© Author: Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
The Ruffier test is one of the tests used to assess the performance of the heart and the fitness of the body as a whole. Due to the fact that no special equipment is required to perform the test, any person can perform it independently and evaluate their endurance independently. But there are a number of contraindications, and in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, various aspects of this study will be described below.
It often happens that a doctor needs to assess the physical performance of a patient. This may be required in various situations, but the most important criterion is always the same - the ability of the heart muscle to adapt to the physical activity of the body. This ability is assessed by the doctor as the increase in heart rate per unit time. There are several modifications of such tests, but the most common is the Rufier test.
The essence of the method. Advantages and disadvantages
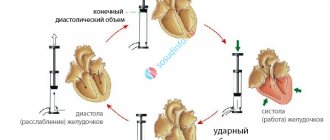
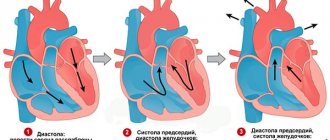
The basic principle of tests to assess the fitness of the heart muscle is to perform simple but intense physical exercises. During the first few minutes, the heart rate is assessed and compared with generally accepted standards or with certain scales. So, for example, when conducting the Ruffier test, squats are used at a fairly intense pace, and when performing the Harvard Step Test (HST), rapid climbs onto a low bench from a standing position are used. The increase in heart rate is subject to a linear relationship - the more adapted the heart is to the load, the less tachycardia after it and vice versa. That is, a trained heart tends to have a normal or even slower rhythm rather than a faster one.
The advantages of such methods are the possibility of independent use, simplicity and accessibility of the method. In addition, the test does not require expensive equipment, as in tests with physical activity during bicycle ergometry or treadmill testing, and therefore can be quickly and informatively used when conducting mass examinations.
Among the disadvantages of the method, one can note the risk of a hypertensive crisis or cardiac arrhythmia, as with any test with physical activity.
Regarding the Rufier test in children, it can be said that the disadvantage is the fact that when calculating the indicator, the child’s age is not taken into account, because the heart rate in children of primary school age is higher than in adolescents and adults. As a result, the Ruffier index in a small child is higher, although he does not have heart failure. As a result, the child may be denied participation in the sports section, which is a reason for frustration for both the parents and the child himself.
Quetelet Index / Also known as Body Mass Index (BMI)
From Zozhnik we will add a few more basic self-tests. BMI allows you to indirectly determine the degree to which body weight corresponds to a person’s height. Roughly speaking, it allows you to determine how fat or thin you are.
You can find out your BMI using this formula. For example, the Quetelet Index was calculated for a girl weighing 41.8 kg and height 152 cm:
Or even simpler: find your height/weight in this table and find out the preliminary results:
By the way, science says that both excessive and insufficient BMI is harmful to life expectancy.
Indications for testing
The Ruffier test and the modified Ruffier-Dixon test are carried out mainly by healthy individuals involved in professional sports, or entering sports schools and sections. In recent years, the Ruffier test has been included in the standards for medical examination of a child before entering an educational institution. This is due to the fact that some cardiac diseases in children can occur hidden, and the child may feel unwell during physical education class. The Ruffier test will help determine whether the child is able to tolerate physical activity.
Functional status check
To begin with, Irina Valentinovna explained that using the phrase “physical state” is incorrect: “There are the concepts of “physical development” and “functional state.” Physical development is the correspondence of anthropometric data and a number of other parameters to the average values of groups of people divided by age and gender.”
If we talk about assessing the functional state, which determines the ability to tolerate physical activity, then to determine it, many tests are used that evaluate the response to physical activity of all interested body systems. Such systems include the cardiovascular system, central, peripheral and autonomic nervous systems, endocrine system, and so on.
Tests to determine the functional state of most systems are complex and cannot be used in everyday life.
By developing a theory about the unity of processes occurring in the body, which says that changes in one of the body systems will sooner or later lead to changes in other systems, it is possible, by conducting simple tests, to assess the state of the system that is most accessible for obtaining indicators. Such systems are the cardiovascular system and the autonomic nervous system; their response to stress can be assessed using heart rate.
Contraindications
Under no circumstances should the Ruffier test be performed on a person suffering from a cardiac disease with chronic heart failure. To determine the functional class in such patients, there are more complex tests (VEM, treadmill), or a 6-minute walk test.
In addition, squats should not be performed by a child or an adult if he has problems with the musculoskeletal system, as this disease may worsen.
Romberg pose training
- You need to stand up straight, put your feet together, so that your heels are connected and your toes are apart. A slightly more complicated version - the feet touch, the toes do not spread apart. The legs and knee joints are not tense, the legs are comfortable.
- Distribute the weight of your entire body evenly on your feet.
- The shoulders are turned, the shoulder blades are down. We try to straighten the spine as much as possible.
- As you inhale, slowly raise your arms to shoulder level, turn your palms up, and as you exhale, lower them.
- We repeat raising our hands 8-10 times.
- We constantly control the spine. The spine is straight throughout the entire exercise.
- We control the feet. Body weight is evenly distributed on both feet.
Bicycle ergometry
Preparation for the procedure
No special preparation is required on the eve of the study.
On the morning of the test, the patient should not take drugs for high blood pressure such as beta-blockers (bisoprolol, metoprolol, anaprilin, etc.), verapamil and diltiazem, since these drugs for high blood pressure reduce the heart rate, causing the doctor to may obtain distorted research results.
In addition, on the day of the study you are strictly forbidden to smoke or drink alcohol. A light breakfast is allowed in the morning.
Regarding children, it can be noted that the child should come to the study sleepy and rested. Parents should explain to the child what the principle of the test is in order to eliminate the child’s worries, since stress causes tachycardia. The child should not run or play active games before the study.
Norm and deviations in children and adolescents
Further assessment of indicators is carried out using tables that take into account the age of children. For first-graders, the test results are as follows:
- excellent – 6,
- good – 6.5 – 11,
- satisfactory – 12 – 16,
- weak – 17 – 21,
- very bad – over 21.
After 15 years the criteria are more stringent. They are distributed according to the given gradations as follows:
- 0;
- 0,5 — 5;
- 6-10;
- 11-15;
- over 15.
An example of the results of an examination of medical school students.
An excellent indicator means that the child can seriously engage in sports, but a very poor indicator means that an examination and special low-intensity training are required, and possibly hospital treatment.
How is the Ruffier test performed?
In the office of the doctor conducting the test, the patient rests and relaxes as much as possible in a sitting position for about five minutes. Next, the doctor counts his pulse in a lying position for 15 seconds. The resulting value is conventionally designated as P1. The patient then performs 30 squats in 45 seconds. This is a pretty intense pace, so if he can't squat that fast, he should do it at a pace that feels comfortable to him.
After squats, the recovery period begins in a lying position. During the first 15 seconds of the rest period, the pulse (P2) is calculated. After another half a minute, the pulse is counted again (at the end of the first minute of rest) for 15 seconds and the P3 value is obtained.
After performing the specified manipulations, the patient rests, and the doctor calculates the Ruffier index.
Harvard step test
This test was developed at the Harvard Fatigue Laboratory under the direction of D. V. Dilla (1936). The test consists of lifting onto a bench 50.8 cm high with a frequency of 30 times per 1 minute. If the subject gets tired and cannot maintain the set pace, the lifts are stopped and then the duration of the work is recorded in seconds until the pace decreases. However, the duration of the exercise should not exceed 5 minutes.
Each lift is performed for 4 counts (preferably with a metronome):
- once - with one foot on the step,
- two - another,
- three - one foot on the floor,
- four - another.
The height of the step and the duration of the load depend on gender, age and body surface area.
Stepping onto a box with dumbbells
Immediately after stopping the exercise, the subject's heart rate is measured in a sitting position. The pulsation number is calculated in the intervals between 1 min and 1 min 30 s (P1) between 2 min and 2 min 30 s (P2) and between 3 min and 3 min 30 s (P3) of the recovery period. Based on the duration of work performed and the number of pulse beats, an index (IGST) is calculated, which allows one to judge the functional state of the cardiovascular system. IGST is calculated using the full or abbreviated formula:
IGST = T x 50 / (P1 + P2 + P3)
where T is the ascent time (in sec); P1, P2 and P3 - heart rate for 1, 2 and 3 minutes of recovery (counted in the first 30 seconds of each minute).
Interpretation of results
In order to obtain the Ruffier index, according to which the fitness of the heart is assessed, a formula is used.
IR = (4 x (P1 + P2 + P3) – 200) / 100
Next, the resulting index is assessed in accordance with the scale:
- Unsatisfactory result, or poor heart function, possibly severe heart failure - more than 15.
- Poor result, poor heart function, or moderate heart failure – 10-15.
- Satisfactory result, average performance, no insufficiency – 6-9.
- Good result, good performance – 3-5 (normal).
- Excellent result, excellent heart function – 0-3 (normal).
Calculation example:
Adult male, 28 years old. P1 at rest before the load = 20, P2 in the first 15 seconds after 30 squats = 25, P3 in 15 seconds after half a minute from the start of rest = 23. IR = {4 x (20+25+23) – 200}/100 = 0.72 . Excellent heart function (normal).
Sometimes a modification of the Ruffier index, called the Ruffier-Dixon index, is used:
Ruffier-Dixon index = ( (P2-70) + (P3-P1) )/ 10.
The results are assessed on a scale:
- A good result corresponds to indicators 0.1-5,
- Average – 5.1-10,
- Satisfactory – 10.1-15,
- Bad – 15.1-20.
Due to the fact that children of different ages have different heart rates (in children it is higher than in adolescents and adults), adapted tables are used to evaluate the Ruffier test in childhood:
Preparing and administering the test
No special additional equipment is required to carry out the analysis. Couch, heart rate monitor, stopwatch. The ideal option is to conduct it with an experienced doctor to prevent unusual situations and the body’s reactions to stress.
Performing the Rufier test:
- Testing is carried out no earlier than 2 hours after eating. You should also not take tobacco or drink strong tonic drinks (tea, etc.).
- We recommend comfortable clothing to allow you to move freely.
- Bring your pulse to a calm, normal state while lying down.
- After 5 minutes of rest, you need to measure the average pulse on the radial artery for 15-16 seconds. P1 value.
- Perform 30 squats in 40-45 seconds.
- Lie down and measure your average heart rate for 15 seconds. P2 value.
- Rest for 30 seconds and measure your pulse again for 15 seconds. P3 value.
In this way, the rate of increase in heart rate under load and its normalization after stopping work is determined. The Ruffier value is calculated, which is used to judge the performance of the heart and the state of the autonomic nervous system.
Formulas and results
Next, use the following formula:
IR = ((P1 + P2 + P3) *4 – 200) / 10, where:
- IR – Individual calculation.
- P1 – pulse before starting work
- P2 – pulse after finishing work.
- P3 – pulse one minute after exercise.
The calculated value ranges from 0 to 21. The lower it is, the more prepared and trained the cardiovascular system is.
Example calculation for a child
For example, when calculating the index using the Ruffier test method, let’s take a child aged 12 years. The child's average heart rate was P1 = 22, after exercise P2 = 33, after rest P3 = 23:
- we add up these indicators: P1 + P2 + P3 = 22 + 32 + 23 = 77;
- multiply the result by 4: 77 * 4 = 308;
- subtract 200 from the resulting number: 308 – 200 = 108; divide the result by 10: 108 / 10 = 10.8.
Therefore, the child’s IR is 10.8.
Proper preparation for the event
There is no special preparation required for the test, however, it is recommended to consider the following recommendations:
- From the moment of awakening, the test taker should not take blood pressure medications or stimulants. Otherwise, the test results will be distorted.
- You should not use tobacco or alcohol. A light breakfast is recommended.
- It is advisable to get a good night's sleep and rest before the test.
- The specifics of the test must be explained to the child to avoid unnecessary worries.
- Avoid stress, games and other activities before the test.
Standards for children
An age group is used to assess the results of children and adolescents. The results are divided into Excellent, Good, Satisfactory, Weak, Unsatisfactory
- The normal value for a child from 7 to 10 years old is 8-9.
- The normal value for a child from 11 to 14 years old is 5-6.
- For teenagers over 15 years old, the normal value is 5.
Standards for children 7 – 10 years old
Standards for children 11 – 14 years old
Standards for children over 15 years old
What do the test results say?
If you are a beginner
The index value obtained from the formula demonstrates your general physical fitness and the capabilities of your heart. If the level is lower than good shape, it means that you really need to work on developing your muscles and heart capabilities. How to do this is described in the article Stroke volume of the heart.
General physical training should begin with simple exercises using your own body weight or small dumbbells.
If you are an experienced athlete
If you have been training for a long time, a low test score (high value in numbers) can mean two things.
1. You pay little attention to heart training. This is especially true for bodybuilders and powerlifters. I recommend including training that develops aerobic capabilities in your annual cycle. This, by the way, is a very wise strategic step, thanks to which you will improve your health and significantly extend your sports career. I'm not saying that a developed heart for you means a direct increase in results from strength training.
2. A low Ruffier-Dixon index may mean that you are overtraining. Ideally, it is necessary to conduct such a test several times with a difference of 2-3 weeks to see the dynamics. If the test result becomes worse, it is necessary to make changes to the program, rest and nutrition.
Step type reaction
- Resting heart rate (pulse) and resting blood pressure are normal.
- Heart rate, SBP and DBP immediately after the Rufier test are normal (see normotonic type of reaction)
- After 1-3 minutes of rest, heart rate increases sharply, and SBP increases.
- Immediately after exercise, the SBP “upper pressure” is lower than after 2 or 3 minutes of rest.
This reaction is unfavorable. Reflects the inferiority of the regulatory mechanisms of blood circulation and is observed after infectious diseases, lack of training, hypokinesia. Reason to consult a doctor if the reaction continues in the future.
If you identify atypical reactions to the Rufier test, you need to repeat the test after some time (1-2 weeks) and if the scenario repeats, consult a doctor.
There are a huge number of factors that can affect the accuracy of determining the type of response of the cardiovascular system to the Rufier test, please consider them before performing:
- smoking before testing
- drinking coffee and caffeinated drinks
- alcohol consumption
- menstrual cycle in women