© Author: Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Counting the pulse in the neck in the area of the carotid artery is the fastest and most easily accessible method that allows you to suspect clinical death in an unconscious person and begin timely measures to resuscitate the victim. In other words, the presence of a pulse in the carotid artery indicates that the person is alive. That is why a medical worker of any specialty, and just an ordinary person, should know how to quickly feel the carotid artery.
In this article:
- What is pulse?
- Correct measurement algorithm
- How to measure pulse using a tonometer?
- How does a pulse oximeter work?
- Benefits of a heart rate monitor
- What can fitness bracelets do?
- Pros of using devices
- How to evaluate heart rate?
Pulse measurement is the easiest and most accessible way to assess the condition of the cardiovascular system. You can determine your indicator at home, while walking, or in any other circumstances. To calculate your heart rate manually, a regular watch with a stopwatch is sufficient, but you can also use modern gadgets that will determine and store the resulting value in memory.
What is pulse?
First, you need to define the basic concepts, figure out what and why you will measure. Not everyone knows that heart rate and pulse are not the same thing. The first indicator reflects the number of contractions of the ventricles of the heart per minute, i.e. how many times during this period the ventricles filled with blood and pushed it into the aorta and pulmonary artery. And the pulse is the number of vibrations in the walls of the arteries that occur due to contractions of the heart.
In a healthy person, these indicators are the same, but in some pathologies they may differ. The norm for an adult is a pulse rate of 60-90 vibrations per minute; in children, the indicator is determined by age. The younger the child, the faster his pulse. When measuring the pulse, the doctor determines several parameters:
- Frequency;
- Filling;
- Voltage;
- Height;
- Rhythm;
- Form.
By taking measurements yourself, you can only find out the frequency. But this indicator also allows you to evaluate the work of the heart, choose the right physical activity, and notice changes in time.
Absence of carotid pulse
A situation where a person has no consciousness and no pulse in the carotid artery indicates that the person has had a decrease in blood pressure to 0 mmHg due to cardiac arrest. Further actions in this case consist of immediately performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) according to the ABC protocol - A (Airway) - ensure airway patency, B (Breathing) - start artificial respiration, C - (Circulation) - start chest compressions. It is necessary to carry out artificial respiration and cardiac massage at a rhythm of 2:15 until blood flow is restored and a pulse appears in the carotid artery or until rescuers (medics) arrive, or within 30 minutes from the heartbeat stopping.
Figure: performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the absence of a pulse in the carotid artery
Correct measurement algorithm
There is a simple heart rate measurement algorithm that can be used in any circumstances. The pulsation can be clearly felt on the wrist, and equally on both hands. For such a measurement, several conditions must be met:
- Place your wrist at heart level in the palm of your other hand;
- Feel the pulse on the palmar side along the edge where the thumb is located (on the side of the little finger the pulse is usually not audible, this is due to the location of the radial artery);
- Wrap your fingers around your wrist so that your index finger is closer to the wrist joint;
- Apply gentle pressure with your fingertips on the wrist in the direction of the radius.
In this case, the middle and index fingers should feel the pulse wave - rhythmic vibrations of the artery wall. It is necessary to note the time and count the number of beats per minute.
Alternatively, you can measure your pulse in your neck. To do this, you need to find the carotid artery: run your fingers from the back corner of the lower jaw down the neck. However, it is believed that determining the pulse on the hand is more comfortable, and its results are more accurate.
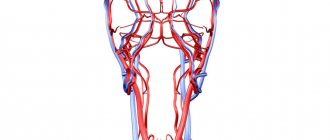
Anatomy of the carotid artery
The carotid artery, along some of its length, is adjacent rather superficially to the skin, so it can be easily and quickly palpated, and thus assess the presence or absence of cardiac activity in a person. This technique allows you to avoid wasting valuable resuscitation time trying to get to the chest and listen to heartbeats on the anterior chest wall.
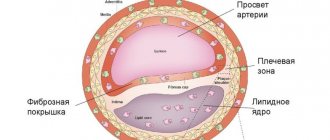
So, the carotid artery is a paired blood vessel originating directly from the aorta on the left (more precisely, from its arch), and from the truncus brachiocephalicus on the right (brachiocephalic trunk). On both sides, the carotid artery, at this length called the common carotid artery, heading upward, passes to the right and left of the esophagus and trachea, and also slightly anterior to the cervical vertebrae.
Closer to the upper surface of the thyroid cartilage of the larynx (the most protruding part of the larynx, also called the “Adam's apple”), the common carotid artery divides into two branches - external and internal. From this level, the external branch is accessible to palpation, since it is covered only by the skin, subcutaneous fat and fascia, in contrast to the internal branch, which extends into the thickness of the muscles. It is on the external carotid artery that you can feel the pulsation by lightly pressing it against the deeper muscles of the neck.
anatomy of the carotid arteries and cervical arteries
How to measure pulse using a tonometer?
You can use special instruments for measurements. There are several options to check your pulse and at the same time find out some other important indicators. One of them is a tonometer. Such a device records pulse and blood pressure, and modern models are capable of:
- Save results in memory;
- Compare indicators with the norm, identify deviations;
- Calculate average values for a certain period;
- Transfer information through applications to mobile devices or to a computer, where you can conduct a full analysis, including using graphs and diagrams.
To get accurate results, you need to take measurements correctly. Measurements are taken in a sitting position, the cuff on the arm should be at the level of the heart. It is important to calm down and comply with all the requirements listed in the instructions for the device.
Automatic blood pressure monitors inflate the cuff themselves and take measurements. The user can only estimate his pulse and pressure using the numbers on the display.
First aid in case of an accident: save a life
It may turn out that at this moment you will look beautiful, young, in a good jacket or dress. Or maybe not very beautiful, for example, without a lower jaw, with a crushed skull, with a crooked scalp sewn together. And they will bury you in a closed coffin, quickly and without unnecessary pathos.
Although I'm sure no, you don't have such perverted fantasies as I do. And I have, because I have seen enough of people who are brought in after a car accident. Already standing at a bus stop, I can imagine the unfastened driver at the moment when the car falls on its side into a cliff, and he shakes himself out the window, and the whole one and a half ton colossus crushes him, releasing his intestines. I've seen that too.
And all because some people still haven’t realized that a car is not an adult toy, but a means of increased danger.
So how can you protect yourself from road accidents? Firstly, traffic rules are the bible that will protect your health and the health of your loved ones. The main thing to do is fasten your seat belts. And even more so, if you are good parents, then buckle your child in the car! Of course, you need to obey the speed limit... And one day my friend, a policeman, said: “Volodya, remember - everyone on the road is a fool! Any person has periods when he gets stuck, when he is inattentive, when he confuses the gas and brake pedals. Therefore, never be distracted from what is happening on the road and always be ready to react to the inappropriate actions of another fool.”
What to do if you see a car accident - are you obligated to help? Obliged! There is criminal liability for failure to provide assistance and leaving someone in danger. And even if the criminal code is not a decree for you, just be human, stop, find out if you need help. How can you help?
Procedure for providing assistance in case of an accident
1. The first thing to do is to ensure the safety of victims and rescuers.
Be sure to install a warning triangle and warning lights. The sign is placed at a distance of at least 15 meters in populated areas and 30 meters outside.
Often, victims in shock fly under the wheels of passing cars, hoping that they will stop. And there are cases when the rescuers themselves are hit by a car at night.
2. Second, call the rescuers:
0911 or 112, ambulance team - 03 (from mobile: 003 or 030).
During negotiations, it is necessary to briefly describe the situation, the number, gender, approximate age of the victims, visible damage and the location of the accident. Leave your coordinates so that later they know who to give the medal for their help and can call back to clarify the location of the accident.
3. Third - direct help.
It begins with the evacuation of the injured person from the car. Here you must remember the eternal rule: DO NO HARM!
Open the door, and if it doesn’t work, carefully knock out the glass and press the sash. Help the victim get out. If it's pinched, don't pull it out! If it didn’t work out, then wait for the rescuers, they have more capabilities. In this case, ensure the fire and electrical safety of the car: turn off the ignition, remove the terminals from the battery. Wrap up the victim, give an analgin tablet from the first aid kit.
If you are alone, grab the victim from the back, running your hands under his armpits, grab his forearms, pull the victim out so that his head lies on your chest (do everything calmly, without fuss, do not overdo it). Place it on a hard surface, without stones or unnecessary objects, and place a small cushion under your head.
Assess the degree of consciousness. If he is conscious, ask about his well-being, what worries him, is it hard to breathe, does he feel his limbs. Let him move his arms and legs.
Breathing and pulse
If the victim is unconscious, determine whether he is breathing?
Breathing is determined by the rhythmic movements of the abdomen; listen with your ear to the movements of air near the mouth. Feel the pulse in your neck (use your index and middle fingers, starting from the corner of the lower jaw, move downwards until you reach the hole where the pulsation is most obvious. There is no need to press hard, do not block the blood flow).
If there is a pulse, but breathing suffers.
Tilt your head back (not possible if you suspect a spinal fracture!), open your mouth, push your lower jaw forward. This will improve the airway in the vast majority of cases. If there are blood clots, mucus, or foreign bodies in your mouth, wrap your finger in a clean cloth and try to remove everything. In addition, you will find an air duct in the first aid kit. Thanks to it, airway patency can be improved. When you insert the air duct into your mouth, make sure that you do not tilt your tongue with the device.
If there is no breathing, but there is a pulse
, inhale into the victim, after pinching his nose and putting a bandage on his mouth. Make sure that during inhalation the chest rises, and the passive exhalation is felt by the noise and movement of air.
There is no breathing, no pulse - you can’t hesitate and wait for help from doctors!
This condition is called “clinical death”. You immediately need to carry out a set of resuscitation measures, which I will write about separately.
Injuries
If breathing and heartbeat are not currently affected, it’s time to pay attention to the skin.
Are there signs of external bleeding? It comes in three types: capillary, venous and arterial.
1. Capillary bleeding
characterized by diffuse saturation of tissues with dark blood, it is not intense, not threatening. Stops with a simple pressure bandage (do not forget to treat the wound with a solution of iodine or brilliant green).
2. Venous bleeding
characterized by a constant, fairly intense flow of dark blood. After treating the wound, apply a pressure bandage. Bleeding can be easily stopped by lightly squeezing the tissue below the wound.
3. Arterial bleeding
intense, pulsating with scarlet blood. Here delay is like death! As soon as you see such a wound, press the vessel firmly with your fingers. If the damaged vessel is superficial, then you will be able to stop the bleeding by strongly squeezing the tissue just above the wound. By the way, take gloves from the same first-aid kit; the infection has not yet been canceled. Take out the tourniquet. In case of arterial bleeding, a tourniquet is applied above the wound, tightly wrapped around the limb. Be sure to record the time of installation of the harness!
It often happens that, in a rush, rescuers forget that it is necessary to relax the tourniquet every half hour in winter and no more than an hour in summer, to allow the blood flow to temporarily restore and nourish the tissues - such patients are brought in ready for limb amputation.
While relaxing the tourniquet, apply finger pressure to the wound.
There is no tourniquet - use twists made of fabric (bandage, scarf, soft fabric), secured with a stick. You cannot make twists from ropes or laces.
Head wounds
should be treated with an antiseptic and bandaged. Place the removed scalp back as best you can and secure with a circular bandage.
Penetrating wound to the chest.
In this case, when the patient inhales, air is noisily sucked into the pleural cavity. Air will begin to fill the pleural cavity, compressing the lungs, heart, aorta and other organs, dramatically disrupting their function. To prevent this, you need to immediately cover the wound either with a sealing cloth from the first aid kit, or with a bag, plastic, or adhesive tape. It is better to fix the bandage while exhaling.
Wound in the stomach.
It is easier for such patients when they bring their knees towards the body (transport them that way). If the wound is open, treat it with an antiseptic from the first aid kit and apply a bandage. We leave all penetrating foreign bodies (knives, glass, fragments) in place, fix them with a bandage so as not to cause more harm, and send them to a hospital facility. The surgeons will figure out what's what.
Patients with injuries are not allowed to drink or eat, no matter how much they ask! Only a doctor can give permission to eat. This is associated with the risk of anesthesia, the risk of aspiration with vomit, and in case of intestinal wounds - leakage of contents into the abdominal cavity.
Limb fractures.
Pain, unnatural position of the injured limb, bone fragments in the wound indicate a bone injury. It is impossible to transport the patient without fixing such a limb, since fragments can damage the tissue surrounding the wound.
They use special medical splints, but you can also make do with improvised materials (skis, ski poles, boards), and place cotton wool or rags under them at the point of contact with the bone. It is necessary to fix at least two joints so that the limb is completely immobilized. The splint is applied over clothing after treating the wound. A bluish, cold limb may indicate excessive compression of the tissues with a bandage.
If a neck fracture is suspected - and now in case of any car accidents - a collar is placed on the neck. There is no special one - you can make one out of towels. In general, spinal cord injury patients are transported on a rigid surface, such as a door, on their back or on their stomach.
Today I have outlined to you the basic knowledge and skills very concisely and briefly, but they will also give you the opportunity not to get confused and not harm the victim, and if done correctly, even help.
Vladimir Shpinev
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Related products: [product](first aid kit)
How does a pulse oximeter work?
Another modern pulse device is a pulse oximeter. Its functions are to determine saturation and count the heart rate (pulse rate). This is a medical device, before using it you need to understand the features of its use.
So, pulse oximeter – what is it and how does it work? The device is equipped with two light sources with different wavelengths and a photosensor that detects the reflection/absorption of light waves by various tissues. The light is partially reflected/absorbed when passing through soft tissues and blood, this makes it possible to determine saturation - the saturation of arterial blood with oxygen as a percentage. The normal rate varies from 95% to 100%; lower values indicate malfunctions in the functioning of the body systems.
To measure your pulse with this device, you need to attach the sensor to your fingertip, press the button and wait a few seconds. The display will show two indicators simultaneously: pulse and saturation. If the values are outside the normal range, a beep will sound.
How to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation yourself?
Each of us hopes that he will not have to carry out resuscitation measures or provide emergency medical care to the victim, but no one is immune from such cases. In emergency situations, first aid must be provided very quickly and correctly. Only then is there a chance for a person to return to life.
Although almost all of us have some knowledge regarding first aid, in most cases it is a strange mixture of stereotypes that are completely inapplicable in practice. For example, everyone has an idea of what chest compressions and artificial respiration are. However, not everyone knows in what situation cardiopulmonary resuscitation is necessary and how to carry it out correctly.
What it is?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a set of measures aimed at returning a person to life in the event of circulatory or respiratory arrest.
In general, all activities can be divided into two large groups - basic and specialized cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Specialized, as the name suggests, is carried out in specialized wards and requires appropriate equipment and medications, as well as education. Here we will consider only basic resuscitation issues.
When is CPR necessary?
Indications for CPR: absence of consciousness, breathing, pulse in the carotid arteries, preagonal, agonal states, clinical death.
If the heartbeat is heard, the pulse and breathing are preserved and even quite rhythmic, resuscitation measures are not required.
Basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation includes three stages (ABC):
· ensuring airway patency (A - Airway);
· performing artificial respiration (B - Breathing);
· performing indirect cardiac massage (C - Circulation).
In practice, there is a universal algorithm of actions for sudden death of adults, which includes all these stages in sequence.
Assessing the presence of consciousness in the victim
First, it is necessary to assess the presence of injury, especially to the head or neck - if injury is suspected, it is possible to move the victim only if absolutely necessary. After this, you can pat or lightly shake him by the shoulders, while loudly asking a question like: “Are you okay?”
Ensuring airway conduction, assessing spontaneous breathing
First, the victim must be laid flat on his back on a hard, flat surface. At the same time, it must be rotated “as a single whole,” without allowing parts of the body to move relative to each other or rotate.
The second is to empty the mouth of liquid contents (with the index and middle fingers wrapped in a piece of cloth) and solid foreign bodies (with the bent index finger). Then ensure the patency of the upper respiratory tract by throwing back the head and lifting the chin or pushing the lower jaw forward. If there is a suspicion of head or neck injury, only the mandible is moved forward.
Third, put your ear to the victim’s mouth and nose and evaluate the movements of the chest during inhalation and exhalation, the presence of the sound of exhaled air and the sensation of air movement (the assessment should take no more than 10 seconds).
Fourth, if after ensuring the airway is clear, breathing is restored and there are signs of blood circulation, the victim should be turned on his side and his head should be placed so that fluid can flow freely from the mouth.
If there is no breathing, the next stage should begin - artificial respiration.
In the absence of special equipment (for example, an Ambu bag), the most effective is mouth-to-mouth breathing, which is carried out immediately after ensuring patency of the airway.
The main disadvantage of this method is the presence of a psychological barrier - it is difficult to force yourself to breathe into the mouth or nose of another, sometimes a stranger and stranger, especially if he has previously vomited.
With your left hand, holding the victim’s head in an tilted position, at the same time cover the nasal passages with your fingers to ensure tightness. Next, you need to take a deep breath, wrap your lips around the victim’s mouth, and inhale. Cover your mouth with any clean cloth beforehand for hygienic purposes.
This procedure should be repeated at a frequency of 10-12 breathing cycles per minute (once every 5-6 seconds). Passive exhalation should be complete (time does not matter); the next air injection can be done when the chest has dropped.
The main criterion for the effectiveness of artificial respiration is the movement of the chest during inhalation and exhalation, the sound of exhaled air and the sensation of its movement. If this is not observed, the airway should be re-cleared and the airway should be checked for obstruction (eg by a foreign body) at the level of the larynx.
If signs of spontaneous breathing appear in the victim, artificial ventilation of the lungs is not stopped immediately, it is continued until the number of spontaneous breaths corresponds to 12-15 per minute. At the same time, if possible, synchronize the rhythm of inhalations with the recovery breathing of the victim.
Circulation assessment
It is carried out in parallel with artificial respiration - you need to determine the pulsation in the carotid or femoral arteries. Easier and better for sleep - light pressure with two or three fingers in the hole between the lateral surface of the larynx and the muscle roll on the lateral surface of the neck.
In addition, non-professional rescuers are recommended to be additionally guided by indirect signs - breathing, coughing, movements of the victim in response to artificial respiration (the assessment should take no more than 10-15 seconds).
After making sure that the patient has no cardiac activity, it is necessary to begin performing indirect (closed) cardiac massage.
The rescuer's hands are placed on the victim's sternum 2-3 cm above the xiphoid process - the part of the sternum located below the place where the cartilages of the X ribs are attached to it. The hands are placed one on top of the other (“locked”) in the lower third of the sternum.
Before starting chest compressions, you should carry out 2-3 intense blows of air into the victim’s lungs and strike with your fist in the area of the projection of the heart (precordial blow). This is sometimes enough for the heart to “start working” again, while “hitting with all your might” on the sternum is unnecessary and dangerous, you could easily break a person’s ribs. After this, chest compressions begin in the anteroposterior direction by 2.5-5 cm with a frequency of 80-100 times per minute.
The forces are applied strictly vertically to the lower third of the sternum using crossed wrists and arms straightened at the elbows, without touching the chest with the fingers. Compression and cessation of compression should take equal time; when the compression stops, the hands do not leave the chest.
Simultaneous artificial respiration and closed cardiac massage
If at the first examination there is no spontaneous breathing, two breaths are first taken, and their effectiveness is simultaneously assessed.
Then, if one person is performing resuscitation, 15 chest compressions should be alternated with two breaths, if two people - 5 chest compressions should be alternated with one breath, stopping chest compressions for 1-2 seconds while blowing air into the lungs.
Mouth-to-mouth breathing is dangerous for the rescuer and can cause infection. It is believed that indirect cardiac massage can be performed without artificial ventilation of the lungs - if there are no special devices for artificial respiration: an Ambu bag, a ventilator, etc. However, this technique is less effective, and if possible, you should still opt for artificial respiration.
Monitoring the condition of the victim during resuscitation
After every 4 cycles of artificial respiration and chest compressions, you need to check the pulse in the carotid artery (within 3-5 seconds). If a pulse appears, chest compressions should be stopped and spontaneous breathing assessed.
If it is absent, you need to continue artificial respiration while simultaneously determining the pulsation in the carotid artery after every 10 blows of air into the lungs.
When spontaneous breathing is restored and there is no consciousness, it is necessary to maintain the patency of the upper respiratory tract and carefully monitor the presence of breathing and pulsation in the carotid artery until the arrival of the resuscitation team.
Irreversible changes in the brain occur 3-4 minutes after circulatory arrest, which is why early help and the start of resuscitation measures are of great importance. Refusal to use resuscitation measures or their cessation is permissible only if biological death is established or these measures are recognized as absolutely futile.
In parallel with resuscitation efforts (without interrupting them), you need to call an ambulance and diagnose the victim’s condition.
Source
Benefits of a heart rate monitor
Tonometers and pulse oximeters are medical devices and are convenient to use at home. But many convenient gadgets have been created for people who prefer an active lifestyle. There is even a special device for measuring pulse, which is called a pulsometer.
Basically, devices of this type look like a wristwatch and are used to assess the effectiveness of physical activity by measuring heart rate. In addition to counting your pulse, heart rate monitors perform many useful functions:
- Calculate the average heart rate;
- Determine the maximum values;
- Allows you to set up an individual training zone and notifies you when you go beyond it with an audible signal;
- Equipped with a countdown timer;
- Show date, time, day of the week;
- Works as a stopwatch and alarm clock;
- They are synchronized with special software to transfer data to a phone or computer, where the dynamics can be analyzed.
Many devices provide additional functions, for example, determining the height or number of laps while running, calculating energy consumption, recording the acceleration of the legs, and others. Some models are equipped with a chest belt. The main advantage of heart rate monitors is the most accurate pulse determination, comparable to ECG data.
What can fitness bracelets do?
One way to check your pulse and get a lot of other useful information is to use fitness bracelets.
The compact device is fixed on the wrist according to the same principle as a watch. It doesn’t interfere with work, walking, training, and it’s even comfortable to sleep with. All this time the device measures:
- Number of steps taken and distance in km;
- Duration of sports training;
- Achievement of set goals in %;
- Volume of calories burned;
- Duration and quality of sleep.
The range of options depends on the model. For example, some devices synchronize with a smartphone, inform about incoming calls and messages, and transfer the results of all measurements to a mobile device for subsequent analysis. All fitness bracelets function as watches and alarms.
Pros of using devices
Such devices are very popular due to their many advantages:
- A person can always evaluate his physical activity and, if necessary, adjust it;
- Calorie counter helps you stay fit;
- Heart rate measurement is carried out in real time with high accuracy;
- The cost of the devices is quite affordable;
- The bracelets look stylish and elegant;
- The device combines many useful functions.
In addition, fitness bracelets are easy to use. With their help, it is convenient to monitor your pulse during training without being distracted by taking measurements. Just place your finger and wait a few seconds for the measurement result.
1
Technology for rapid assessment of the condition of victims in a state of clinical death and coma
In cases where the victim is unconscious, it is necessary to immediately begin determining the pulse in the carotid artery. You should not waste time identifying signs of breathing. Signs of breathing are often subtle. Even if a volunteer takes a breath of artificial ventilation (ALV) while maintaining breathing, this cannot harm the victim in any way. A real threat to life can arise only in two cases: 1. The rescuer’s chest is significantly larger in volume (2-3 times) than the victim’s chest (for example, a child under 5 years old). 2. The ventilation was inhaled at the moment of pressing chest compressions on the victim’s chest.
To identify signs of clinical death or the development of coma in an unconscious victim, it is enough to verify the absence or presence of a pulse in the carotid artery.
Pressing your fingers on the neck in the area of the carotid artery causes very severe pain.
If the unconscious victim does not respond to this painful effect, and he has a pulse in the carotid artery, then this means that he is alive and in a state of coma. In this case, he should be immediately turned onto his stomach. At any second he could choke on vomit or choke on his tongue.
If the victim is unconscious and has no pulse in the carotid artery and there are no signs of biological death, this means that he is in a state of clinical death. It is necessary to begin resuscitation immediately.
When using this tactic to identify signs of clinical death or the development of coma, there is no need to waste time on:
- Questions like: are you okay?
- “braking” the shoulder or putting pressure on pain points;
- detecting signs of breathing.
Signs of breathing are elusive and very often deceptive, which can lead to tragic mistakes. For example, fogging of a shiny object brought to the mouth of a deceased person can be observed several hours after the onset of biological death. Finding out why the villi move around the mouth of the deceased can take hours. Looking for the rise of the chest in men with abdominal breathing, and even in winter in outerwear, is a waste, or rather, a fatal waste of time when every second counts.
If we take into account that artificial respiration inhalation (AI) under no circumstances can cause any harm to an adult, then determining the signs of breathing can be considered doing more harm than good in situations of coma or clinical death. In the case of a coma, a victim lying on his back may choke on vomit at any second, and if clinical death develops, the chance to save him will be missed.
Thus, in order to make the most of all the chances of saving victims in a state of coma or clinical death, it is enough to ensure only the absence of consciousness and the presence or absence of a pulse in the carotid artery. It is the presence or absence of a pulse in the carotid artery that makes it possible to differentiate coma from clinical death.
Without determining the pulse in the carotid artery, it is practically impossible to distinguish the state of coma from clinical death! Focusing only on identifying signs of breathing is a fatal mistake.
Considering that sudden death in front of an eyewitness is extremely rare, and fainting and coma are tens of thousands of times more common (approximately 1:10,000), then when doubt arises about the presence of a pulse in the carotid artery, you should immediately turn the victim onto his stomach.
To begin resuscitation of victims and patients in a coma with diabetes mellitus, alcohol poisoning and strokes, traumatic brain injury, including concussion (the most common sports and household traumatic brain injury) is 100% murder! Incorrect resuscitation of a comatose victim lying on his back and pressing on the sternum with a frequency of up to a hundred times per minute will certainly lead to death in a matter of minutes from vomit entering the respiratory tract and suffocation with one’s own tongue.
2
EXAMPLE
USING TECHNOLOGY for rapid assessment of the condition of victims in a state of clinical death and coma
CONCLUSION 1 Determining the pulse in the carotid artery will allow a volunteer to distinguish a coma from clinical death within 10-15 seconds, without unnecessary loss of time, and save many people who find themselves in extremely critical condition.
CONCLUSION 2 Without determining the pulse on the carotid artery, it is practically impossible to distinguish the state of coma from clinical death! Focusing only on identifying signs of breathing is a fatal mistake. Considering that sudden death in front of an eyewitness is extremely rare, and fainting and coma are tens of thousands of times more common (approximately 1:10,000), then when doubt arises about the presence of a pulse in the carotid artery, you should immediately turn the victim onto his stomach.
CONCLUSION 3 Start resuscitation of victims and patients in a coma with diabetes mellitus, alcohol poisoning and strokes, traumatic brain injury, including concussion (the most common sports and household traumatic brain injury) - this is 100% murder! A victim lying on his back, and even under pressure on the lower third of the sternum up to a hundred times a minute, will certainly choke on his tongue and choke on vomit, which will certainly lead to death in a matter of minutes.
19
| GRADE |
Remote detection of wounds, signs of damage to bones and joints
First you should pay attention to the posture of the victim and the position of his limbs:
- frog pose is a sign of damage to the pelvic bones and hip joints;
- unnatural position of a limb or its deformation - fracture of the bones of the limb;
- the presence of a wound with bone fragments protruding from it is a sign of an open fracture.
If the wounded person is conscious, then any complaints of pain in the extremities should raise suspicion of bone damage. At the slightest suspicion of damage to bones and joints, give the wounded painkillers and, if necessary, apply transport splints.
What is important is not the speed of identifying wounds and damage, but the careful attitude towards the victim. The main thing is to protect him from unnecessary pain and injury. Prevention of the development of traumatic shock and its complications begins with a gentle examination of the victim.
To do this, you should avoid palpating the head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvic bones, arms and legs in order to make a diagnosis: “crunches-not-crunches”, “hurts-not-hurts”. There is no need to mention how the slightest displacement of the temporal bones, fragments of ribs or pelvic and femur bones can result. Such an examination can only be carried out by medical personnel, after mandatory practical training under the supervision of specialists. Any careless touch to the damaged area can be fatal.
For people without medical education (volunteers), it is enough to suspect the presence of a particular injury and act on the principle of overdiagnosis. A neck brace, a forearm splint, an ankle splint, or a pad placed under the knees will never be superfluous.
| GRADE |
EXAMPLE remote detection of wounds, signs of damage to bones and joints
CONCLUSION 1 The use of examining victims by palpation should be excluded from mass training of volunteers in first aid skills, as a technique that leads to unnecessary traumatization of victims and poses a threat to their lives
CONCLUSION 2 Remote detection of the presence of wounds, signs of damage to bones and joints (hyper-diagnosis) is one of the factors in preventing the development of traumatic shock.
How to evaluate heart rate?
Self-monitoring your heart is quite easy, especially with heart rate bracelets and other smart devices. But it is also important to evaluate the results correctly. To do this, you should take into account several nuances:
- The normal pulse at rest is 60-80 beats per minute;
- For women, the rate is 5-10 beats higher;
- The pulse in a lying position is minimal, in a sitting position it increases by 4-6 beats, while standing - by 10-14 beats per minute;
- In winter, the rate may be lower than in summer;
- Throughout the day, the pulse changes from the slowest at night to the maximum at 18-20 hours, increasing at 8-12 hours and about 15 hours, but it all depends on the daily routine of a particular person;
- After eating hot food and drinks, the pulse quickens.
Heart rate is related to physical activity: the more intense it is, the higher the indicator will be. During active sports, the heart rate increases to 150 beats per minute. A level of 200 blows is considered critical; at this level, the load must be reduced. In athletes, the heart muscle is more trained, so the heart rate during exercise grows more slowly than in an ordinary person.
Before checking the pulse on your hand or assessing the performance of special devices, it is worth considering the factors that influence the heart rate. The pulse increases not only due to physical activity. This effect can be caused by stressful situations, overeating or severe hunger, drinking alcohol or smoking, and even massage.
A heart rate deviation of 10% or more from normal may be a cause for concern. For example, if you have a constant rate above 90 beats per minute under the age of 30, you should consult a cardiologist. A decrease to 50 beats or below may also indicate the development of pathological processes in the body. A drop to 40-35 beats indicates a real threat to life.
Pulse measurement allows you to monitor the condition of the body, obtain objective indicators of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, and promptly identify deviations. You can determine the indicators yourself manually or using special devices that monitor the pulse automatically with high accuracy.
How to determine the pulse in the carotid artery?
The technique for determining the pulse consists of the following manipulations. Before palpation begins, it is necessary to free the neck from clothing and visually determine the area of the carotid triangle, the edges of which are the lower jaw, the midline of the neck and the sternocleidomastoid muscle. In this case, it is better to turn the victim’s head in the opposite direction. The side of palpation does not matter, and palpation can be carried out both on the right and on the left. In order to feel the pulse, you need to place two or three fingers (II, III and IV) at the point between the angle of the lower jaw and the anterior surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Next, when pulsation is detected, the main characteristics of the pulse are assessed - rhythm, filling, tension, and the pulse rate per minute is calculated.
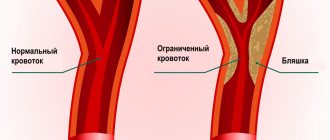
Pulse assessment along the entire length of the carotid artery on both sides is used in patients with suspected thrombosis, atherosclerosis, carotid aneurysm, as well as in cases of suspected heart disease such as aortic insufficiency. In the latter case, rhythmic pulsation in the area of the carotid artery is visually noticeable and is called carotid dancing.
In a person who has suddenly lost consciousness, checking the carotid pulse is necessary to determine whether cardiac arrest has occurred and whether immediate resuscitation is required. In this case, the pulse in the carotid artery is not detected on both sides.