Atherosclerotic plaques are the direct cause of the development of such an insidious and dangerous disease as atherosclerosis. The pathology is characterized by changes in the condition of the vessels, which become fragile, lose elasticity, their lumen narrows, and neighboring organs do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
The formation of plaques can begin at a fairly young age, but pronounced signs of atherosclerosis appear more often after a person reaches 50 years of age. Today we will talk about why deposits form on the walls of blood vessels, what they are, and methods for timely diagnosis and treatment.
What it is
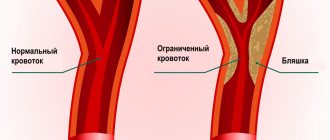
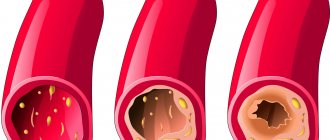
First, it is necessary to explain what atherosclerotic plaques are. The development of atherosclerosis begins with cholesterol deposits on the walls of the arteries, aorta, large and small capillaries, which can be located in any part of the body.
To ensure that all internal organs and the brain are fully supplied with blood, the inside of the vessels is lined with a special layer - the endothelium. With excessive accumulation of lipid substances inside the capillary, its lumen becomes narrower, the endothelium suffers from the introduction of “bad” cholesterol. The walls of the arteries become rougher and tougher.
As the disease progresses, the calcified growths increase in volume and harden, taking on the shape of tubercles, which is why the lumen of the artery may be completely blocked. Plaque formation typically occurs in all areas of the body, and the resulting bumps contain calcium and foreign substances.
Composition and types of plaques
If a person’s blood vessels are soft, elastic, and their tone is normal, then special substances prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. These are wall enzymes designed to dissolve fats that accumulate inside the capillaries. The beginning of the process of formation of pathological tubercles on the walls of arteries involves a combination of negative conditions.
This may be due to poor nutrition with excess animal fats in the diet, damage to the walls of capillaries, which lose their elasticity and become loose. The formation of plaques in blood vessels takes more than one year - first there is an active deposition of cholesterol, only then it becomes overgrown with connective tissue fibers and turns into a pronounced hard tubercle.
A plaque is essentially a core surrounded by a shell consisting of cholesterol and esters. And the environment is a mixture of fats and macrophages, and the fats gradually destroy the macrophages and enter directly into the nucleus. The part of the plaque that protrudes into the lumen of the vessel is a fibrous membrane; it consists of elastin and collagen. The content of these substances determines whether the plaque will rupture or remain intact.
At the stage when the plaque has just begun to form, its structure is semi-liquid, so a particle of the growth can come off, move along the inside of the capillary and completely clog it. At this time, the formations can still resolve with adequate treatment, which is why experts advise paying attention to the primary symptoms of atherosclerosis rather than waiting for dangerous complications.
As the disease progresses, the growth becomes overgrown with calcium, acquiring an increasingly dense structure. A slowly growing calcified plaque does not allow blood to fully flow to the internal organs and the brain (depending on the location), which causes a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients in the tissues.
If we explain the mechanism of formation of plaques in blood vessels, then the process consists of certain stages:
- Deposition of lipids on the vascular wall.
- Connection to the process of leukocytes, which contribute to the development of an active inflammatory process.
- Penetration of monocytes into the vascular wall with the further release of macrophages with a porous structure.
- The beginning of pathological changes in the state of the internal arterial layer.
- Adhesion of platelets to that part of the wall where the process of damage has already begun.
- The release of protective mediators and an increase in the number of cells - this is the reaction of the immune system to what is happening.
- The production of collagen and elastin, the penetration of their particles into the inner layer (endothelium) lining the vessel.
- Hardening of the plaque and its increase in volume.
Plaques are divided into stable and unstable, and the types depend on the volume of formation and its composition. With a complicated form of atherosclerosis, heterogeneous plaques appear. Unstable formations contain most of the fat, their structure is loose, so such plaques are more likely to rupture against the background of the formation of blood clots and complete blockage of the artery.
Stable ones break much less often, since they consist of collagen fibers, which means they have a more elastic structure. They take much longer to form, so they are easier to dissolve at the initial stage of the disease. Growths in which calcium deposits are high are less dangerous than those with a liquid structure; they do not appear, but it is no longer possible to completely dissolve them.
Atherosclerotic formations can have various manifestations:
- do not manifest themselves in any way, since they increase in volume for many years, do not leave the vascular walls and do not interfere with normal blood flow;
- slowly progress, releasing into the lumen of the artery until it is partially blocked;
- provoke a rupture and cause blood clotting from inside the capillary - if this occurs in the aorta or brain tissue, a heart attack or stroke is inevitable.
Heterogeneous plaques have a loose structure, they have many depressions and tubercles, which is why such formations are often ulcerated.
Possible complications
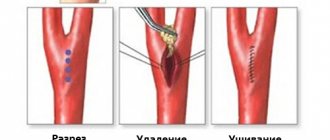
Eversion carotid endarterectomy in our clinic is a safe intervention. We noted serious complications in the postoperative period only in 0.5% of patients. The following complications sometimes occur after surgery:
- Stroke during or after surgery develops for various reasons. Most often, this may be thrombosis of the reconstructed artery or embolism (transfer of a piece of plaque) to the cerebral vessels. The patient should be closely monitored in the early postoperative period to notice neurological problems as early as possible and take action. The incidence of these complications in our clinic was 0.5%.
- Bleeding from the surgical area is potentially life-threatening, as the hematoma can compress the trachea and cause suffocation. Installing drainage allows you to suspect this complication in time and take action.
- Damage to the hypoglossal or recurrent nerve is a consequence of inaccurate technique during surgery. This complication is manifested by loss of voice or deviation of the tongue and difficulty eating and speaking. We have not encountered this in our practice.
Causes of pathological deposits in blood vessels
The formation of cholesterol accumulations in loans can take years, and the patient does not even realize that he is sick, attributing the symptoms to other reasons (fatigue, stress, overload of the body). The main factors that provoke deposits of harmful substances in the capillaries are considered to be poor nutrition and heredity.
But there are other reasons why atherosclerotic disease develops:
- Age category - until the age of 50, signs of the disease appear partially, while the body has the ability to independently cleanse itself of harmful substances and maintain vascular tone. After 50 years, capillaries become weak and brittle, and cholesterol tubercles significantly damage their condition, leading to clear manifestations of atherosclerosis.
- Gender – it has been proven that women develop atherosclerosis several times less often than men due to the support of normal vascular tone by the hormone estrogen. But after 50 years, the chances of getting sick in both sexes become equal, since women begin menopause, and the capillaries become less elastic and undergo pathological changes.
- Heredity - scientists have found that lipid metabolism disorders in the body are the result of gene pathologies transmitted from generation to generation. Therefore, one should not be surprised at a person who suffers from atherosclerosis if several people in his family suffered from this pathology.
- A high amount of cholesterol in the blood plasma - this factor leads to the accumulation of a “bad” type of substance on the walls of blood vessels, their narrowing and cessation of normal blood circulation to organs and tissues.
- High blood pressure – in people who have problems with blood pressure surges, cholesterol deposits occur much faster. The blood vessels are already narrowed due to constant spasm, and lipid metabolism disorders only aggravate the situation.
- Addictions - as a result of the constant entry into the blood of pathogenic substances (carcinogens, mutagens, resins, ethyl alcohol), the vessels narrow and cannot independently control the tone. And the accumulation of cholesterol further complicates the situation, causing atherosclerosis with stenosis of the arteries.
- Concomitant diseases - according to doctors, in patients with diabetes and disruptions in the endocrine system, the accumulation of cholesterol in the blood occurs faster. And atherosclerosis itself manifests itself brighter and more aggressively.
Excess body weight is another reason why atherosclerosis progresses rapidly.
Obese people almost always have problems with blood pressure, they move little and eat poorly. It turns out to be a vicious circle, the way out of which is to reduce body weight, follow a diet, physical activity and timely initiation of treatment for atherosclerosis. Obese patients should take therapeutic measures immediately, while it is possible to reduce the density and volume of plaques.
And it has also been proven that being in a constant state of stress or depression negatively affects the structure of arteries throughout the body. In a dangerous situation, the adrenal cortex secretes a large amount of hormones that provoke vasospasm. Therefore, signs of atherosclerosis, if any, will appear more aggressively in people with an unstable emotional background.
Case study: atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries
A 57-year-old man began to complain of slight dizziness and hearing loss.
Those close to him told him that his gait had become uneven. A week ago, when he suddenly turned his head, he lost his sense of balance and fell, after which the patient came to the doctor. Upon questioning, it turned out that he suffers from hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Takes prescribed medications irregularly. When measuring blood pressure, the tonometer showed a value of 165/95 mm Hg. Art. Suspecting atherosclerotic lesions of the vertebral arteries, I ordered a duplex scan, during which stenosis of the right VA up to 65% and narrowing of the left VA up to 40% were detected. I referred the patient for surgical treatment.
Endarterectomy of the right VA was performed. The patient was also prescribed drug therapy - Rosuvastatin, Acetylsalicylic acid, Perindopril, Metformin. The patient noted a significant improvement - the dizziness stopped and a sense of balance returned.
How the problem manifests itself
If the body is affected by atherosclerosis, then the accumulation of cholesterol will be observed in almost all arteries and vessels. But the manifestations are more often local and depend on the location of the stenotic artery - such symptoms are shown in the photo and posted on websites dedicated to atherosclerosis.
Since many years may pass from the onset of the development of pathology to the appearance of severe symptoms, you need to be aware of the primary signs of atherosclerosis: the appearance of weakness that is not associated with excessive stress and fatigue, a feeling as if “goosebumps are running along the leg, arm or thoracic region,” sudden in a stupor, a feeling of numbness, disturbing on one side of the body - in the arm or leg.
All manifestations of the presence of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels come down to a slowdown in blood flow in the affected area, lack of nutrients and oxygen
Visual impairment also occurs in one eye, the second, as a rule, sees well, and problems with speech and memory - the person becomes forgetful, confuses dates and events, and begins to speak inarticulately. If the formations constantly increase in volume and interfere with the full blood supply to the organ, then pain will be present in this part of the body.
The skin becomes numb, and a constant tingling sensation appears. The symptoms listed above are observed if the plaque has disintegrated and its particles move along the bloodstream. Here, the risk of cerebral hemorrhage and heart attack increases significantly.
Plaques in the thoracic aorta
The main symptoms of cholesterol deposits in the thoracic region are sharp nagging pains near the heart. They radiate towards the neck, shoulder blade, shoulder girdle and upper limb, and the discomfort cannot be relieved by taking Nitroglycerin.
Severe symptoms appear: pain in the head, pallor or bluishness of the skin on the face, decreased performance, a constant feeling of fatigue, problems with reproducing recent events, forgetfulness and inattention, convulsions, fainting or clouding of consciousness. During the period of exacerbation of thoracic atherosclerosis, the patient's blood pressure rises, he complains of shortness of breath and other symptoms of ischemia.
Damage to the blood vessels of the head
If the vessels of the brain are affected by atherosclerosis, then we are talking about the deposition of cholesterol plaques in the CCA (common carotid artery), subclavian and the mouth of the ICA (internal carotid artery). They nourish the brain tissue, therefore, the disease manifests itself in a number of negative disorders:
- decline in performance;
- fatigue and constant fatigue;
- memory losses;
- tendency to depression;
- the appearance of unreasonable fears and worsening anxiety;
- disruptions in visual and auditory functions;
- bleeding in the brain with typical consequences - failure of one of the body parts, neurological disorders, loss of speech or motor function.
Blockage of the paravertebral, subclavian and carotid arteries appears gradually. In the initial stages, a person becomes inattentive, gets tired quickly, and cannot cope with the usual amount of work. Next comes a depressive state, which is not justified.
In the last stages of the disease, when the brain is practically not supplied with oxygen and blood, the patient is lost in space, does not remember events, and acquires signs of dementia. The case may result in a stroke with all the ensuing consequences, including disability or death.
In the peritoneal area
When the abdominal artery is blocked, atherosclerosis manifests itself in a number of symptoms:
- lack of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- aching pain around the navel;
- constant bloating, problems with bowel movements;
- feeling of coldness and numbness in the legs;
- swelling of the tissues of the lower extremities.
In the later stages, intermittent claudication occurs - a person’s leg seems to fail, and as a result, he or she limps when moving.
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
The disease remains asymptomatic for many years. In the second and later stages, a person begins to notice constant fatigue in the legs, even in the absence of significant physical activity.
The last stages of the pathology are characterized by hair loss on the skin of the legs in the shin area, the appearance of trophic ulcers and ulcers. The toes may turn red and take on a dark tint, this is due to a lack of blood supply and the gradual death of cells.
How to get an eversion carotid endarterectomy service (removal of carotid artery plaques)
Indications for surgical treatment of atherosclerosis of the internal carotid arteries are determined by a cardiovascular surgeon; however, to successfully perform the operation and minimize the risk of complications, coordinated interaction between a neurologist, cardiologist, and anesthesiologist is necessary. Our institution employs just such a team of professionals who are ready to help every patient in the fight against cardiovascular diseases. By making an appointment with a cardiovascular surgeon at the clinic, you will receive comprehensive information about the methods of modern diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the carotid arteries, determine the need and timing of surgical intervention. The modern technologies used and the experience of our specialists will help in getting rid of narrowing of the carotid arteries, preventing strokes and maintaining an active and fulfilling life.
The danger of plaque deposits and methods of diagnosis
It is difficult for doctors to make predictions regarding the consequences of the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels. This depends on the duration of the disease, clinical manifestations, and the location of the clogged arteries. When brain tissue is damaged, the consequences are stroke and transistor attack.
In more rare cases, the patient develops memory loss and dementia. If the aorta (chest and peritoneum) is damaged, gangrene of the leg, death of intestinal tissue or its obstruction, and aortic aneurysm may develop. To avoid such serious consequences, you need to pay timely attention to the diagnosis of atherosclerosis.
It is not worth repeating that if a large part of a blood clot breaks off and gets into a small capillary, especially one located close to the heart, a person can die instantly. To detect the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the body, the following methods are used:
- external examination of the patient;
- interview and further collection of anamnesis - it turns out that the patient has addictions, his nutrition, physical activity, body weight and hereditary predisposition to atherosclerosis are assessed;
- blood test for the content of lipids, lymphocytes and other biochemical components;
- Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels - allows you to assess the structure of capillaries and the completeness of the blood supply to tissues;
- X-ray of the aorta - helps to detect calcification, expansion of the aortic window in the early stages;
- angiography using a contrast agent - specialists check the patency of blood vessels and assess the level of stenosis.
Other techniques, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, are used on the recommendation of a doctor if it is necessary to clarify the location of deposits, the structure of plaques and the stage of the disease.
During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish manifestations of atherosclerosis from other diseases accompanied by similar symptoms
Damage to cerebral vessels by plaques should be separated from syphilis of the brain, injuries and neurological disorders. If the aorta is affected, a differentiated diagnosis is carried out to distinguish it from pathologies of the peritoneal organs. Blockage of blood vessels in the legs must be separated from varicose veins and post-traumatic conditions.
Signs of atherosclerosis on ultrasound, Doppler and duplex
Ultrasound is a quick and easy way to assess the condition of the vessels. This is one of the first instrumental diagnostic methods that is prescribed to a patient if a diagnosis such as atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is suspected.
There are 2 methods of ultrasound examination of blood vessels:
- dopplerography;
- duplex scanning.
With Doppler ultrasound, you can only see the speed of blood flow and determine whether it is disturbed. Duplex scanning allows you to evaluate the anatomy of the vessel, its tortuosity, wall thickness and plaques. To diagnose atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, this type of study is prescribed, since it is more informative.
Treatment methods
Treatment of atherosclerosis should begin in the early stages. It is impossible to completely remove atherosclerotic plaques, but it is possible to reduce their volume and soften the structure. Provided that the patient follows medical recommendations and undergoes all necessary procedures.
General principles
First, you should change your lifestyle - give up bad habits, quit smoking and minimize alcohol consumption. Blockage of blood vessels will not disappear on its own, but to maintain the condition of the blood vessels, it is necessary to engage in physical exercise, spend more time in the fresh air, and reduce body weight.
Without following a diet, the fight against atherosclerotic plaques will be unsuccessful. It is worth giving up foods rich in cholesterol - cocoa, chocolate, animal fats, high-fat milk, offal, eggs. And you should also limit the consumption of baked goods, carbonated drinks, pure sugar and salt.
Set of products allowed for consumption:
- nuts;
- beans, legumes;
- berries;
- cabbage (broccoli, white cabbage, cauliflower, sea cabbage);
- greens - dill, spinach, parsley, celery;
- citrus;
- zucchini and eggplant;
- green tea in unlimited quantities.
These products are rich in Omega 3 acids, iodine and vitamins B, C, A. That is why they are so useful to consume. When the flow of ascorbic acid into the body is established, the vessels restore their tone and are less subject to changes.
Procedures such as general massage, acupuncture, and therapeutic exercises help relieve vascular spasm. You can engage in light sports - swimming, walking, jogging. Against the backdrop of proper nutrition, quitting smoking and alcohol, physical therapy sessions and sports will help significantly improve the patient’s quality of life.
Taking medications
Drug treatment of atherosclerosis is based on taking drugs from the following groups:
- statins - Pravastatin, Atorvastatin, Simvastatin (normalize the amount of cholesterol in the blood, controlling its production by the body itself;
- capillary dilating agents - Pentilline, Pentoxifylline;
- drugs that improve blood circulation - Cilostazol;
- lowering cholesterol levels, in addition to statins - fibrates Ciprofibrate, Clofibrate;
- vitamin complexes – Aevit, Ascorutin, Ascorbic acid;
- derivatives of nicotinic acid.
The dosage, necessary medications, course of administration - all this is determined by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous due to the development of side effects and complications, since statins and fibrates can negatively affect liver function if not treated correctly.
Surgical treatment
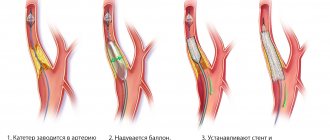
The operation is indicated in severe cases of atherosclerosis, when the disease threatens the health and life of the patient. Stenting is the operation most often performed for problems with blood vessels. Under the control of an angiograph, a balloon with a stent is inserted into the affected area of the body directly into the artery. With the help of gas, the stenotic vessel expands, then a stent is installed there, which will maintain normal blood circulation and prevent the capillary from narrowing again.
Coronary artery bypass surgery - allows you to resume blood flow impaired by blockage. A bypass path of blood supply is created, avoiding completely blocked vessels. For a shunt, a healthy capillary is taken, for example, from the femoral area. If the plaques have completely blocked the lumens of the arteries in the legs, and the limb is already affected by gangrene, the necrotic part is amputated.
If plaques no longer resolve on their own, even with lifestyle changes and diet, doctors may recommend a type of surgery
Expert advice: lifestyle changes
In addition to drug and surgical treatment, lifestyle correction plays an important role. I always recommend that my patients stop smoking, exercise regularly, and make changes to their diet (eat more vegetables, fruits and fish). Patients with diabetes need to periodically donate blood for glycated hemoglobin, follow a low-carbohydrate diet, visit an endocrinologist and take prescribed medications to lower blood sugar.