period of the disease). In doubtful cases, it is advisable to re-test after 3-5 days. A blood test for the presence of IgM class antibodies to infectious agents should be carried out no earlier than 5-7 days from the moment of illness, and IgG and IgA class antibodies no earlier than 10-14 days. This is due to the timing of the production of antibodies by the immune system and their appearance in the blood in the diagnostic titer.
General rules for preparing for stool tests
To collect and transport stool, the patient is given a sterile plastic container with a spoon. The container may contain a nutrient medium (peptone) or a preservative, depending on the type of study.
The release of helminth eggs and protozoan cysts in feces directly depends on the life cycle of the parasites. For this reason, the test results may be negative even if infection is present. For the most reliable results, three stool examinations are recommended with an interval of 3–7 days.
Analysis for enterobiasis
To conduct a laboratory test for enterobiasis, material from the external imprint is taken from the perianal folds. The procedure is carried out immediately after sleep, early in the morning, before defecation and washing. The fence is carried out using a plastic transparent spatula with water-based glue applied to it. To do this, you need to spread the buttocks and apply the spatula with the sticky side to the perianal folds.
After receiving the print, the spatula is placed in a container for transportation. The container label indicates the name and date. The container with the material is delivered to the laboratory; if necessary, it can be stored for 3 days, protected from light at room temperature (+18 - +22C).
A container for collecting material can be taken in advance from the Laboratory office at the address: Obninsk, st. Aksenova, 6a.
Rules for collecting stool
Before submitting the material (3-4 days before), you must stop taking medications (laxatives, castor and petroleum jelly, rectal suppositories). Stool obtained after an enema or barium intake (during X-ray examination) is not allowed for examination.
Before collecting the test, urinate in the toilet. Next, by natural defecation, collect the stool in a bedpan (previously washed and dried). Feces are collected in a clean, disposable container, no more than 1/3 of its volume.
The material must be delivered to the laboratory within 3 hours from the moment the analysis is collected. During this period, it is advisable to store the analysis in the cold (+2...+8C), avoiding freezing.
Throat swab
It is necessary to refuse mouthwash solutions and throat sprays because they kill most of the microbes found in the mucous membrane of the pharynx and reduce their numbers to a minimum. As a result, the analysis, of course, will not show the true number of microbes in the mucous membrane and the bacteria that can cause or have already caused the disease will not be detected in the smear. It is advisable not to eat or drink at all on the day of the test, and if possible, it is better to refuse even a glass of water or a mug of coffee in the morning after waking up. Thus, bacteria need to be given free rein and allowed to multiply freely in the mucous membrane for 2-3 days without exposing them to various antibacterial agents, and only then can the real picture be seen.
Normal indicators
| Index | Result |
| Quantity | 50 ml |
| Color | Colorless, light yellow, straw yellow, yellow, amber yellow |
| Smell | Odorless or non-specific |
| Transparency | Transparent |
| Relative density of urine (specific gravity) | 1003-1035 |
| Urine reaction (pH) | 5.0-8.0 (in children under 1 month – 5.0-7.0) |
| Protein | > 0.140 g/l |
| Glucose | > 2.8 mmol/l |
| Ketone bodies | > 1 mmol/l |
| Urobilinogen | > 34 mmol/l |
| Bilirubin | Not detected |
| Hemoglobin | Not detected |
| Leukocyte esterase | Not detected |
| Nitrites | Not detected |
| Red blood cells | Up to 2 cells per field of view |
| Leukocytes | Up to 5 cells in field of view |
| Epithelium | Up to 5 squamous epithelial cells per field of view |
| Cylinders | Not detected |
| Crystals | Little or no detectable amounts of urates, calcium oxalates, amorphous phosphates |
| Slime | In small quantities |
| Bacteria | Not detected |
| Fungi | Not detected |
Smear in women
At least 36 hours must pass after the last sexual intercourse.
If you were treated with antibiotics, you must first complete the course of treatment, and then wait at least 3 weeks before taking the test.
You cannot take a smear test if women are menstruating or have uterine bleeding.
Before taking a smear, you should not wash yourself, much less use antibacterial soap.
You should not urinate for at least 3 hours before the test. The rule applies to both women and men.
If women have not yet completed treatment, they are taking medications, inserting vaginal suppositories, they must tell the doctor about this, then they cannot take a smear.
When should you take a clinical blood test?
The term general blood test, as a rule, is mistakenly understood as a clinical blood test, since since ancient times in medical practice it has developed that if a doctor prescribed a general blood test, this meant that the analysis would only determine leukocytes, red blood cells and hemoglobin levels, in while a clinical blood test is a much more complex modern analysis of the composition of human peripheral blood, which can be used to diagnose many acute and even chronic diseases. And although a general (clinical) blood test refers to screening methods of examination, that is, accessible, fairly quick, but “not very informative” studies, nevertheless, modern laboratory diagnostics makes it possible to determine dozens of different peripheral blood parameters in a patient, which in the hands of an experienced A therapist or pediatrician allows for very accurate and, most importantly, timely diagnosis of various pathological conditions.