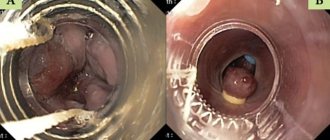
Petechiae are small hemorrhages (hemorrhages) in the upper and middle (less commonly) layers of the skin. Due to the proximity of the epidermis, they are clearly visible. They have the shape and type of small red or purple spots up to 1 cm in diameter. The condition is accompanied by minor associated symptoms.
Petechial rash is not an independent disease, but only one of many manifestations of pathological processes. Specific diagnoses are precisely determined by the typical clinical picture.
Recovery involves both an etiotropic approach, that is, elimination of the underlying disease, and symptomatic measures to correct abnormal manifestations. The effectiveness of treatment depends on its quality, as well as the prospects for complete relief from the unpleasant condition.
Mechanisms of development of the disorder
The development of the disorder is based on a whole group of factors. As a rule, they do not occur in a single system, at least this is not observed so often.
If we talk about pathogenetic aspects in more detail, we can name the following typical mechanisms:
Autoimmune or infectious inflammatory processes
Affecting small vessels throughout the body. As a rule, these are severe disorders such as vasculitis, less dangerous, for example, thrombocytopenic purpura.
As part of these anomalies, increased vascular fragility occurs. A slight physical impact on the tissue is enough to provoke destruction and bleeding under the skin.
Spontaneous outpourings are also possible, for no apparent reason. This is most typical for severe disorders at advanced stages.
Blood clotting problems
Insufficient synthesis of specialized substances responsible for platelet aggregation also leads to their inferiority.
This is how hemophilia can manifest itself, and in the same way malignant diseases of the hematological profile make themselves known (we are not talking about cancer processes). All of these conditions require mandatory treatment in a hospital.
Disturbances in the formation or functional activity of platelets and blood cells
Thrombocytopathies of various types. Pathognomonic (characteristic) signs within the framework of the mechanism are a decrease in the number of these structures or their normal number with a significant drop in functional activity. As a result, the blood becomes too liquid and comes out through the walls of the capillaries, accumulating under the skin.
One way or another, the diseases in question pose a danger to health and life; petechiae on the skin themselves do not threaten anything; moreover, they are informative from the point of view of early diagnosis.
Spontaneous factors
Which do not need to be eliminated by any separate methods. For example, the use of certain medications: thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids and many others. Up to and including antibiotics if used uncontrolled.
Hemorrhages on the skin develop as a result of insufficient coagulation and destruction of blood vessels (as a result of their abnormal fragility).
Such disorders in the early stages may seem not dangerous, but in fact there are a lot of diseases manifested by a petechial rash that can affect health or take life: from hemophilia to cancer processes.
What are petechiae? How do they look?
Petechiae look like a rash, only more pronounced and scary. The spots themselves are tiny patterns that can be purple, red or brown, which is associated with bleeding under the skin.
They are usually flat to the touch and, unlike rashes, will not discolor when pressed - this is a useful way to tell whether any skin abnormality is a rash or not.
Petechiae - photo
Pathological causes
Speaking about specific pathologies that provoke the named symptom, it is worth highlighting:
Autoimmune diseases
Thrombocytopenic purpura, systemic vasculitis and other disorders. For problems of this kind, one thing is typical - the immune system attacks the cells of its own body, in particular blood vessels, leading to small hemorrhages under the skin throughout the body, the number can reach tens and hundreds.
Without quality therapy, recovery is impossible. Some autoimmune processes threaten the patient's imminent death.
Schamberg's disease
A special case of an autoimmune process. It is characterized by inflammation of the capillaries with further microhemorrhages. Does not pose an immediate threat to life if treated promptly.
Infectious inflammations
Chicken pox. Infection with the varicella-zoster virus. This also includes mononucleosis (the culprit is a strain of herpes type 4).
Meningitis, venereal diagnoses, and typhus can provoke hemorrhagic petechiae.
Recovery presents certain difficulties due to the diversity of possible causes. A lot of effort is required to identify and verify the diagnosis.
Sepsis
Blood poisoning in common parlance. This is an infectious generalized inflammatory process that simultaneously affects all structures and tissues.
It poses a huge danger to health and life. Petechial rashes in this case occur spontaneously in the early stages of the disorder. Treatment is urgent, in a hospital setting.
Oncological processes
Tumors. Some neoplasias can provoke hemorrhages. Especially damage to the liver and digestive tract.
This disorder is not always primary. An indirect process such as impaired absorption of nutrients -> scurvy or other hypovitaminosis -> problems with connective tissue synthesis -> capillary ruptures and minor subcutaneous or submucosal bleeding is possible. Urgent treatment of oncology is necessary to achieve correction.
Taking drugs
Many psychoactive substances cause induced changes in blood clotting and destroy blood vessels.
Particularly dangerous in this regard are: opioids (heroin, methadone), cannabinoids (marijuana, synthetic spices), especially artisanal poisons such as “crocodile” and others.
The localization of violations depends on the method of introducing the toxic substance into the body. By injection - local capillaries and even veins are affected, by inhalation - the nose and respiratory tract, etc.
Vitamin C deficiency, scurvy
These days it is relatively rare. The main reason for this process is poor quality nutrition. Nutritional factor. A small amount of incoming vitamin (ascorbic acid) affects the strength of connective tissues.
In addition to petechial hemorrhages, there is gum destruction, weakness, drowsiness, tooth loss, bone fragility, and there is also a high probability of massive bleeding and death of the patient from complications.
Hypercortisolism
Excessive synthesis of adrenal hormones. It is characterized by obesity, skeletal destruction, primarily the spine and other structures are affected, and multiple organ dysfunction is observed.
As the disease progresses, things become much more dangerous. Tumors of the adrenal cortex or pituitary gland are often the immediate cause.
A typical clinical form of hypercortisolism is Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
Use of certain medications
They have already been mentioned: from oral contraceptives to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, thrombolytics and others involved in changing the rheological properties of blood.
Cancer treatment performed
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy negatively affect connective tissue. Even short courses cause major health problems. Recovery takes months, even years.
Causes of petechiae
Petechiae occur when tiny blood vessels (capillaries) burst. When this happens, blood leaks under the skin.
Some of the reasons that can lead to petechiae include:
- local trauma or trauma in which the skin is damaged;
- sunburn;
- allergic reactions to insect bites;
- various autoimmune diseases;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- decreased level of platelets in the blood;
- medical treatments for cancer, such as radiation or chemotherapy;
- leukemia or bone marrow cancer, which leads to a reduction in platelets;
- after severe vomiting or coughing - especially in newborns;
- strenuous activity, such as heavy lifting or childbirth;
- sepsis;
- scurvy;
- vasculitis;
- viral diseases such as dengue fever, ebola and yellow fever can interfere with blood clotting, causing bleeding under the skin.
The use of certain medications can also cause petechiae. Drugs that can cause petechiae as a side effect:
- antibiotics;
- antidepressants;
- contraceptives;
- blood thinners;
- drugs to normalize heart rhythm;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- sedatives.
If petechiae appear after taking any medications, you should consult a doctor.
Causes not related to diseases
Petechiae are not always the result of the course of diseases. These hemorrhages also occur as a result of the influence of a number of natural, safe factors.
- Injuries. Mechanical tissue damage. Mainly bruises. In fractures, petechiae are extremely rare due to the large volume of bleeding. Restoration is carried out immediately, in which case there is a chance to reduce cosmetic defects to a minimum.
- Wearing tight clothes. Compression of the skin and mechanical trauma affect it. The same goes for uncomfortable shoes.
- Compression of tissues with a tourniquet. When carrying out routine diagnostic or therapeutic measures. Intravenous infusion of drugs.
- Physical overexertion. Including labor. Coughing, playing sports, crying, vomiting and other similar phenomena also cause subcutaneous hemorrhages.
- Natural skin aging processes.
The reasons are assessed separately. It makes sense to first exclude pathological factors, only then look for natural ones. This is a matter of timely diagnosis and human safety.
Symptoms
The clinic is determined by the main diagnosis. Generally speaking, several groups of processes can be named.
- Autoimmune disorders. Inflammatory disorders. They are accompanied by both petechiae themselves and pain at the site of the lesion, changes in the laboratory picture of capillary and venous blood.
- Infectious processes. They have approximately the same manifestations. Plus focal symptoms, depending on the specific diagnosis. So, with meningitis, the brain is involved, neurological manifestations occur, mononucleosis, cytomegaly, chickenpox give, in addition to petechiae, a papular rash, the formation of small blisters filled with exudate on the skin.
- Diseases of the hematopoietic system. The main manifestations relate to vascular disorders themselves: frequent heavy bleeding, poor wound healing, decreased regenerative abilities of the body, capillary fragility, weakness, drowsiness, problems with cardiac activity, enlarged liver, spleen, bruising, etc.
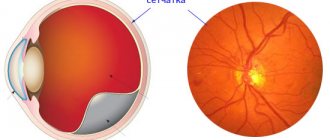
As for the petechiae themselves, they are pinpoint hemorrhages on the skin, form spontaneously, cover the area of the thighs, buttocks, forearms, are found in the groin, on the face, on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (palate, tongue), genitals, and also on the conjunctiva of the eyes ( see photo below).
They have a round, usually regular shape, and rise slightly above the skin. Pain and itching are not typical; petechiae occur without any independent symptoms.
The color varies from purple (deep red) to pink; as the pathological rashes regress, they turn yellow, lose their contours and completely disappear, leaving areas of pigmentation.
Attention:
A cosmetic defect does not go away on its own; you need the help of a specialist.
The duration of the rash's existence varies: from several days to a couple of weeks or even more. Depends on the specific diagnosis, the form of the process, the treatment provided.
Symptoms must be considered within the framework of the primary disease. The one that caused the petechial rash.
When should you see a doctor?
It is highly advisable to have your doctor examine petechiae on the skin and mucous membranes because they may be a sign of a more serious condition. The doctor will evaluate the symptoms and possible causes to determine whether the cause of the petechiae is mild or severe.
If the number of petechiae continues to increase, bleeding may be the cause.
There are also other symptoms that may occur along with petechiae, which are indicators of a severe or life-threatening condition.
These include:
- loss of consciousness;
- confusion;
- heat;
- heavy bleeding;
- Strong headache.
If any of these symptoms occur along with the appearance of petechiae, a person should seek immediate medical attention. Petechiae on the skin and mucous membranes plus the above symptoms are an alarming signal.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a hematologist. A sample list of events is:
- Patient interview. All possible complaints must be identified. A person’s task is to talk about his own well-being in as much detail as possible. The doctor draws up a complete clinical picture, analyzes the symptomatic complex and puts forward hypotheses regarding the disease. This is one of the most valuable diagnostic methods in such a case.
- Anamnesis collection. Past diseases, current pathologies and other important points, including family history, habits, and lifestyle. It makes sense to evaluate all factors to identify the likely origin of the pathological process.
- General blood analysis. The picture can be very different. Depends on the type of disorder, primary diagnosis.
- Coagulogram. An informative technique, the essence of which is to study the rate of blood clotting.
- Bone marrow sampling and biopsy. Used as a last resort. If other methods did not provide a complete answer and an accurate picture of what was happening.
There are not so many methods, however, not all diagnostic methods are named. Depending on the expected primary diagnosis, the list is expanded. It is possible to involve third-party specialists other than a hematologist.
Treatment
Therapy consists of eliminating the primary process.
- Infections require the prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics or drugs to which the pathogen has demonstrated obvious sensitivity. Antiviral agents are indicated if the agent is not bacterial. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used.
- Mechanical damage requires the use of a cold compress.
- Autoimmune processes are the most difficult to treat when it comes to inflammation. Glucocorticoids are used in high concentrations (Prednisolone, Metipred, Dexamethasone), and, if necessary, if there is no effect, immunosuppressants. Suppressing the intensity of the reaction of the body's defenses.
- Sepsis is treated strictly in a hospital setting. Loading doses of antibiotics are used, and nutrient and saline solutions are administered intravenously under constant medical supervision. Typically, patients with this diagnosis are in intensive care.
- Thrombocytopathies require the use of glucocorticoids, plus in some cases the spleen is removed.
- If the cause of the violation was the use of medications, it makes sense to cancel them or reconsider the main course. Strictly with the participation of a specialist.
- Hypovitaminosis involves the introduction of nutrients from the outside. Like scurvy and other pathologies of this kind.
If necessary, red blood cell transfusion and plasmapheresis are performed. The issue is resolved in the hospital, individually.
At the end of treatment, strengthening therapy is prescribed.
What exactly is shown:
- Vitamins of group B, also C, K.
- Angioprotectors. Anavenol, Ascorutin and similar to restore the normal state of blood supply structures, increase their strength and elasticity.
In addition to medication correction, it makes sense to give up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol. It is necessary to fortify the diet and introduce a sufficient amount of protein (dietary meats and legumes are suitable).
Petechial rash leaves cosmetic defects on the skin. They can also be corrected, although the use of special means and specialized procedures will be required.
Forecast
Generally favorable, unless we are talking about serious illnesses.
Autoimmune processes such as systemic vasculitis, pathologies of hematopoietic structures, sepsis, and some forms of infectious disorders pose a great threat to health and life. They are deadly.
Attention:
It is impossible to provide information on prospects without analyzing a specific situation, since there are many diseases that cause hemorrhagic rash.
It is better to address the question to the treating specialist. He will be able to say anything specific only after the diagnosis has been carried out.
Consequences
The main complications, especially without treatment, are:
- Severe massive bleeding.
- Acute shock conditions. For example, when developing sepsis, which quickly takes a person’s life.
- Neurological deficit. Against the background of infections, autoimmune diagnoses.
- Heart problems. IHD, chronic cardiac failure, severe dysfunction.
- Disability. As a result of damage to nerve tissue.
- Death.
Petechiae (intradermal hemorrhages) in themselves are not diseases; they are not an independent diagnosis. Only a symptom, but extremely informative.
It makes sense to undergo a full comprehensive diagnosis as quickly as possible; it is important to urgently identify the probable cause. The prognosis, and possibly the patient’s life, depends on this.
Associated symptoms
If you find red spots in your mouth, you should consult a specialist. As a rule, most of the listed diseases are also accompanied by the following manifestations:
- local pain,
- itching and burning,
- bad breath,
- swelling and inflammation of the gums,
- local temperature rise,
- discomfort when chewing, swallowing, communicating.
If these symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.