Causes of heart murmurs, treatment
A heart murmur is a clinical manifestation of a nonspecific nature, which is not always a symptom of pathology.
For example, quite often a heart murmur in a newborn baby is a manifestation of the baby’s “transitional” state from intrauterine life to independent existence. However, this may also be a manifestation of pathology. Therefore, in addition to examination by a cardiologist, it is necessary to conduct a number of instrumental studies that will help make the correct diagnosis. Under no circumstances should the symptom be ignored. Possible causes of heart murmurs:
- congenital or acquired heart disease;
- VSD, endocarditis;
- infection of the heart muscle;
- damage to the aortic valve;
- anatomical abnormalities;
- mitral stenosis;
- hypertension;
- acute form of pericarditis.
Causes of heart murmurs in adults that are not related to cardiac pathology include age-related changes, chronic stress and psycho-emotional stress, and excessive physical activity.
Symptoms
In addition to noises on auscultation, the patient may have other symptoms during history taking and examination:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- poor tolerance to physical activity;
- cyanosis of lips, acrocyanosis ;
- swelling;
- fainting , dizziness ;
- cough;
- swelling of the neck veins;
- hepatomegaly - an increase in the size of the liver;
- increased sweating ;
- instability of blood pressure ;
- severe shortness of breath;
- asthenic physique;
- chest pain;
- in childhood - retardation in mental and physical development.
The symptom complex and severity of clinical manifestations depend on the underlying disease and the presence of complications:
- hereditary connective tissue dysplasia is characterized by joint hypermobility, increased skin extensibility, asthenic physique, myopia;
- Marfan syndrome is characterized by disproportionately long fingers and limbs, high stature, hypotonia of skeletal muscles, and the presence of signs of heart failure.
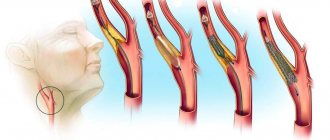
Depending on the existing pathology, the localization of noise changes. In case of aortic pathology, the murmur is recorded on the right in the second intercostal space, in case of disturbances in the functioning of the mitral valve, the murmur is heard at the apex of the heart, in case of dysfunction of the tricuspid valve, the murmur is recorded above the xiphoid process.
Why does a heart murmur occur?
Heart murmurs are systolic, diastolic and systolic-diastolic.
Systolic murmurs are heard at the apex of the heart and can be caused by cardiac pathology or be a symptom of a disease not related to the heart. Doctors most often associate systolic murmur at the apex of the heart in a child with adaptation to the environment.
Diastolic is always associated with heart pathology. The main causes are stenosis of the atrioventricular orifices, insufficiency of the aortic valve or pulmonary trunk.
Why does a heart murmur occur?
- blood regurgitation;
- high blood flow speed;
- the passage of blood into the dilated chamber of the heart through a deformed hole.
Classification
The presence of pathological and functional noise is determined by etiological factors. The former occur with certain diseases, and the latter may be associated with certain overloads of the heart.
Symptoms may be:
- primary (associated with structural heart disorders);
- secondary (occur against the background of another pathology of organs and systems).
During auscultation, it is customary to describe noises according to the following characteristics:
- direction of sound irradiation;
- noise localization;
- pitch;
- attachment to systole/diastole.
Noise is determined by localization:
- in the second intercostal space (right, left, may spill into the axillary region);
- above the sternum;
- at the apex of the heart.
Depending on the causative factor, pathological noise can have different pitches and intensity and appear throughout the entire cycle or during systole/diastole.
Pathological noise has the following forms:
- fusiform;
- decreasing;
- ribbon-shaped;
- growing.
Noises can occur in certain situations, permanently or temporarily.
Why does a child's heart make noise?
There are many reasons, the most common:
- Abnormal state of venous return of the lungs - the pulmonary veins either do not communicate with the atrium on the right, or can fuse with the veins of the systemic circle.
- Pathology of the interventricular septum can develop independently or be combined with other cardiac pathologies.
- Coarctation of the aorta is a complex disease that requires consultation with a doctor: only a specialist can answer what a heart murmur at 2-3 years old means.
- Atrial septal disorder is a congenital heart defect characterized by a hole between the right and left atrium.
Heart murmur in an adult: symptoms
If we are talking about murmurs not related to cardiac pathology, then they can be combined with the following symptoms:
- fatigue, pale skin, weakness are inherent in anemia;
- weight loss, irritability, hand tremors are characteristic of thyroid diseases;
- mood swings, headache, dizziness, tachycardia indicate the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- swelling of the legs, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat appear in late pregnancy.
Clinical manifestations of murmurs associated with cardiac pathology:
- rapid heartbeat, unstable blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- increased sweating during sleep;
- “cold” hands and feet;
- swelling of the limbs;
- chest pain.
On our website you can make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist and learn about the consequences of a heart murmur per month in a child. If necessary, the center can undergo a full range of examinations.
- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
The most common reason for referral to a pediatric cardiologist for infants and children under 5 years of age is a murmur heard in the heart area.
Let's try to figure out what the reason is. The human heart is a rather complex organ that produces a peculiar sound during its operation - noise.
There are different types of murmurs in a child's heart. The murmur can be a consequence of significant circulatory disorders caused by congenital heart disease, or accompany minor deviations in the structure of the heart that do not significantly affect its functioning. Now noises are divided into “innocent” and “pathological”.
“Innocent” noises do not affect the condition of the heart and the general condition of the child’s body. Such a murmur is described as a fuzzy, “short”, limited in area, barely audible sound, not accompanied by other abnormalities; when examining the heart, it is normal. In essence, it is the sound of a healthy heart working due to the peculiarities of its structure.
Quite often, the causes of a murmur in a child’s heart are minor anomalies in the development of the heart. The inner surface of the heart chambers is not perfectly smooth; it has muscle bridges (trabeculae) and pits; the ventricles contain papillary muscles and chordae connected to the leaflets of the atrioventricular valves. When the ventricles contract, protrusions may appear in their lumen, and the configuration of the cavity changes. Moreover, even one single chord or trabecula located in the path of blood flow can create a significant noise picture.
Each heart is unique, having its own individual “trabecular pattern,” just like the pattern on the fingers. There can always be an “anomalous” structure, or even more than one, creating noise.
“Innocent” noises are often heard in newborns and infants and are a consequence of the processes of circulatory restructuring that take place in the cardiovascular system when adapting to extrauterine life.
Noises of a “rough” timbre , clearly audible, sometimes even at a distance, “long-lasting”, spreading over the surface of the chest are called pathological, such noises are usually a consequence of the presence of congenital heart disease (CHD), and may be accompanied (not always) by changes in the electrocardiogram , changes in the X-ray picture of the heart.
Some newborns may not have a murmur at all. Its appearance can occur only after a month, when a certain restructuring of the baby’s blood circulation occurs. A pathological sign is an increase in noise over time.
Unfortunately, it should be noted that the absence of murmur does not mean the absence of heart disease . There are so-called “silent” defects, when there is a defect, but due to the characteristics of the blood circulation it cannot be heard, since there are no specific sounds; an example of such heart defects are:
- atrial septal defect,
- ventricular septal defect in the muscular part,
- open ductus arteriosus with a diameter of 1-2 mm. and etc.
The most informative method of examining children when detecting a murmur in the heart area is an echocardiographic examination (ultrasound of the heart), which is recommended to be carried out without delay, as soon as it comes to the fact that some murmurs are heard in the heart area. This study is safe for the baby’s health and can (should) be carried out immediately after birth, if necessary.
In the presence of congenital heart pathology, observation by a pediatric cardiologist is necessary at intervals corresponding to the severity of the disease. If correction of the defect is necessary, the child should be sent to a cardiac surgery hospital.
Patients with innocent murmurs also require periodic monitoring, as they may experience age-related changes in heart structures. The value and timbre of the noise may change. For this reason, it is recommended to visit the same pediatric cardiologist, who can record the timbre and nature of the noise and their dynamics over time . However, as experience shows, in most cases, no serious problems arise for a long time; children can engage in dancing and sports associated with heavy physical activity.
Make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist and examination by phone +7(495)150-60-03
Services and prices
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children under one year old
RUB 3,800
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children from 1 year to 7 years
3,700 rub.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children over 7 years old
3,600 rub.
Make an appointment
Treatment and prevention
Therapy directly depends on the cause. For murmurs not associated with cardiac pathology, the main emphasis is on treating the underlying disease. In case of endocrine disorders, therapy and adjustment will be carried out by an endocrinologist. If anemia causes noise, the help of a therapist is necessary. Treatment of murmurs associated with cardiac abnormalities is the responsibility of a cardiologist. In this case, both conservative therapy and surgical intervention may be required.
The main prevention will be a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, feasible physical exercise, 8 hours of sleep, preventive intake of vitamins in the spring and autumn, and giving up bad habits.
If you have any questions or need advice from a specialist, please use the registration form on the website. Our specialist will help you understand the problem and tell you what functional heart murmurs are. Registration is available 24 hours a day.
Related services: Cardiac Check-up Diagnosis of heart rhythm disorders by ECG monitoring
Diagnosis and further actions
If you or your child are diagnosed with a systolic murmur, this means that it is necessary to undergo additional examinations in order to identify the specific cause of this phenomenon.
The following diagnostic procedures are used:
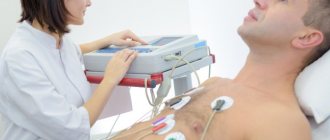
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- Holter 24-hour ECG monitoring;
- chest x-ray;
- echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart);
- functional load tests (bicycle ergometry, step test);
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
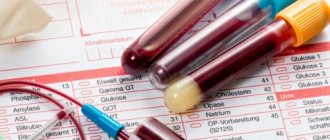
They do appropriate laboratory tests, which include general and biochemical blood and urine tests, rheumatic tests, coagulogram and other specific studies.
In addition, the patient will need to consult a rheumatologist, allergist, and endocrinologist. If no organic changes are detected, then the person is simply put under control. This means that he needs to periodically come to the hospital for preventive examinations. General restoratives (physical therapy or physiotherapy) are also prescribed. If serious pathologies are detected, the patient is prescribed treatment.