Diagnosing coronary heart disease is not always an easy task. In some cases, the diagnosis is beyond doubt. But there are also situations when the patient’s complaints are ambiguous, and studies performed at rest do not completely exclude this serious disease. Then the attending physician prescribes stress echocardiography.
Stress ECHO-KG
Posted at 18:15h in Services by doctor
Stress echocardiography has become a generally accepted technique in recent years, as it is widely used in the diagnosis of heart diseases that lead to myocardial damage due to pathological changes in the circulatory system. The study is carried out to identify pathologies of the heart valves in patients who need urgent surgery, as well as to determine the dysfunction of diastole, recognized as one of the causes of heart failure. The essence of the method is the use of stress tests, with the help of which the contractility of the heart is accelerated, making it possible to determine areas of the myocardium experiencing oxygen deficiency. What are the indications for the test and what are the diagnostic features?
Characteristics of the method
Most patients, after being prescribed stress echocardiography, are interested in what it is and how the procedure is performed.
Determination of local disturbances in individual areas of cardiac tissue indicates the development of a pathological process. As a rule, an electrocardiogram is performed at rest, so it is difficult to identify minimal disturbances in the functioning of the organ. Stress echocardiography, on the contrary, is performed while the heart is stressed, causing an increase in its contractions, which helps to accurately detect coronary artery disease at an early stage of development.
- pharmacological medicines;
- bicycle ergometry;
- cold stimulation;
- transesophageal electrical stimulation;
- hyperventilation of the bronchopulmonary system.
The method also allows you to determine cardiac endurance, which is why it is used annually among professional athletes.
Indications for the study are as follows:
- Surgery on the heart;
- The need to evaluate its performance during the recovery period after a heart attack;
- ECG indicators, swelling and shortness of breath;
- Unsatisfactory results of load application;
- Ischemic disease in the chronic stage;
- Analysis of the effectiveness of therapy;
- Forecast for the development of pathology;
- Suspected angina;
- Work ability analysis;
- Routine examination of professional athletes.
Advantages and disadvantages of the test
The use of each type of stress test has both its advantages and disadvantages.
- Allows you to evaluate the activity of the heart in a state of increased physical activity.
- Possibility of performing diagnostics outside the hospital using portable equipment.
- Qualitative level of assessment of the state of the heart muscle.
- High sensitivity of the method.
- No biological effect on the patient and medical staff.
- The accuracy of the study depends on the skill level of the specialist.
- During exercise, blurred visualization of the left ventricle is possible.
- The development of side effects in the form of dizziness, rapid pulse, discomfort in the chest area.
Despite all the shortcomings, the technique is considered an effective and inexpensive procedure that can diagnose pathological changes in the functioning of the myocardium.
Types of Cardiac Stress Tests
Stress or exercise testing of the heart is used to screen for many serious diseases of the heart muscle.
There are different types of cardiac stress tests. Four of them use radioactive tracers - isotopes used for diagnostic purposes. They are injected into the patient’s blood and provide a clearer picture of the functioning of the muscles, arteries, heart and blood vessels.
These tests help doctors develop a course of treatment.
Types of Cardiac Stress Tests
Stress test with thallium
The thallium stress test is used to determine how much blood flows into the heart and how it changes with exercise. It is also used in monitoring stress levels in patients who have had a heart attack and in determining the cause of symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath. Sometimes this test is done after surgery to evaluate its effectiveness. It will help determine how much blood flow is blocked in the coronary arteries.
During this test, the patient walks on a treadmill until the load reaches its maximum. After this, thallium is injected into the patient's vein and, using a gamma camera, the movement of blood to the heart is monitored. If there is a disturbance in blood flow (as occurs with coronary artery disease), a scintigram (image of the heart) will show areas in which thallium accumulation is reduced. This will be a sign of illness.
Scanning with technetium pyrophosphate
The technetium pyrophosphate scan is another stress test that uses radioactive tracers. This test is done to confirm and detect a heart attack.
2-3 hours before the test, the radioactive isotope Tc-99m (technetium pyrophosphate) is injected into the blood. Then, after some time, a series of images are taken using a gamma camera. If a heart attack occurs, some of the heart cells necrotize (die). The isotope will accumulate in these cells. This cluster will be recorded by the gamma camera.
Checking the movement of the heart walls (radionuclide angiography)
This test is used to check how well the heart is able to pump blood.
The patient, in a supine position, is connected to a cardiac monitor, after which 2 injections of technetium-labeled red blood cells are administered. After this, the patient experiences physical activity, the duration of which is gradually increased.
In a healthy person, the volume of blood ejected during physical activity will increase, but in a patient it may decrease. Also, disturbances in the movement of the left ventricular wall may occur. The same test will show a picture of the functioning of all four chambers of the heart.
Scanning with technetril (sestamibi)
This is another cardiac stress test. It is used to identify areas of the heart where blood circulation is poor. This test is used to diagnose coronary artery disease, to check the effectiveness of drug therapy and the functioning of the heart transplant.
Identical to technetium pyrophosphate stress test.
In what cases is it prescribed?
Experts recommend undergoing stress diagnostics for patients who have received normal ECG and Echo kg readings, but at the same time they have symptoms characteristic of heart disease.
- Diagnosis of myocardial ischemia.
- Assessment of the degree of damage to the coronary vessels.
- Assessment of the functioning of the heart muscle in patients with organ dysfunction.
- Identification of myocardial areas with a high risk of developing ischemic damage.
- Analysis of the status of chronic ischemic heart disease.
- Preparing the patient for minimally invasive procedures on the chest area.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of angioplasty, stenting and bypass surgery.
- Clarification of the possibility of developing complications after cardiac operations.
- Establishing the timing of surgery in the presence of valve defects.
- Determination of the patient's ability to work.
Features of the method
An early sign of weakened blood circulation in the myocardium is a decrease in the number of heart contractions in response to additional load, whereas in a normal physiological state contractions remain unchanged or increase.
- Deterioration in the contractility of the damaged area (visualized by ultrasound).
- Pathological changes during ECG registration (determined by stress test).
- The appearance of pain behind the sternum.
Myocardial movements are preliminarily assessed before testing. After this, the patient is given a medicine that increases the heart rate or is asked to do an exercise test.
Pharmacological testing is associated with more cardiovascular complications than exercise testing. In the case of a load test, it is recommended to rotate the pedals on a bicycle ergometer in a horizontal position. This makes it possible to quickly move the patient to the couch.
How to prepare for research?
At the preparatory stage of the study, the patient is prescribed medications containing nitrates, which can reduce the number of myocardial contractions and also lower blood pressure. The medication is prescribed to protect the heart muscle from the effects of adrenaline produced during stress, which can cause adverse reactions from various organs and systems.
To fully prepare the body for the procedure, you must follow these recommendations:
- The day before the procedure, drinks containing caffeine and alcohol should be avoided.
- It is necessary to avoid physical activity for several hours.
- The last meal is no less than 3-4 hours before the procedure.
- Stop smoking immediately before screening.
On the day of diagnosis, patients are allowed to take nitroglycerin to stop a possible attack of angina. However, the use of funds must be agreed with a specialist.
Cardiac Stress Test - Myocardial Perfusion with SPECT - Nuclear Stress Test
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (Nuclear Stress Test)
Description
Myocardial perfusion with SPECT is a test that uses small doses of a radioactive agent to evaluate blood flow and heart function. Because blood flow to the heart is measured as the heart's activity increases, this test is usually done with exercise. If you are unable to exercise, your doctor may use a drug that increases the activity of your heart, thereby simulating exercise.
Reasons for conducting a nuclear stress test
A cardiac stress test is used to look for previous damage to the heart and the risk of future damage.
Specific reasons for performing this test include:
- Determining a patient's exposure to heart attack risk;
- Determining whether coronary angiography is needed. angioplasty or heart surgery;
- Search for areas of the heart muscle that have poor blood supply;
- Obtaining information about the pumping function of the heart;
- Determining heart damage that occurs after a heart attack;
- Checking the success of angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery.
Possible complications of a cardiac stress test
Complications may include:
- Chest pain;
- Irregular heart rhythm;
- Rarely - heart attack;
- Radioactive exposure.
During testing, technicians will closely monitor for any signs of heart or lung problems. They will be ready to take action if complications arise.
How is a cardiac stress test performed?
Preparation for the procedure
Before testing, tell your doctor if you have a medical condition that limits exercise. If you are unable to perform the exercises, your doctor may prescribe medications to simulate exercise. Tell your doctor if you have the following conditions:
- Bronchial asthma and chronic lung diseases;
- Arthritis. especially in the hips and knees.
For 24-48 hours before the test, do not eat or drink any of the foods or medications listed below:
- Drinks containing caffeine (such as coffee, tea, cola and other soft drinks);
- Products containing caffeine, such as chocolate (including candy, frosting, cakes, pastries, cookies, cocoa, chocolate milk);
- Painkillers that contain caffeine;
- Products that contain theophylline;
- Dipyridamole.
Read labels and ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information about foods you should avoid before the test.
You may be asked not to eat or drink for 4-8 hours before the test.
Wear loose clothing and low heels with rubber soles or tennis shoes.
If you smoke, you should abstain from smoking for 1-2 days, or at least four hours, before testing.
Tell your doctor if you:
- Have allergies;
- Are you taking any medications or dietary supplements?
- Have diabetes;
- For women - you are pregnant or may be pregnant;
- Breastfeed;
- You have prostheses or implants in your body.
Description of myocardial perfusion using SPECT
The test usually consists of two parts. The first part of the test is used to check the heart at rest.
The second part of the test, called stress, examines the heart after exercise or after taking a drug that mimics the effects of exercise. Your doctor will compare your heart's activity during exercise and at rest to evaluate your heart's health.
A blood pressure cuff is placed on one arm to measure blood pressure. An intravenous catheter is inserted into a vein in the other arm. Small, round pads (ECG electrodes) are placed on the chest and connected to an electrocardiograph. This will allow the doctor to monitor your heart rhythm. Blood pressure and heart rate are monitored before, during and after exercise.
A doctor or nurse injects a small amount of radioactive material into your bloodstream intravenously. The radioactivity of these materials is very low. Radioactive isotopes accumulate in the parts of the heart that have the best blood flow and emit signals that can be detected by a special camera. The pictures taken with the camera show all the parts of the heart that are not receiving enough blood. Pictures are taken at rest and during exercise.
The exercise or "stress" portion of the test is usually done on a treadmill. You will begin walking slowly on the treadmill. Every three minutes the speed gradually increases. When you exercise, your heart rate and blood pressure change. At the peak of the load, an additional radioactive substance is injected into the vein, and the load continues for another one or two minutes.
15-30 minutes after the “stress” you will be placed on a special table on which pictures of the heart will be taken.
If you are unable to exercise for some reason, your doctor may use a drug that mimics the effect of exercise on the heart. If you notice any changes or feel side effects, tell the doctor who is monitoring the testing.
If you have coronary heart disease. you may feel chest pain or angina during part of the test. A specialist will be there and may give you medication to reduce your symptoms or stop the test early. Tell your doctor if you experience symptoms of jaw, neck, arm, or chest pain.
After a cardiac stress test
You can go home.
If you receive a medicine that makes your heart work harder, you may experience anxiety symptoms. dizziness, nausea, shaking, or shortness of breath. Tell your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms. There is a possibility that the effects of the medications may last up to 24 hours after testing.
How long will a cardiac stress test take?
The entire test takes 3-5 hours. You can complete the entire test in one day, or the testing can be spread out over several days.
Cardiac stress test - will it hurt?
Usually this test should not be painful. If you receive the medicine, you may feel some discomfort such as redness, chest pressure, pain, or shortness of breath.
Cardiac stress test results
The doctor will compare pictures of the heart taken at rest with pictures of the heart during stress. If your heart is relatively healthy, there should be no difference (or very little difference) between pictures taken during stress and pictures taken at rest. If the heart arteries are partially blocked, pictures taken during stress will look different from pictures taken at rest.
Contacting your doctor after a cardiac stress test
- Symptoms do not go away or get worse;
- Other painful symptoms appear;
- You continue to experience side effects from the medications used during testing.
Which doctor should I go to if I have hemorrhoids?
Load test
When carrying out the method, various stress tests can be used. The type of test used depends on the objectives being pursued and the intended diagnosis. Thus, to detect myocardial ischemia, as well as assess the degree of damage to individual areas after a heart attack, they resort to dynamic loading.
When using a load in the form of a treadmill, the initial readings are taken at rest, and then when regaining strength after stopping the load.
It is preferable to carry out the test with a bicycle ergometer, since the recording of indicators occurs directly during the period of load or at its peak. The best visualization of the organ is achieved when using bicycle ergometry in a horizontal position.
Contraindications
Stress echocardiography with physical activity or drug stimulation of the heart has a number of absolute and relative contraindications, such as:
- Acute phase of myocardial infarction.
- Kidney or liver failure.
- Severe heart rhythm disturbances.
- Heart and respiratory failure.
- Suspicions of inflammatory pathologies of the heart.
- Infectious diseases during exacerbation, etc.
A stress echocardiogram test is performed only after prior consultation with a cardiologist!
Medication tests
In case of intolerance to physical activity, the use of a drug test is recommended, which is quite safe for the body and causes minimal side effects.
Dobutamine test
It is the most widely used test, during which the number of myocardial contractions increases, blood pressure increases, which causes an increase in the organ's need for oxygen. The difference between the heart's need for oxygen and the ability of the coronary vessels to supply it indicates the presence of local pathological processes in the myocardium.
Test with dipyridamole
The test is done with a gradual increase in the dose of the drug. At each stage, the degree of impairment of myocardial contractility is assessed. In the absence of pathological changes, in order to achieve the required heart rate, an additional 1 mg of atropine is administered. A couple of minutes after the administration of dipyridamole, an intravenous injection with aminophylline, which is an antidote, should be given.
What is stress echocardiography
Stress echocardiography is an ultrasound examination of the heart performed during physical exercise, medication, or exposure to electrical impulses. The purpose of the analysis is to monitor the work of the heart during the period of maximum contractions and when consuming more oxygen than at rest.
Stress echocardiography is a safe method for early diagnosis of ischemia and other heart diseases. The advantages of the test include the reliability of the results, lightness and portability of the equipment.
Evaluation of results
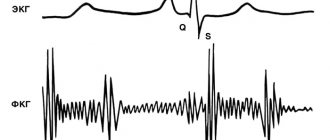
The results of the study are displayed in the form of a two-dimensional graph, which makes it possible to fully assess the quality of left ventricular functioning. Interpretation of the results includes an assessment of the degree of thickening and mobility of the heart muscle tissue in individual areas.
A preliminary analysis of the graphs is carried out by a specialist immediately after their registration. After the screening is completed, the cardiologist can view a video recording of diagnostic indicators in slow motion. The obtained data is stored on disks, creating an information base for the patient with further assessment of the dynamics of heart performance indicators.
Thus, stress echocardiography is a modern method for diagnosing coronary artery disease. The study allows us to determine the initial stage of the disease, when other methods reveal low effectiveness. However, before the procedure, possible cardiac complications associated with excessive load on the organ should be taken into account.