The thymol test (thymoloveronal test, thymol turbidity test, Maclagan test) is not one of the particularly popular biochemical methods of blood testing, however, it is not discounted when identifying certain diseases and is still used in clinical laboratory diagnostics.
Nonspecific reaction based on the interaction with thymol in the veronal buffer of individual plasma proteins
(gamma globulins and beta globulins associated with lipids - low-density lipoproteins), and turbidity of the solution, does not give a clear answer in relation to certain diseases, but often significantly helps in combination with other tests, and in some cases, even ahead of them . This occurs in the initial stages of the disease (hapatitis A in children, for example), when other laboratory tests are still within normal limits. In addition, it has other advantages that do not allow laboratory diagnostic doctors to consign this analysis to oblivion.
What should be the norm?
A tomal blood test shows whether the level is normal or exceeded. The thymol test rate for women is the same as for men. In some cases, certain individual characteristics of the organism may be taken into account. The indicator is assessed by the attending physician.
The norm is a result with a reading from zero to five units.
The study allows you to identify possible health problems:
- liver pathologies,
- kidney inflammation,
- rheumatoid diseases,
- viral infections,
- gastrointestinal diseases,
- and others.
In most cases, if the thymol test is elevated, then pathological processes occur in the liver. If the diagnosis is not confirmed, examinations begin to exclude other diseases.
Reasons for false changes
If the test result shows that the norm for the protein reaction level is too high, then, as already mentioned, the liver is examined first. Until the eighties, this study was used exclusively for diagnosing the condition of the liver; in recent years, more and more attention has begun to be paid to changes in serum protein in pathologies of other organs.
A high rate may also be the result of an incorrectly conducted study, so several factors are taken into account when deciphering:
- individual characteristics of the patient’s body (weight, age, concomitant diseases, etc.),
- time and process of blood sampling (in the morning and only with special devices),
- taking hepatotoxic drugs by patients.
Hormonal contraceptives taken regularly can increase the level of this indicator in the blood of women.
An amazing fact is that in cases of jaundice, in more than half of cases, the thymol test in an adult remains normal. However, when the disease causes complications, thymol increases sharply.
Advantages of thymol test
Usually the thymol test is in addition to bilirubin and enzymes
(transaminases - AlT, AST, alkaline phosphatase) if damage to an organ is suspected, characterized by the variety of biochemical reactions occurring in it. Of course, we are talking about the liver, on the normal functioning of which the implementation of basic life processes in all cells of a living organism largely depends. And what’s interesting is that these indicators may not yet particularly respond to pathological changes and therefore may not exceed or slightly exceed the levels of normal values, and the thymol test will already clearly “creep” upward.
In addition to identifying liver abnormalities, the thymol test, the norm of which is from 0 to 4 SH units, in other cases helps in diagnosing pathological conditions of the heart, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and other organs.
The main advantages of the thymol test are that it:
- Does not require special time and material costs, or the use of complex equipment (reagents are prepared on a magnetic stirrer in a fume hood);
- It is easy to perform (the result is read using an electrospectrophotometer, which is available in any laboratory);
- Makes it possible to start treatment in the early stages of the disease and thus helps to avoid unwanted complications caused by a prolonged inflammatory process;
- Can be used as a good indicator of the effectiveness of therapeutic measures aimed at restoring the functional abilities of the liver tissue.
That is why, despite the wide variety of new laboratory tests, in some cases the thymol turbidity test remains among the main tests that identify pathological conditions of the liver.
Increased rate
A referral for a thymol test is given by the attending physician based on certain indicators. If it is discovered that the thymol test is elevated, the patient may be sent for a repeat test, or an additional examination may be prescribed to confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
An increase in the indicator demonstrates the presence of a pathological process in the body, which shows the likelihood of developing the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis, or another type of nephritis,
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- renal amyloidosis,
- enteritis,
- lupus,
- pancreatitis,
- dermatomyositis.
When the results of the study determine an elevated thymol test, the most unfavorable prognosis may be oncology.
But first of all, the patient has a high probability of progression of liver disease:
- cirrhosis,
- jaundice,
- hepatitis, both viral and toxic or alcoholic,
- fatty liver degeneration,
- organ intoxication.
Sometimes repeated analysis gives normal results. What does this mean - improper preparation for the test or a mistake by the laboratory technician when taking blood.
When results improve
Advertising:
In various liver diseases, attention is always drawn to a decrease in the albumin fraction, which is associated with a violation of their synthesis, and an increase in the gamma and beta globulin fractions. This occurs because albumin is synthesized directly in liver cells, and the affected parenchyma is not able to provide normal levels of albumin. The simultaneous increase in globulin fractions (with a decrease in albumin concentration) is explained by the fact that other components - cells included in the tissue macrophage system - are predominantly responsible for the production of these proteins.
The main reasons causing an elevated thymol test are liver diseases accompanied by damage to its parenchyma:
- Infectious and viral hepatitis;
- Neoplasms localized in the liver;
- Damage to the liver parenchyma by alcohol and, especially, its surrogates;
- Toxic effects of various poisons, heavy metals and some medications;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Fatty degeneration of liver tissue (fatty hepatosis) – accumulation of fat in hepatocytes (liver cells);
- Functional disorders caused by long-term use of oral contraceptives and other hormonal drugs.
However, regarding the liver, it should be noted that obstructive jaundice, although frightening with its external manifestations, in itself does not expand the boundaries of thymol turbidity. This test will be increased only if liver tissue is involved in the pathological process and parenchymal hepatitis develops
.
Other causes of increased thymol test:
- Severe kidney pathology (amyloidosis, pyelo- or glomerulonephritis), in which a large amount of protein is constantly excreted in the urine;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, enteritis with severe diarrhea);
- Tumor processes of benign and malignant nature of various localizations;
- Pathological conditions caused by viral infection;
- Hereditary dysproteinemia (violation of the ratio of serum proteins);
- Myeloma;
- Systemic diseases (SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid polyarthritis, dermatomyositis);
- Septic endocarditis (with rheumatism, the test is not elevated, it remains within normal limits);
- Malaria.
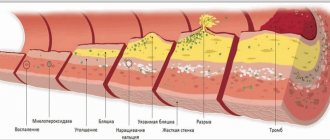
The thymol test can be elevated even in the absence of illness - for example, if a person is overly fond of fatty foods.
In this case, prosperity will also not last indefinitely. Another problem will arise - increased cholesterol, a change in the lipid spectrum... Low-density lipoproteins accumulated in the blood will begin to be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, forming atherosclerotic plaques, which, in turn, will give rise to a pathological process such as atherosclerosis. That is, a constantly elevated thymol test and the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease indicate that an urgent need to change the diet.
Decoding
Even in cases where there is an increase in the thymol test, the reasons are not always serious. This study consists only of confirming or denying the reaction of protein serum. Therefore, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on what the analysis shows.
Decoding the results of a blood test is simple. If the indicator shows no more than five, then the thymol test is normal. However, if the level is above normal data, then you should undergo a full diagnosis, establish a diagnosis and begin treatment.
When, as a result of diagnosis, it is possible to reveal that the thymol test is elevated, the reasons for the deviation should be determined as early as possible. With the development of many diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis or oncology, detection at an early stage of development, this significantly increases the chances of recovery.
Thymol test as a screening test for HIV infection
The basis for screening diagnosis of HIV infection is ELISA analysis. This test has a number of disadvantages: it requires expensive equipment, qualified personnel, informed consent of the patient, and, in addition, obtaining the result often requires a long wait. At the same time, the epidemic situation regarding HIV infection in the Republic of Belarus has already reached such a level of distress at which it is advisable to conduct a screening examination of all patients served in medical institutions.
During the search for other accessible and sensitive rapid methods for diagnosing HIV infection, it was noticed that the majority of HIV-infected people registered at the dispensary have a high level of thymol test. Accordingly, the purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic value of the thymol test as an accessible screening test for HIV infection.
A case-control design was chosen for the study. The experimental group included 125 patients who were registered for HIV infection in the consultation and dispensary office of the Vitebsk Regional Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital. The control group was selected in such a way as to be comparable to the experimental group in terms of gender, age and the presence of chronic viral hepatitis. Persons with elevated levels of ALT and AST were excluded from the study.
In the experimental group, the average value of the thymol test exceeded the normal value by more than 2.5 times and was significantly different from the corresponding indicator in the control group (U-test, p
It can be concluded that in HIV-infected people the average level of thymol test is significantly higher than in the population as a whole. The calculated values of sensitivity (90%) and specificity (94%) allow the use of the thymol test as a mass screening test for the presence of HIV infection. The advantages of the method include its low cost, speed of execution and ease of implementation; In addition, this examination does not require the patient’s consent, and there is no need for pre- and post-test counseling, which saves the doctor’s time. (See Materials of the Second Congress of the Euro-Asian Society for Infectious Diseases: Zhiltsov I.V. et al. “Thymol test as a screening test for HIV infection”
).
"Journal of Infectology"
, 2012, No. 3, supplement, p. 46 - 47.
Recommendations
In some forms of disease, the indicator may remain unchanged. However, in children this analysis usually requires more attention. Because, for example, with the progression of hepatitis A in children, the norm is exceeded, but with hepatitis B, the thymol test gives normal results. It is also possible to increase the serum protein reaction after the child has had hepatitis. For these reasons, it is always recommended to carry out additional diagnostics: one thymol test can lead down the wrong diagnostic path.
For preventive purposes, the described examination is not carried out, since it is not classified as a standard biochemical blood test. However, if there are indications for research, then many specialists, despite the capabilities of modern medicine, in the form of immunological and other tests, still give preference in the old-fashioned way to the thymol test, since the result of this type of diagnosis makes it possible to detect the disease in time and begin to treat it, avoiding complications .
Blood chemistry
Biochemical analysis is one of the main diagnostic methods for confirming the diagnosis, determining the extent of damage to other organs and the adequacy of treatment of the disease.
Clinical analysis of blood cells helps to quickly identify acute surgical, gynecological or therapeutic pathology by excluding inappropriate symptoms and laboratory findings.
The biochemistry of the constituent elements of blood serum is done relatively slowly. This is due to the dependence of the indicators on chemical and physical serum reactions. Such a study must be done in case of diabetes mellitus, hepatitis of various etiologies, cardiomyopathy, diseases of the thyroid and pancreas, etc. For each disease there is its own set of biochemical markers, based on the results of which the diagnosis is confirmed or removed.
Let's try to decipher it ourselves
Advertising:
Decoding the analysis is simple and accessible even to the patient himself: all you need to know is that the laboratory accepts 4 or 5 SH units as the upper limit of normal. And the range of diseases accompanied by an increased thymol test is not so wide.
When deciphering the analysis, you should not judge the quantitative ratio of proteins on your own. One can only assume that for some reason less albumin is synthesized.
In order to find out these indicators in digital terms, other studies should be carried out: determine the concentration of total protein and albumin, isolate protein fractions using electrophoresis, calculate the albumin-globulin coefficient... And if the doctor considers it necessary, these reactions will be performed, and the reader only has to understand that a diagnosis cannot be established based on one nonspecific analysis. In the body, all biochemical processes are interconnected, and the same is true in the laboratory: one test involves the parallel conduct of other studies.
And the last thing:
so that decoding does not cause difficulties and anxiety, it is necessary (as always) to properly prepare for the study. And everything is as simple as always: blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, and during dinner the day before, fatty foods are excluded.