What is cavernous angioma?
Cavernous angioma is a collection of abnormal vessels that is located in the brain or spinal cord and, in some cases, subcutaneously.
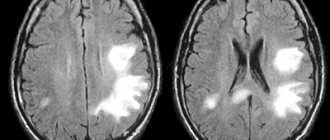
In various literature sources, this disease is also called “cavernous hemangioma”, “cerebral cavernous malformation”, “cavernoma”. Its dimensions vary from microscopic to several centimeters in diameter. It consists of many cavities (cavities) filled with blood and lined with a special type of cells called endothelial cells. Depending on the location in the brain, it can cause epilepsy, be a source of hemorrhages and cause severe headaches. Angioma of the left parietal lobe.
Morbidity
Cavernous angiomas occur in approximately 1 in 100-200 people. In most cases, the first symptoms appear after 30 years of age. In 20% of cases it is a genetically inherited disease, and several tumors are often detected at once.
Causes of angioma and risk factors
The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, with a probability of 50%. According to recent studies, at least three genes are associated with the hereditary form of the disease. A single formation can be detected at the birth of a child or develop during his later life. If parents and relatives did not suffer from this disease, then the angioma is called sporadic. The risk of developing such a tumor is the same for all people.
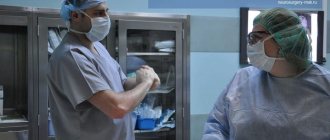
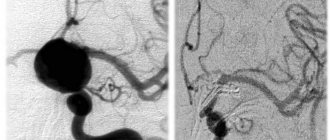
Angioma of the left parietal lobe during surgical treatment. Image: neurosurgery.wustl.edu
Symptoms of angioma
In most cases, cerebral angiomas are characterized by an asymptomatic course, but sometimes they lead to epileptic (convulsive) seizures. The type of seizure depends on the location of the tumor. Also, the presence of a mass in the brain can lead to neurological deficits, such as weakness of the upper or lower extremities, problems with vision, balance, attention and memory. Symptoms can wax and wane in waves, which is associated with repeated hemorrhages and an increase in the size of the angioma and reabsorption (absorption) of blood.
Angiomas are characterized by various types of hemorrhages:
- Slow, without changing size, since the rate of bleeding is approximately equal to the rate of blood reabsorption by the body.
- Profuse, with an increase in size and compression of the surrounding tissue of the brain or spinal cord.
- A leak in which blood enters the tissue of the brain or spinal cord through a defect in the wall of the angioma, ultimately destroying it.
What is cerebral venous angioma
The disease is not aggressive, but its presence should not be ignored. The interweaving of blood vessels are fused balls that expand over time, provoking the development of inflammatory processes in the brain.
The more the brain is affected, the greater the health risk caused by the presence of the formation. This pathology is dangerous for the body due to the rapid growth of angioma, which, affecting the tissues of nearby organs, leads to disruptions in the functioning of the entire body.
It is the brain that is responsible for the quality functioning of all systems. Pathological changes occur and, if not treated in a timely manner, destruction occurs. A patient with a tumor is at high risk of cerebral hemorrhage, which can be fatal.
At the first symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately. Therapy in the early stages of tumor development has a favorable outcome. At an advanced stage of the disease, drug and surgical interventions will not give positive results.
Tumor formation and its types
With angioma, the cells of the vascular body divide, increasing the growth of venous tissue. A benign process occurs in vascular and lymphoid tissues:
- On the inside;
- On the outer surface;
- Simultaneously in both types of epithelium.
The neoplasm is divided by type into two classifications:
- In appearance;
- By source of education.
Division of neoplasms by appearance
- Flattened - a spot of varying sizes with a reddish tint. The main place of distribution is in the neck and face.
- Lumpy - an irregularly shaped speck of dark color. Affects the epidermis and mucous membranes. Inherent in childhood, resolves after eight years.
- Cavernous, or deep, type - growth is directed deep into the layers of the skin. In superficial places, the color varies from reddish to flesh-colored. The preferred location is internal organs.
Venous angioma
Division by origin
- Normal – the tissue of the vascular channels for blood flow grows.
- Capillary, vascular - formed by the plexus of capillary vessels rising above the dermis layer.
- Pustular or inflamed - mainly formed on the mucous membrane of the inner side of the cheek, tongue or gum.
- Lymphangiomas.
- Glomangiomas - formed from arterioles, usually under the nails of the upper and lower extremities.
- Telangiectasia - small blood vessels on the skin become tortuous, tangled, and red. They are clearly visible through the skin.
- Cobweb-like - looks like a cobweb. The color depends on the pressure in the circulatory system.
- Bacterial – bacterial infection caused by microorganisms of a certain type.
- The cavernous is the main place of formation of a blood vessel; it expands and does not narrow, slowing down the flow of blood. The appearance of new cells increases the risk of bleeding due to abnormal connection with the rest. The main localization is internal organs.
Kinds
Venous angioma is an enlarged venous column of vessels collected in a tangle. Depending on the location of the formations, the disease is divided into several types.
Frontal lobe angioma
She is responsible for initiative, correct decision-making, responsibility and showing interest. Therefore, when education is localized in this area, the character of a person changes greatly.
He becomes apathetic, a change in self-esteem occurs, speech is impaired, and inadequacy appears in his behavior and actions.
It is difficult for a person to think logically; he often commits unconscious actions. The patient cannot take responsibility and is unable to independently solve various problems.
Performance decreases, the emotional state is unstable, and over time the person suffers from depression. The patient does not feel cold or heat when touched.
Cerebellar angioma
If there is a tumor in this area of the brain, functional disturbances occur in the body. The patient's muscle movements are not coordinated, he cannot perform smooth movements, so all actions are abrupt. A person’s motor ability is greatly slowed down, all actions are performed in the form of jerks.
There are disturbances in speech, there are serious problems when writing words and sentences. Breathing is impaired, resulting in problems with the respiratory system and skeletal muscles.
It is impossible to cure the disease using medications. With this form of angioma, surgical intervention is indicated.
Angioma of the left hemisphere
There is inconsistency in the work of the muscles of the arms and legs. The patient has speech impairment and changes in gait.
Cerebellar venous angioma
Brain angioma is a benign neoplasm consisting of a plexus of small blood vessels or lymphatic spaces.
Taste preferences change completely. Vision decreases, nystagmus of the extraocular muscles is observed.
Due to impaired blood flow, a person is susceptible to epileptic seizures and convulsions. At an advanced stage of the disease, partial paralysis may occur.
Angioma of the right hemisphere
With this type of disease, the patient experiences a movement disorder. It becomes slow and sharp. Speech becomes slow, writing style changes. A person is bothered by tremors of the arms and legs.
Angioma of the parietal lobe
The patient's coordination of movements is impaired, tactile sensations and pain threshold change, and speech abilities may deteriorate.
Symptoms of the disease
The tumor can occur in any part of the brain. There are venous angioma of the right hemisphere of the cerebellum, angioma of the temporal lobe, hemispheres, parietal and other types.
For a long time, this problem may not make itself felt. But as the disease progresses, the symptoms also increase. When a tumor occurs in the brain, the first thing the patient begins to feel is pain and dizziness. He may also have complaints about:
- speech dysfunction;
- nausea and vomiting;
- poor coordination of movements and frequent fainting;
- vision problems;
- change in taste preferences;
- convulsions and partial paralysis;
- noise and heaviness in the head;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- decrease in intellectual abilities.
As a result of the development of a tumor in the brain, the functions of all sensory organs deteriorate. Against this background, patients often develop depression, which further aggravates the problem.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Features of brain sarcoma
The disease can manifest itself in different ways depending on where the formation is located:
- Frontal lobe. At the same time, a person’s performance deteriorates and depression develops. The patient becomes emotionally unstable, feels apathy, does not control his speech and behavior, coordination of movements worsens, and epileptic attacks occur.
- Parietal lobe. The functioning of the digestive system is disrupted, the patient does not feel pain, cold, heat, or touch. Speech function and coordination of movements also suffer.
- Cerebellar zone. Blood circulation and heart function are disrupted, breathing difficulties arise, which lead to diseases of the respiratory system, and problems arise with skeletal muscles.
- Right hemisphere. A patient with such a problem speaks rhythmically, drawing out his words, his handwriting may change, all movements are disrupted, and there is no smoothness.
- Left hemisphere. The tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients, and the patient is partially or completely paralyzed.
Angiomas tend to gradually increase in size. Because of this, the tumor puts pressure on the brain matter and can cause bleeding in the brain, which leads to the death of the patient.
- Venous discirculation of the brain
The following can lead to hemorrhage:
- large tumor size;
- head injuries;
- significant pressure on the medulla;
- lack of nutrients and oxygen in the brain;
- increased pressure in the arteries;
- sudden tilt or turn of the head;
- excessive physical activity;
- emotional shocks, stress;
- generic activity.
Therefore, it is important to promptly diagnose angioma and carry out treatment.
Symptoms
In addition to the differences between different types of angiomas, there are common symptoms that are characteristic of all types of cerebral venous angioma:
- frequent fainting;
- dizziness;
- paralysis;
- noise in the head;
- tremor of hands and feet;
- disorders ;
- headache ;
- imbalance and coordination of movements ;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- epilepsy attacks
- problems ;
- convulsions;
- disorders ;
- blurred vision;
- decreased mental activity;
- noise in the head;
- change in taste preferences;
- impairment ;
- increased fatigue;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of ability to work.
General symptoms of the disease
Newly formed cells exert pressure on neighboring ones.
The initial symptom of the disease is mild headaches and slight dizziness. The characteristic pathology begins to manifest itself as follows:
- Headaches of various types;
- Frequent dizziness accompanied by nausea;
- Epilepsy attacks;
- Paralysis of individual areas;
- Fainting;
- The vestibular apparatus malfunctions;
- Speech disruptions;
- Convulsive twitching;
- Distortion of information reading by taste buds;
- Changes in visual perception;
- Decreased mental activity;
- Noise hallucinations in the head;
- Disease of the venous system.
Diagnostics
To perform an accurate analysis, a specialist carries out diagnostic measures.
First of all, laboratory tests are prescribed. The patient must undergo a general and biochemical blood test, as well as a general and biochemical urine test.
If the norm deviates, the patient is then prescribed an ultrasound examination to confirm the diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging will determine the presence of formations, identify the location and size of the angioma.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
It is also possible to perform a computed tomography, angiography or x-ray. Only after all diagnostic procedures have been completed can treatment be prescribed.
How to make a diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by neurosurgeons, phlebologists, dermatologists, oncologists and other highly specialized specialists. They prescribe studies that will determine the cause of the problem and the location of the tumor. The presence of a problem can be confirmed using instrumental studies:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- angiography;
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination;
- spinal puncture.
To exclude anomalies similar to venous angioma, differential diagnosis is prescribed.
- Venous discirculation: what is it, brain damage
Treatment
Treatment of education includes taking medications, using traditional medicine, and in advanced cases, surgery.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Drug treatment
It is impossible to cure venous angioma by taking medications. This type of therapy is used only to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Drug therapy is prescribed if there is no threat of hemorrhage. Vascular medications are indicated to improve blood circulation.
Sedatives occupy an important place.
All drugs will only alleviate the patient’s condition, but will not contribute to recovery. A benign formation can only be removed surgically.
Surgical intervention
There are several methods of surgical treatment of the disease.
Treatment of angioma
Angioma is a group of benign neoplasms in the formation of which blood and lymphatic vessels take part.
In severe cases of the disease, surgical removal of the accumulation of blood vessels is performed. A plastic spiral is inserted into the patient's lumen.
If the sclerotherapy method is chosen, a special substance is injected using a special catheter, which clogs the lumens of the vascular bundle and promotes scarring of the tumor. The operation is painful and lengthy.
It is possible to apply a superficial radiation beam to the tumor using a gamma knife. With its help, blood vessels are blocked. Education stops growing and developing, no longer presenting a danger to human life and health.
Liquid embolism can be injected into the collection of vessels, which easily penetrates into the smallest cavities and prevents the growth of angioma. Over time, the area where the tumor grew is replaced by connective tissue.
Diet
Diet plays a big role in treating the disease. The patient should exclude fatty and fried foods from his diet. Minimize the consumption of salt and sugar, coffee, chocolate and baked goods.
Causes of angiomas
Angiomas are minor skin neoplasms consisting of epithelial tissue and blood vessels.
Avoid eating butter, pork, full-fat milk, liver and kidneys. It is necessary to eat vegetables and fruits, fish and seafood, cereals, dried fruits, and herbs.
Brain angioma is a serious disease. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate.
Can it develop into cancer?
Venous angioma of the brain is a benign formation. Therefore, it does not degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
Over time, it can lead to negative consequences and threaten human life. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner for diagnosis and adequate treatment.
If the tumor does not manifest itself in any way, the person does not have behavioral disturbances or deterioration in health, you can live with this type of disease until old age. But in most cases, when diagnosing a tumor, surgical intervention is indicated.
Forecast
An intact angioma may not be detected throughout life and may not cause serious trouble to the patient.
But if a hemorrhagic stroke or vasospasm occurs, the person may become disabled for life or die. Often, rupture of the vascular bundle leads to irreversible processes in brain activity.
Depending on the patient’s age, his general health, and the presence of vascular diseases, a prognosis for the course of the disease is made. A properly prescribed treatment regimen and timely surgical intervention will allow the patient to lead a healthy and fulfilling life for a long time.
Prevention
There are no preventive measures to prevent the development of cerebral venous angioma. Once diagnosed, a person should monitor their health carefully and regularly.
It is important to constantly monitor your blood pressure, not self-medicate and take medications only under the supervision of a doctor. Taking medications without consultation with a specialist can cause hemorrhage.
Women should take oral contraceptives with caution. If you have education, you should limit physical activity. It is important to follow a diet, get proper rest, give up bad habits and monitor your weight.
Compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, a healthy lifestyle, and timely removal of the angioma will allow a person to feel healthy and lead a full life.