Do you need an ultrasound of the veins and arteries of the upper extremities?
Like other research methods, ultrasound of the veins and arteries of the upper extremities has indications for use. The procedure is necessary if you have certain symptoms or conditions:
- swelling and soreness of the arm muscles;
- cramps, numbness, tingling, decreased sensitivity in the hands;
- pallor or cyanosis of the skin of the hands;
- visually noticeable “bumps” in the direction of the veins;
- feeling of heaviness, spasms, “cold hands” effect;
- rapid fatigue and weakness in the hands, even with light load.
Ultrasound is necessary if there is a suspicion of thrombosis and thrombophlebitis. Research is used for Raynaud's disease, autoimmune diseases such as scleroderma and connective tissue diseases. In this case, an ultrasound is needed to assess which area is affected and then choose the right treatment.
Vessel location, anatomy
The radial artery runs on the inside of the elbow. She reaches for the fingers, deviating slightly along the way to the area of the outer surface of the hand. The pronator teres, to which it is attached by connective tissue, is an elastic and elastic muscle layer.
It is the shortest and thickest muscle in the anatomical structure of the forearm.
The vessel approaches the medial edge of the pronator teres and extends further, occupying a position between this muscle fiber, the preradialis muscle and the adductor structure of the carpal joint.
The further path of the vessel lies near the styloid process.
The radial artery is located 10-30 mm distal to the slit incision of the shoulder joint. In the area of the styloid process, the bloodstream shifts to the back surface of the arm.
Here the vessel lies in the gap separating the tendon of the thumb from the short extensor muscle.
This morphological complex ensures the functionality and mobility of the carpal bones and joint capsules. The radial artery supplies tissue cells with oxygen, minerals and other nutrients as it moves.
Next, the vessel runs in the deep layers of the elongated extensor pollicis tendon and moves to the dorsum of the wrist. Here it changes the direction of blood flow and passes through the adductor muscles to the facial plane of the palm.
In the area of the interdigital membrane, the artery smoothly bends and forms an arched configuration, saturating the tissues, muscles and tendons located there with blood. As it moves along the hand, multiple branches extend from the vessel.
Morphological complex of the radial artery:
| Branch | Location and anatomy |
| Reciprocal radial vessel | It begins in the area of the radial cavity of the forearm. Near the lateral epicondyle, the bed anastomoses (connects) with the deep arterial canal of the shoulder joint. |
| Carpal palmar branch | The section of the radial artery that forms the palmar blood supply. It starts from the pronator quadratus and extends towards the elbow joint. |
| Superficial palmar capillary | A small vessel extending from the styloid process down to the joint of the thumb. |
| Dorsal carpal branch | Located in the area of the back of the wrist. |
| Dorsal metacarpal beds | 4 small branches. Anatomically paired, in rare cases separated. They lie between the finger tendons. The proximal and middle phalanges supply blood. |
| Thumb branch | The main blood vessel of this area. Divided into 2 parts. |
| Arterial process of the index finger | Directed along the radius of the corresponding finger. Saturates all its tissues, muscles and tendons with blood. |
In the forearm area, the radial artery can be detected by ordinary palpation. Here, on both sides, there are large venous channels that carry blood to the heart. The vessel is adjacent to the radius, which makes it possible, if the walls are damaged, to quickly press the bed against the hard tissues and stop the bleeding.
What the study shows
During Doppler ultrasound, the diagnostician evaluates the speed and nature of blood flow. Regardless of what disease the specialist suspects, the study helps to accurately establish the nature, location and severity of the problem. To do this, during ultrasound examination of the vessels of the upper extremities:
- The condition of the vascular walls is assessed: are there any thinning, thickening and other changes.
- The width of the lumen of the vessels is determined (whether there are any narrowings or dilations), and the level of patency of the veins is also assessed.
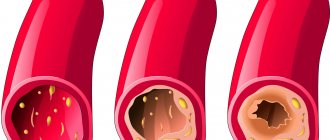
- The presence of proliferation of granulomatous tissue, neoplasms, blood clots, places of compression of blood vessels, and atherosclerotic plaques is checked.
Thus, Doppler ultrasound allows you to make a complete assessment of venous and arterial blood flow, identify disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels, narrowing and deterioration of blood supply to tissues. As a result, the following problems can be detected:
- thrombosis of the veins of the shoulder and arm (size and level of mobility of blood clots);
- inflammation (thrombophlebitis) of the veins;
- angiodysplasia (increase in the number of subcutaneous vessels);
- atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries;
- neoplasms or enlarged lymph nodes near the vessel;
- tissue proliferation in the lumen of blood vessels;
- consequences of arm injuries (fractures, muscle ruptures) affecting the blood vessels.
Functions
The vessel transports the oxygen-enriched main biological fluid of the body from the heart to the tissues of the upper extremities. In some areas, the speed of blood movement reaches 25 cm/s. The radial network of the arms is an integral part of the SSS. Blood circulates through it continuously.
The functioning of the upper limbs and the entire organism as a whole depends on the ease of passage of enriched biological fluid through the arterial bed. The vessel is involved in the systemic circulation. The full physiological circulation cycle takes 23-25 seconds.
The radial artery is located in both arms and has a high intensity of blood flow. The biological fluid in it is of a lighter shade than in the veins due to the significant concentration of oxygen atoms. The morphological complex of the vessel covers all anatomical structures of the upper extremities - from the shoulder joint to the fingers.
Numerous branches are responsible for feeding a specific area. The return duct supplies oxygenated blood to the elbow joint area. The functions of the palmar-carpal branch are the transport of biological fluid and gas exchange in the tissues of the area.
The superficial palmar segment of the radial artery delivers blood to muscle fibers and skin. The dorsal carpal part of the network takes part in providing oxygen and nutrients to the back of the hand. Its functions include maintaining gas exchange in this area of the upper extremities.
The small dorsal metacarpal branches of the radial artery are intended to supply the outer part of the proximal and middle phalanges.
Main functions of the radial artery:
- Regulatory. The expansion and contraction of the diameter of the bloodstream varies the blood pressure in the vessels.
- Exchange. The blood carried by the artery has a relatively stable chemical composition. Active gas exchange occurs in it. Oxygen atoms attach to hemoglobin, and carbon dioxide molecules accumulated in the tissues are removed.
- Protective. The superficial branches of the radiator participate in the heat exchange process, preventing critical overheating of tissues. They reduce the temperature by reflexively expanding the lumen and releasing excess heat through the skin into the external space.
- Immune. The leukocytes, antibodies and immunoglobulins contained in the blood circulating through the radial artery destroy bacterial and viral pathogens.
- Trophic. The artery supports the exchange of metabolic products.
Where can you measure the pulse on the radial artery?
All functions are carried out under the influence of internal and external factors, physiological and chemical changes. Under the influence of pathological processes they can weaken.
How to prepare properly
Dopplerography of the vessels of the upper extremities is carried out with the simplest preparation. The day before the study, you need to give up tonic drinks: coffee, tea, energy drinks. It is important to exclude foods and medications that affect blood flow. The doctor must be notified of all medications taken so that he can adjust the dosage regimen or take into account the possible influence of the medications. It is necessary to give up alcohol 2-3 days in advance, and on the day of the ultrasound examination, do not load the upper limbs.
Lab tests
The radial artery is located in the upper extremities and is responsible for their blood supply. In case of vascular diseases, it is necessary, along with hardware diagnostics, to do some tests. They donate blood to determine the concentration of triglycerides - ester compounds of 3-atomic alcohol.
This is the main form of lipids that provokes atherosclerotic changes. Another important laboratory test for radial artery diseases is a complete blood test for cholesterol. Some of this substance enters the body exogenously - along with food.
The main volume of cholesterol that clogs the blood lumen is synthesized by hepatocytes. It is an important component of cell membranes. It serves as a precursor to steroid-type hormonal compounds and bile acid.
The level of blood saturation with cholesterol and triglycerides is a leading indicator of lipid metabolism in the body. Therefore, in case of vascular diseases, such tests are prescribed first. Donate blood to check the level of antibodies to endothelium in the serum.
Normally they are not fixed. The detection of such fragments in biological material indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process. Antibodies damage endothelial cells through complement-dependent cytolysis. This leads to deformation of the walls and an increase in their permeability.
Online registration for ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities
Clinic Dr. AkNer has modern equipment for conducting informative ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes. Upon completion, the diagnostician issues a written report with a full assessment of the vascular system of the hands and indicating the detected abnormalities. You can use the results obtained repeatedly, taking them with you to consultations with the necessary specialists.
The price of ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities is 4000 rubles. The price includes the research itself, decoding and delivery of results. Additionally, you will receive a comment from an experienced ultrasound diagnostic doctor. To have an ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities, sign up for the procedure at a convenient time. We invite you to use the online registration form or contact us at our contact number. Contact us and we will answer your questions!
June 07, 2021
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor, candidate of medical sciences, Evseeva Ekaterina Leonidovna.
Instrumental diagnostics
The examination is carried out using hardware and laboratory methods. An X-ray of the vessel is performed using radiation angiology. Diseases of the bloodstream are diagnosed using radionuclide, magnetic resonance and ultrasound equipment. Sometimes different methods are combined.
This allows you to compare the data obtained and accurately establish the pathological picture. Different diagnostic options complement each other. Radiation examination provides a conjugate picture of the morphological structure of the vessel, destructive changes in it and obtaining hemodynamic characteristics.
Surgical interventions – endovascular and other measures – are performed under the control of this technology. On conventional radiographic images, the radial artery is poorly visible. Therefore, the combination of sonography (ultrasound method) with Doppler mapping has acquired important diagnostic significance.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging provide important clinical information. The entire network of the radial artery is clearly visible on the sonogram. The image allows you to get an idea of the pathological picture and destructive changes.
This diagnostic method determines:
- shape of the blood channel;
- degree of atherosclerotic and aneurysmal changes;
- wall thickness;
- the size of the lumen.
Sonographic examination determines the size of the aneurysm. This has important diagnostic value, since with a diameter greater than 4 cm there is a high risk of rupture.
Urgent surgical intervention is required. Similar data can be obtained from CT and MRI, which are used to examine the branches of the radial artery. The smallest peripheral vessels are accessible to the magnetic resonance method when using a contrast agent.