If a person says: “I have abdominal pain,” then it is important to understand: behind abdominal pain there may be problems with any organs of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, or small pelvis.
If a person says: “I have abdominal pain,” then it is important to understand: behind abdominal pain there may be problems with any organs of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, or small pelvis. The intestines (ileum, jejunum, colon, sigmoid, colon, transverse colon), appendix, stomach, liver, duodenum, spleen, ureters, kidneys, mesenteric (mesenteric) vessels of the intestine can cause painful sensations in the abdomen. Therefore, pathologies can be gastroenterological, surgical, gynecological, or urological in nature.
Types of pain
Abdominal pain can be very different:
- Acute and chronic . Acute pain occurs suddenly, chronic pain develops gradually, its intensity increases step by step - sometimes over several weeks. In this case, a special type is formed by chronically recurrent abdominal pain. They can suddenly make themselves felt, and then also suddenly pass and resume after a certain period of time.
- Tonic and clonic . With tonic pain, the muscles are very tense, compacted areas appear on the abdomen, and uncontrolled muscle contraction is observed. Tonic pain is accompanied by fairly rhythmic spastic spasms.
- Burning (cutting) and aching – reminiscent of hunger.
The localization of pain can be the abdominal cavity, hypochondrium, areas above or below them.
Pain in the lower abdomen: diagnosis
Since the reasons that cause pain symptoms in the lower abdomen can be different, if they occur, you need to contact different specialists. This could be a gynecologist, urologist, gastroenterologist, therapist, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, venereologist, nephrologist, who will prescribe appropriate diagnostic tests to identify the exact cause of the disease. Their list depends on the accompanying symptoms and may include the following:
- Urine, blood and stool tests;
- or MRI;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs;
- Cholecystography;
- Scintigraphy;
- Colonoscopy;
- Other.
Symptoms
A person who complains of abdominal pain may have different symptoms. Most often it manifests itself in the form of spasms and colic.
- Colic is an attack of primarily stabbing (hence the name) pain. In case of colitis, a person has colitis in both sides, in case of appendicitis or inflammation of the ovaries - in the lower abdomen, in case of poisoning, the localization of colic can be in different parts of the abdomen and most often an additional symptom appears (vomiting, diarrhea).
- Spasms are pain that is accompanied by involuntary muscle contraction. At the same time, the skin turns pale. The pain may cause the person to lose consciousness. If the spasms are due to inflammatory diseases of the intestines or stomach, they are accompanied by fever. Gynecological problems are indicated by spasms accompanied by bleeding.
- Anginal pain is an unpleasant sensation with a strong burning sensation.
- Sharp pain in the area above the navel is a common occurrence with appendicitis.
- A feeling of “fullness” in the lower back may indicate problems with the colon
- Cyclic pain (either intensifies or subsides) is a characteristic symptom of diseases of the bladder and intestines.
- Pain accompanied by severe gas formation indicates improper functioning of the colon.
- Painful sensations accompanied by itching of the anus are symptoms of damage to the rectum.
- Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen , intensifying at rest and disappearing with movement, are the result of problems with blood circulation.
Pain during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period during which it is important for the patient to pay special attention to her health and the reactions of her body. Painful symptoms at this time may be an indicator of pathological processes that pose a threat to the health and life of the fetus and mother, or may be a natural reaction of the body to changes. Its reasons are given in the table below:
| Etiology | Character, what is accompanied by |
| Uterine tone | Pain in the lower abdomen in the early stages of pregnancy is not uncommon in the process of adaptation of the uterine tissues and ligaments to the increase in the size of the organ. If there are no other clinical manifestations, they do not require treatment; however, if present, they can signal a threat of miscarriage. |
| Increased load on the uterine ligaments, calcium deficiency | Painful symptoms during the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, which go away when the pregnant woman relaxes or changes her body position. |
| Placental abruption during pregnancy or during childbirth, and not after it | Vivid pain, accompanied by bleeding or occurring without it against the background of bloating, weakness and dizziness in a pregnant woman. |
| False contractions | Pain of a cramping nature, accompanied by tension of the uterine organ, depending on the situation, can be regarded as a normal phenomenon, or it can signal a threat of miscarriage. |
Causes
What are the causes of abdominal pain, dysfunction of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space?
The cause of colic can be appendicitis, inflammation of the ovaries (in these cases, colic in the lower abdomen), poisoning, or colitis. With colitis, a person has colitis in both sides. If the colic is cramping and is localized both in the abdomen and in the lower back, the pain is more intense, the cause is most often urolithiasis, kidney injuries or pyelonephritis. Colic in the navel area may be a response to irritants of the sensitive mesenteric plexus of the intestine.
Among the common causes of paroxysmal spasms are intestinal obstruction and gastroduodenitis. And uterine endometriosis is most often behind spasms during urination in women.
If abdominal pain is accompanied by increased gas formation and a frequent urge to defecate, then the cause will most often be associated with diseases of the colon.
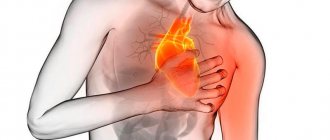
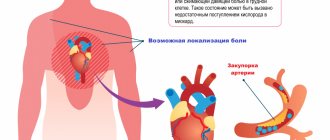
If you have abdominal pain - anginal, and the patient is bothered by an expressive burning sensation - the cause is most often gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). If pain and burning are accompanied by severe tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, and a person complains of pressure in the chest, the cause may be associated with heart pathologies: in particular, such pain is typical for 60% of patients with myocardial infarction.
The cause of abdominal pain accompanied by low-grade fever (the temperature remains at 37.1–37.5 °C for a long time) is most often inflammatory bowel disease.
Pain in the lower abdomen in men
The causes of pain in the lower abdomen in the male population may be associated with pathological conditions of the reproductive and urinary systems. You can see them in the table below:
| Etiology | Character, what is accompanied by |
| Orchitis and epididymitis | Severe pain in the lower abdomen that extends to the groin and even the lower back. |
| Prostatitis | Vivid pain not only in the lower abdomen, but also in the lower back, scrotum, and lower back. |
| Neoplasms of the genitourinary system | Aching pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes more pronounced during sexual intercourse or with prolonged abstinence. |
| Stones in the ureter and lower third of the ureter | Painful symptoms of a spasmodic, girdling nature against the background of elevated body temperature. |
Diseases
Most often, abdominal pain is caused by diseases of the intestines, stomach, pancreas, problems with the gallbladder, as well as hernias.
Intestinal diseases
- Ulcerative colitis is a diffuse inflammation. The rectal mucosa is affected. In the initial forms of ulcerative colitis, inflammation affects only the proximal part (the entrance to the intestine); in advanced forms, the problems affect the entire colon. As the disease progresses and worsens, the patient feels a sharp deterioration in health, the body begins to become intoxicated, the pulse quickens, and in most cases blood appears in the stool. If the disease is not treated, the body can poison itself, and peritonitis can develop - damage to the abdominal cavity that poses a threat to life.
- Enteritis . The small intestine becomes inflamed. At first, the disease is “masked” as a disease, and often accompanies this problem. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the functions of the small intestine are disrupted. Food begins to be poorly absorbed by the intestinal walls. Digestion processes are disrupted.
- Crohn's disease . One or several areas of the intestine can become inflamed. But almost always the inflammation affects the junction of the large and small intestines. One of the most unpleasant aspects is that the inflammation affects the entire thickness of the wall, and a complication of the disease is intestinal obstruction syndrome, the treatment of which requires the adoption of a set of measures related to the simulation of motility and restoration of intestinal function.
- Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora. The number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines is reduced, and pathogenic microflora develops. As a result, gas formation occurs, a person cannot digest food, and bowel movements are disrupted. Very often, the development of dysbiosis is a consequence of incorrect antibiotic therapy or a reaction to stress.
Pancreatic diseases
- Pancreatitis . The most common disease affecting the pancreas is pancreatitis. When the pancreas is inflamed, a person feels severe discomfort in the upper abdomen, and it becomes difficult for the body to digest proteins and fats. Often in everyday life they say in this case: “There are not enough enzymes.” And this really reflects the real picture. In the affected pancreas, the production of lipase, chymotrypsin, and trypsin is significantly reduced.
- Cystic fibrosis is a disease that disrupts the functioning of the pancreas and respiratory system. It is a non-inflammatory pathology. The reason is hereditary factors. A complication of the disease may be the formation of a duodenal ulcer.
Stomach diseases
Some of the most common diseases that affect people of all ages are accompanied by abdominal pain - these are pathologies of the stomach, especially its mucous membrane. The leaders are gastritis, ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Gastritis . It is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The entire stomach or certain parts of it can become inflamed. With gastritis, pain with burning and spasms predominate. The patient is concerned about discomfort after eating, a feeling of a full stomach or, on the contrary, “sucking” and a constant feeling of hunger. Accompanying the disease in the acute stage are vomiting and nausea.
- Stomach ulcer . Pain occurs against the background of characteristic ulcerative damage to the gastric mucosa. Dyspeptic symptoms are pronounced: heaviness in the stomach, a feeling of oversaturation of the stomach, pain in the epigastric region.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (popularly known as “reflux”). The disease is associated with a weakening of the valve between the stomach and esophagus. The result of this weakening is pain, accompanied by heartburn. Very often, gastroesophageal reflux disease appears in patients who have already experienced gastritis or a stomach ulcer.
First aid for an angina attack
If an angina attack occurs, you must follow the instructions received from your attending physician or (if there were no such instructions) follow the algorithm:
- Note the time of onset of the attack.
- Measure blood pressure, heart rate and pulse.
- Sit (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised.
- Provide fresh air (free your neck, open a window).
- Take acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin 0.25 g), chew the tablet and swallow.
You should not take acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) if you are intolerant to it (allergic reactions) and have already taken it that day, as well as if there is a clear exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
6. Take 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin. If in the form of a tablet, put it under the tongue and dissolve; if in the form of a capsule, bite it, do not swallow; if in the form of a spray, inhale (inject) one dose under the tongue without inhaling.
If, after taking nitroglycerin, severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, or a severe headache appears, then you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, pillow, etc.), drink one glass of water and then do not take nitroglycerin.
You should not take nitroglycerin if you have low blood pressure, severe weakness, sweating, severe headache, dizziness, acute impairment of vision, speech or coordination of movements.
7. If the pain has completely disappeared and the condition has improved after taking aspirin and 1 dose of nitroglycerin after 5 minutes, limit physical activity and discuss further treatment with your doctor.
8. If the pain persists for more than 10-15 minutes, you must take nitroglycerin a second time and urgently call an ambulance!
ATTENTION ! If aspirin or nitroglycerin is not available and the pain persists for more than 5 minutes, call an ambulance immediately!
9. If pain persists even after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin after 10 minutes, you need to take nitroglycerin a third time. Wait for an ambulance.
Hernias
Often abdominal pain is caused by peritoneal hernias. They can be umbilical, inguinal, diaphragmatic. Umbilical hernias are more often formed during pregnancy or in the postpartum period, inguinal hernias - with excessive stress, diaphragmatic hernias - defects of the abdominal wall that form as a reaction to improper bowel function, an incorrectly selected corset, or heavy lifting. The insidiousness of diaphragmatic hernias is that at the initial stage of the disease, a person believes that he has typical gastritis - with heartburn and belching, but traditional therapy does not provide treatment, and ultrasound shows that the cause is not inflammation of the stomach, but precisely the presence of a hernia. In toga, to combat pathology, it is not necessary to relieve inflammation or eliminate spasms, but to undergo surgical treatment, which is aimed at strengthening the abdominal wall.
Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts
A special group consists of diseases associated with the gallbladder and bile duct.
- Cholangitis . Inflammation of the bile ducts. The pain is unbearable. Mainly on the right side. It is complicated by the fact that it requires not only quick relief from the attack of pain itself, but also normalization of blood pressure.
- Cholecystitis . Acute pain due to eating fatty foods. Often the pain itself is followed by vomiting mixed with bile. Flatulence (gas formation) and vomiting may occur.
- Gallstone disease is the formation of hard structures – stones – in the bile. Pain in the disease is paroxysmal. Especially if the stones move through the gallbladder and ducts.
Contraindications
An incorrect diagnosis can lead to the fact that treatment will not only be useless, but will provoke serious complications. After all, many medications and physiotherapeutic techniques that are effective for some diseases accompanied by abdominal pain are strict contraindications for other diseases with similar symptoms.
For example, if a number of medications prescribed for pancreatitis are given to patients with hepatic colic, the reaction may be unpredictable. And treating a number of stomach diseases with antibiotics can cause serious dysbiosis.
And absolute contraindications for pain in the abdomen or stomach are self-medication - especially independent decision-making to take a painkiller or antispasmodic. If, for example, such drugs are used by a person whose appendix is inflamed, relief will follow for a while. But this will not be help, but false help to yourself. There are often cases when patients who did not get to the surgeon in a timely manner to remove appendicitis began to experience necrosis of the tissues of neighboring organs.
Under no circumstances should you resort to even seemingly “harmless” means to combat high acidity without making a diagnosis. What seems to be simply a release of excess hydrochloric acid and inflammation of the stomach may turn out to be a symptom of a completely different disease, such as a heart attack.
Also, for abdominal pain with an unclear diagnosis, you should not apply a heating pad with hot water. In a number of pathologies, heat only accelerates the inflammatory process and activates bleeding.
Definition.
Anal pain, as well as pain around the anus or in the rectal area (perianal area), is a fairly common complaint.
Although most causes of anal pain are not related to serious problems, it can become a problem in itself due to the intensity associated with the presence of many nerve endings in the perianal area. Some causes of anal pain can also cause bleeding from the rectum (rectal bleeding), which is a more serious symptom.
The causes of anal pain are usually fairly easy to diagnose. It can be treated well with over-the-counter pain relievers and hot water (sitz baths).
Surveys
An effective examination of a patient who is bothered by abdominal pain consists of an interview, palpation of the abdomen, and laboratory and functional diagnostics.
For a doctor to make a diagnosis, the smallest details are important. For example, even a basic assessment of stool can clarify a lot in the case of abdominal pain.
- Hard lumps (“sheep” feces) are a frequent companion to colitis, elongation of the sigmoid colon, and gastric ulcers.
- Watery stools often accompany poisoning and infectious diseases.
- With a parasitic disease (presence of worms in the intestines), dysbacteriosis, stool particles are usually very loose.
Also, to select a tool and diagnostic technology, an oral interview with the patient is important. The doctor asks the patient how long the pain lasts, whether there are attacks, what exactly causes the pain - physical movements, going to the toilet, eating, taking a certain position.
Diagnostics
The following types of research are especially valuable for identifying the cause of the disease and finding treatment methods for pathologies of the abdominal cavity:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. One of the most prompt measures in diagnosing diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs and identifying the cause of abdominal pain is ultrasound diagnostics. Using ultrasound, you can identify pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, spleen, kidneys, uterus, and ovaries. Many people wonder whether the stomach and intestines are visible on an ultrasound. The stomach cannot be examined using ultrasound; the intestines cannot be examined partially. If the equipment has good resolution, for example, volumetric formations in this area are visible.
- FGDS (gastroscopy, probing, intestinal swallowing) is a diagnostic method that can be used to obtain an objective picture of the condition of the stomach, duodenum, and esophagus. If necessary, you can immediately conduct a rapid test for Helicobacter pylori (the cause of the development of ulcers), do cytology and biopsy to exclude the oncological nature of the disease, and determine “acidity”.
- X-ray. An old, but still practiced method of diagnosis. It can be used as an emergency measure to examine the stomach if for some reason an FGDS cannot be done. In addition, x-rays are informative in identifying diseases accompanied by symptoms of intestinal obstruction. Depending on the nature of the patient’s pain and complaints, traditional X-rays or contrast-enhanced X-rays (irrigoscopy) may be used.
- MRI is a progressive diagnostic method for abdominal injuries, liver enlargement, and an uninformative picture of the abdominal cavity on ultrasound (for example, due to severe flatulence).
- Colonoscopy. One of the most accurate methods for examining the intestines. This is done using a fiber colonoscope. Using the device, you can examine everything - even the most complex areas, including the inner surface of the colon.
- Cholescintigraphy . Isotopic study. It is carried out using a radiopharmacological drug. Informative for problems with the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Blood, urine and canal analysis . In the blood test, special emphasis is placed on ESR (inflammation can be determined by the erythrocyte sedimentation rate), biochemical indicators, and in many types of examinations for abdominal pain, stool is examined for occult blood.
Pain in the lower abdomen in women
As already mentioned, pain in the lower abdomen on the right
, on the left or on both sides at the same time, can arise due to the structural features of the female body and the processes characteristic of it. They are presented in our table:
| Etiology | Character, what is accompanied by |
| Dysmenorrhea | Pain before and during menstruation is constant, but disappears on its own after one to two days. Accompanied by dry mouth, lack of appetite, and bloating. |
| Ovulatory syndrome | Pain sensations extend not only to the lower abdomen, but also to the iliac region. They differ in duration or short-term duration, can have a stabbing or pulling nature and are accompanied by spotting for two to three days after the process is completed. |
| Endometriosis | The cyclical nature of pain that appears or intensifies before menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse. |
| Ovarian rupture | The patient has pain in the right or left lower abdomen. Localization depends on the violation of the integrity of which ovary (left/right) occurred. The pain can be cutting, dull or stabbing and is accompanied by intense sweating, bleeding and pale skin. |
| Myomatous nodes in the uterus | Painful symptoms of a pulling-aching nature occur with large myomatous nodes due to compression of nearby organs and tissues. |
| Torsion of the cyst pedicle | Due to impaired blood flow from the neoplasm, aching pain appears, localized on the left or right, depending on which part of the uterus is affected by the disease. |
| PID: endometritis, myometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, other inflammatory diseases of the ovaries and fallopian tubes | Pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis due to vaginal discharge not associated with menstruation, dyspareunia and an increase in general body temperature. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | The growth of the embryo in the fallopian tube, peritoneum or ovary leads to compression on adjacent tissues, which is accompanied by aching, cramping or cutting pain on one side of the lower abdomen and bleeding. |
What to do?
So, the main thing for abdominal pain is not to self-medicate, and not to delay visiting a doctor and getting a diagnosis.
At the same time, in some cases, it is important not just to make an appointment at the clinic, but to immediately call an ambulance. In what cases is an ambulance required?
- Abdominal pain is very intense.
- Cold sweat appears.
- Severe vomiting of blood begins.
If the pain is not acute, there is no blood in the vomit, the temperature differs from that of a healthy person, but there is no fever, consultation with a therapist, gastroenterologist and diagnosis are recommended.
Timely diagnosis is a guarantee that the most gentle methods will be used to combat the disease. Even if we are talking about surgery.
- Laparoscopy is used to remove gallstones and appendicitis (if the situation is not advanced).
- Laparoscopic funduplication is used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- To effectively solve problems with hernias and strengthen the abdominal wall, surgical hernioplasty is used.
If there are no indications for surgical treatment, the therapeutic effect for many diseases of the intestines and stomach is provided by an integrated approach, which is based on diet therapy, physiotherapy and drug therapy - antibiotics, antiparasitic drugs, corticosteroids, prokinetics to improve intestinal motility.
Severe headaches: what to do
99% of the population experiences a headache at some point in their life. If this pain is periodic and is not accompanied by loss of consciousness and severe neurological disorders, then people adapt to it. And in vain. With proper discipline of the patient, in more than half of the cases, headache treatment is quite successful. Unfortunately, not everyone goes to the doctor on time.
Doctors name many causes of headaches. In the latest classification there are over two hundred of them. The main ones are vertebrogenic (the name is very symbolic - this category includes all types of headaches that arise due to obstruction of blood flow in the back of the head), pain due to migraines, with changes in blood pressure, after traumatic brain injuries and with infectious diseases ( even, for example, with a chronic runny nose).
Psychogenic headaches also occur. This includes tension headaches (mental or physical), as well as pain associated with anxiety and depression. Most often it is an aching, or pressing, or throbbing pain, concentrated in the occipital, temporal or frontal areas, or “spread” throughout the head. Patients agree on one thing: it can be tolerated for quite a long time, more than an hour for sure. And there is no motivation to immediately go to the doctor. This is how they live - for years, decades... A handful of pills, good sleep, timely vacation - and everything returned to normal by itself.
It will hurt and go away
If not only your family and colleagues know about your headache, but even your followers on social networks, and based on its intensity, you can, without measuring your blood pressure, figure out how many and what antihypertensive drugs you need to take this time, or you know exactly what kind tablet and in what dosage it helps, and carry the medicine with you, if your attending doctor raises his eyes to the ceiling and, sighing heavily, coos something confidentially about how “you need to worry and be less nervous,” then such a headache is most likely , will give you the opportunity to procrastinate further. And when your head hurts, you don’t really want to make an appointment, go to the doctor, explain something to someone... In any case, soon the “head will pass” and life will shine with all its colors again.
During a headache attack, people behave quite typically. A person seeks privacy; smells, bright lights and sounds are irritating. Some try to lie down and not move, some, on the contrary, walk around the room without stopping.
Remember Alla Pugacheva’s video about noisy neighbors? There is a wide bandage on the head, the nerves are stretched to the limit. Here is a portrait of a typical sufferer. The world is reduced to the size of a darkened and quiet bedroom. The condition when the head still does not hurt, on the contrary, is accompanied by an attack of violent activity and intense body movements. Everything is familiar.
Pain at its maximum
But one day the pain overshadows everything. It becomes so strong that you immediately understand: this is a “different” pain, unusual, unlike anything else. “Wild” is what her patients call her. Burning, boring, tearing or squeezing the head, piercing, sharp, intolerable, covering the entire head or part of it. This may be accompanied by loss of consciousness or confusion, convulsions, nausea and vomiting, immobility of one limb or half of the body, impaired speech or vision. Anything! After this, you are unlikely to experience any joy in life...
Medical advice will come later. And now - medical observations. In 99% of cases, with such a severe pain attack, people first take “some” pill. From those that are in the medicine cabinet, they were found at a neighbor’s place, they were shown on TV (well, where at first “everything hurts”, and then there is gulpfuls of happiness and the world is beautiful and amazing).
In principle, this is the right tactic. The only problem that most doctors point out is the dosage. With a strong, almost unbearable headache, eager to “drown out” it immediately, people take an absolutely insane amount of painkillers that can “poison” the body for a long time. And then people wait. When it “passes,” when “the pill takes effect,” when morning comes. And when it gets really bad...
If the attack took you by surprise
So, a severe, first-time headache. You are conscious, externally there is no damage. What could it be? Whatever! After all, the brain itself cannot hurt - it has no pain receptors. Pain occurs due to tension or irritation of many pain-sensitive areas located in the head or neck: the skull (periosteum), muscles, nerves, arteries and veins, subcutaneous tissue, eyes, sinuses and mucous membranes. That's why:
Tip #1.
Do not try to diagnose yourself! If you have a severe, sudden, first-time headache, call a doctor! Sit down and call someone adequate and not fussy to help you (in case you lose consciousness). Do not take more than double the dose of painkillers and remember that the medicine takes time to work.
Tip #2.
Before dialing an ambulance, take your temperature. Because a headache can accompany the onset of a viral or infectious disease. In any case, you will give the doctor the opportunity to begin work on making a diagnosis two minutes earlier. Remember, sometimes minutes can save a life.
Tip #3.
Try touching your chin to your chest. If you can’t because the pain in the occipital region is intensifying, feel free to dictate this terrible symptom to the call center operator. Because meningitis is not a toy, but a very dangerous complication of many seemingly harmless acute respiratory viral infections.
Tip #4.
If you have a tonometer, measure your blood pressure. And preferably on both hands. Because a good half of all new cases of hypertensive crises are accompanied by very severe cephalgia. And a hypertensive crisis is already serious. It can easily lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Tip #5.
Remember in detail what happened the day before. There is a special type of headache - toxic. It occurs when poisoned by various chemicals or as a side effect from taking medications. This headache is often caused by drugs that lower blood pressure, nitrates, psychotropic drugs and many other substances. By the way, many teenagers’ lives were saved by the meticulousness of their parents, who inquired in detail from their sick child about the circumstances of the party the day before.
Tip #6.
Look and feel. Even a healthy person can experience a sharp headache after heat or sunstroke, being in a stuffy room, or from carbon monoxide poisoning or car exhaust. By the way, don’t forget about such a thing as amnesia. A person hit on the head sometimes completely forgets the circumstances of the injury. Look at yourself in the mirror, palpate the skin under your hair and neck for bruises, wounds or scratches.
Tip #7.
Don't waste time. The most unpleasant case is the presence of a space-occupying formation in the brain. It could be a tumor, an abscess, or even bleeding. The diagnosis can only be made with the help of neuroimaging, so if you have a headache for a long time, do not delay contacting a neurologist. Remember: headaches have no equal in their diversity!
Tip #8.
If the headache goes away as suddenly as it appeared, no. In some of its types, for example, with intracerebral bleeding, there may be a “bright” period before the most serious complications appear. Wait for the doctor. Don’t rush to write your will and finish the “most important things.” Try to sit comfortably and relax.
Tip #9.
When visiting a doctor, keep a piece of paper ready with a note of exactly what medications you took for headaches. And medical gratitude will have no boundaries!
Attention! If the headache is accompanied by loss of consciousness or confusion, convulsions, nausea and vomiting, immobility of one limb or half of the body, impaired speech or vision, then without any options, call a doctor immediately
. And do not engage in self-medication and mutual assistance.
For those around you, there is only one piece of advice: do not let the patient die from your “care.” Do not try to give water to a person lying unconscious, do not put foreign objects in the mouth during a convulsive attack, do not “flush the stomach” if there is profuse vomiting that does not bring relief, do not shake a dangling arm or leg! Loosen constricting clothing, allow fresh air to flow, and carefully turn your head to the side.
The sooner the patient gets to the hospital, the greater his chances of remaining alive and unharmed. After all, pain can be a manifestation of such serious diseases as stroke, meningitis or encephalitis. Remember, only a doctor can make a diagnosis. And the advice “do no harm” applies not only to doctors...
Valentina Saratovskaya
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Where to go?
The doctors of the 5th Clinical Hospital have extensive experience in performing laparoscopic operations and hernioplasty in Minsk.
In addition to accepting patients who are citizens of Belarus, the 5th City Hospital of Minsk also accepts foreign citizens (on a paid basis). Each of them can undergo comprehensive diagnostics and treatment at the surgical and therapeutic departments.
The hospital has its own clinical diagnostic laboratory, X-ray department, X-ray CT and MRI rooms. The physiotherapy department has all the conditions for conducting rehabilitation programs.
Prevention
Doctors at the 5th Hospital will not only select the optimal diagnostic and treatment option for each patient, but will also advise on how to prevent relapses.
Diet occupies a special place among measures to prevent intestinal and stomach diseases. It is important to learn to maintain balance in nutrition. You should not overeat; you should chew food carefully and slowly. Water and willow tea https://teahelp.ru/tea/herbal-tea/ivan-chaj/ should be consumed in sufficient quantities; coffee is not recommended in this case. At the same time, when choosing a diet, experienced doctors take into account all factors:
- functional state of the intestines, liver, pancreas
- secretory function of the stomach,
- intestinal motility,
- the presence of other concomitant diseases.
In addition to your diet, it is important to reconsider how you store and process food. Do not leave food open in the sun. Avoid damp food storage areas. Otherwise, they may begin to mold and rot. Avoid contact between raw foods and cooked foods.
Exercise therapy is also of great importance in the complex of preventive measures. Instructors-methodologists select their own loads and exercises for each patient.