Toxic encephalopathy
Toxic encephalopathy can develop at any age as a result of acute poisoning with poisons of neurotropic origin or with small but regular or constant intoxications resulting from the characteristics of professional activity.
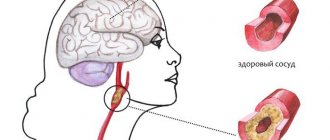
Encephalopathy of this type is an extreme degree of poisoning, when the main areas of the central nervous system are affected, and therefore symptoms caused by mental and nervous disorders always come to the fore. Toxic substances can include heavy metal compounds, high doses of pesticides, gasoline, alcohols and much more.
The course and prognosis of encephalopathy of toxic origin entirely depends on the duration of exposure to toxic substances, their quantity and frequency of infection. The condition of the body itself and the immune system plays an important role. It is also important to understand that poisoning can also occur when toxic substances are exposed to the skin, mucous membranes and through the blood.
Clinical picture of the disease
The symptoms of toxic encephalopathy for the early stage are equivalent to the clinic of ordinary poisoning with the aggressive substance that led to the disease. A distinctive feature is that in addition to the signs of general intoxication, pronounced symptoms of dysfunction of the central nervous system (irritability, anxiety, insomnia, etc.) are added.
If the effect of toxic substances continues, then the degree of damage to brain tissue becomes deeper and more intense, and therefore the patient’s pathological condition worsens. At this stage, we can say that toxic encephalopathy of the brain becomes irreversible, because the changes are practically irreversible.
Main clinical signs:
- prolonged painful headaches;
- sleep disorders (insomnia, drowsiness, interrupted sleep, etc.);
- mental disorders of any type (delirium, overexcitation, hallucinogenic effect, etc.);
- ulceration or thinning of the skin is possible, which is the result of impaired trophism.
In addition to exposure to harmful substances, official medicine distinguishes another type of disease - toxic encephalopathy due to alcoholism. It occurs as a result of prolonged exposure to an addiction on the body. It develops as a result of the destruction of vitamin B1 by alcoholic drinks, which ultimately leads to the death of brain cells.
There are frequent cases of combined encephalopathy of toxic origin, when the body is simultaneously affected by both toxic substances and alcoholic compounds. Patients can themselves aggravate the chronic course of the disease, which they may not be aware of due to the lack of timely diagnosis. In this case, most often the disease is acute in nature with a history of severe symptoms of encephalopathy. The temperature may also rise, and the mental state may acquire a hint of insanity.
Treatment of toxic encephalopathy
Treatment of toxic encephalopathy should begin with the cessation of exposure to the toxic substance on the body. It is also necessary to conduct a full diagnosis in order to identify concomitant diseases, which will allow us to establish the true causes of encephalopathy, confirm its origin and provide the opportunity to prescribe the most effective treatment.
In our medical center, examinations are carried out using modern equipment, which allows us to obtain the most effective results. Remember that only timely consultation with a doctor and timely diagnostic measures can prevent the sad consequences of toxic encephalopathy. If work activity is associated with harmful substances, examination of the body must be carried out regularly. This is the best prevention and most effective treatment method to date.
Diagnostic principles
The diagnosis is based on objective symptoms, results of laboratory and instrumental examinations and anamnesis. In addition to the mandatory examination by a therapist and neurologist, the following are indicated:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemical blood test with determination of glucose, ALT, AST, bilirubin, urea, creatinines and electrolytes;
- according to indications: analysis to determine immunospecific status, neurospecific factors;
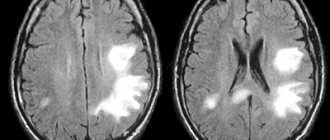
- CT, MRI, angiography;
- specific tests to detect heavy metals and narcotic substances in the body.
If symptoms indicate damage to internal organs, additional research or consultation with specialized specialists may be required. Differential diagnosis is carried out with other forms of encephalopathies and neurodegenerative diseases.
Drug treatment - medications used to treat a disease
Therapy for encephalopathy is always complex and lengthy. Typically used:
- antiplatelet agents - improve cerebral circulation;
- nootropics - improve brain activity;
- vitamins - maintain the normal condition of tissues throughout the body;
- antioxidants - reduce oxidative stress;
- absorbents - remove toxins from the body.
It is very important to select drugs for the patient that will eliminate the factor that caused the disease. Thus, for surges in blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are used, for diabetes mellitus - drugs that lower blood sugar levels, and for high cholesterol - statins. Antidepressants help cope with depressed mood. Tinnitus and dizziness often involve histamines.
Remission
Remission is a period when the symptoms of encephalopathy do not appear. The person begins to feel healthy.
In order for it to last as long as possible with encephalopathy, it is necessary to strictly follow all medical prescriptions and take prescribed medications. During the period of remission, the patient should under no circumstances relax, as this will lead to an exacerbation and rapid progression of the disease.
Treatment methods for encephalopathy
Therapy of the disease is based on the following methods:
- Medication . Medicines are used that are selected taking into account the cause of the disorder.
- Physiotherapeutic . Good effects can be obtained using magnetic and electromagnetic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, ozone therapy, acupuncture, and plasmapheresis.
- Surgical . It is used if conservative methods do not provide improvement in the patient’s well-being. Then a vascular operation is performed, due to which normalization of blood flow in the brain is achieved. Surgery is needed for traumatic brain injury, cancer, and congenital pathologies.
It is also important for the patient to adjust their lifestyle for recovery. You need to get rid of excess weight, start eating right, and play sports. You should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
COST OF TREATMENT FOR MENTAL DISEASES
The duration of treatment in a hospital is from 14 to 90 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL.
AMBULATORY TREATMENT
TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL
Inpatient treatment – accommodation options
| Accommodation in a triple room | 10,000 rub./day |
| Double room | RUB 13,800/day |
| Single room of increased comfort | 16,000 rub./day |
| Treatment in a single VIP ward | 25,000 rub./day |
AMBULATORY TREATMENT
Ambulatory treatment
| psychiatrist | FOR FREE |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist (first appointment) – free of charge during hospitalization | 3,000 rub. |
| Full psychodiagnostics (all tests and procedures) | from 5,000 rub. |
| Appointment with the head physician of the clinic | 4,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist at home | from 4,000 rub. |
FREE CONSULTATION
Causes of encephalopathy
Among the factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- surges in blood pressure, hypertensive crisis;
- atherosclerotic damage to blood vessels;
- diabetes;
- vasculitis;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- high intracranial pressure;
- head injuries.
Before helping a patient, selecting effective medications for him and giving a prognosis for treating the disease, doctors at the Cordia clinic conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and find out what led to the disease. Only after this an individual treatment plan is drawn up.
Symptoms and manifestations
The manifestations of encephalopathy depend on what caused it. Common symptoms of pathology in adults include:
- impaired memory and attention - difficulty concentrating, concentrating on a particular activity, poor memory for recent events;
- headaches, dizziness;
- bad mood, lack of initiative, irritability, tearfulness;
- general deterioration of health, fatigue;
- sleep disorders - insomnia at night and daytime sleepiness.
Timely treatment of encephalopathy is a task that mostly falls on the patient’s relatives and friends, since the patient may simply not notice alarming symptoms. This especially applies to pathologies that manifest themselves poorly. Therefore, in cases where you notice a deterioration in the health of a loved one, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Description of the disease
Encephalopathy is intoxication or chronic cerebral ischemia. It is characterized by multiple neuropsychological and neurological disorders. The disease develops due to two abnormal mechanisms occurring in the body:
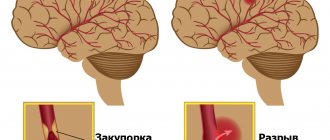
- Deficiency of oxygen supplied to brain tissue cells due to vascular damage due to intracranial/arterial hypertension, thrombosis, diabetes.
- Poisoning of brain neurons by toxic decay products. This problem occurs in alcoholics, drug addicts, substance abusers, and with severe liver and kidney diseases.
According to statistics, people over fifty years of age are more likely to experience the disease. But it also occurs in newborns and pregnant women.
Believing positive reviews about alternative treatment for any type of encephalopathy is a road to nowhere. Only experienced doctors know how to cure this pathology. Therefore, seeking qualified medical help is mandatory.
Mechanism of occurrence
In the 21st century, the pathogenesis of various forms of TE has not been studied in detail and remains questionable. Scientists were able to establish a clear connection between clinical history and morphological deformations that occur in the nervous system. Doctors say that the basis of the disease is the influence of a toxic drug and disruptions in the functioning of the blood supply system to the brain, as a result of injury to the cerebral vessels. Such a harmful process provokes degenerative-dystrophic disorders in soft tissues and the formation of swelling of the meninges. Patients develop disruptions of hemodynamic and liquorodynamic nature, which further worsens the toxic and hypoxic effect on the central nervous system. Subsequently, the patient develops necrotic zones in the cortex and subcortical areas, and fragmentation of myelin structures.
If a certain element is taken into account, doctors are able to identify specific features. They can be associated with the increased sensitivity of parts of the nervous system and the ability of dangerous compounds to accumulate in internal objects of the body.