Symptoms of autonomic dysfunction of the heart
The symptoms of autonomic dysfunction are quite easy to identify, but to make a final diagnosis, the doctor needs to accurately answer the following questions: are these symptoms a sign of an independent disease or a manifestation of another, somatic, neurological, or mental disease? Could they mean the presence of cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system) pathology: hypertension, coronary artery disease, valve defects, myocardial inflammation?
When establishing a diagnosis of autonomic dysfunction, the following are taken into account:
- multiplicity and variety of complaints, mainly related to the cardiovascular system;
- prolonged course with episodes of exacerbations and attenuation of symptoms;
- does not lead to complications (heart failure);
- discrepancy between complaints and objective data, examination results.
Identifies the main and additional diagnostic signs of autonomic dysfunction
. A diagnosis can be considered reliable if there are two or more main and 2 additional signs.
Main features:
- pain in the precordial area of various types (pressing, stabbing, burning, cutting, drilling, aching);
- respiratory disorders - shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air, dissatisfaction with breathing, not associated with physical activity;
- instability of blood pressure and pulse, their inadequate change in response to physical activity, attacks of rapid heartbeat;
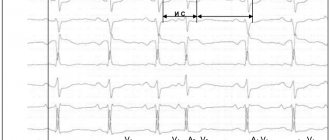
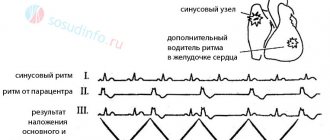
- nonspecific modifications of the ST segment, T wave on the electrocardiogram, early ventricular repolarization syndrome;
- restoration of a negative T wave on the electrocardiogram after physical activity, positive orthostatic and hyperventilation tests with beta-blockers.
Additional signs:
- tachycardia or bradycardia, interruptions in heart function;
- lability of body temperature, low-grade fever, hot flashes, chills, muscle pain, paresthesia;
- dizziness, presyncope and syncope (fainting);
- emotional instability, feelings of anxiety, fear, increased irritability, tearfulness;
- general weakness, fatigue, decreased performance; absence of signs of organic pathology from the cardiovascular system, nervous system, mental disorders.
There are also signs, the presence of which with one hundred percent probability excludes the diagnosis of autonomic dysfunction. They are revealed during examination and additional examination. These are swelling of the legs, moist rales in the lungs, auscultatory noises in diastole, enlargement of the heart (hypertrophy, dilatation), changes on the ECG (left bundle branch block, AV block II-III degree, focal changes, ST segment displacement, rhythm disturbances except for a single extrasystole), changes in blood tests.
Symptoms and manifestations of VSD
A dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system can affect one or several organs at once. Depending on this, there are several types of vegetative-vascular dystonia (also called syndromes), each of which manifests itself in its own way.
| Syndrome | Symptoms |
| hypertensive syndrome | increased heart rate, short-term increase in blood pressure (up to 140-170/100 mm Hg), which decreases without taking medications |
| hypotensive syndrome | decreased blood pressure to 90/60 mm Hg, headaches, weakness, dizziness, cold hands and feet |
| cardialgic syndrome | symptoms resemble angina pectoris, but are not associated with physical activity: nagging, bursting pain and burning in the heart area behind the sternum |
| tachycardial syndrome | increased heart rate up to 90-120 beats per minute, increased blood pressure, a feeling of vibration in the head, redness of the face |
| asthenic syndrome | weather dependence, physical weakness and fatigue in the morning, worsening in the evening, decreased attention, ability to work, and in a lying position - comfortable well-being |
| visceral syndrome | intestinal dysfunction, pain and bloating, flatulence, indigestion |
| respiratory syndrome | soreness and feeling of a lump in the throat, inability to take a deep breath, pain and tightness in the chest |
| mixed form | combination of two or more VSD syndromes |
If vegetative-vascular dystonia is not treated
Any form of vegetative-vascular dystonia significantly affects the quality and lifestyle of a person, depriving him of the opportunity to work and live normally. In severe cases, VSD can be manifested by loss of consciousness, increased heart rate and other dangerous conditions. In addition, if vegetative-vascular dystonia is not treated and controlled, it can develop into serious diseases of those organs in which the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system is disturbed:
- heart (hypertension, ischemia, stroke and heart attack)
- stomach and intestines (intestinal atony (hypotonicity), gastritis)
- kidneys and genitourinary system (urinary incontinence, diseases of the reproductive system in men and women)
- psyche and nervous system (convulsions, panic attacks).
All syndromes associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia are characterized by periodic exacerbations - crises or attacks. During an attack of VSD, all manifestations of the syndrome sharply worsen (tachycardia, fainting, shortness of breath), accompanied by a panic attack for no apparent reason. Such attacks can last a short or long time, and then pass without a trace.
Causes of VSD
The basis of the disease is a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the stability and coherence of the activities of all internal organs and the body as a whole. This is a department of the nervous system that is not subject to the consciousness and control of the human will.
There are many causes of the disease. Among the first are hormonal disorders, including transient ones - during puberty, menopause, and pregnancy. Infectious diseases (including physical detraining after infection), foci of chronic infection (caries, sinusitis, tonsillitis), and allergies play a significant role. Psycho-emotional stress, traumatic brain injuries, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits - smoking, alcohol, unhealthy diet - predispose to the disorder. Hereditary predisposition is important.
Does the treatment of VSD differ for different symptoms?
For severe headaches, abdominal cramps and body aches, it is advisable to take an anti-inflammatory drug or analgesic. The choice of medication will depend on what exactly helps you in such situations.
If you experience frequent dizziness and general weakness, your doctor may recommend drinking 1-2 cups of coffee daily, or taking caffeine tablets.
Soothing and daily walks help to cope with insomnia, anxiety, and palpitations.
In case of pressure changes, paresthesia, loss of consciousness, a comprehensive examination and individual selection of medications that will relieve symptoms are required.
But the key to treating autonomic dysfunction with any set of symptoms will be regular intake of amino acids, which gradually normalize metabolism at the cellular level: glutamic acid, glycine and cystine. Therefore, for dystonia, Eltacin®, a drug with these amino acids, is needed as the main treatment. It helps eliminate the cause of dysregulation, and you will gradually forget about unpleasant symptoms.
Painkillers, heart medications, medications for high blood pressure, and sedatives do not solve the problem of VSD. Autonomic dysfunction with symptomatic treatment will not go away on its own, and over time it will become more pronounced. Dysregulated regulation reduces the body's ability to adapt to any stress, and can become the basis for the development of organic changes and diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment of autonomic cardiac dysfunction
Autonomic dysfunction is a diagnosis of exclusion. After a number of cardiovascular diseases have been excluded thanks to laboratory and instrumental methods (ECG, EchoCG, Holter-ECG, etc.), differential diagnostics should be carried out with neuropsychiatric diseases and only in the last place should one think about vegetatives.
Treatment of a disorder of the autonomic nervous system itself should begin with improving lifestyle: regular physical activity, sports (swimming is a priority), elimination of bad habits, a good night's sleep, optimal nutrition, normalization of body weight, hardening.
Medicines used include adaptogens, daytime tranquilizers, nootropics, vascular drugs, antioxidants, and vitamins.
When and how do signs of dystonia appear?
The tendency to autonomic dysfunction manifests itself in childhood. Children with hereditary dystonia sleep poorly, are often anxious and suffer from night terrors, they find it more difficult to adapt to new conditions and quickly get tired of physical and psychological stress. If such a child is created with favorable conditions in the family, hardened, and regularly added to the diet with vitamins and amino acids, ensure that he gets enough rest and walks in the fresh air every day, then autonomic regulation will be normalized as all systems develop and grow, and the symptoms of VSD in an adult age may not appear at all.
You can be convinced that poor health is a consequence of autonomic dysfunction after a full examination. Many symptoms of VSD are similar to disorders in other pathologies, and it is important not to miss a condition that can be life-threatening.
Manifestations of dystonia are not dangerous, even if you feel very unwell. But if you do nothing for a long time to return autonomic regulation to normal, then you risk losing your health in the future.
The first episodes of crises in VSD are usually associated with severe stress or an age-related crisis. In the future, any minor reason can cause a storm of somatic symptoms, which will not be easy to cope with.
What does a doctor rely on when making a diagnosis?
The condition of vegetative-vascular dystonia may be similar to the symptoms of one or more diseases. But analysis of the data obtained from the patient and the examination results will help the doctor draw the right conclusions.
A hardware examination during the peak of poor health can best help to understand how much vital functions are affected. This determines treatment tactics. With dystonia, disturbances in the functioning of the body do not affect the condition of the tissues for a long time. Therefore, it is possible to differentiate which of the symptoms relates to VSD, and which is part of the disease of some organ.
The reaction to the amino acid complex Eltacin® will also have diagnostic significance. For vegetative-vascular dystonia, the drug will effectively relieve symptoms and improve the general condition during the first two weeks.
Diagnostics
If vegetative-vascular dystonia is suspected, the doctor usually prescribes a comprehensive examination due to the variety of symptoms. Only this approach helps to understand in detail the causes of the disease and methods of its treatment. What is important here is differential diagnosis, which allows one to exclude organic pathology. If VSD is suspected, the patient undergoes consultation with a neurologist, endocrinologist and cardiologist.
Identifying risk factors
Finding out the patient's medical history, the doctor establishes a family history of autonomic dysfunction. It is important if one of your close relatives has a stomach ulcer, bronchial asthma, hypertension, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, or diabetes mellitus. In childhood, vegetative-vascular dystonia can be aggravated by recurrent focal infections - both acute and chronic.
Assessment of the state of the autonomic system
To prescribe effective treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is necessary to assess the initial autonomic tone (at rest) and determine indicators of autonomic reactivity. For this purpose, the patient’s complaints are analyzed, and an EEG (electroencephalography) of the brain is also performed. Autonomic reactions are verified through various functional tests.
Cardiovascular research
Since the causes of the disease are directly related to the condition of the blood vessels, in order to prescribe the correct treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, it may be necessary to undergo Doppler ultrasound of the vessels (neck, brain). It is also possible that your doctor will order an ECG (electrocardiogram).
It is highly recommended not to refuse treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, no matter how insignificant the chosen method may seem to you. If the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe therapy, complete the entire course - do not neglect your own health.