Cerebral leukoencephalopathy is a pathology in which white matter is damaged, leading to dementia. For various reasons, there are several nosological forms. The occurrence of leukoencephalopathy is common for them.
The disease can be caused by:
- viruses;
- vascular abnormalities;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
Other names for the disease: encephalopathy, Binswanger disease. This pathology was first described at the end of the 19th century by the German psychiatrist Otto Binswanger, who named it after himself. From this article you will learn what it is, what are the causes of the disease, how it manifests itself, how it is diagnosed and treated.
Leukoencephalopathy - clinical forms, diagnosis
The medical term “leukoencephalopathy” is used to define a group of diseases accompanied by damage to the white matter and a number of deep structures of the brain.
Rapid progression leads to the formation of senile dementia. In children, there are vascular varieties, congenital forms with a long chronic course. The survival time for this type is longer compared to its multifocal counterpart.
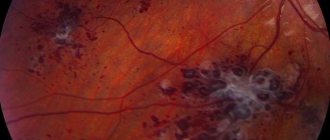
MR image of vascular leukoencephalopathy
To distinguish the pathology from a number of other neurodegenerative diseases with similar clinical symptoms, a classification according to ICD 10 has been developed, which clearly distinguishes the forms of the nosology.
Therapy
Leukoencephalopathy is an incurable disease. But be sure to go to the hospital to choose drug addiction treatment. The goal of therapy is to slow the progression of the disease and activate brain function.
Treatment of leukoencephalopathy is complex, symptomatic and etiotropic. In each case it is selected individually.
Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Vinpocetine, Actovegin, Trental);
- neurometabolic stimulants (Phesam, Pantocalcin, Lucetam, Cerebrolysin);
- angioprotectors (Stugeron, Curantil, Zilt);
- multivitamins, including B vitamins, retinol and tocopherol;
- adaptogens such as aloe extract, vit;
- glucocorticosteroids that help reduce inflammation (prednisolone, dexamethasone);
- antidepressants (fluoxetine);
- anticoagulants that reduce the risk of thrombosis (Heparin, Warfarin);
- if the disease is viral in nature, Zovirax, Cycloferon, Viferon are prescribed.
- physiotherapy;
- reflexology;
- acupuncture;
- breathing exercises;
- homeopathy;
- phytotherapy;
- massage of the collar area;
- manual therapy.
The difficulty of therapy is that many antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs do not cross the BBB and, therefore, do not target pathological lesions.
What is cerebral leukoencephalopathy
Damage to the white matter of the brain is caused in most cases by viruses. Vascular and discirculatory forms are caused by impaired blood supply to a certain area of the brain. Chronic ischemia causes irreversible changes.
Clinical symptoms of the disease more often occur when affected by papillomaviruses. The probability of nosology in patients with HIV is less than 6% according to brain MRI statistics in St. Petersburg.
Forms of vascular origin progress slowly. The chronic course of the disease is characterized by gradual irreversible tissue damage. Mild ischemia provokes the formation of small necrotic areas. Diffuse location leads to neurological disorders.
Forecast
In most cases, the manifestations of initial vascular encephalopathy can be stabilized; patients retain their ability to work and clear thinking for a long time. With a rapidly progressing form, the results of therapy are less noticeable; each stage takes only about 2 years. A relatively unfavorable life prognosis is observed with severe hyperglycemia, stroke, frequent hypertensive crises, and concomitant degenerative changes in cerebral tissue.
Take care of your health in a timely manner. Sign up for a consultation at the Leto clinic by phone. and learn how to treat encephalopathy before it causes irreparable damage to your health.
Types of leukoencephalopathy
The least dangerous form is focal. Formed by chronic inflammatory processes of vascular origin. Lack of microcirculation in a certain part of the brain provokes hypoxia, a lack of oxygen. The death of white matter zones takes several years to develop.
Morphological changes occur more aggressively in hypertension. An increase in intracranial pressure causes ruptures of small capillaries with areas of necrosis of the brain parenchyma. A type of medical language is called “discircular encephalopathy.” Appears in people over 55 years of age.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy has an aggressive course. People with pathology live no more than 5 years. Lethal outcomes are associated with extensive heart attacks and strokes.
Further actions
Although vascular disease cannot be completely cured, usually the doctor’s main efforts after diagnosing this disease are aimed at prolonging the patient’s life, as well as making symptomatic manifestations less obvious
This is why it is so important to see a doctor as soon as possible if symptoms occur. The prognosis in this case will depend solely on the prescribed therapy, as well as the type and stage of development of the disease
Treatment method
The goal of therapy in the presence of the disease is to stop the development of abnormalities in the functioning of the subcortical substance, delay death and alleviate symptoms.
To do this, it is important to identify the root cause and direct efforts to stop the development of this disease. This is a viral disease, so it is necessary to choose the right antibacterial therapy
The basis of treatment is fat-soluble drugs, since water-soluble ones cannot give the desired effect.
According to recent studies, the following were effective: dexamethasone; heparin. Cidofovir also helps improve brain function. This drug helps reduce depression of brain activity.
Drugs should be prescribed only in combination to ensure full results
It is important to pay attention to the presence of concomitant pathologies, as well as the characteristics of the body, in order to be able to choose the appropriate treatment in accordance with all these requirements. Otherwise, you may not only not achieve the desired result, but also provoke the development of additional other related problems and an even greater deterioration of the patient’s condition
Forecasts
With ideal treatment and a non-acute stage of the disease, the patient can live a maximum of 1 year after the first symptoms appear. If the pathology develops acutely, then death occurs within a month.
If present, you should carefully monitor your health to prevent deterioration of your immune system.
It is also important to pay attention to the fact that you need to treat these diseases as quickly and seriously as possible. If you put the underlying disease into remission, you will be able to prevent the development of this disease as well.
In any case, if the disease has already been diagnosed, then no treatment can help - therapy can only delay death and make the symptoms less obvious, but it is impossible to cure the patient.
Although the disease is incurable, with the right treatment, the patient will be able to live on. The main thing is to see a doctor as quickly as possible, since the disease usually develops rapidly
In addition, you need to pay attention to the background against which the disease can often develop. Therefore, in the presence of underlying pathologies, more attention should be paid to the state of health in order to initially prevent the occurrence of such a terrible disease
Classification of types of leukoencephalopathy according to ICD 10
A progressive type of vascular origin (Binswanger's disease) is coded with the symbols “I67.3”. Subcortical dementia with code “F01.2” has been excluded from the classification of diseases of the tenth revision.
Progressive multifocal (multifocal) leukoencephalopathy - “A81.2”. The group of the same name includes phenylketonuria, Alexander disease, and Canavan disease. Pathologies of category “IA” are distinguished for reasons, as they are of autoimmune origin - caused by tissue damage by immunoglobulins of the body’s own. Antibodies become aggressive when the structure of the membrane or the genetic information of the cell changes under the influence of viruses, chemical, and physical factors.
Let's look at the complete classification algorithm:
- Diseases of the circulatory system – “IX. 100-199";
- Cerebrovascular diseases “I60-69”;
- Other cerebrovascular diseases - “I67”;
- Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy – “I67.3”;
- Other specified vascular lesions – “I67.8”.
The international classification of the tenth revision is valid. When encoding the diagnosis, discirculatory encephalopathy, acute cerebrovascular insufficiency, NOS, and cerebral ischemia (chronic) are often encountered.
Clinical symptoms of small focal leukoencephalopathy
Focal symptoms have a subacute course. The initial stages of the disease are identified by neurologists:
- Visual impairment, speech impairment;
- Pathology of the innervation of the muscles of one half of the body;
- Epilepsy attacks;
- Headaches, dizziness;
- Ataxia, anopsia.
Differential diagnosis of focal types is carried out to distinguish them from changes in white matter in HIV and dementia. Spinal lesions occur without impairment of mental functions. Damage to white matter is accompanied by cognitive impairment.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
The cause of multifocal white matter damage is the JC virus, which leads to widespread damage to the nervous system. The disease develops against a background of reduced activity of the immune system. Antiretroviral treatment is expensive, so most people die.
Progressive encephalopathy quickly leads to the destruction of the myelin of most nerve cells. The changes are irreversible, the symptoms gradually increase.
About 80% of the country's population are carriers of human polyomavirus type 2, but encephalopathy does not occur. Only immunodeficiencies in AIDS create the possibility of rapid reproduction of the pathogen.
The immunity of older people cannot cope with the activity of polyomavirus (JC) after immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive therapy after treatment of cancer or organ transplant surgery.
In children, the appearance of pathology is observed after the start of therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Hodgkin's disease.
The 1C virus is transmitted by airborne droplets or fecal-oral routes. The majority of the population is asymptomatic. Provoking factors:
- HIV infection;
- Taking immunosuppressants;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Leukemia.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the only way to identify pathological foci within the white matter. After the appearance of visual impairment, dysarthria, hemiparesis, and aphasia, neurologists will be able to suggest a diagnosis. Final verification is possible only after a microscopic examination of brain biopsies - tissue sections taken from the site of injury.
Treatment
Therapy should be comprehensive, aimed at eliminating or mitigating the manifestations of the underlying disease, protecting cerebral structures from damage due to ischemia and hypoxia, improving tissue microcirculation and blood flow in the brain. The list of events includes:
- Etiotropic treatment. A special diet is prescribed. Insulin therapy is adjusted or hypoglycemic agents are selected. Antihypertensive medications and cholesterol-lowering medications are used.
- Improved hemodynamics. Includes taking phosphodiesterase inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, antiplatelet agents, alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists.
- Neuroprotective therapy. Derivatives of GABA and pyrrolidone, membrane-stabilizing drugs, vitamins, and drugs of animal origin (hydrolysates, hemodialysates) are effective.
In case of pronounced, rapidly increasing narrowing of the carotid artery, especially in combination with acute cerebrovascular accidents, surgery is indicated. It is possible to create an anastomosis with the formation of a bypass for blood flow or endarterectomy with expansion of the lumen of the vessel. In case of anomalies of the vertebral artery, reconstructive interventions are performed.
Discircular encephalopathy
The chronic progressive course of cerebrovascular pathology is accompanied by diffuse multifocal changes leading to hemiparesis, ischemic stroke, and multiple neuropsychological and neurological disorders.
The progression of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is associated with tissue degeneration and the accumulation of aggressive metabolites.
Before using neuroimaging methods, experts attributed most of the causes of cognitive disorders to dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Practice shows overdiagnosis of nosology cases. Nuclear magnetic resonance indicates only a 20% incidence of white matter lesions in elderly patients with vascular disease.
The main difference between the discircular type and a stroke is that it affects not large cerebral arteries, but small penetrating vessels, arterioles. Diffuse damage to small branches causes a number of morphological changes:
- Numerous heart attacks (lacunar);
- Diffuse destruction of white matter;
- Mixed form.
Early detection of any category prevents progression after proper supportive care is given.
Features of periventricular and residual leukoencephalopathy in children
Chronic lack of oxygen supply and prolonged ischemia of brain tissue leads to damage to subcortical structures, hemispheres, and the brain stem. Pathological foci are found deep in the gray matter and are accompanied by changes in subcortical fibers.
Periventricular encephalopathy is characterized by the predominant localization of pathological foci around the ventricles of the brain.
The residual appearance has congenital and acquired causes. The provoking factor in a child is traumatic injuries to the skull, inflammatory processes inside the skull. A separate type, encephalomyelopathy, occurs due to abnormalities in the structure of the vascular network of the brain.
Symptoms of residual encephalopathy in children:
- Cerebral paralysis;
- Oligophrenia;
- Epilepsy;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Restless sleep.
Practice shows the presence of a latent course of nosology in newborns weighing about four kilograms. Clinical symptoms appear after the onset of active blood supply. Cases of dementia in preschoolers and schoolchildren are associated with injuries to the skull.
How long do people live with encephalopathy?
Life expectancy is determined by the clinical form of the disease, the rate of progression, and individual changes in the human body.
Progressive multifocal encephalopathy is accompanied by death 1-3 years after detection. Maintenance therapy increases survival.
Varieties of vascular origin have chronic progression. People with this variety, with proper treatment, live for decades. Reduces the duration of hypertension, pronounced ischemic foci of the brain structure, hemorrhages inside the brain.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of leukoencephalopathy.
To reduce the risk of developing this pathology, the following rules should be followed:
- Strengthen your immune system by hardening yourself and taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- normalize your weight;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- regularly go out into fresh air;
- give up drugs and alcohol;
- quit smoking;
- Avoid casual sex;
- Use a condom for casual sex;
- Follow a balanced diet, which should be dominated by fruits and vegetables;
- Learn to cope with stress;
- and get enough rest;
- Avoid excessive physical activity;
- For diabetes, atherosclerosis and hypertension, you should take medications prescribed by your doctor to compensate for the disease.
All these actions minimize the risk of developing leukoencephalopathy. If you become ill, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible and begin treatment that will help prolong your life.