Our clinic specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system, incl. non-surgical treatment of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus. You will also find help in treating the consequences of intracranial hypertension: depression and nervous exhaustion, vegetative-vascular dystonia, headaches, visual disorders and others. We will be happy to help you!
- Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
- Make a diagnosis
- Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
- Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
- What is intracranial pressure
- What is hydrocephalus of the brain
Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
We actively use methods to normalize intracranial pressure, both classically and without drugs. Some simple measures may be enough to get you back to good health. The effect is usually noticeable already in the first week of treatment.
1. Unloading the venous bed of the head using special methods of soft manual therapy and osteopathy;
Normalization of intracranial pressure: for treatment, sometimes it is enough to eliminate the infringement of blood vessels by the vertebrae
2. Special gymnastics to reduce intracranial pressure (used by the patient independently, developed by the doctor after examining muscle tone); 3. Individual drinking/eating regimen.
Living with increased intracranial pressure is both unpleasant and harmful. The human brain cannot work normally under the influence of excess pressure ; moreover, slow atrophy of the brain substance , this leads to a decrease in intellectual abilities, disruption of the nervous regulation of internal organs (hormonal disorders, arterial hypertension, etc.). Therefore, we will take measures to normalize intracranial pressure as soon as possible.
In the treatment of increased intracranial pressure, it is important to reduce the release and increase the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Traditionally, it is customary to prescribe for this purpose drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid and improve venous outflow (evacuation of venous blood from the cranial cavity). Often it is enough to take the medicine 1-2 times a week.
But still, we strive to free our patients from constant medication use. There are two ways to do this:
- If possible, eliminate the cause of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus;
- Use more non-drug methods for treating cerebral hydrocephalus.
What to do in very severe cases
In very severe cases (for example, cerebrospinal fluid block after neurosurgical operations or congenital cerebrospinal fluid block), surgical treatment is used. For example, a technology has been developed to implant tubes (shunts) to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Use of cranberries in treatment
If intracranial hypertension is a concern, it is necessary to use components with diuretic properties in home treatment to improve the outflow of fluid from the head. One of these components is cranberry. It lowers cholesterol levels in the blood, clears capillaries from the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques, and normalizes the outflow of excess fluid from the body. In addition, the sour berry eliminates inflammatory processes, increases the body's resistance to infections and removes free radicals.
To eliminate the symptoms of ICP, you can use cranberries in several ways:
- Morse. 200 g of berries are washed, kneaded with a mortar and the remaining cake is poured into 600 ml of water; the juice is first squeezed out of the berries. The mixture is boiled for 1–2 minutes, then filtered, 60 g of granulated sugar is poured into it and the berry juice is poured in. The finished fruit drink is mixed and drunk throughout the day, and the next morning a fresh portion of the drink is prepared.
- Kissel. Take 200 g of cranberries, pass them through a blender or simply crush them in a mortar, then add 1 liter of boiling water and add sugar to taste. The composition should rest for a quarter of an hour, after which it is placed on low heat, having previously prepared the starch. For this, 1.5 tbsp. l. starch is diluted with 200 ml of cold water and brought to a homogeneous consistency. When the cranberry mixture has boiled, you need to remove the resulting foam from it and pour in the starch, then cook until thickened. The finished jelly should be drunk the day before, without leaving it in the refrigerator.
- Compote. 400 g of cranberries are boiled in 2.5 liters of water for a quarter of an hour, after which the drink is ready for consumption. If desired, you can diversify the taste with currants, raspberries, cherries and other berries.
It is useful for patients with signs of intracranial and arterial hypertension to eat cranberries even in their pure form, with the addition of a spoonful of honey
Recipes with cranberries for the treatment of intracranial pressure are very popular, since many have heard about the healing properties of the berry. This is not only a tasty treat, but also a way to effectively eliminate the symptoms of ICP thanks to the diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties of cranberries.
Make a diagnosis
Intracranial pressure can be directly measured only by inserting a special needle with a pressure gauge connected to it into the fluid cavities of the skull or spinal canal. Therefore, we do not use direct measurement of intracranial pressure.
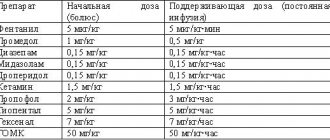
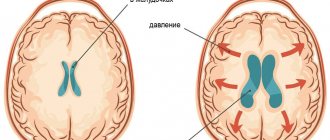
On the left is an MRI scan of a normal brain. The brain matter is shown in gray, the cerebrospinal fluid is in white. Normal size of the fluid spaces of the brain (they are slit-like). The ventricles are visible inside the brain. The subarachnoid spaces are the white border around the brain.
In the center there is internal hydrocephalus. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain in the form of a butterfly is visible. On the right is external hydrocephalus. External hydrocephalus is also an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid outside the brain in the form of a wide white border. The volume of the brain matter is reduced - brain atrophy from fluid pressure
We can confidently judge the increase in intracranial pressure based on the following data:
- Dilation and tortuosity of the fundus veins is an indirect but reliable sign of increased intracranial pressure;
- Expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain (internal hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus) and external hydrocephalus (rarefaction of the medulla) along the edge of the ventricles of the brain, clearly visible on computed x-ray tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
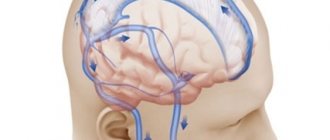
- Violation of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity, established using ultrasound vascular studies.
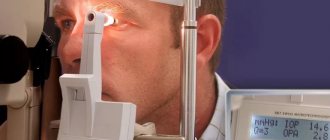
How much the brain suffers from increased intracranial pressure can be judged from EEG data. The gold standard for instrumental examination of patients in our clinic is an assessment of symptoms, brain tomography , fundus images and EEG .
Good optics helps us see the subtle nuances of the fundus vessels
Echoencephalography (Echo-EG) provides indirect and not always reliable data on increased intracranial pressure; it is less reliable than CT and MRI, so we do not use this method.
Effective treatment of intracranial pressure with head massage
Massage is one of the effective ways to treat intracranial pressure.
In order for the technique to give the desired results, you need to do the massage correctly:
- The fingers should be clasped and placed below the back of the head, so that the palms rest on the head.
- In this case, the thumbs should rest on the place where the back of the head meets the neck.
- The next step is to roll the back of your head onto your fingers, for which the chin should be raised slightly upward. In this case, there should be a feeling that your fingers are penetrating deep into the soft tissue. Perform 3-4 times.
- Using circular movements, massage the indicated area with the pads of your thumbs 5 times in one direction and 5 times in the other direction.
- Then, using your thumbs, you need to find those places on the side of the neck that impede the venous outflow from the brain. They will be slightly painful. They are gently pressed in a circular motion 3 times, after which the fingers are lowered a little lower and pressed again 3 times. Thus, you need to massage the entire side surface of the neck to its base.
- The next step is to pull back the skin on the back of the neck. It is collected with your fingers and slightly lifted up. Particular care should be taken to work the area located under the back of the head.
- You can also pull your hair up, doing this with forward movements, holding the lower part of the edging. The hair is pulled back and fixed for 2-3 seconds, after which it is released.
- As you inhale, raise your shoulders towards your ears and lower them as you exhale. Repeat 2-3 times.
- The head is lowered down so that the chin touches the chest, the back should be straight. Then they throw their head back. Repeat three times.
- Then, when you tilt your head forward, you stretch your shoulders towards it, and when you move your head back, you bring your shoulder blades together. Repeat 2-3 times.
Regularly performing such a massage allows you to normalize venous outflow and reduce intracranial pressure.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
Increased pressure on the brain substance can disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system. Hence the characteristic symptoms:
- Heaviness in the head or headaches that increase in the morning or in the second half of the night;
- In severe cases, nausea and/or vomiting in the morning may occur;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (sweating, a drop or increase in blood pressure, palpitations, lightheadedness, etc.) is an almost obligatory symptom;
- Fatigue, “dullness”, easy exhaustion during work or study loads;
- Nervousness;
- “Bruises” under gases (if you stretch the skin under the eyes in the area of the “bruise”, dilated small veins are visible);
- Possible decrease in sexual desire and potency;
- If the human body is in a horizontal position, cerebrospinal fluid is released more actively and absorbed more slowly, so intracranial pressure and its symptoms tend to peak in the second half of the night or in the morning;
- The lower the atmospheric pressure, the higher the intracranial pressure, so the deterioration of the condition is associated with changes in weather.
Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
The reasons we find most often:
- disruption of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation)
- suffered a traumatic brain injury (even a very old one, up to birth trauma)
- meningitis or encephalitis
- congenital structural features of the central nervous system (Arnold-Chiari anomaly, congenital intracranial hypertension, etc.);
- poisoning with brain damage.
Consequences As a result of the disease, brain cells are gradually destroyed, and their place is filled with fluid. The functions of systems controlled by the brain become disordered, and complete or partial loss of vision, hearing, memory, potency, miscarriage, depression, nervous exhaustion and other health problems may occur.
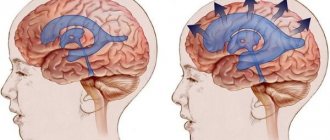
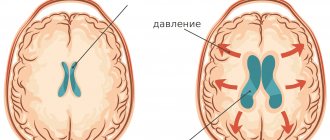
On the left is a normal brain, the liquid (cerebrospinal fluid) is indicated in white. On the right is untreated internal hydrocephalus: brain atrophy, almost the entire cranial cavity is occupied by fluid.
What is intracranial pressure
Wise nature placed the human brain in a protective liquid environment ( subarachnoid fluid spaces ) and provided it with internal fluid cavities ( ventricles ). Thus, the brain is actually suspended in a special fluid - cerebrospinal fluid (also known as cerebrospinal fluid or CSF ). The cerebrospinal fluid is in the cranial cavity under a certain pressure. It is the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid on the brain that is called intracranial pressure .
A normal level of intracranial pressure is very important for the proper functioning of the brain and all processes subordinate to it. We often see a total improvement in the well-being of our patients as intracranial pressure normalizes.
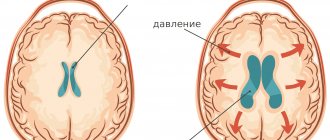
What is increased intracranial pressure? All fluid spaces and ventricles are interconnected by ducts. The liquor is constantly circulating. In some parts of the brain it is released, and then flows through the cerebrospinal fluid ducts to other parts of the brain, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Complete renewal of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs on average 7 times a day. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid causes an increase in its pressure on the brain substance. This is called increased intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension).
Three common causes of chronic increased intracranial pressure:
- too much cerebrospinal fluid is released;
- the cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed fully enough;
- the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways is impaired.
Basic reduction methods
The main goal in the treatment of cranial hypertension is to reduce pressure using conservative methods, the effect of which is to restore cerebral circulation through medication, lifestyle adjustments and special exercises.
To obtain an optimal and long-lasting effect, it is necessary to remove the causes that provoke the disease. Depending on the stage of the pathology and the patient’s condition, the specialist selects treatment tactics and therapeutic measures. Treatment can be carried out both in hospital and at home.
If the increase occurs against the background of brain tumors, then the pressure can be reduced exclusively by surgical methods, when there is a high risk of complications. For this purpose, the following neurosurgical types of lowering ICP are used:
Treatment of intracranial pressure in children
- Shunting (outflow of cerebrospinal fluid occurs through a catheter, which is inserted into the ventricles of the brain).
- Decompression craniotomy (removal of part of the cranial bone to relieve compression of the brain).
- Lumbar puncture (excretion of cerebrospinal fluid through a catheter that is inserted between the lumbar vertebrae).
- Ventricular puncture (outflow of cerebrospinal fluid through a puncture of the posterior or lateral horn of the ventricle).
What is hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus
If intracranial pressure is increased significantly and for a long enough time, the fluid cavities of the brain may expand; this expansion is called internal or external hydrocephalus. Since the cranial cavity is a closed space, the expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain occurs due to a decrease in the mass of the brain matter itself. To protect you from the death of working brain tissue, we will offer you a course of medications, in combination with a set of exercises to reduce intracranial pressure and, if necessary, osteopathic correction.
External hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain (subarachnoid spaces).
Internal hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the internal liquor cavities of the brain (ventricles).
Our clinic pays great attention to finding the root causes of such a condition as increased intracranial pressure. In this case, treatment can be kept to a minimum, and our assistance to patients will be reliable.
Treatment of intracranial pressure with yellow sweet clover
Yellow sweet clover is a medicinal plant from the legume family. Sweet clover has many beneficial properties.
Among which:
- Relieving inflammation;
- Providing an analgesic effect;
- Antibacterial and expectorant effect;
- Improving blood quality;
- Providing a sedative effect;
- Improving blood supply to all organs and tissues;
- Stimulation of cerebral circulation.
Sweet clover contains essential oils, coumarin, vitamin A, vitamin C, B vitamins, flavonoids and bioflavonoids.
To reduce intracranial pressure with the help of yellow sweet clover, you can use the following recipe: take 30 g of plant flowers (2 tablespoons), place in a thermos and pour a liter of boiling water. Infuse the drink for an hour, then strain and add honey. Drink the prepared mixture throughout the day.
When using yellow sweet clover, the dosage should be strictly observed so as not to provoke the development of side effects (dizziness, nausea, increased drowsiness, vomiting). The course of treatment should not last more than 14 days.
Contraindications to the use of yellow sweet clover:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Internal bleeding.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis.
Find out more: Useful properties, cultivation and recipes for using sweet clover