Electrocardiography is the simplest method for studying heart disease. Its result is an electrocardiogram - a graphic image obtained during the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles. Ultrasound of the heart makes it possible to visually examine the internal organ, thanks to a special sensor that conducts rays and receives received impulses. Heart ultrasound (or ECHO CG) provides complete information about the structure of the organ, its size; with such an examination, it is possible to notice even the most minor deviations that affect the well-being of patients.
ECG is the first test on the diagnostic path
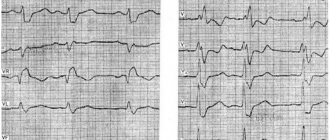
A patient who complains of chest pain to a therapist is almost immediately given an ECG, that is, an electrocardiogram. This is a test that can be performed very quickly in any clinic, hospital, or even at the patient’s home. An ECG is usually the first test to diagnose cardiovascular disease. An ECG should be performed on every patient visiting a cardiologist or with cardiac disease or chest pain. It is also recommended to perform an ECG for healthy people involved in sports professionally and as amateurs. To perform this test, you will need an electrocardiograph that records the functional currents of the heart muscle. Each muscle, including the heart muscle, produces electrical impulses that are recorded by the machine and transferred to paper. A special printout of electrical impulses is an electrocardiogram. An ECG test can detect dangerous cardiac arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, conduction block, tachycardia), as well as a recent heart attack. However, the diagnostic value of the test is limited, because even a correct ECG recording does not clearly exclude serious heart disease, and then a more accurate diagnosis is necessary. An at-home ECG is a safe and quick test. The patient, lying on his back, has electrodes glued or attached to his chest, arms and legs. The test itself takes up to 5 minutes and does not require special preparation. The patient receives the test result immediately after it is performed.
Holter monitoring
Sometimes the work of the heart requires not even regular monitoring, but constant monitoring. Then Holter monitoring is prescribed. An electrocardiograph is attached to the patient’s chest and it records changes in heart function throughout the day – both at home and at work. Usually this method is used after a regular ECG. The indications for it are clear: you need to determine the nature of the disturbances in the rhythm of the heart.
- If isolated rhythm disturbances are detected, this is within the normal range and it is too early to worry
- If hundreds - as a rule, preventive or strengthening therapy is needed
- There are several thousand rhythm disturbances per day - special therapeutic therapy is needed
- Tens of thousands of rhythm disturbances per day - urgent treatment by an arrhythmologist is necessary
- Sometimes rare, but sudden and life-threatening rhythm disturbances are detected, which are treated individually
Heart Echo - evaluates the anatomy, functions and changes in the structures of the heart!
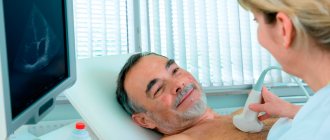
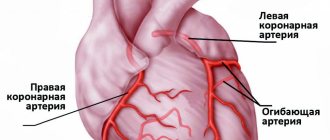
Another test that cardiologists order when they need more information is an echocardiogram, more commonly known as a cardiac echo, simply an ultrasound of the heart. The specialist uses an ultrasound scanner to examine the heart, most often using the transthoracic method. It is non-invasive and does not require special preparation. Usually lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. During the examination, the doctor can evaluate the anatomical and functional aspects of the heart, i.e. confirm or rule out the presence of birth defects, leaks, and structural defects of the heart. He can also evaluate the condition and function of the heart valves, that is, recognize valve defects. Cardiac echo helps evaluate contractility and function of the heart muscle, which are associated with myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and ischemia.
IMPORTANT! An echocardiogram is a repeatable test, but its diagnostic value depends on the experience and skill of the treating physician. In case of diagnostic doubt, the diagnosis should be expanded to include, for example, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT). Transthoracic echocardiography allows you to determine the state of the disease, the degree of its development and the effectiveness of the treatment. An indication for its implementation is also a suspicion of pulmonary arterial hypertension. After this, if in doubt, transesophageal echocardiography can be prescribed.
Advantages of having an examination in our clinic
Among the main advantages of medical treatment are the following points:
- Affordable prices for all types of examinations and surgical procedures
- Wide range of modern equipment
- Highly qualified doctors
- City center location
Other services of our clinic:
- — Ultrasound of internal organs
- - Ultrasound of the uterus
- — Office hysteroscopy
- — Ultrasound of the heart
- — Ultrasound by week of pregnancy
- — Treatment of erosion
- — Treatment of urinary incontinence in women
- — Treatment for lack of orgasm
- — Androgyne in gynecology
Holter ECG - if a heart rhythm disorder is suspected!
Many patients who go to the doctor report that their heart rate is fast or slow, but the ECG is normal. Then the doctor decides to perform a Holter ECG. Holter is nothing more than an ECG, but its duration is 24 hours and sometimes 48. The patient usually has five electrodes attached to the chest, connected to a special device that contains a memory card on which the daily ECG image is recorded. The device is compact and can be attached to a belt. An ECG recorder is most often performed when cardiac arrhythmia, that is, supraventricular arrhythmia, is suspected:
- atrial fibrillation,
- increased heart rate (tachycardia),
- slow heartbeat (bradycardia),
- heartbeat,
- conductivity blocks.
It is also recommended to perform a holter in case of frequent fainting or loss of consciousness.
This test looks for so-called silent myocardial ischemia in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. This is also a study conducted on patients with a pacemaker to monitor its performance. IMPORTANT! An ECG recorder is not invasive, but there are a few things to keep in mind! After putting on the device, the patient should lead a normal lifestyle. To do this, he must keep a special activity diary in which he records individual actions and the periods of time in which they were performed, for example: climbing stairs, eating, driving, rest and sleep times, as well as symptoms such as dizziness, rapid palpitations, fatigue or shortness of breath, etc. The heart rate monitor also monitors your heart rate at night, giving your doctor valuable information. During the test, remember that the electrodes should not come off, and if you notice this, stick them with adhesive tape. During the examination (24 or 48 hours), you should not swim or shower. After the examination, the card with the record goes to a specialist who, using a special program, downloads the data and analyzes it. Usually, after a few days, the patient receives a description of the examination from a cardiologist, with whom he goes for further consultations.
Functional diagnostics of cardiovascular diseases
Electrocardiogram (ECG) of the heart.
Your doctor will likely order a cardiac electrocardiogram , a test that records the electrical activity of your heart and can identify physical abnormalities, abnormal heart rhythms, and evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle. Read more about the procedure.
24-hour Holter ECG monitoring. ABPM.
A regular electrocardiogram does not make it possible to see the dynamics of changes in indicators. Daily Holter ECG monitoring and daily blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) will display the slightest deviations depending on physical and emotional stress and will help to exclude diseases such as ischemia. More information about the Holter monitoring procedure and ABPM
ECHO-cardiogram (ultrasound of the heart)
A very informative examination method is an echocardiogram or ultrasound of the heart . The doctor will prescribe this examination if necessary for an in-depth study of physiological changes in the heart, its vessels and valves. Read more about the procedure.
Ultrasound Dopplerography of vessels (USDG)
To diagnose the condition of blood vessels, the method of ultrasound examination with Dopplerography is used: Doppler ultrasonography of the veins and arteries of the upper and lower extremities, Doppler ultrasonography of the vessels of the neck and head. These tests help diagnose diseases that often lead to blood clots. Read more about the vascular ultrasound procedure.
Additional information can be obtained by taking pictures of the heart using X-rays, scans using CT, MRI or nuclear technology, or using angiography, a special technique that allows blood vessels to be visualized in detail.
Performing an ECG - check the performance of the heart!
You can often hear the term “stress test”; this is nothing more than an ECG with stress, that is, it is performed under increased physical activity. The main purpose of a stress ECG is to check the performance of the heart muscle. The test is used in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, as well as in monitoring patients after coronary angioplasty and myocardial infarction. They are often performed by people with a normal resting ECG but suspected of coronary artery disease. An exercise test is also performed to select the appropriate cardiac rehabilitation. Athletes regularly undergo exercise testing. Most often, the test is performed on a treadmill, less often with a bicycle ergometer. The patient undergoes physical activity on a treadmill in the form of walking and fast walking with variable load and inclination angle of the treadmill. During the examination, the patient is connected to an ECG machine, which constantly monitors the heart and regularly measures blood pressure. The entire test usually takes about 20 minutes. Unless the doctor advises otherwise, the patient should take medications that he regularly takes on the day of the examination. IMPORTANT! The patient for examination should come earlier and rest and be at least 2 hours after eating. Sports clothing and sports shoes are required for the examination. First, a normal resting ECG is performed. Then, in the presence of a doctor who monitors the patient’s heartbeat and condition, an exercise test is performed. The doctor may decide to stop the test when he notices abnormalities, or if the patient complains of chest pain or becomes pale. After the test, an ECG is performed, which shows the recording while the heartbeat calms down. The test shows the blood supply to the heart, blood vessels and the reaction of the heart muscle to increased oxygen demand. There are a number of contraindications to performing stress tests. Exercise testing is not recommended in the presence of infection, fever, resting chest pain, shortness of breath, aortic aneurysm, high blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia, exacerbation of lung disease (asthma), uncontrolled diabetes, and certain valve defects. Due to the low diagnostic value of the test, especially for women, the stress test can only be an additional test, but not decisive in terms of the presence or progression of coronary heart disease. After the examination, the doctor writes a description of the examination. The patient receives an ECG recording along with a description and must return to his cardiologist for interpretation of the results and, if necessary, treatment.
Indications for the procedure
The examination is carried out only with a referral from a cardiologist. A visit to the doctor can be either planned or in case of complaints about heart function.
Frequent symptoms of impaired heart function include conditions such as:
- Compressive pain in the chest, as well as in the region of the heart, which radiates to the shoulder blade;
- Rapid pulse, which causes dizziness and increased heart rate;
- Shortness of breath with minor exertion;
- Periodic fainting;
- Dry barking cough;
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
Particular attention is paid to patients who have suffered a stroke, have congenital heart abnormalities or rheumatism.
Specialists conduct an examination and give a referral to see a doctor if they find:
- extraneous noise in the work of the heart muscle;
- with low or high blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
The following categories of citizens are subject to mandatory examinations, namely:
- Persons with congenital or acquired heart disease;
- Athletes who have a serious load on their heart function;
- Patients undergoing examination before surgery;
- Women who are pregnant.
Computed tomography - helps diagnose heart defects
In a situation where the above tests are not enough or do not give results, the cardiologist may prescribe a computed tomography scan of the heart and coronary vessels (CT). This is a non-invasive examination, unlike coronary angiography, which is performed strictly in cases of acute coronary syndromes. Computed tomography allows preparation of cardiac imaging. The examination consists of assessing the anatomical structures of the heart, coronary arteries and aorta, as well as its branches. Tomography, unlike the above examinations, requires proper preparation and very detailed consultation with a cardiologist and radiologist. Tomography is performed with an iodinated contrast agent, which provides better visibility of the vessels. In order for specialists to prescribe contrast, the patient must first undergo a blood test, which will determine the level of creatinine and thus assess kidney function. If the patient is allergic to contrast, this should be reported to hospital staff prior to the examination. The patient should not eat 4-6 hours before the examination. During tomography, X-rays are used, which is a contraindication for examination of pregnant women. Before the examination, the patient will undergo a puncture - a cannula through which contrast will be injected. During a CT scan, the patient is also given an ECG, so electrodes are attached. Cardiac and vascular CT scans help diagnose heart defects, leaks, abnormal vascular connections, and aortic aneurysms. A separate study is the so-called MSCT examination - that is, computed tomography of the coronary arteries. Some patients in whom a doctor suspects coronary heart disease may have a CT scan of the coronary arteries to evaluate the risk of atherosclerosis. However, it should be remembered that this examination does not usually replace coronary angiography, that is, an invasive examination that is the gold standard in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and coronary atherosclerosis. On the other hand, MSCT has a proven role in assessing the patency of venous bypass surgery in post-bypass surgery patients. After the examination, the patient receives an examination protocol and a description made by a specialist doctor, who must consult with his cardiologist. It should also be remembered that computed tomography is performed only on the direction of a doctor.
Magnetic resonance imaging - recommended, for example, in the diagnosis of myocarditis In addition to computed tomography, there is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart and blood vessels, which uses the physical phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly specialized test that evaluates the heart muscle more accurately than echocardiography (heart echo). As with tomography, magnetic resonance imaging uses contrast. The patient should have a blood test to determine the level of creatinine and therefore the level of kidney function. People with an allergy to contrast should tell their doctor. The patient should be 4 to 6 hours after their last meal. During the examination, the patient has ECG electrodes glued to his chest. The test takes longer and can take between 30 and 90 minutes. In addition, it should be remembered that this examination involves the patient being in a strong magnetic field. The presence of metal prostheses, implants, pacemakers, etc. may be a contraindication to MRI. The condition after implantation of a coronary stent in most cases is not a contraindication to cardiac MRI, but detailed information should be provided by the treating cardiologist. Cardiac resonance allows, among other things, to evaluate:
- functions, thickness and vitality of the heart muscle,
- muscle damage after heart attacks,
- congenital heart defects,
- severity of leak defects and location of leaks.
Cardiac MRI is recommended for the diagnosis of myocarditis, storage diseases, cardiomyopathies, and coronary heart disease. After the examination, specialists prepare a CD with a recording, description and comments, with which the patient must return to the cardiologist who diagnosed him. The examination can only be carried out with a doctor's direction. All of the above studies are non-invasive. However, they are necessary for making the correct diagnosis in the diagnosis and treatment of various cardiac diseases. It is worth remembering that if you have any doubts before the examination, you should ask your doctor all questions. A good and very useful solution is to also prepare a list of questions in advance.
When is MRI better than cardiac ultrasound?
The level of anatomical detail of the heart area on MRI is higher than on ultrasound. During the scan, the doctor receives up to 1000 images of the mediastinal area. The scanning step of a 3 tesla device can be only 0.8 mm. This means that the doctor can look in detail at the condition of the heart itself and the neighboring coronary vessels. In this case, both planar and three-dimensional data will be provided. MRI best visualizes pathologies and diseases such as:
- inflammatory processes in tissues;
- tumor formations;
- blood clots, vascular malformations, occlusions, aneurysms;
- congenital anomalies of the heart structure;
- heart muscle defects;
- pericardial condition.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
Pregnancy and heart disease
Preventive diagnosis of heart disease is very important for women before such an important stage in life as pregnancy.
Therefore, a heart examination is mandatory when planning pregnancy to avoid serious complications. Now, thanks to improved diagnostics and treatment, women with heart disease can usually safely give birth to a healthy baby. Pregnancy and childbirth do not lead to irreversible changes in heart function and do not reduce life expectancy.