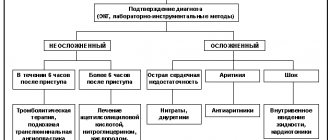
What are hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids (from the Greek haima - “blood”, roe - “flow”) are one of the most common diseases in proctology, which is based on the pathological condition of the cavernous plexuses of the rectum, accompanied by stagnation of blood in them. Hemorrhoids are manifested by periodic bleeding from the nodes, their prolapse from the anal canal and frequent inflammation. Men and women are equally susceptible to hemorrhoids
Classification of hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids. With internal hemorrhoids, there are varicose hemorrhoidal veins, which are located deep in the anal canal, so such hemorrhoids are not visible during a normal examination. In order to see them, you have to resort to special research methods: anoscopy, rectoscopy. Also, such nodes can be identified during digital rectal examination. Such a sign of the disease as prolapse of hemorrhoids can cause bleeding when they are injured during the act of defecation. With significant weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum, such nodes fall out during defecation or significant straining. In addition, the internal nodes, when they fall out and spasm of the anal sphincter, can be infringed. Most often, the first signs of internal hemorrhoids are bleeding.
External hemorrhoids. In this type of hemorrhoid, the hemorrhoids are marked externally and should not be confused with prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. Most often, external nodes manifest as thrombosis. As a rule, bleeding from external nodes does not occur, since they are not injured during defecation. Such hemorrhoids hurt and cause discomfort during bowel movements. But constant stagnation of blood in them can lead to the formation of blood clots in them. Externally, the external hemorrhoidal node can be of different sizes, from 3 mm or more, which depends on its blood supply. An external hemorrhoid is usually covered by skin, while a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid is usually covered by the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
Combined hemorrhoids. As the name implies, with combined hemorrhoids, the patient has a combination of external and internal hemorrhoids.
The occurrence of hemorrhoids
Normally, all people have external and internal hemorrhoidal venous plexuses under the mucous membrane of the anal canal, which are similar in structure to the cavernous tissue of the genital organs. They play a significant role in retaining intestinal contents, ensuring complete closure of the anal canal when they are filled with blood. As a result of the influence of a number of factors, most adults experience an increase in hemorrhoidal nodes, and hemorrhoids begin to develop.
Factors influencing the development of hemorrhoids: constipation, straining; pregnancy, childbirth; hereditary factors; sedentary lifestyle; prolonged standing or sitting; excessive physical activity; practicing some sports (horse riding, cycling, weightlifting); lifting weights; overweight; hot, spicy food; drinking alcohol; prolonged exposure to heat (sauna, hot bath); prolonged diarrhea (diarrhea).
Brief classification
Hemorrhoids are a painful enlargement of the cavernous cavities of the venous plexus of the rectum.
These cavities fill with blood when straining, performing the function of a kind of “pillow” that protects tissues from the traumatic effects of solid feces during the act of defecation. Hemorrhoids are a pressing problem for humanity; about 60% of Earth's citizens experience at least one episode of painful enlargement of hemorrhoids throughout their lives. It must be said that this percentage is much higher in countries that are commonly called civilized.
Anatomically, internal hemorrhoids - hemorrhoidal nodes in the distal (terminal) part of the rectum, and external hemorrhoids , when the nodes are located outside in the anal area.
According to the nature of the course, hemorrhoids can be acute , associated with thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal veins, and chronic , caused by constant overflow of distended veins with blood.
Possible complications
Due to the fact that internal hemorrhoids are much more difficult to diagnose than external hemorrhoids, you can skip the period of possible effective treatment. The effectiveness of all procedures aimed at combating the disease depends on the period in which the patient sought help at the hospital. It is very important for both women and men to pay great attention to their health and undergo regular, complete examinations whenever possible. If, nevertheless, the onset of the disease is missed, then this can lead to such troubles as anemia, strangulation of the node and the occurrence of thrombosis. Anemia occurs due to the fact that a person begins to lose blood with each bowel movement, and with each subsequent time more and more. A lack of hemoglobin will result in weakness, rapid fatigue, and a constant desire to lie down and rest. Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is formed due to the fact that blood stagnates in the area of the body responsible for emptying. Severe pain is the main characteristic of this problem. If inflammation is added to this, then you may encounter an even greater problem - damage to the perirectal tissue.
Reasons for the development of hemorrhoids in women
Chronic hemorrhoids in women, as a rule, develop after 30 years of age; with age, the risk of developing the disease increases. Women suffer from dilated hemorrhoidal veins four times less often than men. However, the risk increases in the presence of permissive factors: • chronic constipation; • prolonged sitting on the toilet; • obesity; • sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle; • diseases occurring with chronic cough; • diseases of the pelvic organs.
A typical cause of acute hemorrhoids in women is pregnancy or childbirth. In such cases, adequate conservative treatment leads to the disappearance of the problem. However, if therapy was untimely or careless, the disease becomes chronic.
How to cure hemorrhoids quickly and permanently?
To know how to cure hemorrhoids, you need to understand what caused it. In addition to pharmaceutical, physiotherapeutic and surgical treatment, lifestyle changes should be made so that this cause is excluded. Only in this case will it be possible to cure hemorrhoids forever.
The main causes of hemorrhoids:
- sedentary lifestyle. People who have to sit in a typical position (drivers, operators) or work in an inclined position are especially affected. The disease also affects people who work while standing (hairdressers, teachers, salespeople);
- excessive loads. The appearance or exacerbation of the disease can be triggered by heavy lifting, pregnancy, or prolonged sitting on the toilet;
- errors in nutrition. Poor nutrition, which causes digestive disorders - a tendency to diarrhea or constipation, also affects the condition of the rectum;
With diarrhea, the rectum and anus are irritated by liquid stool containing poorly digested food. With constipation, the rectal area experiences increased pressure, its mucous membrane is injured by hard masses, and the corpora cavernosa become overfilled with blood when a person strains.
- smoking, alcohol. Drinking alcohol and smoking negatively affect the condition of the walls of blood vessels, which, in combination with other factors, increases the likelihood of developing the disease;
- heredity. The tendency to varicose veins and disorders of the venous valves can be inherited. Therefore, if your family members suffer from varicose veins, treat the condition of your cardiovascular system with increased attention.
In parallel with eliminating the main cause of the disease, various treatment methods are used, the choice of which depends on the stage of the disease. There are 4 of them in total:
- Blood is released from the anus, the patient feels discomfort, but the hemorrhoids do not fall out. The mucous membrane has a characteristic enhanced vascular pattern.
- In addition to bleeding and discomfort, prolapse of hemorrhoids is added. They are able to move themselves into the anal canal. If the nodes prolapse, there may be no bleeding.
- Itching is added to the bleeding and loss of nodes. The nodes have to be adjusted manually; they themselves do not “fall into place.” If the nodes prolapse, there may be no bleeding.
- Hemorrhoids constantly fall out, affecting the rectal mucosa. It is impossible to set them. The patient constantly experiences pain, itching, and severe discomfort. The restraining function of the sphincter is impaired.
Figure 2 - To find out how to cure hemorrhoids, you need to determine the stage of the disease.
Many patients are looking for ways to quickly cure hemorrhoids without any medical intervention. Indeed, the disease at its very beginning can still be cured by using tablets, suppositories and ointments. However, if the process of varicose changes has already started to the stage of node formation, additional treatment methods will have to be used.
Typically, surgical treatment is used when the disease has reached stages 3 and 4. At stages 1 and 2, success can be achieved using conservative methods in combination with infrared photocoagulation, doping (suture, latex rings), sclerotherapy. In some cases, at stage 3, surgical intervention can be replaced by transanal resection of the mucosa using the Longo method.
Figure 3 - To cure stage 3 and 4 hemorrhoids, surgery is used.
Symptoms of the acute form of the disease
Symptoms of acute hemorrhoids in young women are most often associated with pregnancy or childbirth. The appearance of an enlarged hemorrhoid constipation characteristic of this period .
Acute dilatation of hemorrhoidal veins manifests itself with sharp pain , which becomes unbearable during bowel movements. In addition, the pain syndrome can intensify while walking, as well as with increased intra-abdominal pressure during straining, coughing, laughing, and hiccups.
Another characteristic sign of the acute form of the disease is bleeding from the dilated veins of the rectum. This symptom manifests itself as fresh blood on the surface of the stool.
Often hemorrhoids in women are combined with anal fissure. In such cases, blood stains on toilet paper and underwear appear even more often after defecation.
Stages of development of chronic pathology
With chronic hemorrhoids, the pain syndrome is much weaker. Often the only signs of chronic pathology are itching around the anus blood appearing on the surface of the stool from time to time .
The stages of development of internal hemorrhoids differ using the most objective symptom - the degree of stretching of the dilated veins: I. The hemorrhoid is constantly located in the intestinal cavity II. The knot falls out when straining and resets itself back III. The patient has to adjust the knot with his hands IV. One or more hemorrhoids are constantly on the outside and cannot be reduced
At any stage, thrombosis of the dilated veins of the rectum , in which case severe pain syndrome characteristic of an acute attack occurs.
With a long course of the disease, the risk of complications increases ( anemia, neurasthenia, anal fissure, etc. ).
How to cure external hemorrhoids?
A distinctive feature of external hemorrhoids is the hemorrhoidal nodes located around the anus. They consist of varicose veins, which are covered with thin skin, prone to frequent inflammation. Typical irritating factors are mechanical trauma from caked feces during constipation and irritation from liquid feces with an incorrect pH during diarrhea. When blood stagnates in the node, a blood clot forms. The skin over it gradually becomes thinner, and the blood clot comes out. Fresh scarlet blood appears behind it. It is external hemorrhoids that cause the most pain to patients. The nodes hurt especially strongly after defecation, during coughing and sneezing. Seizures occur in patients while walking or at rest, when touching the nodes. Treatment consists of relieving pain, normalizing the condition of the veins with medications, and removing nodes (the method depends on the stage of the disease).
Figure 4 - Internal hemorrhoids are not painful, but still require treatment.
Diagnosis and choice of treatment tactics
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids is carried out by a proctologist using a digital examination. Symptoms such as bleeding, pain, and the sensation of a foreign body in the rectum occur with cancer, as well as with other pathologies of the lower intestine.
Therefore, the general list of examinations may include sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, as well as laboratory tests.
At the final stage of diagnosis, treatment tactics are chosen. Acute hemorrhoids are treated conservatively, and in the chronic form of the disease they resort to surgery, giving preference to minimally invasive treatment methods.
The exception is cases when surgery is temporarily contraindicated. For women, this is pregnancy, the postpartum period, as well as situations when it is necessary to stabilize the general condition of the patient. This situation can arise during acute infections or during exacerbation of severe chronic diseases.
Causes
The root cause of hemorrhoids is a violation of the inflow and outflow of blood in the cavernous bodies of the rectum. Normally, the corpora cavernosa (also called cavernous bodies) help control the urge to defecate: when filled with blood, they “swell” and help retain feces in the intestines, and after a successful bowel movement, blood flows out and the corpora cavernosa shrink.
If the inflow/outflow regulation is disrupted and the corpora cavernosa have been engorged with blood for a long time, this causes the vascular walls to dilate and thin, making them much more susceptible to rupture or erosive lesions, which in turn cause inflammation and can lead to blood clots.
Factors that provoke venous stagnation
The following predisposing factors can provoke long-term venous congestion in the corpora cavernosa:
- Physical inactivity.
A low level of physical activity (due to sedentary work or simple laziness) causes extensive disturbances of venous blood flow throughout the body - and in the rectum in particular.
- High loads.
Ultra-high physical activity associated with lifting weights causes excessive tension in the abdominal muscles and rectal area, which also leads to disturbances in the venous blood flow.
- Chronic constipation.
The presence of feces in the rectum causes a constant, permanent filling of the cavernous bodies with blood, as mentioned above.
- Venous pathologies.
Impaired blood flow in hemorrhoidal veins can be caused by various vascular diseases.
- Oncology.
Tumor formations in the rectum cause disturbances in the inflow/outflow of blood due to mechanical compression of the venous vessels or their deformation due to tumor growth (in later stages).
- Diarrhea.
Severe diarrhea, especially caused by poisoning or infectious diseases, causes congestion of the venous system of the rectum, which leads to dilation of blood vessels or even micro-ruptures, followed by an inflammatory process.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
Bearing and giving birth to a child is often accompanied by multiple disturbances in the pelvic venous circulation system, which can (but not necessarily) lead to the appearance of hemorrhoids.
- Obesity.
The presence of excess weight, by analogy with physical inactivity, also leads to multiple disturbances of venous blood flow.
- Bad habits.
Chronic alcohol abuse or long-term tobacco smoking provokes varicose veins, which primarily affects the pelvic region and lower extremities.
- Heredity.
Low hereditary elasticity of the venous vessels of the rectal area creates a predisposition to hemorrhoidal disorders - although it is not considered as their direct cause.
Methods for treating hemorrhoids without surgery
Conservative treatment of painfully enlarged hemorrhoids should be carried out comprehensively, affecting all factors contributing to the development of the disease. It is necessary to normalize the stool, because constipation and diarrhea equally seriously injure the inflamed node.
If the cause of hemorrhoids is an attack of diarrhea, every effort is made to cure the disease that caused the stool disorder. Constipation is fought with a diet that includes a large amount of dietary fiber (prunes, dried apricots, oranges, apples). For persistent constipation, mild laxatives (Duphalac) are prescribed.
In order not to irritate the intestines, spices, salt, vinegar, smoked foods, as well as carbonated drinks and alcohol are excluded from the diet.
The pain increases the spasm of the internal sphincter, which contributes to stagnation of blood in the veins. To relieve pain and spasms, use warm baths with potassium permanganate or herbal decoctions.
Painkillers, antispasmodics, blood thinners, and medications that promote tissue regeneration are prescribed as drug therapy. Preference is given to “local” therapy: ointments are used for external nodes, and suppositories for internal nodes.
Attention! The prescription of drugs depends on the location of the hemorrhoid, the stage of development of the disease, the phase of the process, the presence of concomitant diseases and the general condition of the body. Therefore, we recommend not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Treatment
INITIAL CONSULTATION
from 5,000 rub.
Treatment methods
Currently, different methods of treating hemorrhoids are used. They are divided into conservative (without surgery), minimally invasive and surgical.
In the early stages of the process, one is usually limited to the first two approaches. Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is necessary in severe cases.
Treatment without surgery
Treatment of chronic hemorrhoids is usually used in the early stages and is aimed at preventing further development of the disease and preventing exacerbations. This can be achieved by:
- preventing constipation;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels, increasing the tone of hemorrhoidal veins;
- prevention of bleeding from hemorrhoids.
To normalize stool, the first aid is diet and lifestyle changes: increased physical activity, abdominal massage. Only if these measures are ineffective, laxatives are prescribed.
To strengthen the walls of blood vessels, as prescribed by a doctor, drugs are used that increase the tone of the veins - venotonics. They can be used both in tablets and capsules for oral administration and for topical use.
To prevent and treat bleeding from hemorrhoids, topical preparations containing sodium alginate can be used. However, treatment without surgery is only possible for internal hemorrhoids without prolapse of nodes and frequent exacerbations. If periodic bleeding leads to the development of anemia (anemia) and interferes with general health, surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is necessary.
In case of acute hemorrhoids (exacerbation), treatment is aimed, first of all, at quickly eliminating inflammation and other symptoms, alleviating the patient’s condition and restoring the impaired quality of life.
It consists in:
- fast and effective pain relief;
- prevention of vascular thrombosis and resorption of existing blood clots;
- limiting inflammation.
For effective pain relief during exacerbation, local anesthetics, antispasmodics and analgesics are usually used. In order to resolve existing blood clots and prevent vascular thrombosis, heparin-based drugs are used. To limit inflammation, reduce swelling, itching and burning sensation, hormonal steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually used as prescribed by a doctor.
Conservative methods of treating hemorrhoids also include treatment with leeches (hirudotherapy). The saliva of leeches contains the enzyme hirudin, which thins the blood, dissolves existing blood clots and prevents the formation of new ones. This technique is usually used in combination with other treatment methods.
Minimally invasive treatment methods
Hemorrhoid treatment methods that allow the removal of hemorrhoids with minimal trauma to surrounding tissue are called minimally invasive. At their core, they are surgical procedures, but such interventions practically do not deprive the patient of his ability to work. These include infrared photocoagulation, cryotherapy, ligation of nodes with latex rings and some other methods. Sometimes hemorrhoids are treated with a laser.
With infrared photocoagulation, special thermal infrared rays are applied to the pedicle of the hemorrhoid. As a result, the vessels supplying the hemorrhoid are damaged. The blood supply to the node stops, and after some time it dies.
Cryotherapy
- This is the freezing of hemorrhoids using liquid nitrogen. As a result of short-term powerful cold exposure, the tissues of the node die and are rejected after some time. The moment of exposure does not cause serious pain to the patient, and after the nodes are rejected, no scars remain. This method gives the best effect in the second and third stages of the disease.
Another method of treating hemorrhoids called ligation with latex rings is also widely used. With this method of treatment, a dense latex ring is placed on the stem of the node. It compresses the vessels feeding the node. After some time, the tissues, deprived of blood supply and nutrition, die and, together with the ring, come out during bowel movements.
Minimally invasive procedures are usually performed on an outpatient basis. If pain occurs after the intervention, its duration ranges from several hours to two days. The pain is usually moderate and can be easily relieved with conventional painkillers. Patients do not require sick leave; they can start working in a few hours.
Surgical removal
Surgery to remove hemorrhoids is now resorted to only in the most difficult cases - for example, at the third or fourth stage of hemorrhoids, when other methods are ineffective. This operation is performed in a hospital using intravenous anesthesia, spinal or local anesthesia. Depending on the type of operation, the patient spends 2 to 7 days in the hospital.
Radical treatment of pathology
Minimally invasive methods
Doctors treat chronic hemorrhoids with surgical methods. At the initial stages of the disease, preference is given to minimally invasive techniques, which are carried out on an outpatient basis (without placing the patient in a hospital) and provide for a short rehabilitation period.
An important advantage of low-traumatic operations is a short list of contraindications. The list of methods that are suitable for most patients includes: • sclerotherapy (injection into dilated veins of substances that cause “soldering” of the walls of dilated veins); • infrared coagulation (cauterization of the leg of the node); • ligation of the internal hemorrhoid with latex rings.
Sclerotherapy and infrared coagulation are used at stages I – II of the development of internal hemorrhoids. The effectiveness of these methods at stage I is 85%, and at stage II – about 72%. If the node is ligated with latex rings, the effectiveness exceeds 93%.
Operation hemorrhoidectomy
Hemorrhoidectomy is the removal of enlarged hemorrhoids using surgical methods, that is, using a scalpel.
Such treatment must be carried out in a hospital. The rehabilitation period is much longer and is less well tolerated by patients. Therefore, surgical removal of nodes is carried out only in the last stages of the disease , when minimally invasive techniques are no longer effective.
Hemorrhoidectomy can be combined with disarterization of hemorrhoids under ultrasound control. This method is often used for stage III internal hemorrhoids.
The choice of surgical intervention method depends on the number of enlarged nodes, their location, as well as the presence of complications and concomitant pathologies.
How to deal with the disease at different stages
The expansion of hemorrhoidal veins requires an immediate response already at the initial stage of its development. In this case, it is necessary to clearly establish why hemorrhoids occurred in a particular situation, and try to reduce the negative influence of factors to a minimum. In addition, it is important to begin eliminating the consequences of changes as early as possible in accordance with the stage of the disease:
- At the first stage of hemorrhoids, drug treatment with topical drugs with anti-inflammatory, regenerating, analgesic and venotonic effects is recommended. Sclerosis of hemorrhoidal veins can also be used. Patients are also advised to follow a diet and increase physical activity.
- The second stage of hemorrhoids involves the same treatment as in the first stage, but with the use of oral medications (local ones are also included in the treatment regimen). In addition, radical methods for eliminating hemorrhoids are used: sclerotherapy, ligation, laser removal of nodes, cryotherapy or coagulation of nodes.
- The third stage of hemorrhoids requires more radical measures, and therefore conservative therapy gives way to surgical treatment - hemorrhoidectomy and vein disarterization and the use of various technologies (laser, radio waves). Latex ligation of nodes is also used at this stage.
- The fourth stage of hemorrhoids is complicated by complete prolapse of the nodes and a high probability of thrombosis and heavy bleeding. Effective methods of treating hemorrhoids at this stage are laser coagulation and hemorrhoidectomy (laser or radio wave). For vein thrombosis, thrombectomy is performed. Conservative therapy for this degree of disease is ineffective.
Regardless of what stage of hemorrhoids occurs, in parallel with the methods described above, it is necessary to apply preventive measures. They are most often aimed at eliminating the causes of hemorrhoids. This allows you to lengthen the relapse-free period and avoid further progression of the disease.
Treatment during pregnancy and after childbirth
Treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women and in the early postpartum period does not involve surgical intervention. The fact is that the reasons for the dilation of the veins of the rectum during this period are physiological in nature: • changes in hormonal levels; • increased intra-abdominal pressure; • increase in circulating blood volume; • straining during childbirth.
After childbirth, hormonal levels gradually normalize, which leads to the disappearance of the tendency to constipation. The volume of circulating blood decreases, intra-abdominal pressure decreases, the body's defenses are restored and all conditions for recovery are created.
Therefore, in most cases, a painful node that occurs during pregnancy or after childbirth disappears on its own under the influence of standard methods of conservative treatment.
Attention! When conservatively treating hemorrhoids in pregnant women, as well as in women during lactation, care should be taken. Some active ingredients of topically applied drugs still enter the bloodstream and can harm the child. Therefore, treatment must be done under the supervision of a physician.
How to cure hemorrhoids during pregnancy?
Doctors have to think especially carefully about how to cure hemorrhoids after childbirth or during pregnancy. Many medications are prohibited to be taken during pregnancy and lactation, so most often doctors achieve stabilization of the patient’s condition, eliminate pain, and begin full treatment after the end of lactation.
Lactation consultants have their own point of view on the issue of drug treatment during lactation. They draw women's attention to the fact that many medications are prohibited from taking during pregnancy and lactation due to the fact that their effect on the child has not been thoroughly studied. Therefore, we cannot say unequivocally that all of them bring harm to the child. It may well be that when the appropriate studies are carried out, many drugs will be allowed to be taken. In the meantime, the Ministry of Health prefers to play it safe; women have at their disposal a minimal arsenal of means to solve “delicate” problems.
Figure 7 - To treat hemorrhoids during pregnancy, be sure to consult a doctor.
Reviews from patients about the operation
We analyzed patient reviews about the rehabilitation period after hemorrhoid removal. The analysis showed that the severity of pain, difficulty with defecation and bleeding after surgery depends on the size and number of nodes removed.
Patients who have consulted a doctor with a single small node speak of surgical intervention as a completely tolerable procedure, with a short rehabilitation period.
When it comes to several large nodes, treatment will be lengthy. If the doctor recommends a minimally invasive method, you will have to remove one node per week, so the healing process will take several weeks. A surgical operation will remove all pathological elements at once, but in this case the rehabilitation period may also take several weeks.
Therefore, we recommend that you consult a doctor in a timely manner in order to intervene at an early stage of the disease. Additional information about preparing for surgery and rules of behavior during the rehabilitation period can be read in the article “Treatment of hemorrhoids in men.”
Relapse Prevention
If you have already had hemorrhoids removed, there is an increased risk of the disease returning. To protect yourself from relapse, you should follow the recommendations of doctors: 1. Watch your stool (it is advisable to achieve daily morning bowel movements). 2. Be careful with “weight loss” diets (see point 1). 3. If you have a sedentary job, do gymnastics regularly. 4. Treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pelvic organs (gastroenterology, urology, gynecology) in a timely manner. 5. Avoid physical and nervous overload.
Nature has prepared a woman for childbirth, so the venous vessels of the rectum in women are more resistant to stress than in men. If you follow the rules, the disease will not return.
Prevention of hemorrhoids
To prevent the development of hemorrhoids or prevent its further progression, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations.
- Make sure you have regular bowel movements and avoid constant constipation. Remember that this problem can be associated not only with poor nutrition, but also with insufficient physical activity and low water consumption. Drink at least 1.5 liters of plain water every day to soften your stool and make bowel movements easier.
- Limit in your diet foods that increase blood flow to the pelvis: spices, spicy, pickled and smoked foods, and especially alcohol. Give preference to vegetables and fruits that are rich in fiber and improve bowel function.
- Try to walk and swim more, especially if you have to stand or sit for a long time during the day. By the way, this will also prevent varicose veins in the legs, which often accompanies hemorrhoids. Active movements will prevent blood from stagnating in the legs and pelvis.
- Don't lift heavy objects.
- Try to wash the anus area with cool water after each bowel movement. This way you will not injure the mucous membrane and give your blood vessels a workout. If it is impossible to wash, use cold wet wipes.
- Perform special exercises to prevent hemorrhoids. The simplest of them is to squeeze the muscles of the perineum and anus, and then relax them. This exercise can be done several times a day in any environment. The main thing is regularity.
Is it possible to cure chronic hemorrhoids with folk remedies?
Unfortunately, chronic hemorrhoids cannot be cured using conservative methods. “Folk” methods give a short-term effect. Similar results will be obtained with “home” drug treatment.
The unpleasant symptoms of the disease may disappear for a while, but the disease will develop unnoticed by you. In the future, the following complications may develop: • anal fissure; • anemia; • nervous exhaustion; • infectious processes (proctitis, paraproctitis, etc.).
It should also be noted that under the mask of hemorrhoids a deadly disease such as rectal cancer . Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear, you should urgently consult a doctor to find out an accurate diagnosis and begin adequate treatment.
Don’t waste time on self-medication, come to an appointment with a proctologist!
How to cure internal hemorrhoids?
Internal hemorrhoids rarely cause discomfort and are hardly noticeable. The nodes are located under the mucous membrane of the rectum, so the patient cannot see or feel them. However, thrombosis also develops in such “quiet” nodes. The presence of the disease can be suspected by the presence of blood during bowel movements (including on toilet paper), pain of varying intensity, an occasional feeling of incomplete bowel movement, and itching in the anus. Neglected hemorrhoids fall out, and then conservative treatment is no longer sufficient. The treatment method depends on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, conservative methods can be used; in the later stages, minimally invasive or surgical intervention is indicated.
Figure 5 - Hemorrhoids are located internally and/or externally.
What medications are used to treat hemorrhoids?
Drugs are selected depending on the stage of the disease.
- At stage 1 of the disease, suppositories and ointments are effective that can normalize blood circulation, relieve pain, relieve inflammation, relax the walls of the rectum and sphincter: Hepatrombin, Anuzol, Fitor, Proctosedyl, Relief, suppositories with sea buckthorn oil, Proctosan.
- At stage 2, stronger drugs are used: Aescusan, Detralex, Etamzilat, Neuflan, methyluracil ointment.
- At stages 3 and 4, the main effect is provided by surgical intervention. In addition to it, Gepatrombin, Troxevasin, Prednisolone, Mafinide are used.
- To normalize digestion, laxatives or fixatives, bacterial complexes (probiotics, symbiotics), enzymes, and agents to improve peristalsis are used.
- To increase the performance of veins and reduce inflammation in hemorrhoids, phlebotropic drugs, for example, Glivenol, are used.
Hemorrhoids, like other diseases, do not accept self-medication. All medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Even if the medicine helps your relatives and friends very well, it is quite possible that it will harm you personally.
In the process of searching for ways to cure hemorrhoids without surgery, patients inevitably encounter various traditional methods. You need to treat them very carefully. Consider whether you are ready to apply apple cider vinegar, lemon or onion juice to inflamed hemorrhoids, or insert cloves of garlic into the anus. Before using herbal teas or decoctions, make sure you are not allergic to them. The use of herbs, oils, meals and tinctures can help relieve inflammation, but will not cure varicose veins. As a result, the disease will be masked and will only get worse.
Figure 6 - To cure hemorrhoids during pregnancy, be sure to consult a doctor