Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) - what is it?
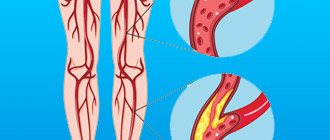
Deep vein thrombosis is a disease in which blood clots (thrombi) form in the lumen of the deep veins. The lower extremities are most often affected.
The mechanism of development of deep vein thrombosis
As the disease progresses, the health of the deep vessels is at risk. If treatment is not prescribed in time, there can be serious consequences.
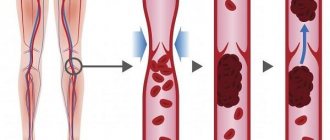
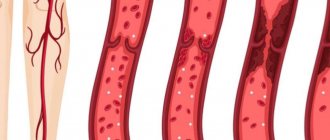
Mechanism of thrombus formation
The formation of a blood clot always follows one scenario: first, damage occurs (trauma to the vessel wall), platelets rush to the site of damage, which stick together into a strong clot and adhere to the wound. Next, fibrin threads are formed, and the vessel receives a “patch.” Over time, the tissues are restored, the blood clot dissolves as unnecessary.
A useful mechanism that saves people from blood loss due to injury can become dangerous when there is an excess of platelets - thrombophilia. An excess of these blood cells results in blood clots that are too large for minor injuries. The second important factor in thrombus formation is the very presence of damage. Thrombosis becomes a pathology if it begins in the absence of injury to the vascular wall.
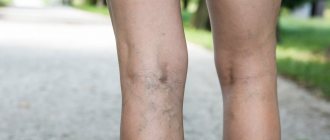
Deep vein thrombosis with varicose veins
Very often, deep vein thrombosis becomes a complication of varicose veins.
Deep vein thrombosis is often a complication of varicose veins
The severity of the disease will depend on the location of the blood clot and its size. If there is no complete blockage of the vessel, there may be no symptoms of the disease.
Deep vein thrombosis - causes of DVT development
Deep vein thrombosis most often occurs when several factors combine:
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- when blood flow slows;
- in case of damage to the vascular walls.
There are risk factors that provoke the occurrence of thrombosis, these are:
- elderly age;
- smoking;
- overweight;
- the use of certain medications, including oral contraceptives;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- some operations;
- injuries that damage blood vessels.
Prevention of relapse
Basic principles of prevention
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node occurs as a complication of hemorrhoids, therefore, prevention of relapse consists in preventing the occurrence of enlarged hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a disease with a hereditary predisposition. Therefore, if there has already been one attack, there is a high probability of relapse. However, the implementation of a negative scenario is possible in the presence of additional risk factors: ___• pregnancy, ___• taking hormonal drugs, ___• overweight, ___• constant diet violations: eating spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, ___• abuse of thermal procedures (bath and sauna) or regular hypothermia, ___• work involving prolonged sitting or heavy physical work.
Necessary precautions
Most often, acute thrombosis occurs as a consequence of prolonged bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation). Therefore, you need to achieve daily bowel movements with a diet rich in fiber.
It is advisable to refrain from physical and nervous overload, as well as from hypothermia and overheating of the lower half of the body. You should not abuse alcohol, as well as spicy, smoked and salty foods.
When working “sedentarily”, you need to take regular breaks, during which you should perform hemorrhoid-preventing exercises. Many chronic diseases can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, so taking care of your health is a reliable prevention of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Dangerous for the development of hemorrhoids and obesity. With this pathology, intra-abdominal pressure increases, the rheological properties of the blood change, problems with stool arise, and hormonal levels are disrupted. Therefore, normal weight is not only beauty, but also health.
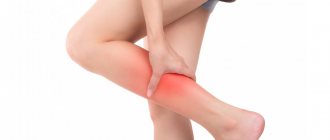
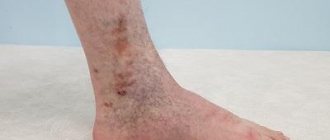
What symptoms develop with deep vein thrombosis?
As a rule, symptoms do not appear immediately, only if the blood clot enlarges. If a clot ruptures, shortness of breath, chest pain, and hemoptysis may occur.
The development of the disease can be recognized by the following symptoms:
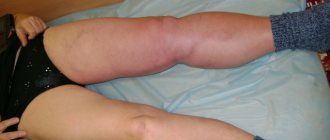
- swelling of the legs;
- bluish skin tone;
- pain when moving.
The main symptom of deep vein thrombosis is leg pain!
If you have these signs, you most likely have deep vein thrombosis. Stages or variants of the course determine the method of treatment.
If the blood clot comes off
The thrombus is not always firmly attached to the wall of the vessel. When a clot is superficially attached, a simple surge in pressure, a blow, or a careless movement is enough for the clot to come off and travel through the circulatory system. Moving through the vessels, the detached thrombus sooner or later reaches the most important organs, and usually the pulmonary vein, if the thrombus was venous, or the left atrium, if arterial.
Pulmonary thrombus
In the most dangerous cases, blockage of the large vessels of the lung occurs, after which death occurs within a few minutes. A less severe option is infarction-pneumonia, when a blocked vessel bursts and the lungs begin to fill with venous blood, which is accompanied by acute pain and hemoptysis. In this case, the patient has every chance of survival.
The mildest case, when a blood clot enters the pulmonary veins, is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure in the lungs, pain, shortness of breath, and suffocation. If you call an ambulance right away, the patient is likely to survive.
Coronary thrombus
If a blood clot located in the left atrium or coronary arteries breaks off, the patient is at risk of: myocardial infarction, stroke if the blood clot enters the brain through the bloodstream, infarction of the intestines or kidneys if the arteries leading to them are blocked, as well as blood stagnation and gangrene with subsequent loss limbs if the blood clot gets into the large arteries of the arm or leg.
Deep vein thrombosis - diagnosis
The main method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis today is ultrasound duplex scanning. With ultrasound scanning, you can determine the location of the thrombus, its size, and condition (is it attached to the walls of the vein or dangling in the lumen - floating).
Doctor Malakhov A.M. performs ultrasound diagnostics of deep veins of the lower extremities
Phlebography and radionuclide scanning are also prescribed to assess venous blood flow. The state of microcirculation is assessed based on rheovasography data.
Surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis
If a patient has a severe form of thrombosis of the lower extremities, the most effective treatment method is surgery - thrombolysis. A timely operation makes it possible to restore full blood flow if the diagnosis is deep vein thrombosis. Only timely intervention can completely cure the patient from this serious condition. Thrombolysis is performed only in hospital settings and by very experienced endovascular surgeons. Treatment after surgery is also aimed at the same goal - resorption of blood clots.
In addition to thrombolysis, there are two more surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis - thrombectomy with angioplasty and installation of a blood clot trap - a vena cava filter.
Surgical methods for treating deep vein thrombosis
How to treat acute thrombosis of external hemorrhoids?
Possibilities of surgical treatment
There are two main operations for the treatment of acute thrombosis of an external hemorrhoid: removal of the entire node or just the thrombus from it. The first operation is called economical (partial) hemorrhoidectomy (removal of only the external hemorrhoid), the second is thrombectomy. Both operations are effective in terms of eliminating pain within 2-3 days after their implementation, however, after an operation to evacuate a blood clot, a relapse (reoccurrence of a blood clot) is more common.
Economical (partial) hemorrhoidectomy of a thrombosed node involves incision of the skin around the node, its isolation and removal along with the thrombus. The operation can be performed under local anesthesia.
After removal of a hemorrhoid, a small wound surface is formed, which can cause pain, especially during bowel movements. But usually the pain is much less pronounced than in the presence of a thrombosed node, and only sometimes requires taking tablet painkillers.
Thrombectomy is performed through a skin incision over the thrombus, after which the thrombus is removed and 1-2 sutures may be placed at the incision site. This intervention is almost always performed under local anesthesia.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment (tablets and local remedies - ointments and suppositories) is mainly aimed at relieving pain caused by a blood clot, reducing swelling and inflammation of the hemorrhoid, and normalizing the frequency and quality of stool. Pharmacies offer a large number of drugs for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease, but they are all approximately equal in effectiveness and can be used to treat acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid. Local remedies (ointments and suppositories) mainly have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Topical agents with an anticoagulant effect in the treatment of acute thrombosis are effective only for the temporary prevention of new blood clots or, if the drug contains an analgesic component, for pain relief. Tablets are also used for pain relief (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, paracetamol) and normalization of venous blood flow in the pelvis (in the rectal area), for example, flavonoids. In addition, conservative treatment is also carried out after surgery to eliminate possible postoperative symptoms. A conservative treatment regimen can only be determined by a specialist, and it is better to select a combination of drugs in each specific case, depending on the characteristics of each patient.
Deep vein thrombosis - treatment in Moscow
Modern Moscow medicine offers several methods of treating deep vein thrombosis, the use of which depends on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, you can get by with thrombolytic drugs if you have deep vein thrombosis. Treatment (Moscow is a city where there are world luminaries in phlebology) must be very qualified. In the later stages, such therapy is dangerous due to the possible separation of the blood clot and the occurrence of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery. If severe circulatory disorders and deep vein thrombosis are observed, treatment is surgery (thrombectomy).
Deep vein thrombosis - conservative treatment
Conservative treatment can only stop or slow down the progression of the disease. Such therapy can also be prescribed as part of complex treatment.
Principles of conservative therapy:
- compression therapy (elastic compression) – the result of such an effect is the elimination of the mechanisms of progression of varicose veins; without such therapy, conservative treatment is impossible;
- the required level of compression is achieved through the use of special knitwear (special medical product), in this case it is important to choose the correct size of the compression knitwear;
- compression hosiery can relieve swelling, pain and increased fatigue of the lower extremities;
- the desired result is achieved with constant use of elastic compression.
Deep vein thrombosis treatment with medication
This involves a course of treatment with anticoagulants (drugs that prevent blood from clotting). The average duration of such a course is at least 3 months, and sometimes longer. A combination of drugs differing in their mechanism of action is provided. An important stage in the drug treatment of DVT is the selection of blood thinning drugs. To prevent gastrointestinal complications, some medications are administered parenterally.
Pharmacotherapy is often carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe forms of the disease, patients who have suffered thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery or thrombosis of the vena cava are annually hospitalized in the therapeutic or cardiology department for 2-3 weeks, where infusion hemorheological and cardiotonic therapy is carried out.
Deep vein thrombosis - treatment at home
Today, along with traditional methods of treating the disease, traditional medicine is practiced if deep vein thrombosis is determined. Treatment with folk remedies is used as a complement to the main treatment.
The first thing to do is thin the blood. If you have deep vein thrombosis, treatment with traditional methods includes consuming the following products:
- onion and garlic;
- sunflower seeds;
- cocoa;
- beets;
- Apple vinegar;
- tomatoes or tomato juice;
- Hercules;
- oatmeal;
- cranberries;
- oatmeal;
- lemon;
- cherries;
- viburnum.
Blood thinning should be approached with caution so as not to provoke bleeding. It is not recommended to consume fatty and meat products if you have deep vein thrombosis. Photos and results of improper treatment are available on the Internet.
Every day you can eat one spoon of a mixture made from crushed garlic, two tablespoons of unrefined vegetable oil and one tablespoon of honey.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
If doctors recommended thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid, this means that conservative therapy is not indicated in your case. You should not try to treat thrombosis with “traditional” methods.
If treatment is inadequate or absent, complications may develop: ___• bleeding, ___• gangrene of the node, ___• paraproctitis (purulent melting of peri-rectal fatty tissue).
In some cases, the affected node may open on its own and free itself from the blood clot. At the site of the “bump,” a fold of skin is formed – an anal fringe, which causes unpleasant sensations (itching, weeping) and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
Deep vein thrombosis - reviews from our patients.
Feedback from our patient about the treatment of deep vein thrombosis in
Anita, 38 years old, Moscow.
I would like to thank the clinic staff for their professionalism. With their help, I began to trust traditional medicine again. Before I went to the clinic, I was repeatedly subjected to various medical procedures for deep vein thrombosis in my legs. At first I had varicose veins with a complication, for which I had an operation to “stitch the veins.” As a result of this, I practically became disabled. On the advice of my friends, I turned to the doctors of the MIFC clinic, who returned me to a full life. It’s good that everything worked out without surgical intervention. Anita, 38 years old, Moscow.
Patient's review of the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in our center
Andrey, 40 years old, Krasnogorsk.
Due to frequent stressful situations and bad habits, I developed problems with my legs, or rather, poor circulation. My legs often swelled, turned blue, and sometimes hurt when walking. I accidentally saw an article on the Internet about vein thrombosis, and the symptoms described coincided with my feelings. I was just recently recommended to a phlebology clinic, and I decided to go for a consultation. Doctor Malakhov A.M. diagnosed: acute deep vein thrombosis. At first they calmed me down and told me that in this case it would be impossible to do without surgical intervention. Since there was no other choice, I agreed and did not regret it. The operation in the vascular department of the city hospital, where I was urgently hospitalized, to remove the blood clot was successful and without complications. Now my life is not in danger, thanks to the doctors of the MIFC clinic for their professionalism and “humane” attitude towards patients! Andrey, 40 years old, Moscow.
Preparation for the procedure
If the doctor decides to undergo thrombectomy, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes foods that cause gas formation in the large intestine (cabbage, legumes, fresh fruits and juices from them). The ban also includes products that cause a rush of blood to the rectum and/or have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane (smoked meats, spicy foods, alcohol).
Immediately before the procedure (in the morning and evening before the operation), you will need to cleanse the intestines using a Microlax microenema.
Preparation for thrombectomy is carried out when the patient's condition allows it. In case of severe pain and an impressive size of the node, bowel cleansing is not performed, and in the event of a threat of severe complications, surgical removal of the blood clot is carried out on an emergency basis.
Frequently asked questions from our patients on the Internet about deep vein thrombosis
How to understand that there are blood clots in the veins?
Only a specialist, phlebologist or vascular surgeon can reliably understand that there are blood clots in the veins. And even a specialized specialist will need instrumental support and ultrasound examination of blood vessels. You can assume that you have blood clots in your veins based on the following signs:
- Edema.
- Blueness of the skin.
- Soreness, swelling of tissues, redness of the skin along the veins.
If there are blood clots in the veins, how to recognize them, symptoms and treatment?
Blood clots in veins can be recognized using duplex ultrasound scanning. The presence of blood clots in the veins is indicated by the following symptoms: swelling, pain, discoloration of the limb. The best option for diagnosis, as well as subsequent treatment, is to contact a good phlebological center.
How to recognize a blood clot on the leg?
In order to recognize a blood clot on the leg, you must seek professional medical help. As an option, do an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower limb. The best solution would be to consult a specialist, a phlebologist.
How to identify blood clots in the legs?
From the point of view of modern diagnostics, the best way to determine blood clots in the legs is ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower extremities.
A blood clot in a vein, how does it form?
A blood clot in a vein is formed as a result of a complex chain of biochemical reactions, during which a network of insoluble fibrin molecules is formed from fibrinogen molecules. Blood cells are fixed in the latter, creating a dense intravascular structure, which is a thrombus.
How to identify a blood clot?
A thrombus can be detected using various methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and good ultrasound. The latter method has the best price-quality ratio and is the gold standard for diagnosing thrombosis.