Decoding the results of the analysis for total protein
The normal level of total protein in the blood ranges from 60 to 83 g/l. Levels may vary slightly depending on the reagents and equipment in the laboratory, as well as other factors such as age, gender and testing method.
If this indicator is not normal, in order to make a diagnosis, it is necessary to perform additional tests to determine which protein concentration is decreased or increased.
If total protein in the blood is elevated, this may indicate the following factors:
inflammation or infection (eg, hepatitis B or C, HIV)
Bone marrow disease (eg, multiple myeloma or Waldenström's disease)
This indicator is also elevated during pregnancy.
Low levels of whey proteins may indicate:
· bleeding,
liver pathology
kidney pathology (for example, nephrotic syndrome or glomerulonephritis)
· malnutrition
malabsorption (eg, celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease)
· extensive burns
agammaglobulinemia
General information
Preventive examination and diagnosis of most diseases begin with blood tests. Total protein
is an important analysis that is required in many cases. The movement of proteins in the bloodstream and their changes are natural processes. In a number of pathologies it is disrupted. The liver is mainly responsible for the circulation of proteins. Disturbances in the functioning of this organ affect protein metabolism.
Proteins are necessary for the body to build tissues and cells, produce hormones, enzymes, produce antibodies and a number of other vital processes. In addition, they transport metabolic components in the bloodstream and deliver them to cells that need such substances. When there is insufficient nutrition, proteins are used by the body as a source of energy. In addition, they are responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance.
There are two types of serum proteins: globulins and albumins. The former are responsible for immune functions, blood clotting, transport of biochemical compounds, and are part of hormones and enzymes. Albumin synthesis occurs in the liver. They maintain osmotic pressure.
Deviation of indicators from the norm is not always caused by pathological reasons; in some cases it is explained by a certain physiological state. Deviations are divided into absolute and relative. A physiological decrease or increase in protein levels can be caused by prolonged periods of immobility, pregnancy, lack of protein in the daily diet, excessive water load or fluid loss. A relative pathological increase in the amount of protein is associated with blood thickening, which is caused by fluid loss (for example, with severe diarrhea, vomiting). A relative pathological deficiency of proteins is observed when there is an excess of fluid in the bloodstream. The reason for this may be disruption of the heart, kidneys, or hormonal balance. An absolute excess of protein may indicate the presence of an infectious disease and a number of other pathologies. Absolute protein deficiency has the greatest clinical significance. As a rule, it is caused by a decrease in albumin levels. In this case, we can talk about low viability of the organism. The cause of this pathological condition may be gastrointestinal pathology, chronic intoxication, malnutrition, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, and endocrine disorders.
Call us
+7
Increased total protein: what does it mean?
This situation is rare, and yet it does occur. The first reason for this condition may be dehydration, but this problem is quite easy to deal with. The second reason is more serious – blood cancer. In this case, lymphocytes overproduce an abnormal amount of immunoglobulin, which no longer has a useful function, but quantitatively affects the value of the total protein.
Get tested for total blood protein in Moscow at the Meditsina clinic
A blood test for total protein is used to diagnose a huge number of diseases of almost all organs and systems. You can donate it at the Meditsina clinic, located in the Moscow ZAO area. We have our own laboratory, where a wide variety of analyzes of biological material are carried out using modern equipment.
In addition, our clinic employs qualified doctors who correctly interpret test results and prescribe effective treatment if necessary.
Here you will also find affordable prices for medical services - check out the price list to find out how much a particular test costs. You can make an appointment with a doctor, as well as tests, by phone or online.
Causes of protein deficiency
- Impaired liver synthetic function
- the central metabolic factory. It is here that blood plasma proteins are formed: albumins and most globulins, which largely mediate the maintenance of homeostasis in the body.
This is accomplished by forming oncotic pressure: protein molecules, due to their chemical nature, attract water, thus exercising control over water-salt metabolism. An important consequence can be drawn from this: when the concentration of proteins in the blood serum is low or when they increase in the intercellular fluid and tissues, which is especially characteristic of inflammatory processes accompanied by increased vascular permeability, edema develops - water goes beyond the arteries and veins.
In diseases manifested by damage to hepatocytes (toxic or infectious agents), edema also occurs - and mainly on the lower half of the body and limbs. We wrote about this in more detail in this article:
- Nutritional factors
- fasting, generally leading to protein-energy deficiency, or an unbalanced and uncompensated plant diet with nutraceuticals, accompanied by a lack of essential amino acids in the diet - that substrate for the construction of cells and tissues that the body cannot reproduce on its own, from available elements and with the help of those present enzymes.
Below we have provided a small table with essential amino acids and the foods in which they are concentrated. We hope that this will help you competently organize and choose the type of nutrition that suits you.
| Valin | Isoleucine | Leucine | Lysine |
| eggs | soybeans | peas | chum salmon |
| milk products | peanut | perch | lentils |
| beef | egg yolk | turkey | chicken and turkey |
| lentils | pink salmon | milk | mutton |
| Methionine | Threonine | Tryptophan | Phenylalanine |
| eggs | sunflower seeds | turkey | beans |
| meat | pollock | squid | almond |
| milk and dairy products | zander | milk | cashew |
| mackerel | sesame | pistachios | cod |
- One of the most common pathologies that leads to difficulty absorbing protein from food is reduced acidity of gastric juice.
Hydrochloric acid produced by the parietal cells of the mucosa activates proteolytic enzymes and, in addition, promotes the swelling of protein molecules, facilitating enzymatic processing of food. It is also a powerful nonspecific protection factor that has a strong bactericidal effect - in particular, against protozoa, parasitic worms, bacteria and viruses.
The widespread popularity of self-administration and frequent prescription of proton pump inhibitors (“Omez”) has become a cause of serious concern among scientists about the likely consequences of their long-term use not only on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but on the body as such.
In addition to the effects of medications, disruptions in the folate cycle
(or rather, in the three main genes that regulate it: MTHFR, MTR, MTRR), since it is this that ensures the formation of the main mediator of the parasympathetic system - acetylcholine, which also stimulates the parietal cells of the stomach. When a mutation is detected, additional support for the body is necessary, aimed at reducing the concentration of homocysteine that accumulates in such conditions - an amino acid known for its damaging effect on the endothelium (the inner lining of the vessel) and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic damage.
We recommend
“Vitamin D: top 30 foods with its high content” Read more
On the other hand, along with insufficient formation of acetylcholine, there is an increase in the inflammatory mediator - histamine. This occurs due to a disruption in the processes of its neutralization, normally carried out by methylation reactions. Considering that histamine is also an activator of gastric juice secretion, we can draw a logical conclusion: the effect of the folate cycle on the digestive system is somewhat ambiguous. It is logical to assume that under conditions of excessive intake of this biogenic amine, not only erosive lesions of the gastric mucosa develop, but also, due to increased permeability of the intestinal wall, structural elements of bacteria enter the systemic bloodstream - an inflammatory process is observed, and not limited to the gastrointestinal tract.
Another possible cause of hypochlorhydria is atrophic gastritis
- an autoimmune disease, accompanied by a decrease in the number of functioning cells due to their death during the “attacks” of antibodies from an immune system gone crazy, which ceases to clearly distinguish between what is “ours” and what is “foreign”.
- Damage to the gastric mucosa
: ulcers, gastritis, erosion. Despite the widespread belief in people’s minds that inflammation of the epithelial lining is purely caused by H. pylori, this cannot be compared with one hundred percent truth.
Firstly, infection occurs in early childhood, so the very concept of infection in adolescence or adulthood is more likely an ephemeral rarity than a truth as such.
Secondly, everything depends on the strain of the bacterium: not all of them are aggressive (or at least so strongly pathogenic that clinical manifestation and inflammation of the gastric mucosa itself appear) - and this entails mandatory diagnosis (at least before prescribing 2 weeks of antibiotic therapy). Considering the widespread distribution of the latter, which has already led to total resistance of the microflora (inhabiting both the distal parts of the small and large intestines of humans) to chemicals, as well as the bacterial past of mitochondria, our small power plants, selflessly producing energy, the decision to eradicate Helicobacter It should be well thought out by the doctor or nutritionist that resorting to more gentle therapy with nutraceuticals.
Helicobacter actually adapts (unlike most microorganisms) to the unfavorable conditions of the gastric environment: having a specific enzyme that breaks down urea, it alkalizes its habitat by releasing ammonia. However, pathology develops only when it disseminates - spreads from the pyloric region bordering the duodenum along the entire perimeter of the stomach.
Stress often leads to damage to the gastric mucosa
: it is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system with the subsequent release of adrenal medulla hormones into the blood, which, in turn, affecting the secretory apparatus of the kidneys, stimulate their release of a vasoconstrictor. It is the narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, including those that supply blood to the stomach, that leads to subsequent ulceration of the mucous membrane.
- Impaired breakdown and absorption of proteins in the intestine.
The first is characteristic of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, in which its secretory cells cease to form and release a sufficient amount of enzymes into the blood (and not only proteolytic ones). The second accompanies malabsorption syndrome and celiac disease - another autoimmune disease that, unfortunately, has ceased to be such a rarity today.
- Violation of bile formation and bile outflow,
which leads to the impossibility of not only the emulsification of fats, but also the activation of pancreatic enzymes. Helminthic infestation, blockage of the biliary tract by stones, decreased fluidity of this secretion due to the predominance of cholesterol over other components (bile acids and phospholipids) - a large number of possible causes necessitate careful laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, which build the missing puzzles in the clinical picture of the disease.
- Kidney diseases:
Normally, protein molecules are not filtered into primary urine due to their bulky size. However, if the renal filter is damaged (the formation of “holes” in it), massive proteinuria is observed, as evidenced by the detection of proteins in a general urine test.
Causes of low blood protein
Heart disease may cause hypoalbuminemia
- Impaired albumin formation in liver diseases: cirrhosis, tumors, hepatitis, hepatosis.
- Decreased protein synthesis due to chronic and acute heart failure.
- Impaired protein absorption due to endocrine disorders, inflammatory processes in the intestines, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
- Accelerated breakdown of albumin as a result of infectious infections, extensive injuries and burns, rheumatic pathologies, sepsis.
- Increased protein loss in nephrotic syndrome, characterized by damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys.
- Impaired glomerular filtration of the kidneys as a result of damage to the renal blood vessels in diabetes mellitus.
- Insufficient protein intake during strict diets and fasting.
- In newborns, the cause of HA may be immaturity of liver cells.
- Pregnancy.
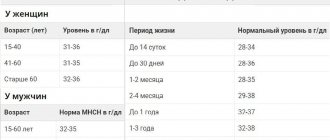
Reference values for total protein
| Age | Women, g/l | Men, g/l |
| 1 day – 4.3 weeks | 42–62 | 41–63 |
| 4.3 weeks – 6 months | 44–66 | 47–67 |
| 6–12 months | 56–79 | 55–70 |
| 12–24 months | 56–75 | 56–75 |
| 24 months – 14 years | 60–80 | 60–80 |
| 14–60 years | 64–83 | 64–83 |
| > 60 years | 62–81 | 62–81 |