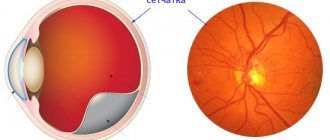
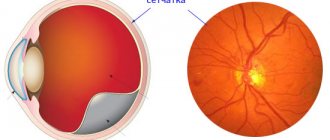
The medical term retinal angiodystonia describes a pathological process accompanied by a deterioration in the blood supply to the fundus of the eye, which is responsible for the perception of visual information. Despite the fact that this anomaly is accompanied by certain symptoms and can lead to irreversible deterioration of vision, angiodystonia is not an independent disease. According to the ICD classification, it refers to a kind of “side effect” of systemic diseases.
Classification
In ophthalmology, it is customary to classify angiodystonia of retinal vessels only according to the origin of vascular insufficiency. Based on this, several groups of the disease are distinguished:
- Diabetic angiodystonia
- a complication of diabetes mellitus. It develops against the background of thinning of the vascular walls, loss of elasticity and their destruction. Diagnosed in patients who do not receive quality therapy or violate their diet. It is considered the least common form of pathology.
- Traumatic angiodystonia
- develops as a result of abnormal pressure on the vessels in the neck or impaired blood supply to the head, accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. The only form that is accompanied by visually noticeable symptoms is hemorrhage in the eyes.
- Hypertensive angiodystonia
- a condition that occurs in patients with chronic high blood pressure. Deterioration of vision provokes a prolonged spasm of the retinal arteries, as a result of which the general blood circulation in the vessels of the eye is disrupted. More often than other forms it leads to irreversible loss of vision.
- Hypotonic angiodystonia
- a pathology that occurs against the background of a slowdown in venous blood flow and a decrease in blood pressure. Accompanied by the formation of blood clots and hemorrhages in the eyes. It is also accompanied by neurological symptoms, including dizziness and fainting.
Angiodystonia, which develops during pregnancy, is classified into a separate class. Unlike previous options, it is transient in nature, that is, it does not require special treatment measures and elimination of the disease. Due to several temporary factors:
- increasing the volume of circulating blood;
- changes in vascular tone under the influence of hormones;
- increasing the overall load on the body.
Quite often, this disorder goes away on its own after childbirth, but in some cases the birth process provokes a sharp increase in the pressure of the blood vessels in the eyes and their rupture. As a result of this, a woman in labor may lose her vision within 3-4 months, but only if the problem is not detected in time.
Good to know! If in a previous birth a woman encountered a dangerous form of retinal angiodystonia, the doctor may insist on terminating the subsequent pregnancy due to the risk of complete loss of vision.
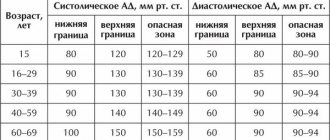
About arterial hypotension
It is worth understanding that arterial hypotension is not an independent disease; it is only a symptom that indicates an insufficiently high level of pressure in the vascular system.
In some cases, low blood pressure is a normal variant that does not require medication correction at all. For example, some people always have low blood pressure, which is their individual characteristic. Hypotension in athletes is an adaptive reaction in response to prolonged physical activity. People living in high mountains also have lower blood pressure numbers. In this case, their indicators are a compensatory reaction to lower atmospheric pressure.
But there are also pathological conditions that cause a decrease in blood pressure:
- Primary arterial hypotension. It occurs with neurocirculatory dystonia due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system with a predominance of its parasympathetic part. Experts call it hypotension.
- Secondary arterial hypotension. A symptomatic condition caused by a number of pathologies of the cardiovascular, nervous or endocrine systems. In addition, it can develop against the background of anemia, chronic intoxication, prolonged infectious lesions, irrational treatment tactics (large doses of antihypertensive or antihistamines, antidepressants).
Causes
Retinal angiodystonia can develop against the background of diseases and conditions of a general (systemic) nature, in which significant fluctuations in vascular tone occur. Normally, these processes are strictly controlled by the nervous and hormonal systems: if it is necessary for certain tissues to actively work, more blood is sent to them by relaxing the walls of the arteries and increasing their diameter, and less “important” organs are switched to saving mode by increasing vascular tone and reducing their diameter
Failures of the regulatory mechanism lead to uncontrolled spasm of arteries and veins, which causes oxygen deficiency in the tissues. This is exactly what happens with retinal angiodystonia: the tissue does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen and begins to atrophy.
There are several reasons for the development of vascular insufficiency in the eyes:
- mechanical head injuries, resulting in increased intracranial pressure, including birth injuries in children;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- frequent stress that provokes hypertensive crises;
- chronic alcoholism and drug addiction, as well as long-term smoking;
- intoxication with chemicals and heavy metals;
- intoxication of the body due to infectious diseases;
- menopausal changes in the body of women;
- endocrine diseases - thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, tumor diseases of the adrenal glands.
Age-related weakening of blood vessels plays a major role in the development of vascular insufficiency. Due to a lack of collagen, their walls lose elasticity and firmness, which is why retinal vascular angiodystonia is often diagnosed in people suffering from varicose veins.
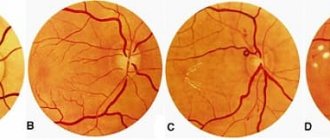
Types of angiopathy
Fundamentally, angiopathy can be divided into two groups: local damage to the retinal vessels and systemic.
In the first case, angiopathy is characterized by vascular damage at the local level (that is, at the level of the eye) - for example, changes in blood vessels with myopia.
In the second case, angiopathy reflects changes in the whole organism. Perhaps this is the most interesting and important group. Based on the condition of the blood vessels, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, atherosclerosis, systemic diseases, vascular pathology of the head and neck, even in some cases heart rhythm disturbances, etc. can be identified earlier than the therapist. An examination by an ophthalmologist is mandatory if a person has cardiac pathology, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Hypertensive
Due to high blood pressure, the inner walls of blood vessels (intima) are damaged. These special microdamages contribute to the development of hardening of the arteries, which disrupts the metabolism of the retina. The veins become congested, the outflow of blood from the retina becomes difficult, which leads to the development of oxidative stress. Dense arteries begin to compress the veins, creating favorable conditions for the formation of blood clots.
Hypotonic
Develops due to low pressure in the blood vessels. Perfusion decreases and ischemia develops.
Dystonic type
Vascular spasms significantly worsen and provoke the formation of dystrophy and retinal tears, which can lead to retinal detachment.
Diabetic
An increased level of glucose in the blood provokes metabolic damage to the vessel wall, especially in the microvasculature, which in turn incredibly aggressively disrupts metabolic processes in the retina.
Traumatic
Due to injuries to the skull, cervical spine, or eyeballs, increased pressure or disruption of blood flow may occur due to compression of the vessels leading to the eyeballs. Post-concussion paralysis of the arterial muscles develops.
Mixed type
Symptoms of several forms of angiopathy are layered on top of each other, the disease proceeds with severe symptoms and quickly progresses to complex stages.
For myopia
The arteries are usually narrow and their course is straight. In conditions of a stretched eyeball, the arteries do not reach the periphery, which leads to retinal ischemia and the development of dystrophies. This, in turn, threatens retinal detachment.
Symptoms
Angiodystonia of the visual organs rarely manifests itself as a disturbance in the perception of visual images.
, especially at the initial stage of development. This is why the disease is almost never detected in the early stages. As it progresses, the patient may notice:
- sensation of painless pulsation in one eye;
- the appearance of sudden flashes of light in the field of vision;
- gradual deterioration of vision - narrowing of its fields (darkening or clouding of the image at the edges), general blurriness of the picture;
- development of myopia.
Important! One of the visually recognizable signs of retinal angiodystonia is a change in the color of the sclera: yellowish spots form on it, pinpoint hemorrhages or a clear pattern of capillaries periodically appear.
The disease may also be accompanied by additional symptoms indicating the root cause of the pathology:
- in the traumatic form - headaches, paresthesia, dizziness and fainting, deterioration of cognitive functions and memory, chronic fatigue;
- with hypertension - acute headaches, sudden jumps in blood pressure to a maximum, accompanied by nausea;
- with hypotension - apathy, weakness, dizziness and nausea.
The higher the degree of pathological changes in the retina, the more intense the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of retinal dystrophy: how to identify the disease
Persons who are predisposed to developing the disease should visit an ophthalmologist 1-2 times a year. The main danger of the anomaly is that in the first stages it is asymptomatic. However, over time, signs of violations begin to appear more and more noticeably.
It is important for the patient to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Loss of brightness of colors in the perception of the surrounding world. Contrast appears less and less.
- The outlines of objects and contour lines of objects lose clarity. The patient wants to turn on the light or add lighting in order to gain the perceptual features that were inherent to him before.
- While reading a book or looking through a newspaper, a person discovers that he does not see all the letters even with glasses that previously made his vision sharp and clear. The same thing happens with reading texts on the Internet.
Gradually, all these changes lead to loss of quality of vision near and at long distances. Then a spot appears in the visibility zone that interferes with viewing. At first it is slightly cloudy, still transparent, then it grows and becomes completely dark. Over time, a person loses the ability to distinguish faces and see objects in the environment.
Age-related macular degeneration affects both eyes, one of which more rapidly loses the ability to see normally. The second eye may be affected by pathology after 4-7 years. When you detect the first signs of an anomaly, you need to carefully monitor your health.
Diagnostics
Retinal angiodystonia is diagnosed using a standard set of procedures
designed to detect vascular anomalies:
- rheoencephalography - study of cerebral vessels to determine the intensity of blood supply;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - ultrasound examination of individual basins of the bloodstream, which reveals arterial and venous insufficiency;
- electrocardiography is a classic method for recognizing signs of systemic cardiovascular disorders;
- retinal angiography.
The most informative research method is ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye using a special lens. This method allows the doctor to visualize vascular changes in the retina, establish their location and determine the degree of complexity. To find out the causes of the disease, laboratory blood tests are carried out (for sugar, hormones, etc.).
Treatment of retinal dystrophy
Glasses will not solve the problem of AMD; even the highest quality lenses cannot improve the situation. The light that is projected onto the retina still distorts the visual image. Dr. Trubilin’s clinic uses the most effective techniques.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy is carried out in two main areas:
- Intravitreal administration of drugs that inhibit the growth of new vessels.
- Laser therapy using photodynamics and coagulation.
Properly provided medical care and a properly formulated diet are of great importance. Patients are prescribed vitamins, mineral supplements, antioxidant formulas, peptides, biological regulators, and medications to lower blood cholesterol levels.
Continued research in this area has led to the creation of new generation drugs such as Ranibizumab (Lucentis) and Aflibercept (Eylea). These agents are directly injected into the eye, suppressing the pathological proliferation of vascular structures. The use of such pharmacology stabilizes the situation and has a beneficial effect on the quality of vision. The full course is 2 years (5 injections per year). Significant changes become noticeable after the first injection. Doctors are also evaluating the possibility of introducing a Dexamethasone implant.
Treatment methods
Retinal angiodystonia is always treated comprehensively. The main direction of therapy is to eliminate the cause of vascular insufficiency. Treatment also includes correction of some habits:
- quitting smoking and alcohol or minimizing them;
- stabilization of physical activity - increasing activity with obvious physical inactivity and restrictions with increased loads;
- changing the daily routine, alternating activity and rest;
- following a diet appropriate to the underlying disease.
Treatment also includes taking medications that help restore blood supply to the retina. Local remedies in the form of drops that improve eye nutrition are often used - Mildronate, Trental and their analogues. More focused therapy is prescribed depending on the type of disease.
Treatment of hypertensive angiodystonia
Since hypertensive angiodystonia of the retina can result in a catastrophe for vision with a sharp increase in blood pressure, patients are recommended to take medications on an ongoing basis that regulate this indicator - Captopril, Tenoric and their analogues. Additionally, a complex of drugs is prescribed to help stabilize vascular tone and eliminate factors contributing to their spasm:
- sedatives - motherwort and valerian, Corvalol;
- antiarrhythmic drugs - "Verapamil";
- diuretics (if necessary, quickly reduce blood pressure) - Enalapril or Hypothiazide.
To reduce current symptoms, analgesics and antispasmodics can be prescribed.
Treatment of hypotonic angiodystonia
In the hypotonic form of the disease, drugs are used to increase and stabilize blood pressure. The drugs chosen are predominantly of natural origin containing extracts of lemongrass, ginseng and echinacea. These plants are powerful adaptogens, strengthen the immune system and help improve vascular tone.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- means for improving cerebral blood circulation - “Piracetam”, “Pantocalcin”;
- local drugs to enhance microcirculation - “Taufon” and “Emoxipin”;
- vitamins with components beneficial for vision - “Lutein Complex” and “Aevit”.
For any type of disease, the effectiveness of conservative therapy increases with the use of physiotherapeutic methods: magnetic therapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis. Any medications and procedures can only be used after consulting a doctor!
Recommendations from ophthalmologists
After completing the course of therapy you must:
- use sunglasses when outdoors;
- When reading, writing, working at the computer, use high-quality lighting and take regular breaks;
- perform special exercises;
- enrich your diet with foods that are good for your eyesight;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- give up bad habits (smoking, alcoholic drinks).