The medical term retinal angiodystonia describes a pathological process accompanied by a deterioration in the blood supply to the fundus of the eye, which is responsible for the perception of visual information. Despite the fact that this anomaly is accompanied by certain symptoms and can lead to irreversible deterioration of vision, angiodystonia is not an independent disease. According to the ICD classification, it refers to a kind of “side effect” of systemic diseases.
General information
Cerebral angiodystonia is a functional pathology, which is characterized by changes in the venous and arterial tone of cerebral vessels, as well as a decrease in their adaptive abilities. Cerebral angiodystonia is formed as a result of a violation of nervous vascular regulation, which leads to:
- venous congestion in the brain;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Cerebral angiodystonia of cerebral vessels is a functional disorder in which the arteries and veins remain morphologically intact - there are no signs of thrombosis or atherosclerosis .
Angiodystonia of cerebral vessels occurs in 1.7% of the population. Every third patient suffering from pathology is of working age. The main danger lies in the fact that the disease can complicate diagnosis and mask the clinical picture of serious diseases of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems.
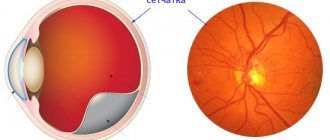
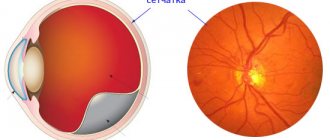
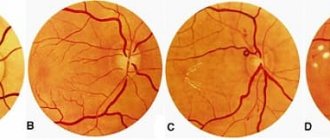
Retinal angiodystonia is a disease that affects the vessels supplying the bottom of the eyeball. Pathology can develop at any age. One option is spastic angiodystonia of the retina, which develops as a result of prolonged spasm of the venous and arterial network of the fundus.
Classification
Based on its origin, cerebral angiodystonia is divided into:
- Primary form. It is an independent disease, also known as neurogenic angiodystonia.
- Symptomatic form. Changes in vascular tone are the result or complication of an underlying pathology, for example, arterial hypertension .
By localization they distinguish:
- Local form. The affected area has a clear localization and is limited.
- Diffuse or systemic form. Changes are observed in all areas of the brain.
With the flow:
- Crisis angiodystonia. The paroxysmal form is characterized by a periodically occurring sharp deterioration in well-being against the background of complete well-being.
- Constant angiodystonia. Cerebral circulatory disorders are persistent and persistent.
Type:
- Hypertensive type. Develops against a background of constantly elevated blood pressure. The development mechanism is associated with vasospasm, which develops against the background of contraction of smooth muscle tissue in the vascular wall, and leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the vessel, which negatively affects blood circulation.
- Mixed type. It is formed as a result of instability of the condition of the walls of blood vessels, which alternately contract and relax. Pathology is directly related to the psychophysiological state of the patient.
- Hypotonic type. Develops in people with low blood pressure - hypotension.
It is characterized by a relaxed state of the vascular wall and an increase in the lumen of arteries and veins.
According to the degree of severity, which is determined by the clinical picture of vascular pathology:
- mild form of dystonia;
- moderate angiodystonia;
- a pronounced form of cerebral anhidystonia.
Background pathologies
Almost always, angiodystonia develops against the background of other cerebral pathologies. Sometimes it occurs due to infectious or endocrine diseases. Background processes include:
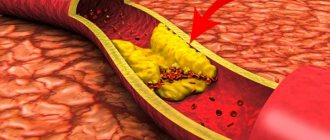
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries. With this pathology, endothelial damage occurs and fatty plaques form. Due to the thickening of the walls of blood vessels, the elasticity of the arteries decreases, which can result in a decrease in muscle tone.
- Hormonal disorders. Most often, angioedema is combined with diseases of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland. Decompensated diabetes mellitus also leads to vascular damage.
- Chronic infectious diseases that affect not only the brain, but also other organs.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Psycho-emotional disorders, stress.
- Systemic vascular diseases – vasculitis. Such pathologies can be either infectious or autoimmune in nature.
- Allergic reactions.
If the cause of this syndrome cannot be determined, this does not mean that it does not exist. In most cases, the development of dystonia is preceded by any disorders of the endocrine system or head trauma. In cases of damage during childbirth, the syndrome may develop much later (at school age).
Causes
The main factors and pathologies that lead to the development of cerebral vascular anhidystonia:
- impaired regulation of the autonomic nervous system;
- endocrinological diseases: hypothyroidism ; pheochromocytoma ; diabetes ; hyperthyroidism ;
- neuroinfections: encephalitis , meningoencephalitis , meningitis ;
- acute or chronic form of intoxication: hangover syndrome; food poisoning ; poisonous gas intoxication; consumption of alcohol, drugs, nicotine;
- long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- pathology of internal organs;
- psycho-emotional disorders associated with neuropsychic overstrain, prolonged stress, lack of sleep;
- occupational pathology (exposure to loud noise, vibration disease);
- hypertonic disease.
In children, the disease develops against the background of a congenital pathology of the central nervous system. Quite often, the pathology of vascular tone is associated with psychosomatics. The lack of skills to get rid of neuropsychic stress, an unconstructive approach to solving the problem (addictive behavior or abuse of alcoholic beverages) leads to chronic stress, which negatively affects the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Preventive techniques
To reduce the likelihood of developing pathology, you need to adhere to the rules of prevention. When angiodystonia develops in people, such actions can help get rid of the subsequent development of the disease or slow it down.
Adviсe:
- Exercise more.
- You need to devote enough time to rest.
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Properly selected diet.
- Lose or gain weight if necessary.
- You cannot smoke or drink alcohol.
- Constant use of medications, visiting a specialist for examination.
Many people do not understand what cerebral angiodystonia is, they think that they are just tired and feel slightly unwell. The disease develops calmly, complications and serious consequences are not observed, the quality of life of patients worsens many times . Therefore, you should immediately contact a medical specialist if you experience regular headaches.
Diseases affecting the brain significantly worsen the well-being of patients, and therefore require regular treatment. If therapy is not used in a timely manner, diseases can significantly disrupt the processes in such an organ. This negatively affects all body systems. Vascular diseases disrupt the blood supply to the head and other parts. Due to this, the patient suffers from pain and associated symptoms.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of cerebral angiodystonia is nonspecific. Characteristic signs of pathology:
- Mental and emotional disorders that manifest themselves: memory impairment; excessive fatigue; mood lability; superficial sleep; absent-mindedness; decreased interest in events happening around; lack of hobbies and any interest; complete apathy; increasing time to fall asleep.
- Autonomic disorders in the form of: instability of blood pressure ; rhythm disturbances and shortness of breath; feeling of rapid heartbeat .
The clinical picture is formed from several syndromes. The predominance of a particular syndrome depends on the condition of a particular organ or system (congenital or acquired pathology). For example, with congenital heart disease, it is cardiac neurosis .
Syndromes that accompany cerebral angiodystonia:
- Cardialgic syndrome. Patients complain of retrosternal pain in the heart area of a burning, aching, bursting nature. The pain syndrome is more pronounced in the area of the apex of the heart and is short-term in nature (from several minutes to 1 hour). The pain attack stops on its own when the patient is distracted. The syndrome is accompanied by feelings of anxiety, fear, agitation and shortness of breath.
- Breathing syndrome. Occurs in 85% of patients suffering from angiodystonia. Characteristic symptoms: feeling of lack of air; discomfort along the upper respiratory tract and discomfort in the lungs.
The paroxysmal (crisis) form of angiodystonia includes 3 types of crisis:
- Sympathoadrenal crisis. Characterized by the following symptoms: instability of blood pressure; sudden feeling of fear or anxiety; increased body temperature; dryness and pallor of the skin; sudden headache of aching nature with a feeling of pulsation; feeling of rapid heartbeat; tremor, trembling in the limbs. The crisis ends with general weakness, and in some cases, excessive urination.
- Parasympathetic crisis . Characteristic symptoms: dizziness; decreased blood pressure; bursting headache; excessive moisture of the skin; dyspnea; decreased heart rate.
- Mixed crisis. Symptoms of sympathoadrenal and parasympathetic crises are characteristic.
According to severity they are distinguished:
- Easy. The duration of the attack is no more than 20 minutes and is manifested by one separate syndrome.
- Average. The duration of the attack is 20-60 minutes, manifested by two syndromes. After the crisis, exhaustion is noted, which can last 1-2 days.
- Heavy. The attack lasts more than 1 hour and is manifested by 2 or more syndromes. Convulsive seizures and severe autonomic dysfunction are characteristic. After an attack, exhaustion can last 2-3 days, and the ability to work is significantly reduced.
The clinical picture of angiodystonia depends on the form of pathology:
- Hypertensive type. The disease occurs as a dyscirculatory encephalopathy and is characterized by a pronounced decrease in some psychophysiological indicators (pace of thinking, memory, attention, speed of reactions). The clinical picture is manifested by specific autonomic disorders: noticeable pulsation of the vessels of the head and neck; extrasystolic arrhythmia ; increase in heart rate at rest and during excitement.
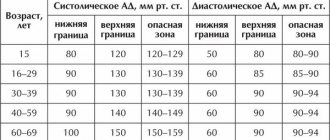
- Hypotensive type. Registered when systolic blood pressure decreases below 100 mm Hg. Art. Characteristic autonomic disorders: tendency to faint (loss of consciousness is associated with insufficient blood supply to the brain); chilliness of the limbs. Patients have pale skin, the skin feels moist and cold to the touch. Blood pressure levels normalize with physical activity and decrease at rest. There is a decrease in peripheral vascular tone.
- Angiodystonia with venous dysfunction. The pathology is formed against the background of changes in the tone of the venous vessels of the brain, which leads to venous stagnation. The symptoms of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome are characteristic: increased sensitivity to loud sounds and bright light; irritability ; apathy; aching headache; vomit; nausea.
Treatment of the disease
Based on the diagnostic data obtained, the doctor prescribes therapeutic therapy. It is based, first of all, on normalizing vascular tone indicators. Timely and properly selected treatment will not only relieve symptoms, but also cure the source of cerebral angiodystonia.
In order to normalize blood flow in most cases, a specialist may recommend taking a course of special physical therapy - exercise therapy. This method of treatment actively promotes the training of vascular reactions occurring in the brain. At the same time, the entire body heals.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
It is important to choose the right mode that suits your biorhythms, which will allow you to work and rest for the optimal amount of time. We should not forget about proper nutrition, which is why the treatment program includes a diet compiled by a professional specialist in this field.
The healing process will be accelerated if you do not forget about walking and giving up bad habits (if you had them before the onset of the disease). An individual rehabilitation program is often developed.
The most effective medications will be the following:
- Clonidine, Methyldopa, Propranolol are vasoactive agents ;
- Pentalgin, Bral, Ketonal - good relief from pain ;
- Corvalol, Persen, Tenoten, Afobazol, Seduxen, Novo-Passit - sedatives ;
- Melaxen, Donormil - help you sleep peacefully and fully ;
- Captopril, Bisoprolol, Tenorik - are prescribed as good antihypertensive drugs ;
- Eufillin - if hypertension is noted ;
- Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine are effective remedies for symptoms of depression ;
- Verapamil, Diltiazem - relieve arrhythmia ;
- Piracetam, Pentoxifylline, Pantogam, Vinpocetine - improve the flow of blood into the brain and regulate blood circulation.
You should also use vitamins and antioxidants to generally strengthen the body. All drug dosages are calculated by a specialist.
Advice from the people
Traditional methods of treatment can be used as preventative measures, as well as in combination with basic (medicinal) therapy prescribed by a doctor. The main bias is towards sedatives, since it is necessary to relieve nervous tension, which contributes to the development of tone.
Recommended:
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- tinctures of knotweed, valerian or motherwort;
- physical training;
- walking (from 2 to 5 km);
- warm relaxing baths (2-3 times a week);
- sleep (at least 8 hours) + daytime rest (40-60 minutes).
Tests and diagnostics
Cerebral angiodystonia is a diagnosis of exclusion when, as a result of the examination, functional and organic changes in the vessels of the brain are not detected. Due to the diversity and nonspecificity of the clinical picture, the diagnostic search can take months.
Several specialized specialists take part in the differential diagnosis: cardiologist, neurologist, psychiatrist and endocrinologist. At the initial stage, a family history and heredity of autonomic dysfunction are established: the presence of disorders in the blood circulation of the brain in close relatives. Concomitant pathology is revealed. Often such patients are simultaneously diagnosed with:
- allergic reactions;
- ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- skin diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- endocrinological pathology;
- rhythm disturbances, arrhythmia .
Instrumental diagnostic methods used for cerebral angiodystonia:
- electrocardiography;
- functional tests;
- CT scan;
- electroencephalography.
Concomitant diseases
Violation of vascular tone is accompanied by many diseases:
- Encephalopathy. This disease occurs due to a chronic cerebral circulation disorder, resulting in the death of brain cells. Accompanied by intellectual, vegetative and emotional disorders. At first, the disease is functional and reversible, but if atherosclerosis joins angiodystonia over time, the defect becomes irreversible.
- Hypertonic disease. The pathology is based on a sustained increase in systolic blood pressure above 140 mm Hg. Due to the increased tone of the vascular walls, the minute-by-minute volume of blood circulation in the large and small vessels of the brain decreases, which is why it suffers from ischemia and hypoxia.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis. It is characterized by pain in the heart, rhythm disturbances and fluctuations in blood pressure. Usually has a mixed type.
Prevention and exercises for cerebral angiodystonia
The development and progression of cerebral angiodystonia can be prevented by following simple rules:
- review your diet;
- change your lifestyle;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do gymnastics and sports.
Exercises for cerebral vessels are aimed at improving venous outflow from the head. Massage of the cervical-collar area and exercises to relieve muscle spasm in the cervical spine are effective. Regular exercises for the blood vessels of the brain have a positive effect on the condition of the vascular wall and overall well-being.
Treatment
The main direction in the treatment of cerebral vascular pathology is lifestyle correction.
Patients are advised to maintain a work-rest schedule, get enough sleep, and completely stop drinking alcohol and smoking. Complex treatment of andystonia includes several areas:
- Drug therapy. Medicines are selected depending on the clinical symptoms. Sleeping pills, anxiolytics and sedatives are prescribed for anxiety, sleep disturbances, and excessive agitation. Drugs with a reverse, stimulating effect are used for severe apathy.
- Healing Fitness. Exercise therapy exercises have a strengthening effect on the entire body, have a positive effect on the condition of the vascular wall and blood circulation in the brain; psychotherapy. The use of rational psychotherapy and autogenic training with periods of relaxation is effective.
- Dieting. The emphasis in nutrition should be on the content B vitamins
The doctors
specialization: Neurologist / Therapist
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
1 review
Listratov Stanislav Dmitrievich
no reviews
Pantyukhina Irina Nikolaevna
2 reviews Find a doctor and make an appointment
Medicines
PentoxifyllineCavintonVasobralCapoten
Painkillers:
- Ketonal;
- Pentalgin;
- Took.
Vasoactive drugs:
- Propranolol;
- Methyldopa;
- Clonidine.
Sedative medications:
- Treatment of cerebral vessels: folk remedies, traditional medicine
- Afobazole;
- Persen;
- Corvalol;
- Seduxen;
- Novo-Passit.
Antihypertensive drugs:
- Tenoric;
- Kapoten;
- Edarbi.
Drugs that improve cerebral circulation:
- Vinpocetine;
- Pentoxifylline;
- Piracetam;
- Pantogam.