Injuries, wounds, and poisoning can trigger the stoppage of the body’s main “motor”—the human heart. Stopping blood circulation entails the cessation of tissue and gas exchanges. Without blood flow, waste products accumulate inside the cells, and carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. Metabolism stops, cells begin to die due to lack of oxygen and intoxication with metabolic products.
In this case, it is very important to at least try to carry out resuscitation measures - cardiac massage. There is a limited time allotted for this procedure - only thirty minutes. After this period, clinical death becomes irreversible.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest
Signs indicating cardiac arrest are: stopping the pulse (inability to feel the pulse in the carotid artery); respiratory arrest (the patient’s chest is motionless, a mirror brought to the mouth and nose does not fog); dilated pupils that do not respond to light; loss of consciousness, and the person does not come to his senses when hearing loud sounds or patting on the face; bluish-gray skin tone.
If there are fresh wounds on the body, then when the heart stops bleeding from them stops.
Content:
- Symptoms of cardiac arrest
- Types of heart massage
- The essence and algorithm of massage
- Rules for performing massage
Types of heart massage
Today, there are two methods of cardiac massage: direct (open) and indirect (closed).
Direct massage is carried out exclusively by qualified medical professionals and only in certain conditions: in particular, during surgery on the thoracic or abdominal organs. The essence of the procedure is to directly compress the heart muscle with your hands through an incision in the chest or abdomen (in this case, the massage is carried out through the diaphragm). Due to the complexity of performing direct massage of the heart muscle, it cannot be performed by people without appropriate medical education and training.
Indirect (closed) massage of the heart muscle can be performed in any conditions. This is the simplest way to help restore cardiac activity. No medical devices are required to perform it.
Indirect cardiac massage provides that during pressure on the chest, the chambers of the heart will also be compressed. As a result, blood will enter the ventricles from the atria through the valves, and then go into the vessels. Thanks to rhythmic pressure on the chest, the movement of blood through the vessels will not stop. As a result, the organ’s own electrical activity and independent functioning are activated.
Of course, a cardiac massage can only be successful if the algorithm of action is carefully followed and the rescuer follows the approved technique for carrying out resuscitation measures. Massage must be combined with artificial ventilation. Each pressure on the victim’s chest provokes the release of about five hundred milliliters of air. When the compression stops, the same portion of air is sucked into the lungs. As a result, passive inhalation and exhalation occur.
The essence and algorithm of massage
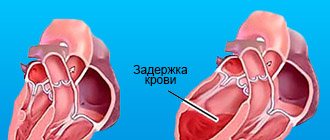
External cardiac massage is a rhythmic compression of the heart by compression between the sternum and the spine. Experts note that the chest of a person with cardiac arrest becomes more pliable due to loss of muscle tone, making it easy to perform compressions. The person providing assistance, if the NMS technique is followed, can easily displace the chest by three to five centimeters. Compression of the heart leads to a decrease in its volume and an increase in intracardiac pressure.
Rhythmic pressure on the chest area results in a difference in pressure inside the heart cavities, the blood vessels that extend from the heart muscle. Blood from the left ventricle travels through the aorta to the brain, while from the right ventricle it flows to the lungs, where it is oxygenated.
After the pressure on the chest stops, the heart muscle straightens, intracardiac pressure decreases, and the chambers fill with blood. As a result, artificial circulation is recreated.
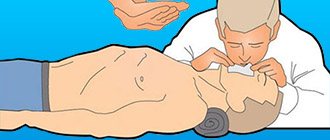
You can perform a closed massage of the heart muscle only on a hard surface. The person must be placed on the floor. After this, it is necessary to perform the so-called precordial punch. It should be directed to the middle third of the chest. The impact height should be thirty centimeters. However, according to recent data, the value of the precordial stroke is significantly reduced, and many experts do not recommend starting resuscitation measures with it. In order to conduct a closed cardiac massage, the person providing assistance places the palm of one hand on the other, after which he begins to carry out uniform pushes according to the established technique.
Features of the procedure in children
When performing artificial ventilation for babies under one year of age, the mouth-to-mouth and nose technique is used. If the child is older than one year, the mouth-to-mouth method is used.
Small patients are also placed on their back. For babies under one year old, place a folded blanket under their back or slightly raise their upper body, placing a hand under their back. The head is thrown back.
The person providing assistance takes a shallow breath, seals her lips around the child’s mouth and nose (if the baby is under one year old) or just the mouth, and then blows air into the respiratory tract. The volume of air blown in should be less, the younger the patient. So, in the case of resuscitation of a newborn, it is only 30-40 ml.
If a sufficient volume of air enters the respiratory tract, chest movement occurs. After inhaling, you need to make sure that the chest drops. If you blow too much air into your baby's lungs, this can cause the alveoli of the lung tissue to rupture, causing air to escape into the pleural cavity.
The frequency of insufflations should correspond to the breathing frequency, which tends to decrease with age. Thus, in newborns and children up to four months, the frequency of inhalations and exhalations is forty per minute. From four months to six months this figure is 40-35. In the period from seven months to two years - 35-30. From two to four years it is reduced to twenty-five, in the period from six to twelve years - to twenty. Finally, in a teenager aged 12 to 15 years, the respiratory rate is 20-18 breaths per minute.
Rules for performing massage
For the emergency measures taken to be effective, it is extremely important to follow the cardiac massage technique. Only in this case, the efforts made to restore the victim’s cardiac activity can be justified.
When performing cardiac massage, the following rules should be observed:
- The rescuer kneels in front of the victim lying on the ground or floor. It doesn't matter which side he is on. However, if the rescuer is right-handed, it will be more convenient for him to perform a precordial blow if he places his right hand towards the victim.
- Place the base of your right palm slightly above the xiphoid process. The thumb should be directed either towards the chin or towards the victim’s abdomen.
- The arms of the person performing chest compressions must be fully straightened. When the chest is displaced, the center of gravity must be moved to the chest of the person being assisted. As a result, the rescuer will be able to preserve his strength. If you bend your arms at the elbow joints, they will quickly get tired.
- For resuscitation to be successful, first aid must arrive within half an hour. The frequency of pressure on the victim’s chest is sixty times per minute.
- The depth to which chest compressions must be performed is three to five centimeters. In this case, the person providing assistance should not take their palms off the victim’s chest.
- The next pressure on the chest should be done only after it returns to its original position.
- During NMS, rib fractures are possible. This is not a reason to stop resuscitation measures. The only clarification is that pressure should be performed a little less often, but their depth should remain the same.
- Simultaneously with NMS, artificial respiration is also performed. The ratio of chest compressions to ventilation should be 30:2. Compression on the victim's chest provokes exhalation, and the return of the chest to its original position is a passive inhalation. As a result, the lungs are saturated with oxygen.
- During resuscitation measures, more attention should be paid to closed cardiac massage rather than artificial respiration.
Algorithm for performing indirect cardiac massage
Closed cardiac massage will be effective only if it is performed in accordance with the algorithm. You must proceed as follows:
- First of all, determine the place where the compression will be carried out. There is a common belief that a person's heart is on the left. This is not entirely true. In fact, you should not press on the left side, but on the center of the chest. This is extremely important, because if you apply compression to the wrong place, you can not only fail to achieve the desired effect, but also cause harm. The point that we need is located in the center of the chest, at a distance of two fingers from the center of the sternum (where the ribs touch).
- Place the heel of your palm at this point so that your thumb “looks” either at the victim’s stomach or chin, depending on which side of him you are on. Place your second palm crosswise on top of the first. Please note that only the base of the palm should be in contact with the body of the person you are helping. Fingers should remain hanging.
- Don't bend your elbows. It is necessary to apply pressure using your own weight, and not the strength of your arm muscles, because otherwise you will quickly get tired, and the force of pressure at each point will be different.
- With each pressure, the victim's chest should drop to a depth of five centimeters. In other words, the compression must be strong, because this is the only way you will be able to properly disperse the blood throughout the body so that it delivers oxygen to the brain.
- Artificial ventilation is performed between compressions. Its cyclicity is two breaths for every fifteen shocks.
Signs that resuscitation was successful are the appearance of a pulse in the area of the carotid artery, as well as the reaction of the person’s pupils to light.
Conducting a closed heart massage for a child
Unfortunately, sometimes there are situations when, for one reason or another, a child’s heart stops. In this case, the reaction of people nearby should be immediate - the baby must immediately begin closed heart massage, since every second of lost time brings a tragic outcome closer.
In infants, clinical death can be caused not only by sudden death syndrome, but also by neurological diseases, sepsis, drowning, airway obstruction, acute bronchospasm, pneumonia, severe trauma or serious burns and other diseases.
Indications for chest compressions for infants and older children are: sudden deterioration in the child’s condition, fainting, absence of heartbeat when palpating the carotid artery, cessation of respiratory activity, lack of pupillary response to light.
Features of the procedure for children
Carrying out resuscitation of children has a number of features.
First of all, chest compressions should begin in babies immediately after signs of clinical death have been detected. At the same time, artificial respiration is carried out, before starting which it is necessary to ensure the free passage of air through the respiratory tract.
Indirect cardiac massage in newborns is performed with little effort. Infants are placed on their backs, with their shoulders facing them. The thumbs should touch the front of the chest, and their base will be on the lower third of the chest.
In addition, a closed massage of the heart muscle of a newborn can be performed by placing it on your forearm, and holding its head slightly tilted back in the palm of your hand.
When performing NMS, children under one year of age should use only two fingers for pressure - the second and third. The frequency of compressions should be from eighty to one hundred per minute.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Heart massage for children aged one to seven is done while standing to the side of them, using the heel of the palm.
When resuscitating children over eight years old, massage is done with both hands. The main thing when performing NMS for a child is to carefully calculate the strength. Excessively strong pressure can lead to damage to the chest, which, in turn, can lead to injuries to internal organs and the development of hemo- and pneumothorax.
Preparing for artificial respiration
Before performing expiratory artificial respiration, the patient should be examined. Such resuscitation measures are contraindicated for facial injuries, tuberculosis, poliomelitis and trichlorethylene poisoning. In the first case, the reason is obvious, and in the last three, performing expiratory artificial respiration puts the person performing resuscitation at risk.
Before starting expiratory artificial respiration, the victim is quickly freed from clothing squeezing the throat and chest. The collar is unbuttoned, the tie is undone, and the trouser belt can be unfastened. The victim is placed supine on his back on a horizontal surface. The head is tilted back as much as possible, the palm of one hand is placed under the back of the head, and the other palm is pressed on the forehead until the chin is in line with the neck. This condition is necessary for successful resuscitation, since with this position of the head the mouth opens and the tongue moves away from the entrance to the larynx, as a result of which air begins to flow freely into the lungs. In order for the head to remain in this position, a cushion of folded clothing is placed under the shoulder blades.
After this, it is necessary to examine the victim’s oral cavity with your fingers, remove blood, mucus, dirt and any foreign objects.
It is the hygienic aspect of performing expiratory artificial respiration that is the most delicate, since the rescuer will have to touch the victim’s skin with his lips. You can use the following technique: make a small hole in the middle of a handkerchief or gauze. Its diameter should be two to three centimeters. The fabric is placed with a hole on the victim’s mouth or nose, depending on which method of artificial respiration will be used. Thus, air will be blown through the hole in the fabric.