Causes of chest heaviness
Physiological factors
As a rule, a person experiences an unpleasant heaviness in the chest when there is severe fear or anxiety. There is a feeling that everything is shrinking inside, nagging or aching pain appears. Symptoms are accompanied by interruptions in work or a feeling of cardiac arrest. Discomfort in the chest is sometimes perceived as the onset of a heart attack, but the condition returns to normal immediately after the person calms down and the traumatic factor disappears.
Depression
Heaviness with aching pain in the chest, which is most pronounced in the first hours after waking up, is pathognomonic for masked depression. Patients are concerned about discomfort in the precordial area, sometimes the condition is aggravated by pressing or squeezing pain. Characterized by the absence of mood changes typical for depression, patients are confident that they have a cardiac disease.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
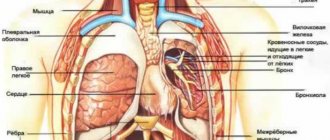
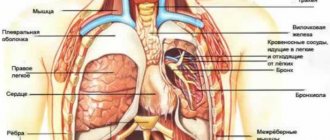
Heaviness and discomfort in the chest projection are often associated with cardiac problems. In such cases, symptoms are more typical for middle-aged and elderly people. Unpleasant sensations are often combined with tingling or pain in the heart area, shortness of breath during exercise, and swelling of the lower extremities. Heaviness in the chest is a manifestation of heart lesions such as:
- IHD.
Stable angina is characterized by periodic episodes of chest tightness and squeezing pain. Severity develops at the beginning of paroxysm, provoked by physical activity or stress. Sometimes the symptom continues to bother the patient even in the periods between attacks of angina. - Myocarditis.
The pathology manifests itself suddenly and is more common in young patients. A person complains of heaviness with moderate aching chest pain, accompanied by shortness of breath and fever. Sometimes there are interruptions in the heart rhythm. - Pericarditis.
With exudative inflammation of the pericardium, patients feel increasing heaviness, tightness in the chest, and progressive shortness of breath. Changing body position does not affect the intensity of symptoms. Swelling of the neck veins and puffiness of the face are usually noticeable. - Cardiomyopathy.
Non-inflammatory heart disease is characterized by constant or periodic heaviness in the chest, which bothers a person for several months or even years. The manifestations are moderate and do not interfere with normal life, so patients consult a doctor only if the problem worsens and heart failure develops. - Cardiac tamponade.
Patients experience sudden heaviness in the chest, inability to breathe deeply, severe weakness and cold sweat. The condition is life-threatening and, without medical attention, ends in collapse or acute heart failure. - Post-infarction syndrome.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of pressing pain and heaviness in the chest 2-4 weeks after myocardial infarction. Patients notice a deterioration in their health, an increase in shortness of breath and weakness, and discomfort in the chest cavity. Often the clinical picture is supplemented by fever.
Heaviness in the chest
Respiratory diseases
Damage to the bronchopulmonary system is another common cause of heaviness, pressing and squeezing sensations in different parts of the chest. The symptom most often occurs as part of typical inflammatory processes: acute and chronic bronchitis, pneumonia. Discomfort increases during coughing attacks or attempts to take a deep breath. Heaviness in the chest is accompanied by fever, weakness, and the release of mucous or purulent sputum.
In chronic processes - tuberculosis, pneumoconiosis - patients complain of periodic tightness in the chest area, incomprehensible discomfort or aching sensations. Manifestations occur without any visible provoking factor and persist for many months. When the pathology worsens, the heaviness in the chest is replaced by a dull pain.
Attacks of heaviness and a feeling of chest compression are observed during exacerbation of bronchial asthma. Unpleasant symptoms develop as harbingers of a paroxysm of suffocation and are accompanied by nasal congestion, itching, and coughing. During the interictal period, patients with moderate and severe asthma experience heaviness in the chest.
Mediastinal lesion
Heaviness and periodic pain in the chest occur with chronic mediastinitis. Symptoms are mild, periodically they intensify and are supplemented by fever. Patients complain of pressing or dull pain without clear localization, discomfort when taking a deep breath and coughing. Similar manifestations occur with mediastinal neoplasms: thymoma, lymphoma, cysts.
Rare causes
- Poisoning
: citrate intoxication, hydrogen sulfide poisoning. - Digestive diseases
: GERD, achalasia cardia, dilatation of the esophagus. - Emergency conditions
: anaphylactic shock, heat stroke, toxic pulmonary edema.
Causes
When carrying out diagnostic measures, a specialist may identify several pathologies. They contribute to the fact that patients complain of pain in the back and chest. Why does this happen? The main causes of diseases are:
| Organ systems | Pathological conditions |
| The cardiovascular system | Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, myocarditis, pericarditis, aortic aneurysm |
| Respiratory system | Tracheitis, bronchitis, tuberculosis, dry pleurisy, pneumothorax |
| Digestive system | Pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| Musculoskeletal system (spinal diseases) | Osteochondrosis, scoliosis |
| Nervous system | Intercostal neuralgia, other mental illnesses |
| Injuries and bruises (esophageal rupture, rib fractures) | |
| Malignant neoplasms (breast cancer) |
Angina pectoris
A syndrome accompanied by pressing pain in the middle of the sternum and a burning sensation in the heart area. The cause of this condition is a disorder of the coronary circulation of the heart muscles. The occurrence of pathology is influenced by age, gender and hereditary factors. According to statistics, men over the age of 50 suffer more often from coronary heart disease (CHD) and angina attacks.
Obesity, hypertension, alcohol and drug addiction, physical inactivity, frequent stress and mental stress are also considered predisposing factors. Because of its peculiar manifestation, angina pectoris is often called “angina pectoris” or coronary heart disease. Pain in the heart area can radiate to the back, arm, neck, and lower jaw. Shortness of breath, dizziness, numbness of the fingertips, shallow breathing and cough appear (most often occurs in a lying position due to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation).
Myocardial infarction
A form of coronary artery disease, which is necrosis of the heart muscle associated with a sudden cessation of coronary circulation. The main causes of heart attack are atherosclerosis of the heart vessels, vascular thrombosis, coronary artery embolism, cardiac malformations, and surgical obstruction. Most often, the pathology occurs among men whose age is 40–60 years.
Predisposing factors also include obesity, arterial hypertension, smoking and alcohol abuse, diabetes mellitus, and inflammatory heart disease. The main symptoms are frequent attacks of angina pectoris, pain in the chest area becomes stronger and longer lasting. In a typical form of heart attack, patients complain that there is something pressing in the sternum, while at the same time the pain can radiate to the shoulder, shoulder blade, lower back, abdomen or neck, rarely to the thigh.
For some time, the pain syndrome reaches its peak and can persist for up to 60 minutes or more, either weakening or intensifying behind or in front of the chest.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
A pathological process in which inflammation of the walls of the esophagus occurs due to the release of gastric or duodenal contents back into it.
Why does my back hurt around the shoulder blades?
Excess weight and overeating, psycho-emotional stress, depression, smoking, frequent periods of gestation, diaphragmatic hernia, and some medications (nitrates, calcium antagonists, beta-blockers) increase the risk of developing the disease.
The main clinical manifestations of GERD are heartburn, which increases when bending forward or physical activity, after a heavy meal, and when lying down, belching with a sour or bitter taste. Nausea and vomiting are common. Another common symptom is chest pain after eating, which sometimes causes back pain at the level of the heart, bad breath, increased salivation during sleep, and hoarseness.
Fractured ribs
Damage to the chest, characterized by a violation of the integrity of the arched flat bones. The severity of the injury depends on the type of fracture and damage to nearby tissues. Most often this is damage to the lung tissue and pleura, esophagus, heart and blood vessels. The greatest danger is when there are fractures of several ribs or their fractures into many small parts.
The causes of rib fractures are: road accident, blow to the chest with a blunt object, fall from a high height, compression, gunshot and sports injuries. Symptoms of injury are pain in the sternum and back, shallow and intermittent breathing (associated with pain when trying to inhale air), forced body position - bending towards the broken rib, chest deformation, crepitus.
Mammary cancer
Malignant neoplasm affecting the mammary glands. According to statistics, breast cancer occurs 100 times more often in women after 40 years of age than in men. The development of a tumor is preceded by several pathological conditions: menstrual cycle failure, infertility, lactation disorders, hyperplasia and other inflammations of the reproductive system, obesity, diabetes mellitus, AIDS, arterial hypertension and others.
In addition, it has been proven that if close relatives have a history of cancer, then the likelihood of developing it in the younger generation increases significantly. Like most malignant tumors, breast cancer is difficult to recognize in the early stages due to the lack of any signs. Only after some time, when the tumor is significant in size, do the first symptoms appear:
- patients complain that the chest hurts on the right or left, depending on the side of the lesion;
- there is a lump in the mammary gland;
- There is a deformation of the breast and a change in its size.
Retraction of the nipples also occurs, bloody or yellow discharge appears from them, enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes, swelling in the shoulder and mammary gland. Body temperature can reach high values due to tumor disintegration. Sometimes, even after surgery, the pain does not go away for a long period.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive examination begins with a general practitioner or family doctor. The specialist conducts a physical examination and identifies the leading pathological syndrome, and if necessary, sends the patient for consultation with specialized specialists (pulmonologist, cardiologist). To establish a diagnosis, the results of instrumental and laboratory tests are necessary, of which the following are most often prescribed:
- X-ray of the OGK.
Radiation diagnostics helps to differentiate cardiac and pulmonary pathology. Damage to the respiratory system is manifested by focal infiltrates, rounded shadows, and increased vascular pattern. Signs of cardiac problems are changes in the size and configuration of the heart shadow, congestion in the lungs. - Electrocardiography.
An ECG evaluates the electrical activity of the myocardium. The cardiogram reveals a decrease in the voltage of the waves or their inversion, deviation of the heart axis, and signs of disturbances in the myocardial conduction system. Daily ECG monitoring and bicycle ergometer test are of great diagnostic value. - Echocardiography.
Ultrasound diagnostics shows structural and functional abnormalities in the activity of the heart. The method is necessary for diagnosing pericarditis (effusion in the heart sac), cardiomyopathy (expansion of cavities or thickening of the walls of the organ). EchoCG allows you to measure the contractile function of the left ventricular myocardium. - Invasive methods.
In case of pathological processes in the pericardium, a diagnostic puncture is performed for bacteriological and cytological examination of the exudate. In case of coronary artery disease, coronary angiography is performed to assess the extent of vascular damage. The functional state of the myocardium is determined by perfusion scintigraphy. - Laboratory diagnostics.
Analyzes are of auxiliary value. In case of cardiac pathology, an extended biochemical study is indicated with determination of the lipid spectrum and acute phase parameters, measurement of myocardial markers. Diagnosis of pulmonary diseases requires microscopy and sputum culture.
Echocardiography
What sensations accompany the development of a tumor?
The formation and development of a cancerous tumor is rarely accompanied by discomfort or pain; pain occurs when large nerves of the chest wall are involved in the tumor. Often, with a 5-centimeter tumor there may be no discomfort; even a disintegrating cancer ulcer may be painless.
The infiltrative-edematous form, when the tumor spreads throughout the gland as inflammation, in most cases begins with local painful sensations, accompanied by redness and swelling of the skin and an increase in the size of the gland.
Without an examination, it is impossible to find the cause of discomfort, which can equally indicate either a minor health problem or a major disaster. To identify pathology of the glands, different methods are used; only a specialist will determine which diagnosis is right for you. A mammologist at the international clinic Medica24 will offer the best way to eliminate health problems, and will never dismiss your feelings as insignificant. Sign up for a consultation by phone
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Heaviness in the chest occurs when various organs and systems are affected, so self-medication at home is unacceptable and is fraught with the progression of the underlying disease and the development of complications. Patients experiencing chest discomfort are advised not to delay contacting a therapist. If squeezing pain is felt in the chest, the person experiences suffocation, febrile fever, and requires emergency medical attention.
Conservative therapy
Treatment measures are selected after identifying the causes of the condition. Heaviness in the chest does not require special symptomatic therapy and disappears after eliminating the underlying pathology. All patients are prescribed a gentle motor regimen, maximum limitation of stress and traumatic factors. Medicinal effects include drugs from the following pharmacological groups:
- Antianginal agents
. Used in combinations for long-term therapy of coronary heart disease. They are supplemented with antiplatelet agents to prevent myocardial infarction and thrombosis. Nitrates are recommended to relieve angina attacks. - Anti-inflammatory drugs
. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated for myocarditis and pericarditis, acute respiratory diseases. They act pathogenetically and also relieve discomfort and pain. If nonsteroidal drugs are ineffective, corticosteroids are taken. - Antibiotics
. Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed for pneumonia, pleurisy, purulent bronchitis as etiotropic treatment. Penicillin antibiotics are effective for inflammatory lesions of the heart due to rheumatism. To treat tuberculosis, 3-4 specific drugs are combined. - Antiallergic drugs
. Leukotriene receptor antagonists and mast cell membrane stabilizers are used for basic therapy of bronchial asthma. Classic antihistamines are used as pathogenetic therapy for many inflammatory processes with an allergic component. - Metabolic drugs
. To improve the delivery and utilization of oxygen in the myocardium under conditions of ischemia, it is necessary to take cytoprotectors. Therapy is enhanced with ascorbic acid and B vitamins, which accelerate metabolic processes in the body.
What does discomfort in the chest of a mature woman indicate?
Most often, unpleasant sensations are caused by manifestations of fibrocystic mastopathy, when inadequate hormone production leads to the formation of cysts and scar changes that disrupt the normal circulation of blood and lymph in the glandular tissue. Since the development of mastopathy is asymmetrical, local discomfort can be observed in one gland and does not always repeat itself cyclically. Unpleasant sensations can also be caused by a neurological disorder such as intercostal neuralgia.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly