Heart murmurs
- an acoustic phenomenon associated with changes in blood flow in the heart and blood vessels. There is a point of view according to which heart murmurs are a problem exclusively for children. Indeed, about 90% of functional noise is found in children and adolescents. However, scientific experts have revealed a fairly wide prevalence of heart murmurs (about 77%) in young people aged 20 to 28 years.
Most cardiologists agree that in adults, the presence of a heart murmur clearly indicates some kind of cardiac pathology and is a reason for a complete cardiac examination.
Types and types of heart murmurs
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish between organic heart murmurs
(indicating cardiac pathology) and functional (“innocent” murmurs). Organic heart murmurs are murmurs caused by a defect (congenital or acquired) or other heart disease.
Most often the cause
organic noise is a valve or septal defect (ventricular or atrial septal defect). In terms of timbre, organic noises are hard, rough, persistent; by intensity – loud, sharp; long in duration, carried out beyond the borders of the heart, into the interscapular or axillary region; persist and intensify after physical activity; are equally audible in any body position and are associated with heart sounds.
Functional noise
in the heart were called “innocent”, because are not associated with the presence of heart disease, can be heard in other diseases not related to heart pathology.
In terms of timbre, functional noises are soft, musical, inconsistent, of low intensity, short, not carried out beyond the heart, weaken after physical activity, their character changes depending on the position of the body, and are not associated with heart sounds.
A more detailed classification of heart murmurs is represented by the following types of murmurs:
Systolic murmurs
- Holosystolic (pansystolic) murmurs.
- Midsystolic (systolic ejection) murmurs.
- Early systolic murmurs.
- Mid-late systolic murmurs.
Diastolic murmurs
- Early high-frequency diastolic murmurs.
- Mid-diastolic murmurs.
- Presystolic murmurs.
Continuous (systole-diastolic) murmurs
Why does a child's heart make noise?
There are many reasons, the most common:
- Abnormal state of venous return of the lungs - the pulmonary veins either do not communicate with the atrium on the right, or can fuse with the veins of the systemic circle.
- Pathology of the interventricular septum can develop independently or be combined with other cardiac pathologies.
- Coarctation of the aorta is a complex disease that requires consultation with a doctor: only a specialist can answer what a heart murmur at 2-3 years old means.
- Atrial septal disorder is a congenital heart defect characterized by a hole between the right and left atrium.
Causes of heart murmurs
The following causes of heart murmurs are identified:
- High blood flow speed.
- The flow of blood through a narrowed or deformed opening into the dilated chamber of the heart.
- Regurgitation of blood (return flow) through an incompetent valve.
heart murmurs in children
may occur due to minor anomalies in the development of the heart (additional trabeculae, chords, open oval window, elongated Eustachian valve, septal aneurysm, etc.), which do not affect the development of the child and do not cause harm to his health. Sometimes a functional heart murmur occurs in a child due to intense, rapid and uneven growth of the child (growth murmur).
If a child has a functional heart murmur
may be truly “innocent”, then in adults it may indicate the presence of some pathology, for example, the presence of a heart defect.
In any case, if you have a heart murmur
, it is better to immediately contact a cardiologist for an examination.
Heart murmurs in adults
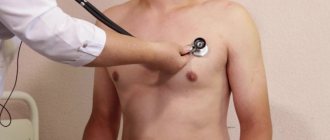
Sometimes, when listening (auscultating) the heart, doctors talk about the presence of some kind of “murmur”. What are these sounds? Are they dangerous to health? Are these signs of heart disease? Let's try to figure it out.
The article was published in the new issue of the journal of the Center for High Medical Technologies.
Read the entire issue
The work of the heart is always accompanied by sounds. In the vast majority of cases there are two of them. They are called the first and second heart sounds because they follow each other and together make up the cardiac cycle. The sounds are associated with vibrations of various structures of the heart, as well as the muscles and walls of blood vessels during the movement of blood. The cardiac cycle consists of two large phases. The first phase, which begins with the first sound, is systole, when blood is expelled from the heart into large vessels (aorta and pulmonary artery) by the force of muscle contraction. Therefore, the first heart sound is also called systolic. The second phase begins with the second sound and is called diastole. At this time, the heart muscle relaxes, and the chambers of the heart are filled with a new portion of blood. Another name for the second sound is diastolic. Heart sounds have certain characteristics that characterize their duration, sonority, and time of occurrence.
All other sounds that occur while listening to the heart are usually called “murmurs”. The characteristics of noise depend on the general condition of a person, his constitution, rhythm frequency and many other factors. It is important to understand that any sound outside the normal two-tone cardiac cycle requires full evaluation and attention.
Noises are divided into two large groups: organic and functional.
The first group - organic murmurs - occur with various structural changes in the heart. This means that they are based on heart defects - congenital or acquired. The murmur may indicate, for example, damage to the heart valves - valve stenosis, valvular insufficiency, or a combination of both. Organic noise also appears in cardiomyopathy (expansion of the cavity of the heart chambers or hypertrophy (thickening) of the myocardium), endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart (endocardium), acute pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardial layers lining the outside of the heart). All of these pathologies are very serious and life-threatening conditions requiring urgent medical intervention. Therefore, the presence of a “murmur” in the heart is an important signal for additional diagnostics and detection of the disease.
The second group of murmurs, the so-called functional murmurs, are either not associated with the heart or are based on anomalies that do not affect its functioning. The causes of functional noise are varied. They can occur as a result of vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as during periods of rapid growth in children and adolescents. Also, sometimes they indicate some structural features of the human heart that arose during prenatal development. In this case, systolic murmur can accompany a person throughout his life. In addition, functional noises can be caused by the anatomical features of the large bronchi, located next to the aorta and pulmonary artery, which simply “squeeze” these vessels with accelerated blood flow through their valves. Long-term overstrain, both mental and physical, can contribute to the appearance of noise. One of the common causes of sound phenomena is pregnancy, during which the volume of circulating blood in the mother’s body increases for optimal blood supply to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, changes in intracardiac blood flow also occur with the auscultation of a systolic murmur. In some cases, functional murmurs, although not associated with problems in the heart itself, often indicate other, sometimes serious, diseases. Functional noise can also appear against the background of metabolic disorders. For example, with anemia (decreased hemoglobin in the blood), thyrotoxicosis (excess of thyroid hormones) or fever.
Very often, the patient does not even suspect the presence of a heart murmur, much less the type and cause of its occurrence. A heart murmur can be diagnosed by a doctor by listening to it. You need to see a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
Symptoms of a heart murmur:
- Increased heart rate at rest and during light exercise.
- Labored breathing. Pay attention to your health if even walking causes you to feel short of breath.
- Chest pain that gets worse after exercise.
- Blue lips and fingertips that occur after fast walking or running.
- Swelling of the limbs.
The presence of one or more of the above symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. And remember, a heart murmur is not always caused by a serious illness. But you should still undergo a timely examination to exclude such a disease or, if it is detected, to begin treatment in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of heart murmurs
- Auscultation is a highly informative method for diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, based on listening to sound phenomena associated with the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- Angiography.
- Chest X-ray.
- Echocardiography (ECG).
- Cardiac catheterization.
- Load tests.
Samples used to measure heart murmur intensity:
- Breathing (increased sounds from the right side of the heart on inspiration, increased sounds from the left side of the heart on exhalation).
- Valsalva maneuver (forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed).
- Physical activity (isotonic, isometric, wrist dynamometry).
- Positional changes (changing the patient’s body position, squats, raising legs from a lying position).
- Extrasystole or atrial fibrillation.
- Pharmacological interventions (inhaled drugs).
- Temporary arterial occlusion (external compression of both arms with a bilateral air cuff).
If any pathologies of the cardiovascular system
It is recommended to carry out treatment depending on the etiology of the disease.
Treatment and prevention
Therapy directly depends on the cause. For murmurs not associated with cardiac pathology, the main emphasis is on treating the underlying disease. In case of endocrine disorders, therapy and adjustment will be carried out by an endocrinologist. If anemia causes noise, the help of a therapist is necessary. Treatment of murmurs associated with cardiac abnormalities is the responsibility of a cardiologist. In this case, both conservative therapy and surgical intervention may be required.
The main prevention will be a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, feasible physical exercise, 8 hours of sleep, preventive intake of vitamins in the spring and autumn, and giving up bad habits.
If you have any questions or need advice from a specialist, please use the registration form on the website. Our specialist will help you understand the problem and tell you what functional heart murmurs are. Registration is available 24 hours a day.
Related services: Cardiac Check-up Diagnosis of heart rhythm disorders by ECG monitoring
Diagnostics
If murmurs are detected during listening by a pediatrician, neurologist or cardiologist, then the patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. It includes:
- conducting an electrocardiogram (shows disturbances in the functioning of the heart, for example, disturbances in rhythmic activity or chamber hypertrophy);
- performing radiography (demonstrates the boundaries of the hematopoietic organ and the condition of both lungs);
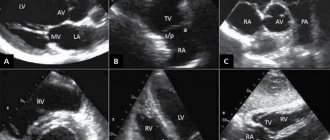
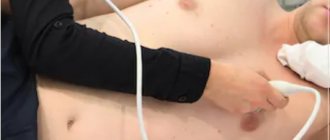
- carrying out echocardioscopy (ultrasound examination will show the condition of the valves, vessels and cavity of the heart, growths, narrowings and pathologies).
The main task of the doctor is to accurately differentiate the type of eshum. We need to thoroughly understand what is the true reason for their appearance. This will help you not waste time and prevent a serious illness from developing.
You need to remember that even if you listen to noises, but the child does not have any complaints, there is nothing to worry about. Those noises that are accompanied by pallor of the skin, blueness of the nasolabial triangle, shortness of breath and elevated temperature should be alarming. The baby may complain of chest pain, be capricious and refuse to eat. In such a situation, urgent examination and consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Arrhythmia in children
Arrhythmias in children can appear at any age, but are more common during the neonatal period, at 4-5, 7-8 years and in adolescents [3].
In many cases, arrhythmias are asymptomatic and are detected during routine examinations. The higher prevalence of arrhythmias in children of pubertal age is associated with hormonal age-related changes. In this case, children complain of palpitations during exercise or at rest, weakness, fatigue, headaches, insomnia, periodic chest pain and increased blood pressure. Heart failure develops quickly, especially in children of the first year of life, and can lead to sudden cardiac death syndrome. Other causes of arrhythmia in childhood:
- damage to the nervous system in the perinatal period;
- congenital dysregulation (immaturity) of autonomic regulation of cardiac activity;
- childhood infections or previous congenital infections;
- endocrinological diseases;
- dehydration with prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, sweating;
- hypo- and hyperthermia;
- congenital and acquired heart defects and conduction tract anomalies.
Complicated pregnancy and childbirth, fetal malnutrition, prematurity, intrauterine infections contribute to arrhythmias in children, and, as a rule, in children with a history of arrhythmias, various cardiac diseases are detected in close relatives.
Preventive recommendations
The main preventive measure includes careful attention to your health; you should pay attention to even minor diseases in order to prevent them from developing into inflammatory processes or rheumatism.
The next point is a balanced diet and healthy food. The diet should include fresh vegetables and fruits, cottage cheese, meat, and fish. Dried fruits are a must - dried apricots, raisins.
Every day you need to take walks in the fresh air, go out into nature, and walk in the park more often. It is also important to completely give up bad habits, especially smoking.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
In severe cases, surgical interventions are performed to install an artificial pacemaker, cardioverter-defibrillators, radiofrequency and cryoablation (destruction of the focus generating pathological impulses with electricity or deep freezing). In emergency cases, intravenous administration of antiarrhythmic drugs is prescribed. First aid for arrhythmia in children is to provide fresh air, clear the airways and ensure rest. In the first minutes, you can apply an ice pack to the child’s face, tilt his head down for a couple of minutes, and press on the root of the tongue. Drug therapy is used as prescribed by the doctor. The choice of drug depends on the type of arrhythmia and the individual characteristics of the patient. Tablets for arrhythmia are prescribed by a cardiologist or therapist; you cannot take them yourself. Besoprolol, amiodarone, nadolol, atenolol or other β-blockers are prescribed.
Now our path lies in the functional diagnostics room
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a method of graphically recording electrical phenomena occurring in the heart. An ECG is recorded using a special device - an electrocardiograph. In this case, the electrical potentials are amplified 600-700 times and recorded in the form of a curve on a moving tape. ECG recording is carried out using electrodes placed on various parts of the body. Using this method, various disturbances of the rhythm and conduction of the heart, as well as overloads of its various parts, are determined.
The sound characteristics of noise can be assessed not only by simple auscultation, but also using a research method such as phonocardiography (PCG). It is based on graphic recording of sounds accompanying heart contractions. Mainly heart sounds and murmurs are recorded. The resulting image is called a phonocardiogram. It significantly complements auscultation and makes it possible to objectively determine the frequency, shape and duration of sounds, as well as their changes in the process of dynamic observation of the patient. This method is used to diagnose functional murmurs and cardiac malformations. It is also important for rhythm disturbances, when with the help of auscultation alone it is difficult to decide in which phase of the cardiac cycle the sound phenomena occurred. The analysis of phonocardiography and the diagnostic conclusion on it are carried out only by a specialist. In this case, auscultatory data are taken into account. For correct interpretation of PCG, synchronous recording of a phonocardiogram and an electrocardiogram is used. The method is good and absolutely safe, but is currently being replaced by
Echocardiography (EchoCG) is a simple ultrasound examination, only the point of application is the heart. Using this method, you can accurately determine the source of noise or exclude heart disease.
Types and causes of arrhythmias
Normal heart rhythm is called sinus rhythm.
It is determined by the autonomic conduction system of the heart. There are several centers that initiate impulses of electrical activity: normally, the sinus node (the main pacemaker) is of primary importance; the atrioventricular connection (the second pacemaker) is less active; the weakest and most scattered impulses are formed in the His bundles and Purkinje fibers. Arrhythmias are nomotropic and heterotropic, periodic or constant, associated with pathological excitation of myocardial cells. Nomotropic are called dysfunctions of the sinus node, which, however, remains the main pacemaker (sinus arrhythmia). Sinus bradycardia and tachycardia are caused by changes in the rate of impulse occurrence during normal operation of the sinus node.
Sinus tachycardia - increased heart rate. Normal heart rate readings are:
- 90-100 beats per minute. for children under 10 years old;
- 80-90 beats per minute. for children from 10 to 15 years old;
- 64-74 beats per minute. for persons from 15 to 60 years old;
- 50-60 beats per minute. for people over 60 years of age [1].
Causes of sinus tachycardia: physical activity, stress, phobias, neuroses, diseases of the endocrine system, menopause, hypoxia, fever, intoxication, trauma, myocarditis and pericarditis, cardiosclerosis, brain damage.
Sinus bradycardia - a decrease in heart rate - as statistics show, develops mainly in men. In its pathogenesis, hypertonicity of the vagus nerve is important in conditions such as increased intracranial pressure, neoplasms, bruise or concussion, meningitis and encephalitis, hemorrhagic stroke; reflexively hypertonicity of the nerve can develop and lead to arrhythmia - with spasms of renal, gastric, intestinal, or biliary origin.
The activity of the parasympathetic nervous system increases with hypoxia and myocardial ischemia, exposure to quinine, digitalis, morphine, and increased levels of bilirubin and bile acids.
Sinus arrhythmia - the generation of impulses by the sinus node with varying regularity - occurs with an alternate increase in the influence of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The causes of sinus arrhythmia are considered to be changes in the blood levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide, bile acids, lactate, certain medications, hemorrhage in the heart muscle and heart injury.
Heterotopic arrhythmias are associated with failure of the main pacemaker or disruption of their conduction from the sinus node and below. In this case, its functions are taken over by the lower parts of the conduction system, generating replacement rhythms.
Common causes of heterotopic arrhythmias:
- increased activity of the parasympathetic system;
- heart tumors and injuries;
- overstretching of the myocardium (cardiomyopathy);
- poisoning with alcohol, digitalis, quinine, β-blockers;
- infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever, typhoid fever, influenza and other viral infections);
- hyperkalemia;
- congenital heart diseases.
Arrhythmias of this type are represented by weakness of the sinus node or blockade, mainly in people over 50 years of age;
sinoatrial and atrioventricular blocks, blockade of one or both branches of the His bundle. In these cases, the rhythm of heart contractions is set by weaker pacemakers, since normal conduction is not carried out. The rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted when the excitation of myocardial cells changes. The causes of such violations are: IHD; violations of water-salt balance; hypoxia; chronic intoxication; injuries to the chest, heart, brain; cholecystitis, urolithiasis. Disorganization of the heart rhythm is also associated with abnormalities of large vessels and disorders of neurohumoral regulation. As a result, arrhythmias such as flickering, fluttering and paroxysmal tachycardia are formed. Abnormal automaticity is associated with ischemia or infarction, increased potassium ions and tachycardia.
Extrasystoles - additional, outside the main rhythm, heart contractions, followed by a longer pause - can be single, paired, multiple, associated with the rhythm. Paroxysmal tachycardia is a temporary sudden increase in heart rate, followed just as suddenly by its normalization. During this period, the heart is less well supplied with blood due to a decrease in minute volume, blood pressure decreases, dizziness, heart pain, and loss of consciousness are possible. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is registered 2 times more often in women, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia – in men. Flutter - very frequent regular contractions of the atria (up to 380 per minute) and ventricles (up to 300 per minute) - are associated with the appearance of re-entry foci in the right atrium.
Atrial fibrillation has a more severe course. Fibrillation - irregular contractions of the atria or ventricles due to erratic electrical activity of the heart - is caused by multiple re-entry foci generating impulses at a very high frequency. Blood stagnates in the atria and blood clots form. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by the appearance of several foci generating frequent impulses, but no actual contraction of the ventricle occurs. Atrial fibrillation never occurs in healthy people.
How to choose a clinic to visit?
The need for multiple visits to a cardiologist in order to determine the motility of the changes that are occurring requires choosing a medical center in the patient’s area of residence, which simultaneously includes all the required parameters for diagnosing the condition.
Our Help Desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor” will help you make your choice, the information base of which is systematized and convenient for viewing data, allowing you not only to choose a medical institution, but also to immediately arrange a call to a cardiologist at home or register the time for his visit within the medical center.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Bibliography
- Guzovskaya, E.V. Pathophysiology of the heart: textbook/ / E.V. Guzovskaya, S.F. Nepomnyashchy; GBOU VPO IGMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia - Irkutsk, IGMU - 48 p.
- Zatonskaya, E.V. Epidemiology of arrhythmias (review of literature data)/ E.V. Zatonskaya, G.V. Matyushin, N.G. Gogolashvili, N.N. Novgorodtseva - Text: direct // Siberian Medical Review, 2021.- No. 3.- P.5-16.
- Sozonov, A.V. The role of a single-channel electrocardiogram at home in the diagnosis of heart rhythm disorders in children / A.V. Sozonov, Yu.A. Trunova, O.S. Pokusaeva-text: direct // Russian Journal of Cardiology, 2021.-No. 24 (add.) – P. 18-19.
- Hingorani P., Natekar M., Deshmukh S., Karnad DR, Kothari S., Narula D., Lokhandwala Y. Morphological abnormalities in baseline ECGs in healthy normal volunteers participating in phase I studies // Indian. J. Med. Res. - 2012. - Vol. 135. - P. 322-330.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist