Heart murmurs in children: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Boo-tup, bu-tup... Having applied a phonendoscope to the child’s chest, the doctor hears two heart sounds. However, sometimes, in addition to these tones, noise can be heard.
What are the types of heart murmurs? Where do they come from? And what to do if such noise is detected?
With these and other questions, we turned to Tatyana Mikhailovna Frolova, a pediatric cardiologist and functional diagnostics doctor at the Expert Clinic Smolensk.
— Tatyana Mikhailovna, what is a heart murmur and where does it come from?
A heart murmur occurs when there are any obstacles to the flow of blood in the heart itself or in large vessels. Normal blood flow can be figuratively compared to a wide, full-flowing river that flows and murmurs regularly, and the movement of blood in the presence of obstacles can be compared to a mountain river flowing along an uneven path and therefore heard from afar.
Turbulence of blood movement is the main mechanism for the appearance of heart murmurs in both adults and children.
— Is a heart murmur a diagnosis or a syndrome?
Neither one nor the other. This symptom is one of many that occur in various pathologies.
— Many mothers associate heart murmurs in a child with defects. When is a heart murmur a temporary situation, and when should you worry?
It is difficult to conclude from noise alone and its characteristics whether this situation will be temporary or not. Therefore, the child’s condition, all sound characteristics of the noise, data from additional research methods are taken into account, and always in dynamics. For example, in some cases, even in the presence of a defect, the situation may resolve favorably after some time: the heart defect may self-destruct during the child’s growth, or the need for surgical correction of the heart defect will disappear.
— Are there physiological murmurs in the child’s heart?
Yes. Heart murmurs occur in newborns and are also observed in the first year of life. They are associated with intensive growth of the body, when the heart does not have time to grow as quickly. Heart murmurs can also occur between the ages of 4 and 7 years, during adolescence.
— Why do pathological heart murmurs occur in a child?
In most cases, the cause of pathological heart murmur in children is a heart defect (congenital or acquired).
The division of murmurs into pathological and functional, previously used (before the era of echocardiography/ultrasound of the heart), has lost its relevance today. Therefore, in order not to “miss” a defect, any noise - even one that meets the functional criteria - should be a mandatory reason for an in-depth study using echocardiography.
Heart ultrasound for adults and children: when is it prescribed and what will it show? Read more
— What age is critical for the occurrence of heart murmurs in children?
It is more correct to talk about the critical period for the occurrence of not the noise itself, but the reasons for its occurrence.
The first period is from the 3rd to the 8th week of pregnancy, when the heart is formed. At this stage, defects can form that lead to noise.
What can a fetal MRI reveal? Find out here
The second period is until the child is one year old. At this time, both physiological and functional and pathological (depending on the cause) noises can be heard.
All periods of intense growth of a child’s heart are also critical for the appearance of murmurs. Murmurs at this time can be observed even in the absence of heart pathology (physiological murmurs).
Infectious and colds in preschool age make an independent contribution, one way or another capable of causing changes in the heart, accompanied by murmurs.
How does ARVI manifest in children? Ulyana Vladimirovna Chemova, a pediatrician at the Expert Clinic Smolensk, tells the story.
— Is there a relationship between increased blood pressure and heart murmurs?
Rarely. A heart murmur is not the main manifestation of high blood pressure in a child, i.e. he may or may not be. And if it is present with high blood pressure, then it is mostly functional.
What should a child’s blood pressure be and how to measure it correctly? Neurologist at the Expert Tula Clinic, Anna Georgievna Sycheva, tells the story.
Perhaps the only serious reasons leading to murmur with high blood pressure are stenosis and coarctation of the aorta.
— Can a cold or infectious disease suffered by a baby cause a heart murmur?
Yes. In this case, different scenarios are possible. The infectious agent can affect the heart itself. In this case, the development of pericarditis, myocarditis, and endocarditis is possible. Against the background of illness, the child develops a heart murmur, which is considered a complication of infection.
In the presence of infection, a congenital pathology that had not previously manifested itself may appear. For example, a child has a slight narrowing of a large vessel leaving the heart. Infection, tachycardia, fever, intoxication lead to an acceleration of blood flow, and murmurs become obvious.
In addition, the acceleration of blood flow in itself can cause murmurs, even in the absence of any pathology in the heart.
— Can a baby’s heart murmur occur due to low hemoglobin?
A low hemoglobin level (anemia) by itself cannot cause murmur. However, with a lack of hemoglobin, one or another degree of oxygen starvation naturally develops. As a result, in order to deliver the required amount of oxygen to organs and tissues, the heart has to contract more often. Acceleration of blood flow, tachycardia, leads to noise.
— Can anemia be suspected by some external symptoms? What signs should alert a mother?
Symptoms of anemia are nonspecific and can occur with many other diseases. Their occurrence is caused by a lack of oxygen.
Signs of anemia include: fatigue, poor exercise tolerance, pale skin and mucous membranes, heart murmur, and frequent colds.
How many times a year should a child get colds? Ulyana Vladimirovna Chemova, a pediatrician at the Expert Clinic Smolensk, tells the story.
— Tatyana Mikhailovna, if a pediatrician listens to a child’s heart murmur at an appointment, is this always a reason for further examination by a cardiologist?
Absolutely yes, regardless of the noise characteristics. The assessment of noise by ear is quite subjective, therefore, in order not to “miss” the pathology, the pediatrician must refer such children to a cardiologist for further examination.
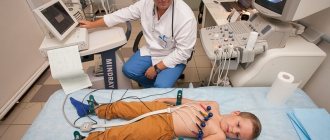
— If there is a heart murmur, what kind of diagnostics does the baby need to undergo so that the doctor can determine whether it is a functional murmur or a pathological one?
First of all, this is echocardiography, which allows one to evaluate the anatomical features of the heart, its layers, valve apparatus, and some functional features.
The second mandatory research method is electrocardiography. It makes it possible to find out the state of the myocardium, whether there are any rhythm disturbances, signs of overload of the heart, etc.
— Do any heart murmurs require treatment?
More precisely, talk about the reasons that cause them. Of course no. If these noises are physiological, they do not need treatment. If they are associated with another cause (anemia, viral infection, etc.), treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. In the case of significant heart defects, this is only surgical correction.
— Is a heart murmur a contraindication for playing sports?
In most cases, no. Physical activity commensurate with the state of health is allowed even with defects - of course, under certain conditions (for example, if it is compensated, there are no complaints or circulatory disorders). Observing such a patient over time (over time) is of great importance in order to determine the effect of sports on the child’s condition. All nuances must be discussed with the doctor in advance.
— How to protect a child’s heart from pathological murmurs? Tell us about prevention
If we equate pathological murmurs with congenital heart defects, then we need to talk, accordingly, about the prevention of defects.
Activities include proper pregnancy planning, correct behavior of a woman during pregnancy (optimal nutrition, infection prevention, taking vitamins).
How to properly prepare for pregnancy? The chief doctor of the Expert Tula Clinic, obstetrician-gynecologist Olga Evgenevna Malafeeva tells
If a woman takes any medications before a planned pregnancy, she should definitely consult with a doctor regarding their use and the possible effect on a future pregnancy and fetus.
After birth, it is necessary to perform an ECG and ultrasound of the heart for up to a year, especially in the presence of murmurs. This will make it possible to identify the defect at an early stage and make the right decision in each specific case.
If all these stages have passed without problems, then the prevention of acquired heart defects is carried out. It is carried out throughout a person’s life and includes the prevention of infections, primarily those directly affecting the heart. This also includes timely, competent treatment of acute and chronic foci of infection as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician.
Sports activities are important.
If any heart murmur occurs, consult a doctor promptly.
You can make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist here
Please note: consultations are not available in all cities
For reference:
Frolova Tatyana Mikhailovna
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Orenburg State Medical Academy in 1997.
In 1998, she completed her internship in the specialty “Pediatrics”.
In 1999-2001 she completed postgraduate studies by correspondence and has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences.
In 2014 - professional retraining in the specialty "Pediatric Cardiology", in 2017 - in the specialty "Functional Diagnostics".
Currently he holds the position of pediatric cardiologist and functional diagnostics doctor at Clinic Expert Smolensk LLC. Receives at the address: st. 8 March, no. 20
Classification
Knowing what functional cardiopathy is, it is recommended to monitor the child. To make an accurate diagnosis, the changes are divided into groups according to the classification as follows:
- Mitral valve prolapse.
- Additional one or more papillary muscles.
- Their location is incorrect.
- Greater mobility of chords in the cavities of the heart due to increased length.
- Bifurcation of the papillary muscles.
- Attachment of chords outside the anterior or posterior valves.
- Enlargement of the ring at the site of attachment of the tricuspid valve.
- Displacement of the septal valve.
- Increase or decrease in the lumen of the aorta.
- Changes in the number of tricuspid valve leaflets in a child or adult.
- Valve prolapse in the inferior vena cava.
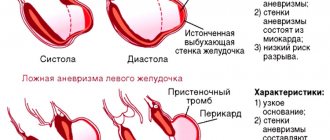
- An aneurysm of various sizes located in the interventricular or interatrial septum.
- Non-closure of the oval window.
If the listed functional changes do not disappear during adolescence, the pathology is called connective tissue dysplasia.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic non-infectious inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract. The causes of asthma are not fully understood, but it is believed that heredity and adverse environmental influences play a large role. Asthma triggers can be allergens (pollen, mold, animal dander), adverse environmental effects (cigarette smoke, polluted air, cold climate), viral infections (flu, colds).
More details
Bronchial asthma
Obesity and hypertension
Every year, the number of overweight and obese children and adolescents around the world is growing. According to WHO, in 2021, 38.3 million children under 5 years of age had such problems. Over the past 20 years, no progress has been made in reducing excess body weight in this age group. Among children aged 5 to 19 years, the global prevalence of obesity was 6.8% in 2021, up from 2.9% in 2000.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, obesity is a chronic, complex disease that can cause serious harm to health. It is determined by a variety of conditions, including behavioral (poor diet, poor sleep patterns, certain medications, lack of physical activity) and psychosocial factors, as well as genetic predisposition.
Excess body weight has been proven to be associated with poor health not only in childhood, but also in later adult life, with an increased risk of developing diseases such as arterial hypertension, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, asthma, musculoskeletal diseases, and some types of cancer. , non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, anxiety, depression, as well as low self-esteem and a generally lower quality of life. Therefore, parents need to monitor the child’s BMI (body mass index), encourage him to eat right and engage in active sports, monitor his sleep pattern (lack of sleep is associated with weight gain), reduce the time watching TV and using gadgets (no more than 2 hours per day). day). The American Academy of Pediatrics does not recommend watching television for children under 2 years of age.
BMI calculator for children and teenagers
Proper nutrition for your child includes eating plenty of vegetables and fruits, whole grains, lean meats, low-fat dairy products, drinking plenty of clean drinking water, avoiding processed foods, and limiting foods and drinks with added sugar and high sodium content. For normal growth and development, children 3–5 years of age should be active throughout the day, and children 6 years of age and older and adolescents should receive moderate to vigorous physical activity every day, for 60 minutes or more.
What are adenoids?
Adenoids are three of the six lymphoid formations (tonsils) of the so-called lymphoid “Pirogov’s ring”: two tubal tonsils (located around the mouths of the auditory tubes) and the nasopharyngeal tonsil (located in the center of the nasopharynx vault. In addition to these three tonsils, the “Pirogov’s ring” includes two palatine tonsils tonsils (tonsillar) and one lingual (located at the root of the tongue in front of the epiglottis). The function of the “Pirogov ring” is very important. This is the main “guard” of the body at the “entrance gate” from possible infection. Everything that enters our body from the outside: air for breathing, food and water, everything undergoes careful control by the lymphatic formations of the nasopharynx and oropharynx (“Pirogov’s rings”). And inflammation is nothing more than the body’s response to an infectious agent (virus, bacteria or fungi), with the aim block the infection, prevent it from entering the body, destroy and remove it.
Development factors
A special place is occupied by a persistent increase in blood pressure. With FKP, they attach importance to figures of more than 140/90 mmHg. If the cause of such manifestations is not cardiac pathology, then other forms may develop. More often, signs of hypertrophic or dilated cardiomyopathy appear.
With a significant increase in pressure, the load on the myocardium and blood vessels increases. The walls lose their former elasticity, and over time the process of blood circulation becomes difficult.
People over the age of 55 who have kidney pathology or a disorder of hormonal regulation are most prone to hypertension.
All heart cells are rich in various proteins. If there is a defect in any of them, the work of the muscle walls changes. If the examination fails to establish the exact cause of the symptoms, then they are inclined to think of a genetic predisposition to cardiomyopathy.
With oxygen deficiency in tissues, ischemia gradually develops. In most patients, the disorder occurs due to pathology of the arteries of the heart. Older people are prone to atherosclerosis. The lumen of the vascular walls narrows due to the deposition of cholesterol.
Pathology becomes a predisposing factor for the development of functional cardiopathy. Age over 50 years, smoking, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure are important.
Pathology appears not only in children and older people. Pregnant women, being in the third period, or in the first months after childbirth, are also at risk of getting sick. This is due to hormonal changes and temporary changes in hemodynamics.
Normally, women have an increase in circulating blood volume. Additionally, stress and blood pressure affect the body. When a newborn baby is born, secondary cardiopathy occurs. They are reversible. Timely treatment of diseases that cause symptoms leads to restoration of health.
Constipation
The causes of constipation in children are usually: stress associated with potty training a small child too early; a feeling of embarrassment when using the toilet in public places and children's institutions, for example, in a kindergarten; reluctance to interrupt games and interesting activities by going to the toilet; fear of pain and discomfort during bowel movements. Constipation can be caused by taking certain medications (iron supplements, painkillers, anticonvulsants), poor diet (diet low in fiber), insufficient fluid intake, and certain diseases (pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, neurological disorders, allergy to cow's milk).
Pay attention to the following symptoms: bowel movements less than twice a week, hard stools, pain during bowel movements, the child reports a feeling of incomplete bowel movements, complains of abdominal pain, tries to avoid bowel movements, has bloating in the lower abdomen underwear, traces of liquid or pasty stool are found. If constipation lasts more than 2 weeks, the child does not eat, loses weight, has a fever, or blood is found in the stool, seek medical help immediately.
Diagnosis of constipation usually includes a physical examination and personal and family history. In some (complex) cases, to determine the cause of constipation, the doctor may prescribe laboratory tests (blood tests - aimed at identifying conditions such as anemia, hypothyroidism, celiac disease; stool analysis - shows the presence of blood in the stool, signs of infection, inflammation; urine analysis - helps diagnose a bladder infection caused by constipation); functional tests (anorectal manometry); imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, abdominal x-ray); rectal biopsy (for diagnosing an abnormal development of the large intestine of congenital etiology - Hirschsprung's disease).
Treatment of constipation in children consists of adjusting the diet (high-fiber foods are introduced), maintaining a drinking regime, changing bowel habits, using medications (laxatives, glycerin suppositories) and enemas (only on the recommendation of a doctor).
Prevent constipation by eating high-fiber foods (the recommended amount of dietary fiber is 14 g for every 1,000 calories) and drinking enough fluids; regular physical activity; a clear daily routine, defining not only the usual meals, games, walks and sleep, but also the time to go to the toilet; reviewing the medications the child is taking (if one of them causes constipation, ask the doctor to recommend a different drug).
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease accompanied by itching, redness, dryness, weeping, crusting and lichenification (thickening of the skin, increased patterning and pigmentation disorders).
Treatment of atopic dermatitis involves an integrated approach: eliminating factors that cause exacerbation of the disease, restoring the barrier function of the skin and its hydration, using anti-inflammatory local and medicinal agents.
You can read more about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children here
Atopic dermatitis in children
Diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome
Diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome includes assessment of clinical manifestations, laboratory and imaging studies.
The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the presence of Sappor criteria, including:
- episodes of thrombosis, even a single episode;
- pathology of pregnancy;
- death of a normally developing fetus before ten weeks;
- premature labor;
- two or more miscarriages;
- presence of anticardiolipin antibodies;
- detection of lupus anticoagulant.
The diagnosis of “antiphospholipid syndrome” is considered reliable if a person is twice diagnosed with at least one clinical and laboratory criterion.
Laboratory diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome is considered reliable if the following conditions are met:
- moderately elevated or high levels of antibodies to cardiolipin are determined twice. The minimum interval between examinations is 12 weeks;
- a test for lupus anticoagulant in blood plasma is performed twice, with an interval of 6 weeks.
The diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome is confirmed if both studies show positive results. In addition, it is necessary to establish the fact of prolongation of the phospholipid-dependent phase of plasma coagulation. For this purpose, a number of specialized tests are used. When plasma from a patient is mixed with plasma from a healthy person, test results do not change, whereas when phospholipids are added, the results are normalized. In addition, if APS is suspected, other coagulopathies that are characterized by similar symptoms and laboratory parameters should be excluded.
Functional cardiopathy in a child
Cardiopathy most often appears under the influence of unknown factors. The reasons considered to be the main ones in the development of the disease are the following:
- hereditary predisposition;
- previous heart attack;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- valve dysfunction;
- constant tachycardia;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements;
- metabolic disorders - diabetes, obesity;
- alcoholism;
- complicated pregnancy;
- radiation treatment or chemotherapy;
- drug use;
- past infectious diseases;
- accumulation of iron in the myocardium – hemochromatosis;
- the formation of granulomas in the wall of the heart due to inflammation;
- accumulation of abnormal protein in the myocardium;
Almost all patients experience a combination of several causes.