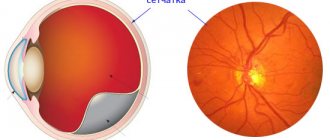
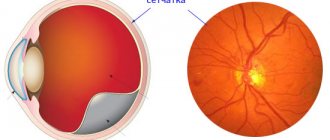
The medical term retinal angiodystonia describes a pathological process accompanied by a deterioration in the blood supply to the fundus of the eye, which is responsible for the perception of visual information. Despite the fact that this anomaly is accompanied by certain symptoms and can lead to irreversible deterioration of vision, angiodystonia is not an independent disease. According to the ICD classification, it refers to a kind of “side effect” of systemic diseases.
Classification
In ophthalmology, it is customary to classify angiodystonia of retinal vessels only according to the origin of vascular insufficiency. Based on this, several groups of the disease are distinguished:
- Diabetic angiodystonia
- a complication of diabetes mellitus. It develops against the background of thinning of the vascular walls, loss of elasticity and their destruction. Diagnosed in patients who do not receive quality therapy or violate their diet. It is considered the least common form of pathology.
- Traumatic angiodystonia
- develops as a result of abnormal pressure on the vessels in the neck or impaired blood supply to the head, accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. The only form that is accompanied by visually noticeable symptoms is hemorrhage in the eyes.
- Hypertensive angiodystonia
- a condition that occurs in patients with chronic high blood pressure. Deterioration of vision provokes a prolonged spasm of the retinal arteries, as a result of which the general blood circulation in the vessels of the eye is disrupted. More often than other forms it leads to irreversible loss of vision.
- Hypotonic angiodystonia
- a pathology that occurs against the background of a slowdown in venous blood flow and a decrease in blood pressure. Accompanied by the formation of blood clots and hemorrhages in the eyes. It is also accompanied by neurological symptoms, including dizziness and fainting.
Angiodystonia, which develops during pregnancy, is classified into a separate class. Unlike previous options, it is transient in nature, that is, it does not require special treatment measures and elimination of the disease. Due to several temporary factors:
- increasing the volume of circulating blood;
- changes in vascular tone under the influence of hormones;
- increasing the overall load on the body.
Quite often, this disorder goes away on its own after childbirth, but in some cases the birth process provokes a sharp increase in the pressure of the blood vessels in the eyes and their rupture. As a result of this, a woman in labor may lose her vision within 3-4 months, but only if the problem is not detected in time.
Good to know! If in a previous birth a woman encountered a dangerous form of retinal angiodystonia, the doctor may insist on terminating the subsequent pregnancy due to the risk of complete loss of vision.
Angiospasm of the retina: treatment
For vasospasm, etiotropic therapy is not carried out, since it has not yet been developed in modern medicine. Methods of pathogenetic treatment of the disease are used, which are aimed at reducing pressure and dilating blood vessels undergoing spasms, as well as restoring impaired blood flow in the ischemic zone.
If the unfavorable manifestations of vasospasm are not eliminated in a timely manner, this can lead to a severe decrease in vision and, as a consequence, to a partial or complete loss of the ability to see.
Therefore, the doctor, having diagnosed the corresponding pathology in the patient, immediately after the examination prescribes antispasmodics to the patient. As part of treatment, electrophoresis and vasodilators are recommended.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, as well as saluretics, help reduce intraocular pressure. In cases where the desired effect does not occur, a special irrigation system can be installed in the retrobulbar space. The pathology is also stopped by instillation of solutions of special drugs: beta-adrenergic receptor blockers. Sometimes medications are administered intramuscularly (this mainly happens when the disease is accompanied by high blood pressure).
Short-term narrowing of small branches of the central nervous system is not considered dangerous, but if the attack lasts more than 10-15 minutes, irreversible serious changes occur in the retina due to lack of trophism. Therefore, the prognosis for the treatment of the disease varies - it all depends on the form of the pathology. As for the prevention of vasospasm, it usually comes down to enhanced monitoring of blood pressure, as well as blood glucose levels.
On the Ochkov.Net website you can view a large selection of contact lenses from popular manufacturers and order them in a few clicks.
Causes
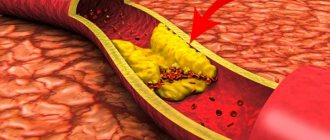
Retinal angiodystonia can develop against the background of diseases and conditions of a general (systemic) nature, in which significant fluctuations in vascular tone occur. Normally, these processes are strictly controlled by the nervous and hormonal systems: if it is necessary for certain tissues to actively work, more blood is sent to them by relaxing the walls of the arteries and increasing their diameter, and less “important” organs are switched to saving mode by increasing vascular tone and reducing their diameter
Failures of the regulatory mechanism lead to uncontrolled spasm of arteries and veins, which causes oxygen deficiency in the tissues. This is exactly what happens with retinal angiodystonia: the tissue does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen and begins to atrophy.
There are several reasons for the development of vascular insufficiency in the eyes:
- mechanical head injuries, resulting in increased intracranial pressure, including birth injuries in children;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- frequent stress that provokes hypertensive crises;
- chronic alcoholism and drug addiction, as well as long-term smoking;
- intoxication with chemicals and heavy metals;
- intoxication of the body due to infectious diseases;
- menopausal changes in the body of women;
- endocrine diseases - thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, tumor diseases of the adrenal glands.
Age-related weakening of blood vessels plays a major role in the development of vascular insufficiency. Due to a lack of collagen, their walls lose elasticity and firmness, which is why retinal vascular angiodystonia is often diagnosed in people suffering from varicose veins.
Angiopathy during pregnancy
Since in pregnant women the blood volume increases several times with the growth of the fetus, the blood vessels increase accordingly. Changes in the circulatory system cause angiopathy in pregnant women. Additionally, it is provoked by a hormonal factor, which is observed in the first trimester. In the second and third trimester, a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance occurs due to the functioning of the uteroplacental circulatory system. Another reason that can provoke angiopathy in pregnant women is gestosis. Identifying such a pathology in pregnant women carries risks, since standard treatment methods cannot always be used in this situation. In some cases where there is a risk of retinal detachment, the doctor may recommend a cesarean section.
Symptoms
Angiodystonia of the visual organs rarely manifests itself as a disturbance in the perception of visual images.
, especially at the initial stage of development. This is why the disease is almost never detected in the early stages. As it progresses, the patient may notice:
- sensation of painless pulsation in one eye;
- the appearance of sudden flashes of light in the field of vision;
- gradual deterioration of vision - narrowing of its fields (darkening or clouding of the image at the edges), general blurriness of the picture;
- development of myopia.
Important! One of the visually recognizable signs of retinal angiodystonia is a change in the color of the sclera: yellowish spots form on it, pinpoint hemorrhages or a clear pattern of capillaries periodically appear.
The disease may also be accompanied by additional symptoms indicating the root cause of the pathology:
- in the traumatic form - headaches, paresthesia, dizziness and fainting, deterioration of cognitive functions and memory, chronic fatigue;
- with hypertension - acute headaches, sudden jumps in blood pressure to a maximum, accompanied by nausea;
- with hypotension - apathy, weakness, dizziness and nausea.
The higher the degree of pathological changes in the retina, the more intense the symptoms of the disease.
Prevention of angiopathy
Treatment is not just about taking medications. It is very important to maintain a proper diet and change your lifestyle. The diet should be low in salt and animal fats, high in potassium and magnesium. The patient should also increase physical activity. If intense exercise is contraindicated for a person, it is necessary to select a set of gymnastic procedures adapted to his activity and capabilities. Sometimes walking or cycling is enough. It is important that the exercises are performed systematically.
In order for the blood vessels, including the blood vessels of the eyes, to be in normal condition, it is important to follow simple rules:
- Do not abuse alcohol, get rid of nicotine addiction.
- Prevent the development of hypertension, diabetes and other provocateurs of angiopathy.
- Periodically undergo courses of treatment if the disease is chronic.
- Carry out a preventive examination every year, even if there are no obvious vision problems.
- When angiopathy is detected in pregnant women, in order to avoid retinal detachment, a cesarean section is recommended.
The eyes are an important organ, without which a person would not be able to receive so much information from the outside world. Retinal angiopathy can deprive a person of a normal life and make him disabled. Therefore, any visual impairment, even minor, must be accurately diagnosed and corrected in an ophthalmology clinic. And serious diseases such as diabetes and hypertension must be constantly monitored.
Diagnostics
Retinal angiodystonia is diagnosed using a standard set of procedures
designed to detect vascular anomalies:
- rheoencephalography - study of cerebral vessels to determine the intensity of blood supply;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - ultrasound examination of individual basins of the bloodstream, which reveals arterial and venous insufficiency;
- electrocardiography is a classic method for recognizing signs of systemic cardiovascular disorders;
- retinal angiography.
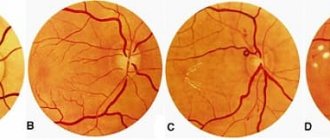
The most informative research method is ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye using a special lens. This method allows the doctor to visualize vascular changes in the retina, establish their location and determine the degree of complexity. To find out the causes of the disease, laboratory blood tests are carried out (for sugar, hormones, etc.).
Accommodation indicators
The ability of the eye to accommodate is measured in diopters or linear values.
- Functional rest of accommodation - disaccommodation - focusing to infinity in the absence of an accommodative stimulus in the visible zone. The accommodation area is the distance along the main optical axis of the eye between the extreme points of clear vision (near and far).
- The volume of accommodation is the range of changes in refractive index, expressed in diopters, when focusing on the nearest and most distant points of clear vision.
- Accommodation stock (reserve) is the unused part of the accommodation capabilities at a certain point in the visual field, located at a given distance.
In the process of ophthalmological diagnostics, absolute and relative indicators of accommodation can be determined. Examination of each eye separately gives absolute values. Diagnosis of both eyes, performed with a certain convergence (reduction) of the visual axes, makes it possible to determine relative indicators.
The functions of accommodation are inextricably linked with convergence. At the same angle of convergence of visual lines, the degree of accommodation in people with different indicators of visual acuity is not the same. For example, uncorrected farsightedness in children (hyperopia) can lead to accommodative convergent strabismus.
Violation of accommodation can manifest itself in the following forms:
- spasm of accommodation;
- paralysis and paresis of accommodation;
- accommodative asthenopia;
- presbyopia (age-related decrease in accommodation).
Children and young people are most susceptible to accommodation spasms. This spasm is caused by functional disorders in the ciliary body, which leads to weakened vision both near and far. The spasmodic ciliary muscle remains in a state of accommodating tension even in situations where its relaxation is required. The development of accommodation spasm is especially facilitated by educational overload; This is why this type of disorder occurs predominantly among schoolchildren and students. According to the results of statistical studies, every sixth student has accommodation disorders caused by muscle spasms.
Paralysis and paresis (partial paralysis) of accommodation can also be a consequence of injuries and the action of toxins. In addition, this type of accommodative disturbances is often provoked by neurogenic factors. In this case, the degree of myopia may not change or increase insignificantly, but the acuity of normal and presbyopic vision decreases at close distances. In any case, paralysis and paresis lead to a reduction in accommodative reserves and a decrease in the overall volume of accommodative capabilities.
Accommodative asthenopia often results from incorrect selection of glasses or lenses for farsightedness and astigmatism. Inadequate optical correction causes rapid visual fatigue, redness of the eyes, itching in the eyelids, dry sclera and an increasing sensation of foreign particles in the eye (chronic blepharoconjunctivitis). Visual discomfort can cause headaches, nausea and even vomiting, which is associated with excessive tension of the eye muscles with limited accommodation reserves.
Age-related accommodation disorders (presbyopia) develop due to gradual involution (reverse development, age-related degradation) of the lens under the influence of external factors and a gradual decrease in the rate of metabolic processes in old age. Over time, the lens loses elasticity, thickens, and becomes less transparent; the eye muscles are no longer able to give it the required curvature and provide sufficient optical refractive power with such changes.
Treatment methods
Retinal angiodystonia is always treated comprehensively. The main direction of therapy is to eliminate the cause of vascular insufficiency. Treatment also includes correction of some habits:
- quitting smoking and alcohol or minimizing them;
- stabilization of physical activity - increasing activity with obvious physical inactivity and restrictions with increased loads;
- changing the daily routine, alternating activity and rest;
- following a diet appropriate to the underlying disease.
Treatment also includes taking medications that help restore blood supply to the retina. Local remedies in the form of drops that improve eye nutrition are often used - Mildronate, Trental and their analogues. More focused therapy is prescribed depending on the type of disease.
Treatment of hypertensive angiodystonia
Since hypertensive angiodystonia of the retina can result in a catastrophe for vision with a sharp increase in blood pressure, patients are recommended to take medications on an ongoing basis that regulate this indicator - Captopril, Tenoric and their analogues. Additionally, a complex of drugs is prescribed to help stabilize vascular tone and eliminate factors contributing to their spasm:
- sedatives - motherwort and valerian, Corvalol;
- antiarrhythmic drugs - "Verapamil";
- diuretics (if necessary, quickly reduce blood pressure) - Enalapril or Hypothiazide.
To reduce current symptoms, analgesics and antispasmodics can be prescribed.
Treatment of hypotonic angiodystonia
In the hypotonic form of the disease, drugs are used to increase and stabilize blood pressure. The drugs chosen are predominantly of natural origin containing extracts of lemongrass, ginseng and echinacea. These plants are powerful adaptogens, strengthen the immune system and help improve vascular tone.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- means for improving cerebral blood circulation - “Piracetam”, “Pantocalcin”;
- local drugs to enhance microcirculation - “Taufon” and “Emoxipin”;
- vitamins with components beneficial for vision - “Lutein Complex” and “Aevit”.
For any type of disease, the effectiveness of conservative therapy increases with the use of physiotherapeutic methods: magnetic therapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis. Any medications and procedures can only be used after consulting a doctor!
Complications
Prolonged spasm can lead not only to a decrease in visual acuity, but also to its complete loss. The frequency of attacks causes severe discomfort and disability due to the fact that patients lack the ability to anticipate the period of development of the next fragment. The progressive form of the disease entails an increase in intraocular pressure. Over time, the patient develops secondary ophthalmopyrtension and develops ocular migraine. Rapid attacks are tolerated without complications.
Prevention and treatment of accommodation spasm
False myopia in the absence of adequate treatment and correction leads to the development of true organic disorders. Constant spasm prevents normal vasculature (blood supply) of the ciliary muscle, as a result of which it weakens. This is the mechanism of development, in particular, of chorioretinal dystrophy with functional accommodative weakness. Currently, it is the spasm of accommodation that is considered as the main cause of childhood myopia (first false, and then true myopia).
Our ophthalmological center has everything necessary to identify and effectively eliminate false myopia in both children and adults. The treatment uses not only eye drops and eye exercises, which the patient can do himself at home, but effective hardware techniques that can be used to relieve accommodation spasms in several sessions: quickly and harmlessly!
Treatment of accommodation spasm consists, first of all, in a system of visual exercises and training on special computer simulators. Mydriatic drops (dilating the pupil), laser treatment, magnetic and electrical stimulation are also used. Good results are achieved by massage of the cervical-collar area, the course of which is recommended twice a year. Vitamins and a varied diet are prescribed as general strengthening therapy. For students, it is extremely important to normalize the work and rest schedule, which necessarily includes periods of physical activity.
Drops to relieve spasm of accommodation
Eye drops that dilate the pupil (Irifrin, Tropicamide, Midriacil, etc.) are usually used at night. This makes it possible to provide a relaxing effect on the accommodative muscle that is sufficient in strength and time, while maintaining the patient’s ability to have good vision during the day.
In addition, so-called “vascular and vitamin” drops - Taufon, Emoxipin, etc. - can be prescribed in complex therapy. They improve microcirculation in the tissues of the eyeball and help improve visual functions.
Exercises for false myopia
Gymnastics for the eyes, aimed at training accommodation, primarily involves focusing the gaze on equidistant objects.
The most popular exercise is the so-called “mark on glass”, which consists of the following:
A mark (about 5 mm in size) is attached to the window glass; it can be a small sticker or a spot drawn with a marker or any other means at hand.
After this, you need to move 0.5 meters away from the glass and find a distant object (tree, building, etc.) on the street (behind this mark), then you need to alternately look from the indicated distant landmark to the mark.
The exercise is performed 10-20 times per “approach to the window.” During the day you need to repeat the gymnastics 3-5 times. This allows you to develop a spasmodic accommodative muscle of the eye.
Timely measures taken to prevent spasm of accommodation are effective prevention of more serious disorders accompanying true myopia.
Manifestations of the disease
Retinal vascular angiopathy is painless and practically asymptomatic and is detected during an ophthalmological examination. Patients may complain of decreased visual acuity and blurred vision; progression of myopia; the appearance of lightning and flashes in the eyes.
In some cases, increased nosebleeds and temporary loss of vision are noted. An ophthalmological examination reveals retinal dystrophy.
Popular questions about vascular spasms of the extremities
What causes spasms?
The cause of vascular spasms in the extremities is a number of diseases such as angiospastic syndrome, obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis, diabetes mellitus. Also, spasms of the blood vessels of the arms and legs occur as a reaction to prolonged exposure to cold, nicotine intoxication or frostbite.
How long to treat vascular spasms of the extremities?
Some medications for spasms of blood vessels are recommended for use throughout life, others - as part of a therapeutic course, which depends on the degree of the disease.
Which doctor treats vascular spasms?
After identifying symptoms associated with vascular spasms of the extremities, you must consult an angiologist or phlebologist.