Cerebral encephalopathy in adults is a rather complex disease. Treatment of encephalopathy involves the simultaneous use of several methods of restorative medicine.
Brain Clinic specialists have extensive experience in treating cerebral encephalopathy in adults of various origins, and will be able to correctly and safely restore its functioning without any side or negative effects on the body.
Call and make an appointment! Our treatment helps even with the most severe cases, when other treatments did not help!
| Initial consultation and examination 2,500 | Therapeutic and restorative neurometabolic therapy from 5000 |
Who's at risk
The following categories of people are at risk:
- with atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- with unstable blood pressure;
- with diabetes mellitus (treatment prescribed by an endocrinologist);
- alcohol abusers;
- after a brain injury;
- with liver disease (consult a hepatologist);
- working in hazardous industries (fumes of caustic chemicals);
- over 60 years old;
- with a sedentary lifestyle;
- with obesity (consulting a nutritionist will help to cope with the problem).
- smokers;
- suffering from vasculitis, arteritis.
Types of encephalopathy
Hypertensive
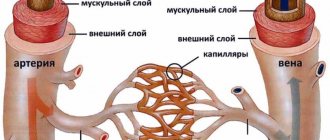
With increased pressure, damage to the vascular bed of the brain occurs. It has been proven that with long-term hypertension, a change in the walls of the arteries occurs: the replacement of muscle cells with connective tissue (sclerosis), which leads to a decrease in vascular permeability.
In addition, small arteries lengthen and acquire pathological tortuosity, which also disrupts the metabolic processes of the brain.
For the vessels of the brain, pressure changes are much more dangerous than simply increased pressure. Often, degenerative processes develop in the first and second degrees of hypertension, when there are no “prohibitively high” blood pressure values.
Diabetic
In diabetes mellitus, pathological processes occur in the inner lining of blood vessels (endothelium), which leads to disruption of the nutrition of brain tissue.
An increased level of glucose in the blood leads to the glycosylation reaction of protein molecules. This is a “springboard” for the development of vascular pathology. Diabetes mellitus is characterized by damage to small blood vessels (arterioles, capillaries).
Discirculatory
It includes both pathological changes in blood vessels due to atherosclerosis and the presence of lesions in the brain tissue. Atherosclerotic plaques cause vascular obstruction, which leads to a decrease in blood flow to the brain tissue.
In this case, the following changes occur in the nervous tissue: cell atrophy, as well as the breakdown of the myelin (outer) sheath of nerve fibers, which is responsible for conducting nerve impulses.
Alcoholic
It is damage to blood vessels and brain tissue as a result of abuse of alcoholic beverages or their surrogates.
Toxic
Severe poisoning from poisons and chemicals leads to brain damage.
Post-traumatic
It is usually a consequence of trauma and cerebral edema.
Encephalopathy in children
It occurs as a result of a viral infection or against the background of oncological processes.
Hepatic encephalopathy
Develops in severe liver diseases (hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis), when the detoxification function of the liver is impaired. In this case, brain damage occurs precisely as a result of the presence of toxic metabolites in the human blood.
Classification
Taking into account the prevailing disorders, encephalopathy of vascular origin can be venous, atherosclerotic, hypertensive and mixed. In most cases, the disease progresses slowly; rapidly worsening and remitting forms are less common. According to severity they are distinguished:
- 1st degree. There are no neurological symptoms, and there is a slight decline in cognitive function.
- 2nd degree. Includes obvious motor and cognitive impairments, progressive emotional disturbances.
- 3rd degree. Essentially, it is dementia combined with severe mental and neurological changes.
Stages of the disease
The first , in which initial symptoms appear: absent-mindedness, forgetfulness, decreased performance, headache, tinnitus. Patients usually associate this condition with fatigue and rarely consult a doctor at this stage.
Doctor's advice
It has been noted that encephalopathy develops less frequently and much later in people who are engaged in mental work or who like to read frequently and have a need to obtain new information. There are 90-year-old professors and teachers who continue to engage in scientific work, and at the same time have excellent memory and intelligence. For those who lead an associative lifestyle and have an initial level of education, the diagnosis of “Encephalopathy” may be relevant at 30 years of age. To prevent the disease, you should solve crossword puzzles every day, read classical literature, periodically memorize poetry, retell the contents of books you read, movies you watched.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Therapeutic effects at this stage are the most effective and can almost completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Secondly , the patient’s performance is significantly reduced, he becomes slow, his speech is “sticky”. Minor speech impediments may occur. A characteristic feature of this stage is a change in the patient’s personality; he becomes irritable, angry, and touchy.
The third is characterized by gross disturbances and manifests itself with significant brain damage. Characterized by changes in speech (gross defects), a shaky, shuffling gait, trembling hands, extreme slowness, and serious memory impairment. The patient's personality may change beyond recognition.
Diagnostics
In the initial stages, the manifestations of dyscirculatory vascular encephalopathy are easily corrected with adequate treatment of the underlying disease, therefore patients with vascular pathology are recommended to undergo regular examinations to identify the first symptoms and prevent progression. The examination program includes:
- Neurological examination. At stage 1, the neurological status is unchanged. Subsequently, tremor, limb weakness, and focal symptoms are determined.
- Assessment of mental and intellectual status. This is done through conversation and special tests.
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist. Allows you to detect changes in the fundus. Includes determination of the visual field, ophthalmoscopy.
- Electrophysiological methods. Electroencephalography and rheoencephalography are recommended.
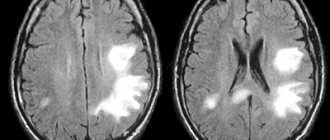
- Visualization of blood vessels. When confirming the probable vascular origin of the disease, MRA, duplex scanning and Doppler sonography are informative.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Performed as part of differential diagnosis with other cerebral pathologies.
To clarify the diagnosis of the causative disease, the patient may be referred to a cardiologist, nephrologist or endocrinologist, and prescribed an ECG, coagulogram, and tests to determine the level of sugar, lipoproteins and cholesterol.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- forgetfulness;
- attention disorders;
- memory impairment;
- slowness;
- "viscosity of speech";
- speech defects (omission of letters, replacement of words, difficulty finding a synonym, lack of long sentences);
- gait disturbances (unsteadiness, difficulty maintaining balance, tendency to fall, clumsiness when turning);
- headache, dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- drowsiness, fatigue, weakness;
- sleep disorders (difficulty falling asleep, shallow sleep, frequent awakenings at night);
- decreased performance, inability to do more than one thing at a time;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs: urinary incontinence, up to complete loss of control over urination, in advanced cases - fecal incontinence;
- “poverty” of emotions (loss of interest in others, apathy, withdrawal into oneself, a feeling of detachment, uselessness, lack of expression of emotions);
- decreased intellectual potential (in the severe stage, the patient sometimes cannot count to 10).
Treatment
Considering the variety of factors causing encephalopathy, treatment should be carried out in the following areas:
- Eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Improving blood supply to the brain.
- Prescription of drugs that protect nerve cells from damage.
For encephalopathy, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Neuroprotective drugs. These drugs are highly effective in treating encephalopathy disorders. They improve trophic processes in nerve cells, provide protection and restoration of cell membranes from damage. The most commonly prescribed drugs are: Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Encephabol, Cortexin.
- Improving blood microcirculation in the vessels of the brain is achieved by prescribing drugs such as Actovegin and Kurantil.
- Hypotensive (blowing blood pressure). Preference is given to drugs with a long action (about 24 hours) in order to avoid hypertensive crises. If one drug is insufficient, a combination of drugs is prescribed. The most commonly used are ACE inhibitors (Enalapril, Lisinopril, Fosinopril), beta blockers (Nebilet, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol), diuretics (Hypothiazide), Indapamide, Spironolactone. .
- Statins are drugs that lower blood lipid levels. Typically prescribed are Atorvastatin (Atoris), Simvastatin (Simvacard), and Rosuvastatin (Rozart). In addition, to correct lipid levels, you must adhere to a low-calorie diet.
- Antioxidants - these drugs protect the cell from pathological oxidation processes and the effects of toxic free radicals. The use of the drug Mexicor for encephalopathy is effective.
- Antiplatelet agents - by reducing platelet aggregation, blood circulation in small vessels improves. Usually medications such as Aspirin and Clopidogrel are prescribed.
- Monitoring glucose levels is mandatory for diabetes mellitus.
- Detoxification - promotes the removal of toxic metabolites from the body; this therapy is especially effective for alcoholic and hepatic encephalopathy. In cases of severe intoxication, plasmapheresis (hardware purification of blood plasma from toxins) may be required.
After drug treatment, special attention should be paid to the patient’s rehabilitation:
- Compliance with the work and rest regime.
- Normalization of sleep.
- Maintaining a diet if necessary (for obesity, diabetes).
- Dosed physical activity.
- Spa treatment.
Encephalopathy is very insidious, since the initial manifestations of the disease are very nonspecific and can be regarded by a person as chronic fatigue. In addition, it is sometimes very difficult to determine which factor leads to brain damage.
Encephalopathy often develops as a result of several causes affecting the body at once. This means that the boundaries of each type of encephalopathy are very blurred. That is why in the treatment of this condition it is justified to prescribe several groups of drugs with different mechanisms of action.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://mir.ismu.baikal.ru/src/downloads/2581419b_uchebnoe_posobie_distsirkulyatornaya_entsefalopatiya.pdf 2. https://dep_ninh.pnzgu.ru/files/dep_ninh.pnzgu.ru/hronicheskaya_nedostatochnost_mozgovogo_krovoobrascheniya.pdf
Rate, How helpful was the article?
4.4 21 people voted, average rating 4.4
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Treatment of organic pathology and mental disorders
First of all, the cause of organic pathology should be established. Treatment tactics will depend on this.
In case of infectious pathology, antibiotics sensitive to the pathogen should be prescribed. For viral infections - antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. For hemorrhagic strokes, surgical removal of the hematoma is indicated, and for ischemic strokes, decongestant, vascular, nootropic, and anticoagulant therapy is indicated. For Parkinson's disease, specific therapy is prescribed - levodopa-containing drugs, amantadine, etc.
Correction of mental disorders can be medicinal and non-medicinal. The best effect is shown by a combination of both methods. Drug therapy includes the prescription of nootropic (piracetam) and cerebroprotective (citicoline) drugs, as well as tranquilizers (lorazepam, tofisopam) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine). To correct sleep disturbances, hypnotics (bromizoval, phenobarbital) are used.
Psychotherapy plays an important role in treatment. Hypnosis, auto-training, Gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, and art therapy have proven themselves well. This is especially important when treating children due to possible side effects of drug therapy.