When a patient complains of pain in the heart area or the doctor has any suspicions, the specialist always refers the patient to an electrocardiogram, or, as it is commonly called, an ECG.
When a patient complains of pain in the heart area or the doctor has any suspicions, the specialist always refers the patient to an electrocardiogram, or, as it is commonly called, an ECG.
This study is non-invasive, completely safe, but at the same time very informative. To avoid distorting the ECG results, cardiologists recommend not ignoring the rules for preparing for this study.
What does the ECG show?
The study is a safe and effective procedure and can be prescribed to all people without exception, even children. ECG allows for timely and accurate detection of cardiovascular pathologies and the correct choice of treatment regimen.
The cardiogram makes it possible to determine the following features:
- heart rate;
- myocardial wall thickness;
- disturbances of potassium-magnesium metabolism;
- myocardial damage;
- characteristics of the pacemaker;
- record the source of pain (cardiac pathology or not).
With proper preparation of the patient for the study, an ECG allows you to identify and diagnose the following pathologies:
- arrhythmia;
- tachycardia;
- cardiomyopathy;
- IHD;
- heart attack;
- pericarditis.
Electrocardiogram: the essence of the study.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a common and very informative test that is used to assess the condition of the heart.
The electrocardiogram is recorded on a special tape, while sensors are attached to certain places on the body, picking up electrical impulses and reflecting them in the form of jagged lines fixed on the tape. Any deviations in the ECG pattern must be interpreted by a cardiologist and functionalist; any medical specialists, especially emergency doctors, must be able to read the ECG in acute conditions.
Unlike an ultrasound examination of the heart, an electrocardiogram will not show structural or morphological changes and their shape, but will allow you to find out the following points:
- heart rate and rhythm;
- myocardial thickness;
- electrolyte disturbances in the blood (changes in potassium and magnesium levels);
- circulatory disorders in the heart muscle;
- correct operation of the pacemaker.
Thus, an ECG allows one to suspect or serves as a clear diagnostic confirmation of many heart diseases, including heart attack, arrhythmia, tachycardia, blockades, myocardial problems, coronary artery disease, myocarditis and many others.
Study frequency
When conducting an ECG, sensors that are attached to the chest do not have any harmful effects on the body. The sole task of these sensors is to capture and transmit cardiac impulses. Thus, an ECG does not cause any harm to the human body, even if the study is performed daily.
Doctors believe that the following frequency of ECG is justified:
- healthy population under 40 years of age can conduct the study once a year;
- people with chronic diseases and patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases - the ECG schedule is determined by the attending physician, as a rule, once a quarter;
- workers associated with risk, for example, the Ministry of Emergency Situations, etc. doctors advise having an ECG every six months;
- people who have crossed the forty-year mark should undergo a heart examination every 3-6 months, the frequency depends on the state of health and will be determined only by a doctor.
Types of ECG of the heart
There are several types of ECG of the heart muscle. They allow the patient’s health to be assessed as objectively as possible under different conditions.
The classic electrocardiography procedure described above is carried out over a short period of time and helps to assess the condition of the organ at the time of the procedure. However, a number of heart problems manifest themselves only during certain human conditions - eating, physical activity or sleep, and therefore it is very difficult to record an attack in a clinic at a doctor’s appointment. In order to solve the above problems, it is necessary to do special types of electrocardiography.
Holter ECG monitoring . Today, continuous Holter ECG is common, providing continuous recording of the work of the heart muscle for 24-72 hours. It is also called 24-hour electrocardiography. Now there are even devices that are implanted under the skin (in the area of the heart) and provide continuous recording for 1 year.
Another type of 24-hour electrocardiography is intermittent ECG monitoring. It is used when symptoms of cardiac muscle dysfunction do not appear very often. It does not have to be done in a clinic. The device for such measurements is portable and can, if necessary, be worn on the wrist like a watch. The back panel of the device is equipped with small metal disks that work on the principle of electrodes. When symptoms of cardiac pathologies appear, you need to press a button on the device and data recording will begin.
Stress ECG . In some cases, patients need to have a stress ECG. During it, a person performs physical exercises: running on a treadmill, etc. The results of such electrocardiography are compared with the data obtained after the corresponding procedure at rest. This allows for the most effective assessment of heart function.
It is important to know that in some cases, stress electrocardiography is contraindicated. It is imperative to inform your doctor about high blood pressure, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, heart and lung diseases, suspected heart attack, etc.
Rules for preparing for an ECG
Many people have no doubt that an ECG requires absolutely no preparation. Sometimes in such patients the result of the cardiogram may be false. There may even be elements indicating the development of heart pathology. To eliminate the risk of receiving false results, cardiologists recommend not ignoring the rules for preparing for an ECG.
You need to start preparing the day before the test.
- Maintaining complete calm - on the eve of the study, it is necessary, if possible, to completely remove yourself from stressful situations. Experiences and high anxiety can distort the results of the cardiogram.
- Get a good night's sleep - be sure to get a good night's sleep the night before the test. A tired body contributes to abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, as it functions in an enhanced mode.
- Drinking alcohol before the study is strictly prohibited. The fact is that alcohol causes blood to thicken, as a result of which the heart muscle begins to work much stronger and more active.
- Proper nutrition - do not overload the body with too much dinner or breakfast. On the eve of the study, it is advisable to exclude heavy foods from the diet and avoid fatty foods. Otherwise, the body will devote all its energy to digesting food and the heart will be forced to work harder.
- Refusal of physical activity - a cardiogram will show reliable results if you refuse to play sports the day before and do without jogging and exercise in the morning.
- Avoid thermal procedures - you cannot visit baths and saunas before taking a cardiogram. Doctors also advise against taking baths. Any thermal procedures can increase blood circulation and heart function, which will distort the result of the study.
- Taking medications - it is not recommended to take any medications the day before the examination, other than those prescribed by the doctor on a regular basis. In this case, you must inform your doctor about the medications you are taking.
On the day of the cardiogram, the following recommendations should be followed:
- give up coffee - it is advisable to avoid drinking coffee on the day of the study, this applies to all caffeine-containing drinks; it is strictly forbidden to take energy drinks;
- exclude the use of creams before the procedure - do not apply any greasy lotions or creams to the chest; these cosmetics can form a thin film on the surface of the body through which the electrodes will have poor contact;
- stop smoking 3 hours before the test - you must stop smoking, as nicotine can cause severe vasoconstriction, which leads to excessive heart activity;
- choose the right clothes - sensors that record heart impulses are installed in the chest area, as well as in the calves and wrists, these areas of the body will need to be exposed before the study, so choose clothes that will be easy to remove and will not create any interference for the installation of electrodes .
Main indications for an ECG
Traditionally, ECG diagnosis is carried out:
- to record the electrical activity of the heart muscle;
- searching for the causes of unexplained pain in the chest area;
- Diagnose heart disease if symptoms are present (eg, dizziness, irregular or rapid heartbeat, fainting, difficulty breathing);
- Identifying side effects of taking medications, assessing the degree of their impact on heart health;
- checking the operation of implants (pacemakers, etc.);
- diagnostics of heart health (if there are signs and risk factors for the development of pathologies - hereditary predisposition, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, blood pressure, etc.);
- assessment of heart function (ECG of pregnant women) with increasing load on the body.
Why ECG results may be distorted
As practice shows, most often distortion of ECG results occurs for the following reasons:
- incorrect installation of electrodes - this error is not always caused by medical professionals, for example, if the patient applied a greasy cream, then the sensor simply cannot be fixed in the right place and correctly take data;
- high excitability - if the day before there was stress and the patient did not have time to relax before the procedure, then the heart rate will be higher than normal;
- taking medications - the heart is very sensitive to taking various medications, in particular tranquilizers, antidepressants, nootropics and sedatives.
If the ECG results are far from those required or desired, you should not panic, but carefully analyze whether the rules for preparing for the study were violated. Correct diagnosis can eliminate any violations.
Carrying out an ECG
Electrocardiography can be carried out as part of a comprehensive therapeutic or cardiological examination or be an independent diagnostic procedure. Modern equipment allows you to conduct an affordable ECG in the clinic and at home.
During electrocardiography, the person is in a horizontal position. Special electrodes are attached to the legs, arms and chest. They connect to the ECG machine, the doctor checks all the settings and starts the process. Analysis of cardiac muscle activity is displayed on a paper electrocardiography tape.
During the diagnosis, you should lie still and maintain a natural breathing rhythm. Sometimes during the ECG procedure, the doctor will ask you to hold your breath. The whole process takes about 5-10 minutes and is absolutely painless and safe. There are currently no contraindications for its implementation.
Pathologies in ECG
An electrocardiogram different from normal may indicate various diseases and disorders of the heart.
Diseases may include:
- arrhythmia;
- atrial hypertrophy;
- blockade;
- ischemic disease;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- thromboembolism;
- hypokalemia;
- tachycardia;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- myocardial infarction.
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is characterized by the fact that among the normal contractions of the heart there are also contractions with deviations from the norm, the heart beats less often or more often than necessary, the size of the cardiogram teeth is not the same in each heartbeat.
Such ECG features may indicate arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia can be dangerous and lead to thromboembolism, heart failure and even cardiac arrest in the absence of timely treatment and assistance.
Atrial hypertrophy
With left atrial hypertrophy on the ECG, the P wave in leads 1 and 2 is double-humped, and in V1 it is negative and long.
Atrial myocardial hypertrophy is an increase in the thickness of the myocardial wall of the heart, in conditions of chronic overload of the heart with volume and pressure. Hypertrophy can lead to cardiac arrhythmia.
Blockade
With bundle branch block, the ECG shows a widening of the QRS interval, and with complete blockade, the ST segment and T wave become negative.
Blockade is a slowdown in the conduction of an electrical signal through the conduction system of the heart. Causes heart rate to slow to less than 50 beats per minute.
Ischemic disease
With coronary heart disease on the ECG, the ST segment is slightly lowered, and the T wave has a shallow negative value.
Coronary artery disease is stenosis of the coronary arteries resulting from atherosclerosis. As a result of arterial blockage, myocardial infarction may develop.
Pericarditis
With pericarditis, the ECG shows a slight rise in the ST segment from the ascending knee of the S wave, concave downward, and the T wave is positive. In chronic pericarditis, the ST segment is not elevated, and the T wave is negative and sharp.
Pericarditis is an inflammatory lesion of the serous membrane of the heart, manifested in the appearance of fluid in the area of the pericardium and fibrosis, which leads to difficulty in the functioning of the heart.
With timely diagnosis and treatment, the patient makes a full recovery.
Myocarditis
With myocarditis, the ECG often shows depression of the ST segment and a negative T wave. But not always, there are other ECG features that indicate myocarditis, such as a change in the duration of the PQ interval, signs indicating blockade of the left or right leg of the PG and heart rhythm disturbances .
Myocarditis is damage to the muscular lining of the heart as a result of inflammatory processes. Leads to heart failure, shortness of breath, cardiac arrhythmias, discomfort, pain in the heart area and other symptoms.
If myocarditis is detected, hospitalization and treatment are required.
Thromboembolism
With thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries on the ECG, the RS-T segment is shifted upward and a negative T wave is observed in leads V1-V4.
Thromboembolism is a blockage of a vessel by a blood clot and disruption of blood flow.
If thromboembolism is detected, urgent hospitalization and treatment are necessary.
Hypokalemia
With hypokalemia, the ECG shows a large U wave in the initial form of the disease, and in severe forms, ST segment depression and a deep negative T wave.
Hypokalemia is a reduced concentration of potassium ions in the blood. May cause fatigue, weakness, breathing problems, intestinal obstruction and other disorders.
Treatment is aimed at replenishing potassium levels in the body.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is characterized by an increase in heart rate above 90 beats per minute at rest. With tachycardia, an increased QRS segment may be observed on the ECG.
Tachycardia is a symptom that indicates the presence of a number of diseases, most often the endocrine and nervous systems.
When tachycardia is detected, further diagnostics are required to identify the cause and eliminate it.
Myocardial infarction
With myocardial infarction, the ECG in one case may show both the absence of ST segment elevation and the Q wave, as well as ST segment elevation and deformation, a large Q wave and a pointed negative T wave.
Myocardial infarction is an acute, life-threatening disease that requires rapid hospitalization and surgical treatment.
Myocardial infarction occurs due to thrombosis of the coronary artery, resulting in blockage of the artery, partial or complete cessation of blood supply and the beginning of the process of tissue death.
How is ECG diagnosed?
The electrocardiography procedure is painless and quick:
- A patient enters the ECG diagnostic room.
- He takes off his clothes to the waist and rolls up his pants, exposing the shins of his legs.
- The doctor lubricates the sensors with gel and attaches them to the patient’s body, fixing them.
- The doctor asks the patient to take the desired body position on the couch, standing or on a bicycle ergometer.
- The diagnostician turns on the ECG machine and begins recording a diagram.
- The doctor removes the sensors from the patient’s body, asks to wipe the body with gel wipes and gets dressed.
- The doctor analyzes the electrocardiogram, makes a diagnosis, gives recommendations and further instructions.
With 24-hour Holter monitoring, the doctor places sensors on the patient's body that are connected to a small portable device that collects electrocardiographic data continuously throughout the day. The sensors and ECG device are hidden under clothing and the patient wears them for 24 hours. Then he returns to the doctor, removes the device and sensors. The doctor analyzes the ECG, draws conclusions and makes a diagnosis for the patient.
ECG interpretation
The doctor deciphers the electrocardiogram; only he can identify diseases, make the correct diagnosis and give further directions. A person without medical education should not deal with ECG interpretation.
When deciphering an electrocardiogram, the diagnostician pays attention to the duration, amplitude, shape, frequency, repeatability and other parameters of the following elements of the cardiogram:
- P wave;
- PQ segment;
- Q wave;
- R wave;
- S wave;
- ST segment;
- T wave
Why is electrocardiography performed?
Electrocardiography is one of the mandatory points of any planned medical examination. All patients, even in the absence of complaints and symptoms, must be periodically diagnosed, as this allows possible health problems to be detected in a timely manner and treatment can be started immediately.
In patients with cardiovascular diseases, electrocardiography should be performed more often to monitor heart function and well-being, as well as assess the quality of therapy.
The method is used regularly if the patient has problems with blood pressure, obesity, or irregular heart rhythm.
Options
List of parameters determined by electrocardiography:
- Potassium imbalance.
- Magnesium imbalance.
- Heart rate.
- Zones of necrosis.
- Possible disturbances in the blood supply to the myocardium.
- Thickening of the walls of the heart.
Preparing for electrocardiography
- The specialist must save the necessary personal data of the patient, indicating the date and time of ECG registration, as well as the medical history number.
- Preparation involves positioning the patient correctly during the procedure and connecting the electrodes. The patient should lie down on the couch. In rare cases, for certain illnesses or injuries, a sitting position is acceptable.
- After the patient is in the desired position, the nurse will clean the areas of the skin where the electrodes will be attached. To do this, she uses a special degreasing agent.
- Each electrode is treated with sodium chloride solution. A special gel is applied to them to improve conductivity.
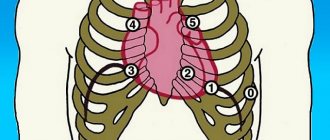
What is meant by leads?
Schemes that record differences in indicators are usually called “leads”. During electrocardiography, a specialist monitors the work of the heart in different leads on a graphic image. It is customary to consider standard leads, enhanced leads and chest leads.
Standard leads:
- I standard lead - the difference in potentials on the right and left hands.
- II standard lead - the difference in potentials on the left and right legs.
- III standard lead - difference in potentials on the left arm and left leg.
Reinforced leads:
- AVL (left hand).
- AVF (left leg).
- AVR (right hand).
Chest leads – 6 leads V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6.
Correct fixation of electrodes
When conducting electrocardiography, electrodes are used for fixation on the lower and upper extremities, as well as electrodes for the chest. The quality of perception of electrical impulses depends on the quality of the location of the electrodes on the patient’s body. Therefore, the algorithm of actions should be as strict as possible.
Electrodes for standard leads have special colors:
- Right hand – red electrode.
- Left hand – yellow electrode.
- Right leg – black electrode.
- The left leg is a green electrode.
After fixing the electrodes on the limbs, electrodes are applied to certain areas of the patient’s chest:
- Electrode V1 is the area at the level of the fourth intercostal space on the right side of the sternum.
- Electrode V2 is the area at the level of the fourth intercostal space on the left side of the sternum.
- Electrode V4 is fixed earlier than V3. Electrode V4 should be attached in the area of the fifth intercostal space on the left side, taking into account the midclavicular line.
- Electrode V3 is the area between electrodes V2 and V4.
- Electrode V5 is the area of the fifth intercostal space, taking into account the anterior axillary line.
- Electrode V6 – area at the level of the fifth intercostal space (in the center of the axillary line).
Holter monitoring ECG+BP. What you need to know. Tips for preparing for the procedure.
Daily ECG monitoring is an instrumental method for diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, based on recording during the day the electrical activity that occurs during the activity of the heart muscle (myocardium) and changes depending on the presence of certain heart diseases in the patient.
The 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring system allows:
- Assess the functional activity of the myocardium, its rhythm and conductivity in conditions of a usual lifestyle, emotional and physical activity.
- Assess the state of the heart at rest, during sleep.
- Determine the presence of cardiac rhythm disturbances, record their cyclic changes, the number of repeating episodes during monitoring, duration, intensity, nature (ventricular, supraventricular) and conditions for the occurrence of arrhythmia. It is important that daily registration of extrasystoles (untimely heartbeats) reveals whether their number is within normal limits or not.
- Identify the form of angina (stable, unstable), including asymptomatic (painless) myocardial ischemia. The method determines the number and duration of episodes, as well as the conditions, load threshold and pulse rate under which ischemia develops. If there is pain in the heart area, the cause of its occurrence is identified (lack of blood supply, osteochondrosis, neuralgia).
- Trace the connection between the patient’s subjective sensations and the objective readings of the device.
- Make an accurate diagnosis, prescribe adequate treatment and monitor the effectiveness of medications taken by the patient.
- Assess changes in heart function in the presence of a pacemaker.
Holter monitoring, in contrast to the standard ECG, is a more reliable and informative method with a large number of analyzed parameters.
Registration of heart function is carried out throughout the day (if necessary, up to 7 days), so all unstable, transient disturbances are recorded on the device.
An undoubted advantage of the latest models of the device for Holter ECG monitoring is the presence of an additional function for monitoring daily BP (blood pressure).
This research method is used in the following cases:
5. Routine examination of persons subject to surgery on the heart and other organs - patients with diabetes mellitus (diabetic angiopathy - pathology of blood vessels, including coronary ones)
Holter monitoring may be prescribed if the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- pressing or burning pain behind the sternum and in the region of the heart, with or without irradiation (radiating under the left shoulder blade, into the left arm or not);
- pain in the left half of the chest of a different nature, with a clear connection with or without physical activity;
- characteristic pain in the heart area at night (usually in the early morning) hours - characteristic of Prinzmetal's angina
- feeling of lack of air, episodes of severe shortness of breath with a suffocating cough;
- periodic interruptions in the functioning of the heart, a feeling of cardiac arrest; frequent dizziness and/or fainting.
Daily Holter technique
The Holter device is a portable recorder weighing less than 0.3 kg, attached to the patient's body with a special belt. After degreasing the skin with an alcohol solution, electrodes are attached to certain points of the chest area.
During the study, the patient is given a diary in which all activities, sleep time, medications taken, sensations, complaints, and well-being are noted hourly.
The doctor recommends certain physical activity (climbing stairs, brisk walking) to analyze the functioning of the heart during and after intense exercise.
Otherwise, the patient leads his usual lifestyle. After the time has passed, you must return to the clinic to remove the device.
Features of the examination, how to prepare.
The patient does not need to prepare specially for this study. The exception is men with heavily hairy chests. To ensure a tight fit of the electrodes, you will need to shave your hair.
The day before, you can take food and liquid in the usual quantities; in the morning before the procedure, a light breakfast is allowed. Alcohol and coffee should be avoided, as well as the number of cigarettes smoked, as these products can have a significant impact on the contractility and conduction functions of the heart muscle.
During monitoring there are no restrictions in the usual lifestyle and diet, but:
- You cannot take water treatments to avoid damage to the device;
- mechanical and thermal damage to the device must not be allowed;
- Do not stay near power lines;
- You should not allow stress with increased sweating, as this may cause the electrodes to come off.
- working hours and occupation;
- time and type of rest;
- list of food products and drinks;
- housework;
- physical exercise;
- emotional condition;
- duration and quality of sleep;
- taking medications with an exact time indication; this aspect is very important if Holter blood pressure monitoring is carried out in parallel;
- the presence of unpleasant or painful sensations in the heart area, dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, etc.
- Wear tight-fitting clothes made from natural fabrics. It is better not to wear loose clothing, as it may cause the electrodes to peel off from the body. And synthetic fabric can become electrified, which will distort the device’s readings. There should be no metal elements on clothing above the waist.
- Do not overcool or overheat the device.
- Do not expose it to water or other liquid.
- Do not place it on vibrating surfaces.
- Do not stay near electrical equipment or transformer boxes.
- Do not use a laptop or mobile phone for more than 3 hours a day. Do not bring the gadget closer than 30 cm to the Holter ECG monitoring device. Do not go close to a running microwave oven.
- Do not sit or lie on the device. Place it so as not to press it while you sleep.
- Make sure that the electrodes do not come off.
- Do not undergo physical therapy or have x-rays taken during the examination.
- Ask your doctor in advance if you can exercise during the test.
Wearing a Holter device does not cause any particular inconvenience - it is lightweight, compact, and silent. Some discomfort may be associated with the inability to shower, as well as with an obstacle to being too active or in your favorite sleeping position.
Holter heart rate monitoring is not limited to wearing the device. During the procedure, the patient keeps a diary in which he notes:
Rules for the patient!
In order for the results of daily monitoring of the electrical activity of the heart to be as accurate as possible, you need to adhere to certain rules:
Decoding the results
After removing the device, the recording data is entered by the doctor into a computer - decoder. The digital system analyzes the data, which is reviewed and corrected by the doctor, and then a conclusion is written based on it.
The standard transcript necessarily indicates information about the heart rate, ventricular and supraventricular extrasystoles (rhythm disturbances), rhythm pauses, changes in the PQ and QT intervals. The identified pathologies are illustrated with electrocardiogram printouts for the monitoring period.
Decryption time takes about 2 hours. After reviewing the results, the attending physician will prescribe appropriate treatment.
The undeniable advantage of the method is the ability to carry out it in familiar home conditions and without interruption from work or study. An easy and painless examination using a Holter device provides an objective picture of the heart’s activity, which makes it easier to prescribe effective therapy.
If you find yourself with the symptoms listed above, you should immediately contact a cardiologist for a comprehensive examination.
Sign up for a consultation 8 (879 3) 32 23 15
Cost of ECG in our clinic
We provide the following services in the field of cardiology and ECG diagnostics:
- Primary appointment with a cardiologist - 1500 rubles;
- Repeated appointment with a cardiologist - 1400 rubles;
- ECG with interpretation - 500 rubles;
- ECG without interpretation - 250 rubles;
- Interpretation of an ECG done in another clinic - 300 rubles;
- Daily Holter ECG monitoring - 2200 rubles;
- Comprehensive daily monitoring of blood pressure + ECG according to Holter - 3500 rubles;
- Bicycle ergometry (stress tests) - 1800 rubles;
- “Healthy Heart” program - 6,500 rubles;
- Daily blood pressure monitoring - 1700 rubles;
- Tropanin test - 400 rubles.
You can make an appointment for an ECG with a doctor through the online form on the website or by phone 8
and
+7 (4872) 49-57-57
.
All articles "